The purpose of this study was to analyze the prevention and control effects of the three-phase global tuberculosis control strategy, and analyze the influencing factors.
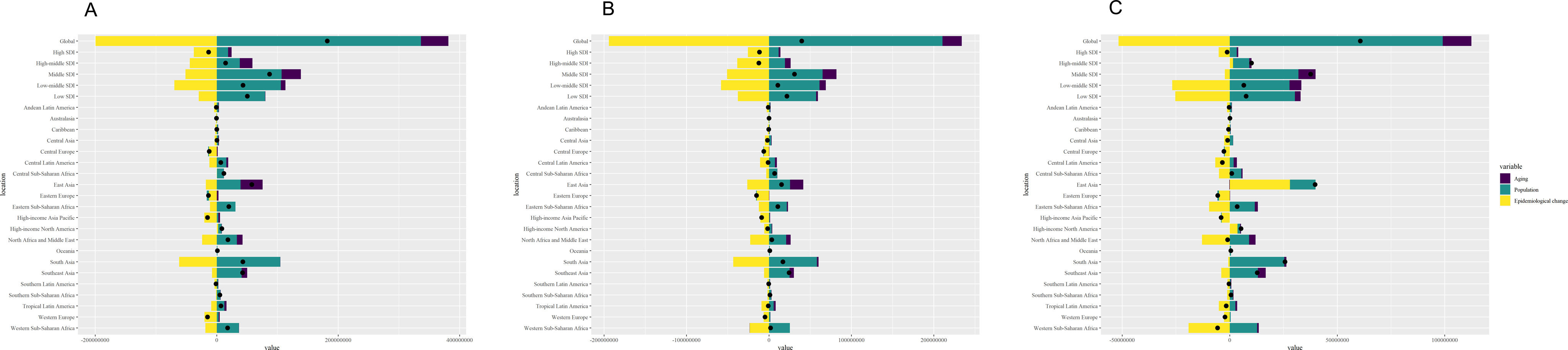
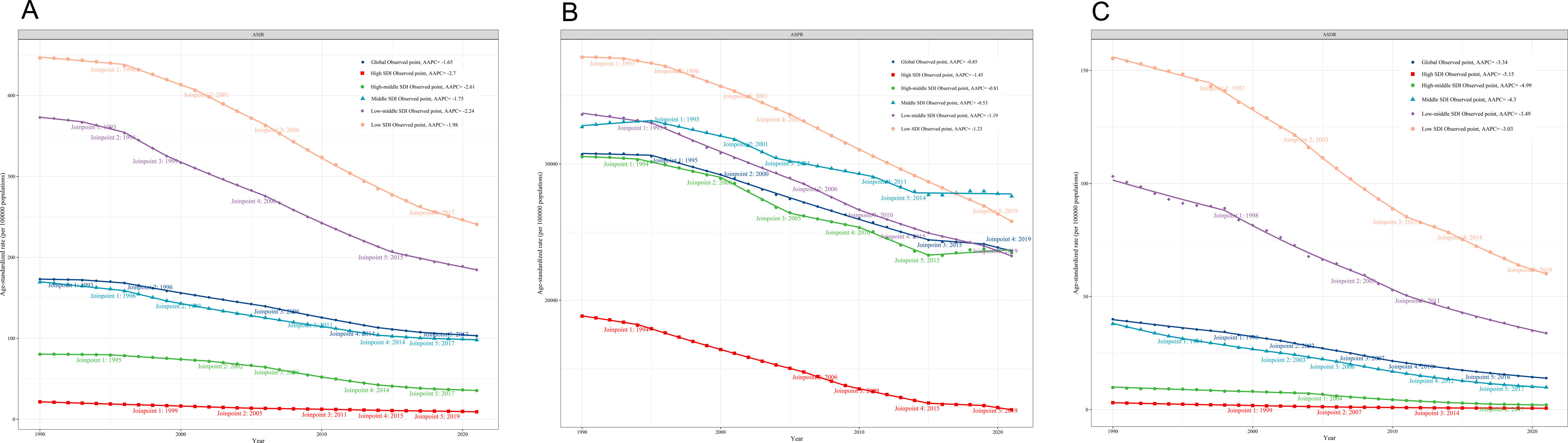
MethodsWe collected age-standardized incidence, prevalence, and mortality (ASIR, ASPR, and ASDR) data from the Global Burden of Disease Study (GBD 2021) database. Annual percentage change (AAPC) of ASIR, ASPR and ASDR were analyzed by Joinpoint regression. Correlation and decomposition analyses explored related epidemiological factors.
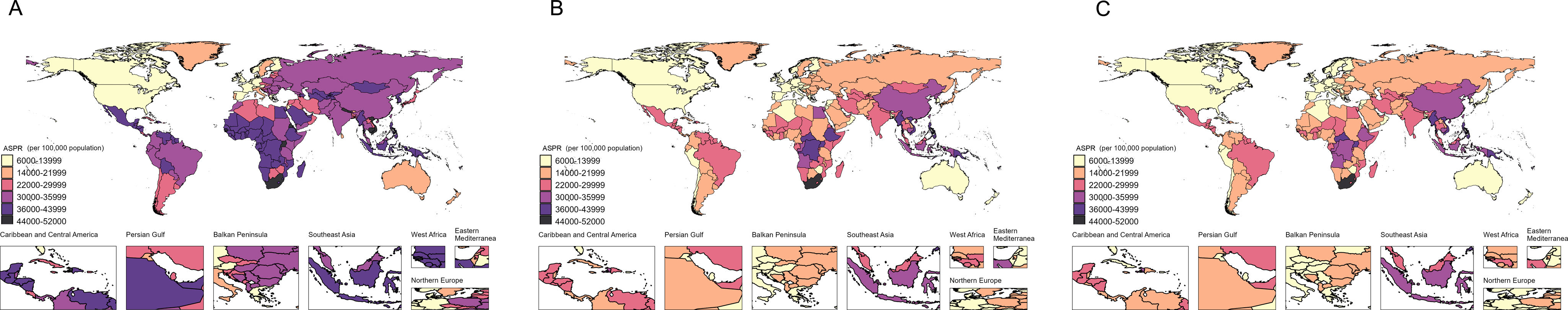
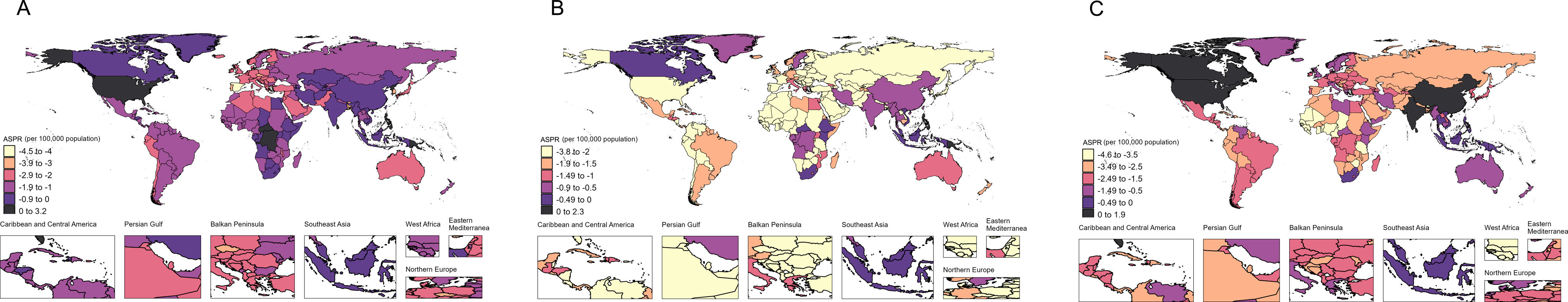
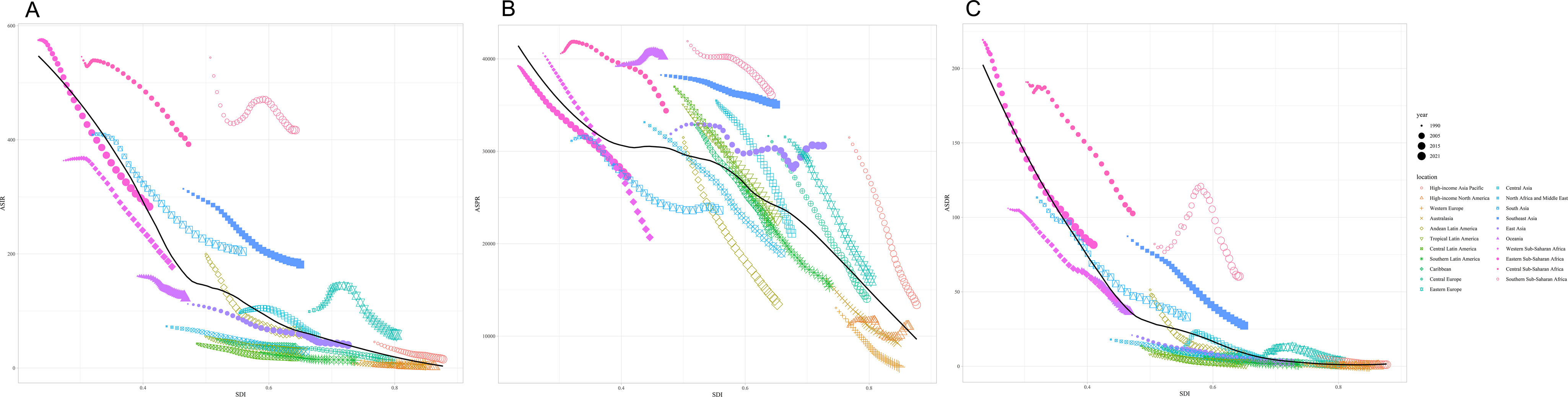
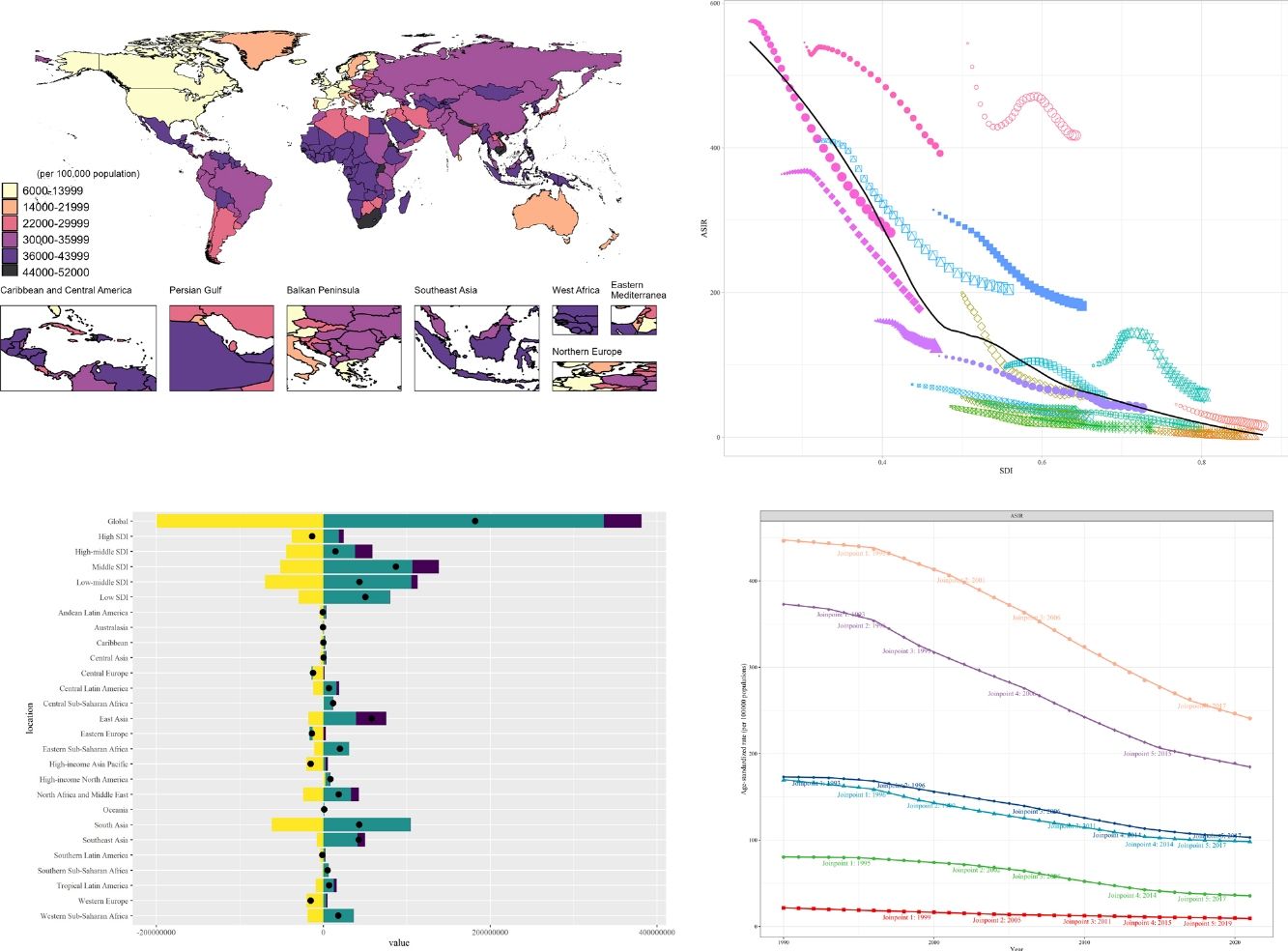
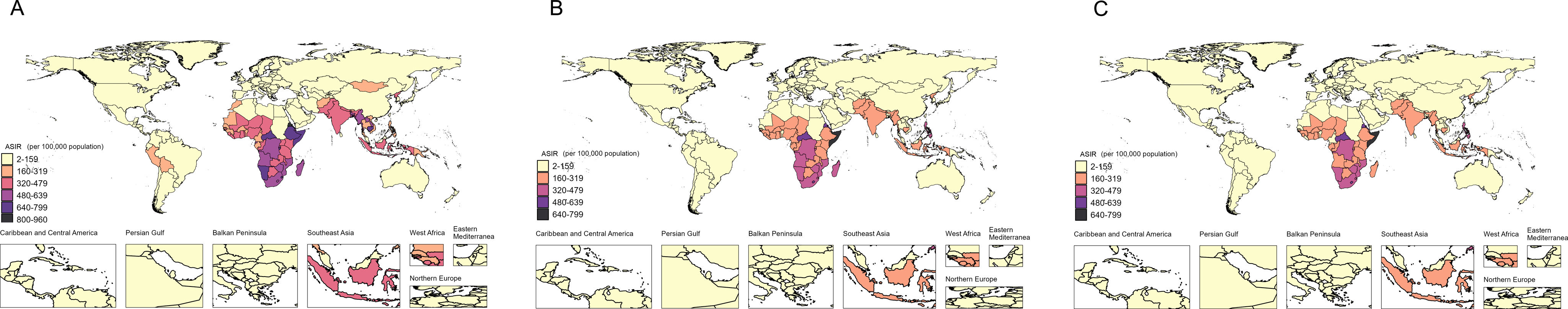
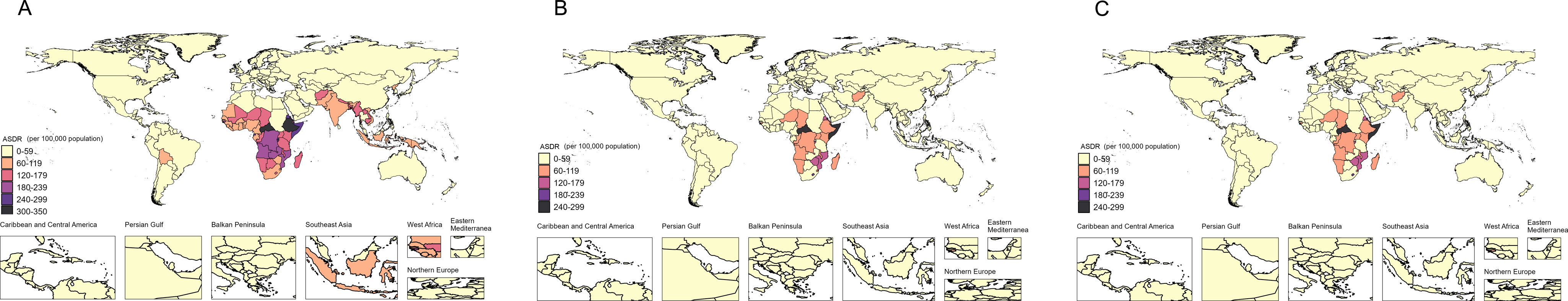
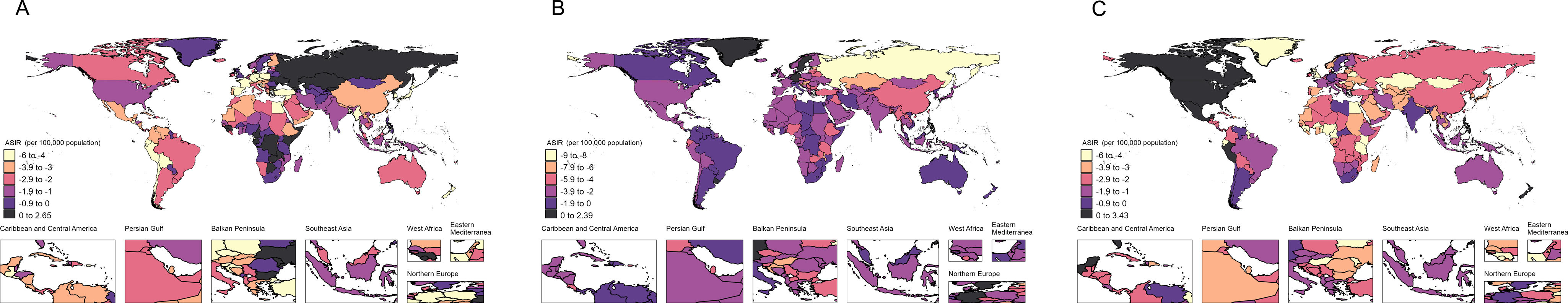
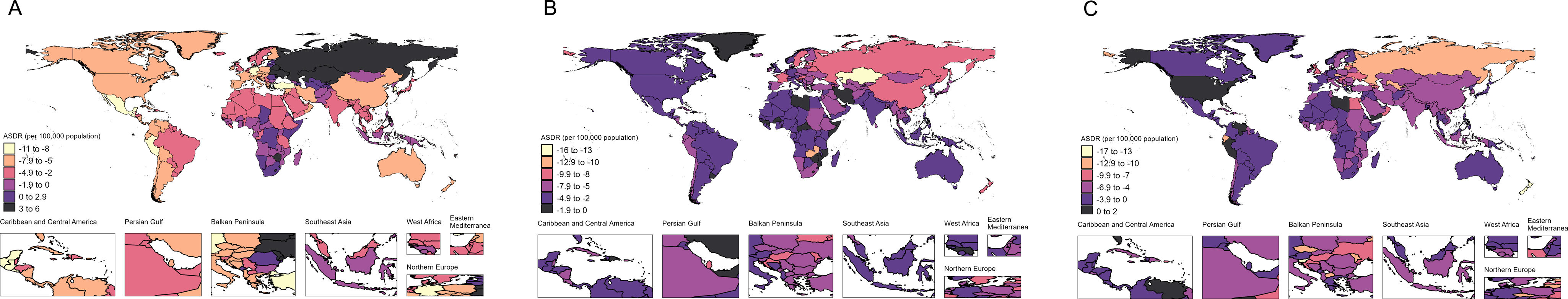
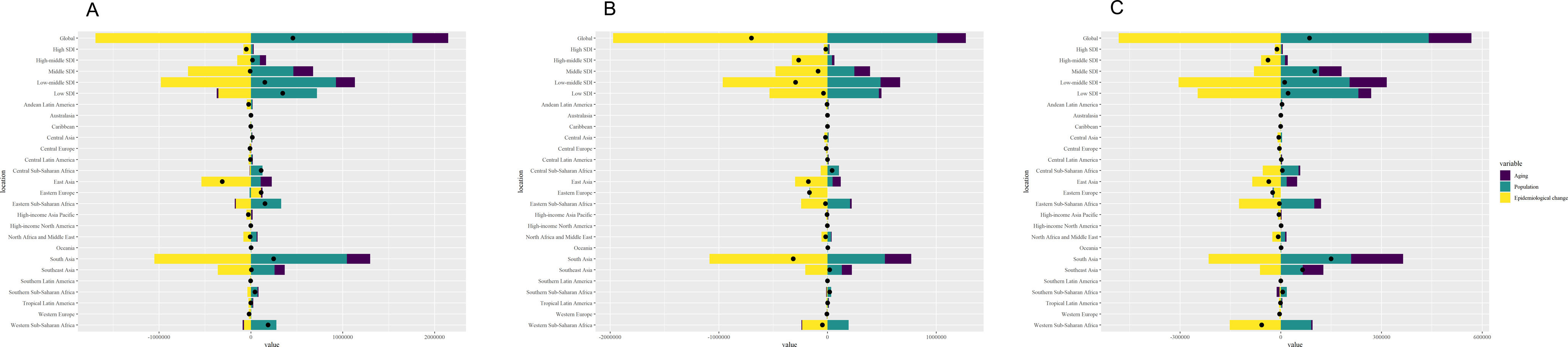
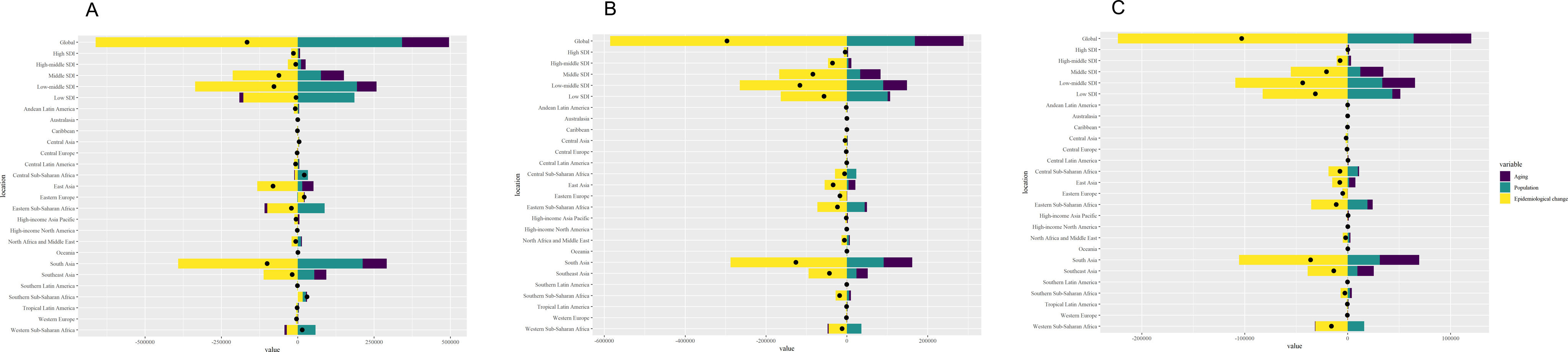
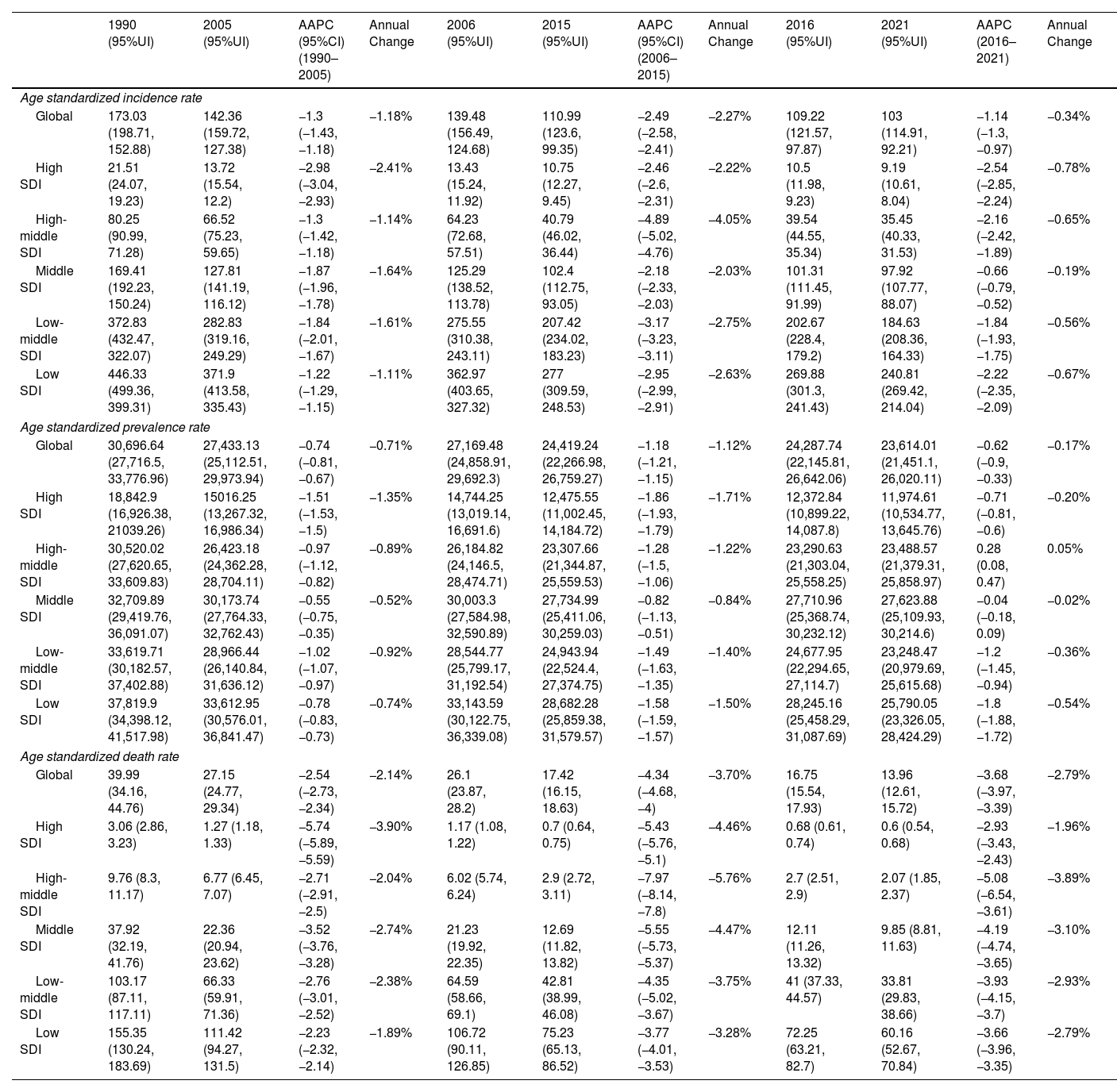
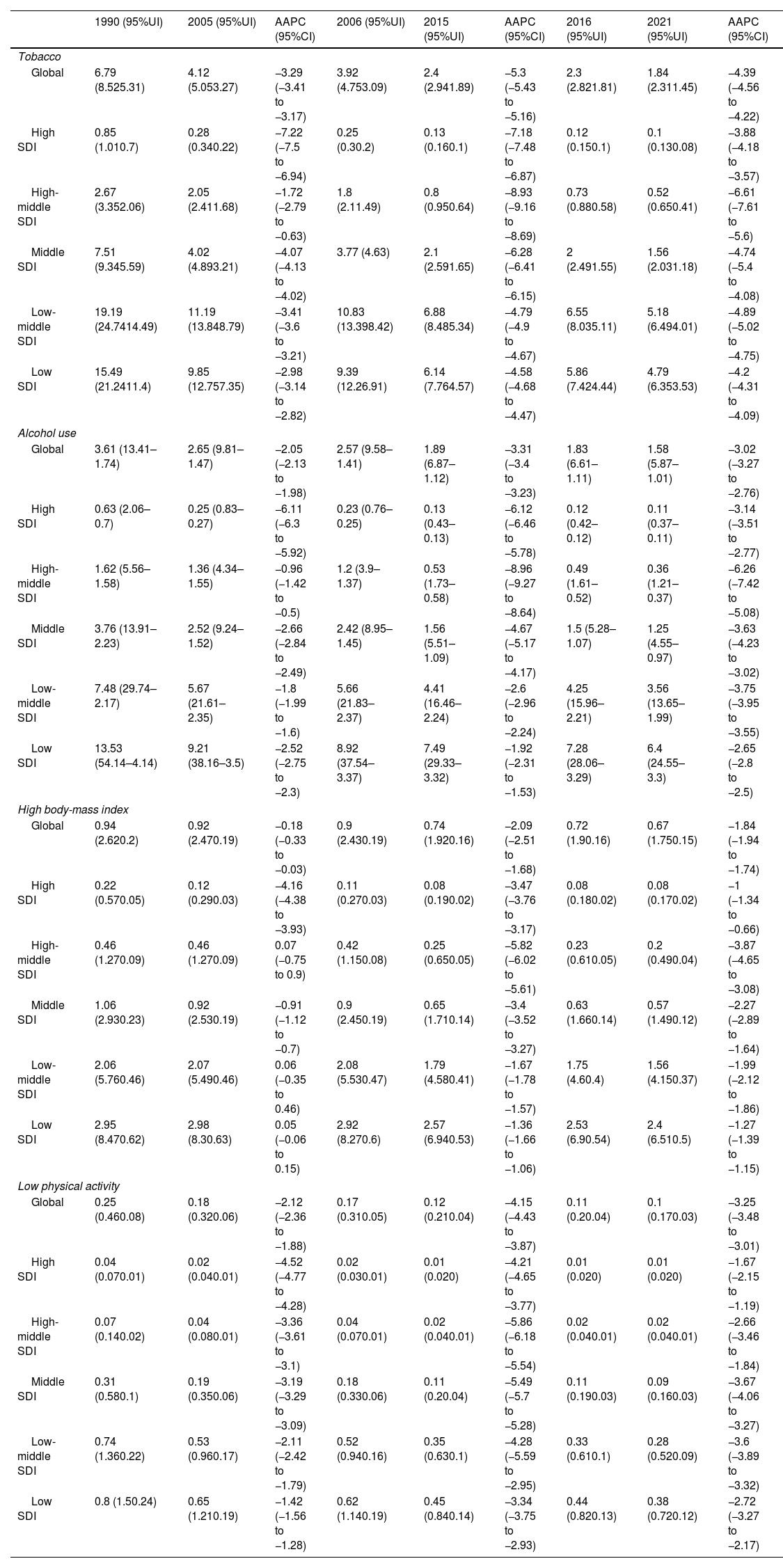
ResultsAt the global level, in the first phase Directly-Observed Treatment Strategy (DOTS), the annual reduction in incidence was 1.18%, and prevalence was 0.71%. In the second phase Stop TB, the cumulative mortality decrease was 56.44% which met the desired goal. However, the cumulative decrease of prevalence was only 20.45%. In the third phase End TB, annual rate of reduction in mortality was 3.33%, while the annual rate of reduction in incidence was 1.14%. ASPR showed a large decrease in both low socio-demographic index (SDI) and high SDI regions, the decrease in medium SDI region was small, which might be dominated by demographic factors at the DOTS stage, changed to epidemiologic in the Stop TB stage and to aging factors in the End TB stage.
ConclusionThe control of TB morbidity and mortality had a great achievement in all the 3 different phases of the TB control strategy, and a concerted global effort is still needed in phase 3 to reach the END TB goal. TB prevalence control needs to be emphasized, especially in the middle and high SDI areas.