No cases of drug-induced hypereosinophilic obliterative bronchiolitis (HOB) have been previously reported in the literature, and, to our knowledge, this is the first documented case of sulfasalazine-induced BOH in a patient with ulcerative colitis.
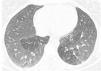
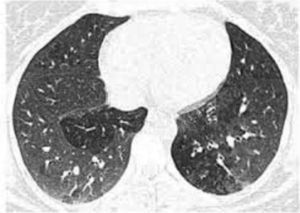
A 61-year-old man, non-smoker, with a history of ulcerative colitis, who had been receiving sulfasalazine treatment for more than 3 years, consulted in January 2012 with a 6-month history of dry cough and progressive dyspnea. Spirometry showed severe airflow obstruction (FEV1=890ml [30%]; FVC=1670ml [44%]; FEV1/FVC=[53%]). High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) revealed bilateral pulmonary opacities, predominantly in the upper lung regions. Clinical laboratory tests showed eosinophilia in blood and in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (7.6g/l and 80%, respectively). The patient was diagnosed with eosinophilic pneumonia; sulfasalazine was switched to 40mg prednisone once a day, resulting in clinical and functional improvement. The patient was not followed up. In September 2013, he presented again with a 5-month history of dry cough and progressive dyspnea. He had discontinued prednisone prematurely, and against our advice, had started taking sulfasalazine again. Spirometry showed an obstructive ventilatory defect (FEV1=905ml [31% predicted]; FVC=1300ml [34% predicted]; FEV1/FVC=[69% predicted]). Arterial blood gases revealed hypoxemia, HRCT found bilateral areas of mosaic attenuation (Fig. 1), and clinical laboratory results showed 1.9g/l eosinophils in blood. Fiberoptic bronchoscopy showed hyperemia throughout the tracheobronchial mucosa, endobronchial biopsy found prominent eosinophil inflammation, and 32% eosinophils were seen on the bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) leukocyte formula. Sulfasalazine was withdrawn, and the patient began treatment for HOB with 40mg prednisone once a day and nebulized bronchodilators and corticosteroids, producing notable clinical and functional improvement. In November 2013, the patient's FEV1 was 2900ml (114%) and FVC 3810 (105%). We recommended a gradual reduction over the course of several weeks of the initial dose of corticosteroids to the minimum maintenance dose for normal lung function and control symptoms. The patient also received formoterol/budesonide.
Cordier et al.1 recently characterized HOB as a new eosinophilic respiratory disease.1 These authors established 3 diagnostic criteria: (1) eosinophils in blood>1g/l (and/or >25% eosinophils in BAL); (2) persistent airflow obstruction in lung function tests, with a post-bronchodilator FEV1/FVC ratio<70% and FEV1<80% predicted, with no improvement after 4–6 weeks of treatment with inhaled corticosteroids (2000μg/day beclomethasone or equivalent) − other functional parameters indicative of obliterative bronchiolitis are a decrease in forced expiratory flow between 25% and 75% of forced vital capacity (FVC) and an increase in the residual volume/total lung capacity ratio and (3) inflammatory bronchiolitis with significant eosinophilic infiltration on lung biopsy and/or signs of bronchiolitis on HRCT.1,2
HOB may be idiopathic, associated with asthma, or an integral part of an established disease (e.g., Churg–Strauss syndrome, hypereosinophilic syndrome, allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, or adverse drug reaction).1 To date, no cases of drug-induced HOB have been reported. However, a report published some time ago described a 28-year-old man with minocycline-induced pulmonary eosinophilia. Cordier et al. reassessed this case and attributed it to possible iatrogenic HOB.3
In our case, sulfasalazine was the etiological agent for this specific syndrome. While reports of drug-induced HOB in the literature are rare, specialists should be aware of this clinical entity, since early diagnosis is the mainstay of treatment.
Please cite this article as: Katsenos S, Antonogiannaki E-M, Psathakis K. Bronquiolitis obliterante hipereosinofílica inducida por sulfasalazina. Arch Bronconeumol. 2016;52:108.