Antifibrotic therapy only reduces disease progression in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) or progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF), highlighting the need for more effective therapeutic strategies. Whether combining nintedanib and pirfenidone is safe and tolerable in real-world setting is poorly known.
MethodsWe conducted a multicentre, retrospective study of patients with IPF or PPF who had received a combination of nintedanib and pirfenidone and primarily assessed safety and tolerability. Secondary objectives included assessment of dose reduction, treatment cessation, survival, and lung function outcomes.
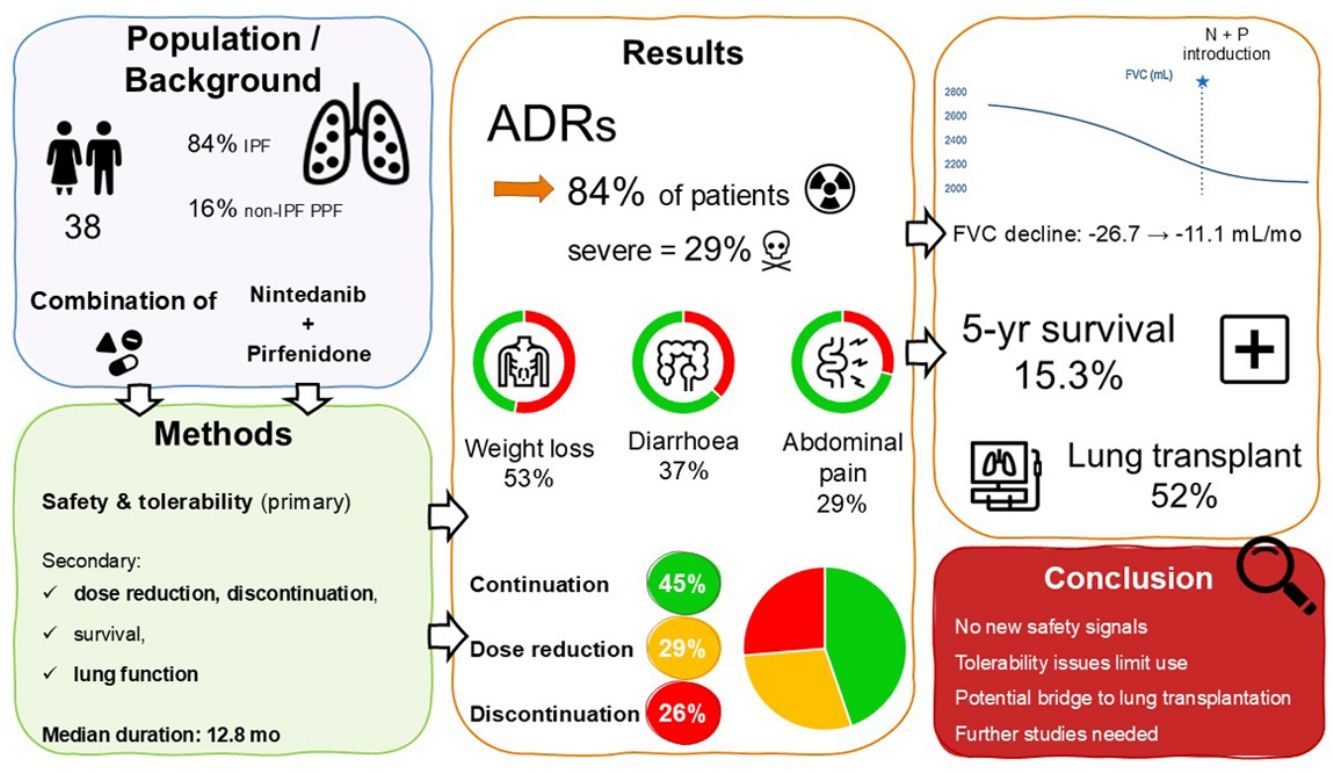
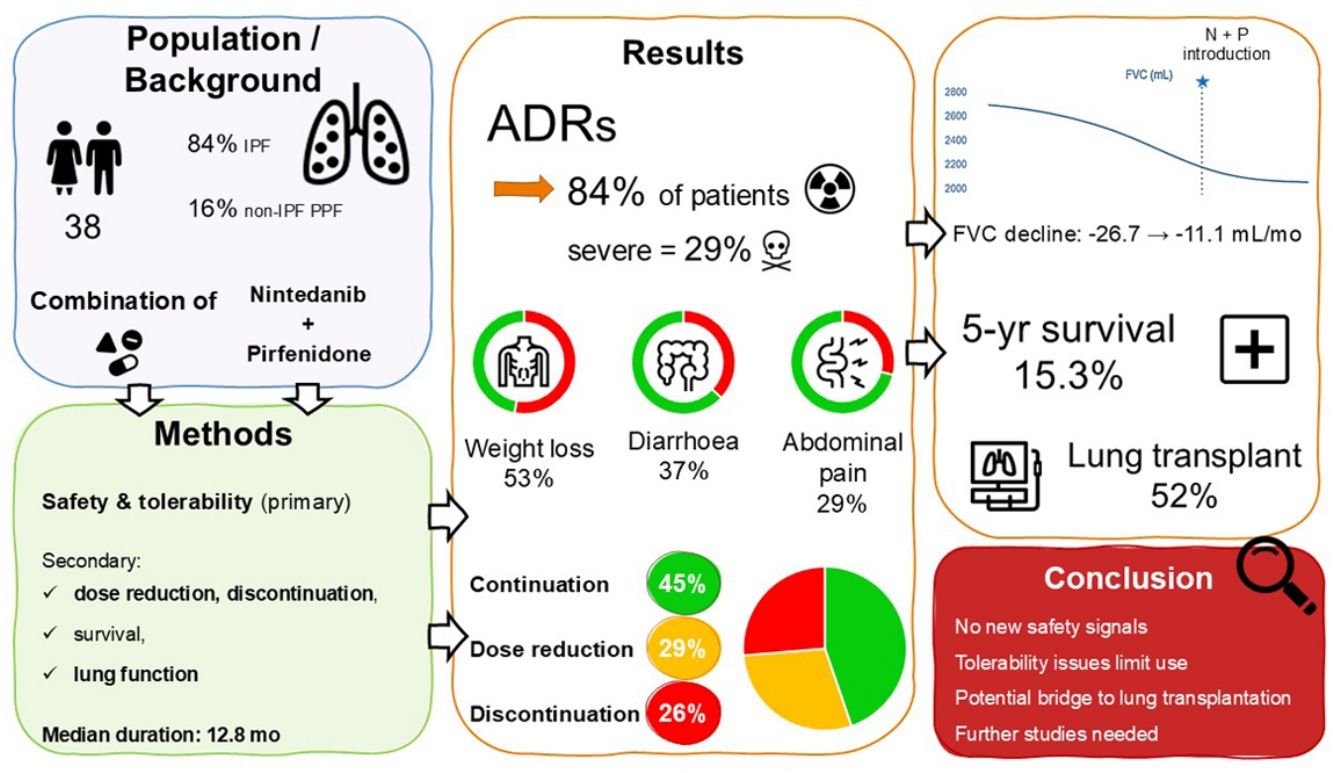
ResultsWe included 38 patients (84.2% with IPF) who received combination therapy between 2014 and 2024. Adverse drug reactions occurred in 84.2% of patients (severe in 28.9%): weight loss (52.6%), diarrhoea (36.8%), abdominal pain (28.9%). Dose was reduced in 28.9% of patients, and combination was discontinued in 26.3%. Median follow-up was 17.4 months; the median duration of combination therapy was 12.8 months. The rate of decline in FVC decreased from −26.7 before the initiation of the combination to −11.1mL/months during combination therapy. The median survival from diagnosis was 28.5 months, with a 5-yr survival of 21.7%. Among patients listed for lung transplantation, 11 (52.4%) underwent transplantation, of whom 6 had continued the combination until the transplantation.
ConclusionAlthough no new safety signal arose, combination therapy is challenging in real-world setting due to poor tolerability especially weight loss. It can nevertheless be a viable treatment option in some patients, particularly as a bridge to lung transplantation. Further studies are needed to confirm the efficacy of this combined therapeutic strategy.
Fibrotic interstitial lung diseases (ILD) encompass a wide spectrum of diseases, associated with respiratory symptoms, exercise limitation, impaired quality of life, and the potential progression to respiratory failure and death. Among them, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) is the most frequent and prototypical disease, associated with a risk of disease progression and a dismal prognosis [1]. Progressive pulmonary fibrosis (PPF) refers to ILDs other than IPF, harbouring a disease behaviour comparable to IPF, with progression of fibrosis despite appropriate management [2–4]. With some variation depending on the underlying ILD diagnosis, one third of patients with non-IPF ILDs develop PPF [5,6], a disease course which is associated with a poor outcome similar to that of IPF [4].
The antifibrotic drugs pirfenidone and nintedanib are approved worldwide for a treatment for IPF, and are generally used as monotherapy. Both drugs approximately halve the rate of annual decline in forced vital capacity (FVC) [7,8], and could reduce mortality and exacerbation rate [9]. Similarly, nintedanib has demonstrated efficacy and is approved in patients with PPF [1,10]. There is weaker evidence that pirfenidone may also slow disease progression in patients with PPF [10–12], and pirfenidone is not approved nor recommended in this indication [1]. In most cases however, antifibrotic monotherapy is not sufficient to halt disease progression in both IPF or PPF, highlighting the critical need for more effective drugs and therapeutic strategies.
Pirfenidone and nintedanib are synthetic molecules administered orally. There is evidence indicating that each drug has distinct mechanisms of action within the fibrotic cascade [13–15], providing a theoretical rationale for combining them to further reduce lung function decline [16,17]. Pharmacokinetic studies did not show relevant pirfenidone–nintedanib interactions [18,19]. However, their side effect profiles partially overlap, notably with digestive adverse events and asthenia. Even when used as monotherapy, their tolerability is often a limiting factor to long-term continuation, leading in real-world studies to dose reduction or even discontinuation [20–22], and potentially hampering the long-term benefits of treatment.
Experience of the use of these drugs in combination is limited to 3–6 months clinical trials, and to a few short-term observational studies [18,23–25]. Data on long-term safety and tolerability of combination therapy are limited. In this retrospective, multicentre, observational study, we aimed at assessing the tolerability and clinical outcomes of the combination of pirfenidone and nintedanib in patients with IPF or PPF treated in real-world setting, with a special focus on the subgroup of patients in whom the combination therapy was given as a bridge to lung transplantation.
MethodsStudy design and ethicsWe conducted an observational study in 6 centres with expertise in ILD (five from France and one from Spain). Data were collected retrospectively from electronic medical records.
This study was conducted with respect to the Declaration of Helsinki. In French centres, each patient was informed through a notice letter about their right to oppose the collection of their personal data, in line with French regulations. Informed consent signature was waived. The study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Hospices Civils de Lyon and was registered with the national data protection agency (Commission Nationale de l’Informatique et des Libertés, number 23-5137). In the Spanish centre, all patients signed an informed consent and were included in the patient registry of the ILD Unit of the Hospital. Approval was obtained from the Institutional Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the Hospital Universitario de la Princesa (Registration #3775).
PopulationEligible patients had a diagnosis of IPF according to the criteria of the ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT [1], or a diagnosis of PPF according to the INBUILD trial definition [12]. Each participating centre reviewed its cases of IPF and PPF and extracted from electronic medical records the data on patients receiving combination therapy.
Inclusion criteria were: (i) age of 18 years or older, and (ii) a decision of combination therapy with pirfenidone and nintedanib taken during a multidisciplinary discussion, with combination therapy being allegedly taken by the patient for at least one day. The baseline date was that of the initiation of combination therapy, during the study period from July 2014 to April 2024. Follow-up was censored on April 30, 2024.
DefinitionsAdverse drug reaction (ADR) referred to any adverse event that occurred during follow-up and was attributed by the authors to either of the antifibrotic treatments.
Severe diarrhoea was defined as grade III or more as per the Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE). The severity of liver enzyme elevation was graded according to CTCAE. Severe ADRs included a weight loss exceeding 10% of the initial body weight, severe diarrhoea, elevation of liver enzymes grade II or more, and/or any ADR resulting in hospitalization.
We defined discontinuation of combination therapy as the permanent cessation of either or both antifibrotic drugs for any reason other than death or lung transplantation.
Antifibrotic drugsPirfenidone and nintedanib were initiated concomitantly or sequentially, left to the discretion of the treating physician, which was discussed in multidisciplinary meeting in all cases. Initial dosage, as well as down titration and/or temporary interruption of antifibrotics in case of adverse events, and the use of antidiarrheal medications, were at the discretion of the treating physician. Body weight was measured at the time of performing pulmonary function tests during hospital visits. If data were available, we reported the criteria for transitioning from monotherapy to combination therapy, as indicated in the multidisciplinary discussion report. We retrospectively categorized cases in two groups: “bridge to transplantation” and “disease worsening not suitable for lung transplantation”. All patients benefited from “full healthcare coverage” due to advanced disease, and both antifibrotic drugs were reimbursed by the French or Spanish public social security, respectively.
Objectives and outcomesThe primary objective was to evaluate the safety profile of the combination therapy, with a detailed account of ADRs. Secondary objectives were to describe the factors leading to prescribe both drugs in combination, to describe the proportion of patients who required dose reductions or discontinued combination therapy, as well as the timelines and the underlying reasons for these treatment adjustments. Additionally, we assessed changes in combination therapy exposure over time and evaluated overall survival. An exploratory analysis was conducted to investigate the association of combination therapy with changes in lung function, especially FVC, before versus while receiving combination therapy. Finally, we analyzed the subgroup of patients receiving combination therapy as a bridge therapy to lung transplantation to explore potential trends regarding clinical outcomes, safety and transplant eligibility in this population.
Statistical analysisThe statistical analysis plan was predefined. Continuous variables were presented as mean (± standard deviation), or median (with interquartile range [IQR]) if not normally distributed (as assessed by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test). Means were compared using Student's t test for data with a normal distribution. For non-normally distributed data, the Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used for comparisons. Medians were compared using the Mann–Whitney U test, as appropriate. Categorical variables were analyzed using either the Chi-squared test or Fisher's exact test, based on expected frequencies. We used the Kaplan–Meier method for survival analysis, defining all-cause mortality as the event for overall survival. For analysis of combination therapy cessation, the event of interest was defined as the discontinuation of either pirfenidone, nintedanib, or both drugs. To compare the rate of lung function decline up to 24 months before, and while receiving combination therapy initiation, we modelled monthly trends for each pulmonary function parameter, as estimated by the mixed-effects model. A statistically significant difference between the slope before and while receiving combination therapy was determined by the Wald test on the interaction coefficient between slope and the presence of combination therapy. All pulmonary function measurements recorded one month after discontinuation of combination therapy or more were excluded, regardless of the reason for discontinuation. All tests were two-sided. No adjustment for multiple comparisons was done. Missing variables are presented as such.
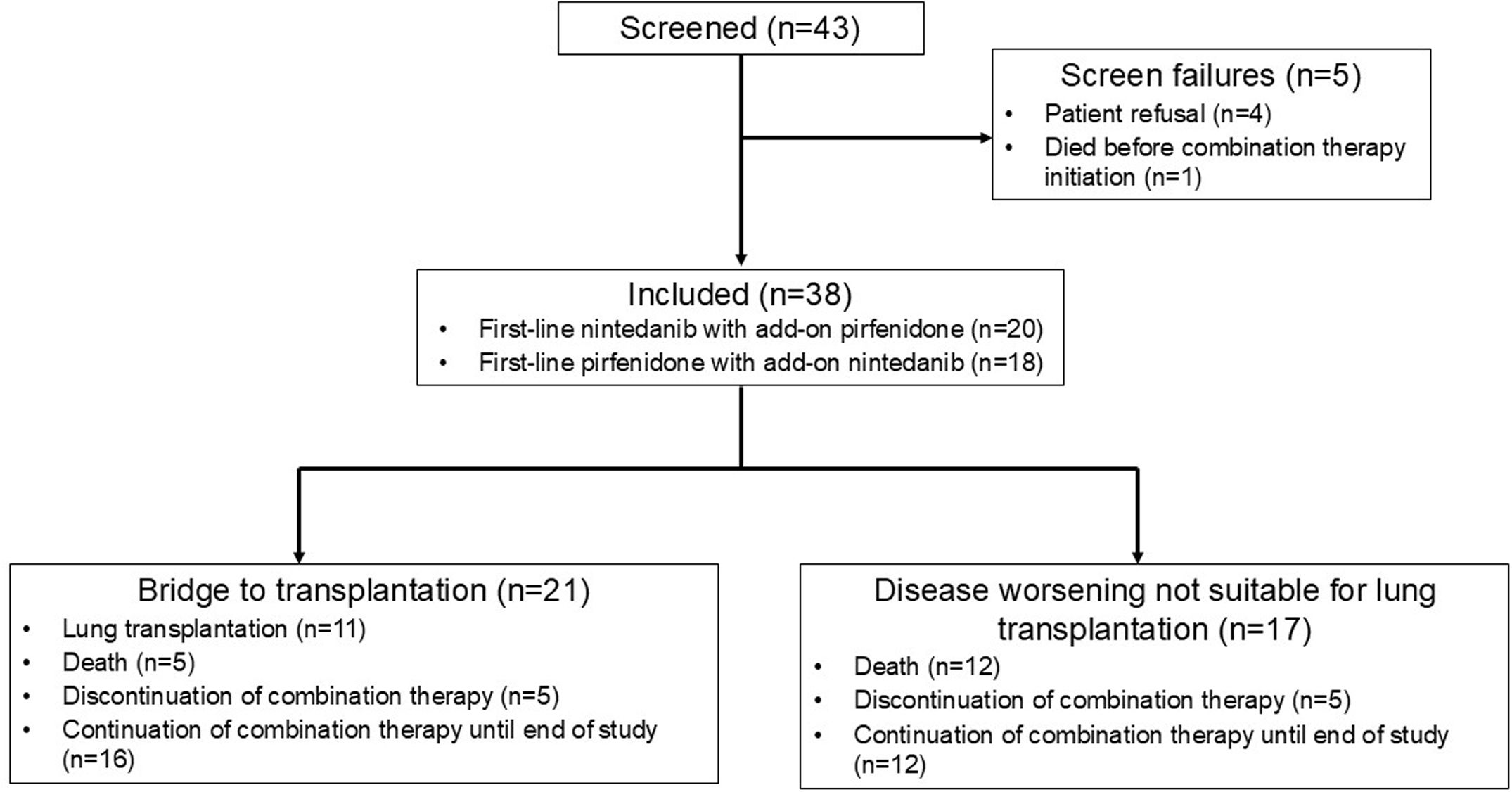
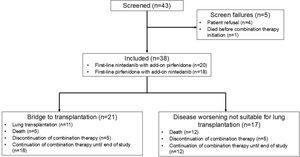
ResultsPopulationAfter each participating centre reviewed their cases of IPF and PPF and extracted from electronic medical records the data on patients receiving combination therapy, 43 patients were assessed for eligibility; 5 were excluded as they did not initiate the combination therapy (4 patients refused, and one patient died before the initiation of combination therapy); 38 patients who received a combination therapy of nintedanib and pirfenidone between July 2014 and April 2024 and meeting the inclusion criteria were analyzed (Fig. 1). In all cases, the decision to initiate combination therapy was driven by disease progression despite ongoing antifibrotic treatment. In addition, for 21 patients, combination therapy was used as a bridge to transplantation. No patient was denied antifibrotic combination therapy for economic reasons.
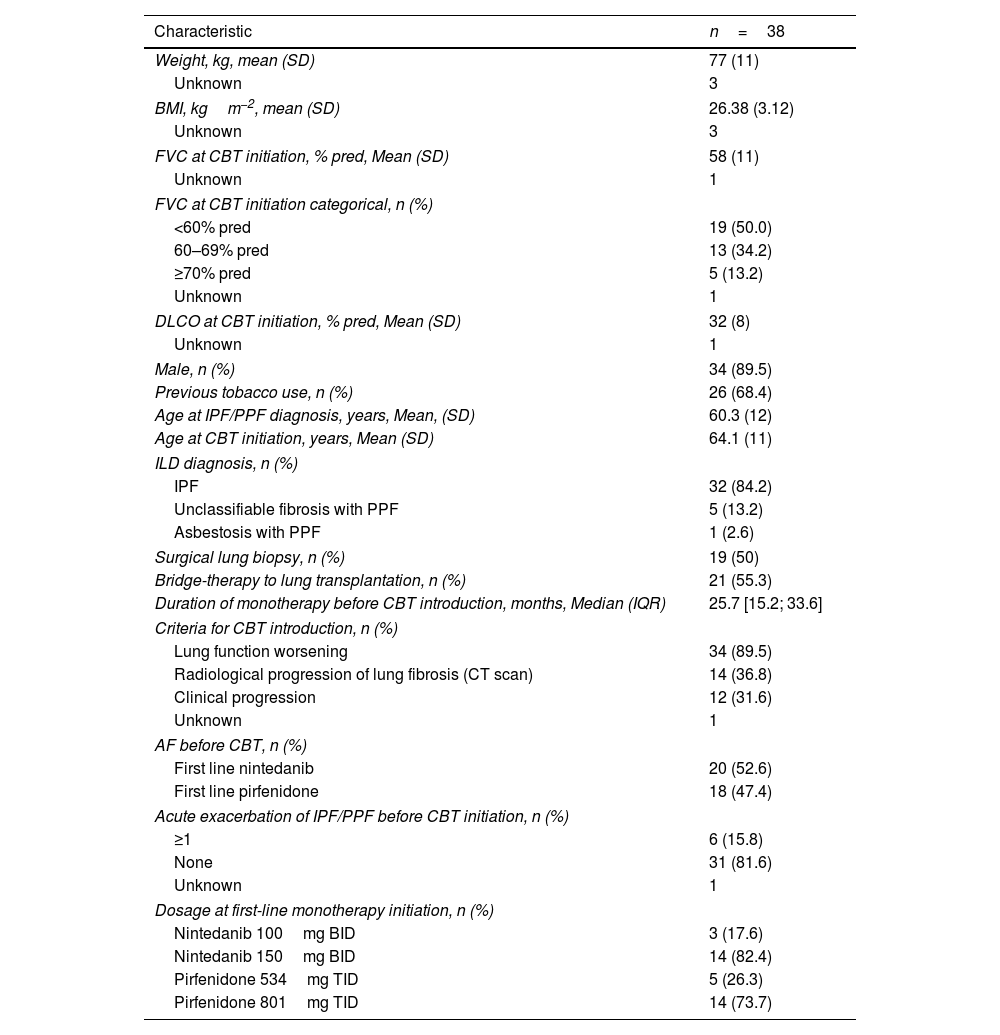
Patients’ characteristics at the time of initiating the combination therapyThe mean age at IPF/PPF diagnosis was 60.3±12 years (Table 1). At combination therapy initiation, mean FVC was 58±11% of predicted value, with 50.0% of patients with an FVC<60% of predicted value. Mean DLCO was 32±8%. IPF represented 84.2% of ILD diagnosis, followed by PPF due to unclassifiable fibrosis (13.2%) and asbestosis (one patient). Twenty-one patients (55%) were listed for transplantation. The criteria for initiating combination therapy included lung function worsening (89.5%), radiological progression of lung fibrosis (36.8%), and clinical worsening (31.6%), with multiple criteria potentially applicable to the same patient. No change in the indication for combination therapy occurred during follow-up. Twenty patients (52.6%) were on nintedanib as first-line monotherapy. At the initiation of combination therapy, the starting dose of nintedanib as second agent was 150mg BID in 82.4% of cases, and 801mg TID in 73.7% of cases when the second agent was pirfenidone.
Patients characteristics at inclusion.
| Characteristic | n=38 |
|---|---|
| Weight, kg, mean (SD) | 77 (11) |
| Unknown | 3 |
| BMI, kgm−2, mean (SD) | 26.38 (3.12) |
| Unknown | 3 |
| FVC at CBT initiation, % pred, Mean (SD) | 58 (11) |
| Unknown | 1 |
| FVC at CBT initiation categorical, n (%) | |
| <60% pred | 19 (50.0) |
| 60–69% pred | 13 (34.2) |
| ≥70% pred | 5 (13.2) |
| Unknown | 1 |
| DLCO at CBT initiation, % pred, Mean (SD) | 32 (8) |
| Unknown | 1 |
| Male, n (%) | 34 (89.5) |
| Previous tobacco use, n (%) | 26 (68.4) |
| Age at IPF/PPF diagnosis, years, Mean, (SD) | 60.3 (12) |
| Age at CBT initiation, years, Mean (SD) | 64.1 (11) |
| ILD diagnosis, n (%) | |
| IPF | 32 (84.2) |
| Unclassifiable fibrosis with PPF | 5 (13.2) |
| Asbestosis with PPF | 1 (2.6) |
| Surgical lung biopsy, n (%) | 19 (50) |
| Bridge-therapy to lung transplantation, n (%) | 21 (55.3) |
| Duration of monotherapy before CBT introduction, months, Median (IQR) | 25.7 [15.2; 33.6] |
| Criteria for CBT introduction, n (%) | |
| Lung function worsening | 34 (89.5) |
| Radiological progression of lung fibrosis (CT scan) | 14 (36.8) |
| Clinical progression | 12 (31.6) |
| Unknown | 1 |
| AF before CBT, n (%) | |
| First line nintedanib | 20 (52.6) |
| First line pirfenidone | 18 (47.4) |
| Acute exacerbation of IPF/PPF before CBT initiation, n (%) | |
| ≥1 | 6 (15.8) |
| None | 31 (81.6) |
| Unknown | 1 |
| Dosage at first-line monotherapy initiation, n (%) | |
| Nintedanib 100mg BID | 3 (17.6) |
| Nintedanib 150mg BID | 14 (82.4) |
| Pirfenidone 534mg TID | 5 (26.3) |
| Pirfenidone 801mg TID | 14 (73.7) |
AF: antifibrotic therapy; BID: bis in die (twice a day); BMI: body mass index; CBT: combination therapy; CT scan: computed tomography scan; DLCO: diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; FVC: forced vital capacity; ILD: interstitial lung disease; IPF: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; PFT: pulmonary function tests; pred: predicted value; PPF: progressive pulmonary fibrosis; SD: standard deviation; TID: ter in die (three times a day).
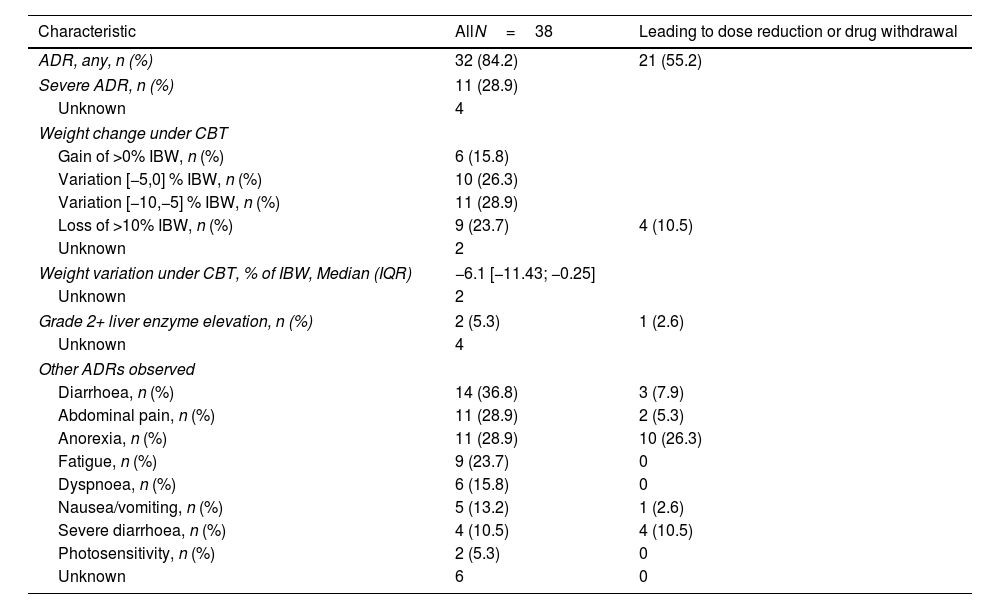
Following the start of combination therapy, 84.2% of patients (n=32) reported at least one ADR, and a severe ADR was reported in 28.9% of patients (n=11) (Table 2). Hospitalization was required to manage ADRs in 3 cases (Fig. S1): grade 3 diarrhoea in 2 patients, and liver enzyme elevation in one patient.
Adverse drug reactions. More than one adverse reaction can occur in a single subject.
| Characteristic | AllN=38 | Leading to dose reduction or drug withdrawal |
|---|---|---|
| ADR, any, n (%) | 32 (84.2) | 21 (55.2) |
| Severe ADR, n (%) | 11 (28.9) | |
| Unknown | 4 | |
| Weight change under CBT | ||
| Gain of >0% IBW, n (%) | 6 (15.8) | |
| Variation [−5,0] % IBW, n (%) | 10 (26.3) | |
| Variation [−10,−5] % IBW, n (%) | 11 (28.9) | |
| Loss of >10% IBW, n (%) | 9 (23.7) | 4 (10.5) |
| Unknown | 2 | |
| Weight variation under CBT, % of IBW, Median (IQR) | −6.1 [−11.43; −0.25] | |
| Unknown | 2 | |
| Grade 2+ liver enzyme elevation, n (%) | 2 (5.3) | 1 (2.6) |
| Unknown | 4 | |
| Other ADRs observed | ||
| Diarrhoea, n (%) | 14 (36.8) | 3 (7.9) |
| Abdominal pain, n (%) | 11 (28.9) | 2 (5.3) |
| Anorexia, n (%) | 11 (28.9) | 10 (26.3) |
| Fatigue, n (%) | 9 (23.7) | 0 |
| Dyspnoea, n (%) | 6 (15.8) | 0 |
| Nausea/vomiting, n (%) | 5 (13.2) | 1 (2.6) |
| Severe diarrhoea, n (%) | 4 (10.5) | 4 (10.5) |
| Photosensitivity, n (%) | 2 (5.3) | 0 |
| Unknown | 6 | 0 |
ADR: adverse drug reaction; CBT: combination therapy; IBW: initial body weight; IQR: interquartile range.
The most common ADR was weight loss, with the loss of 5% or more of initial body weight in 52.6% of patients and more than 10% of initial body weight in 23.7% of patients. Under combination therapy, the median maximal weight loss was −6.1kg [−11.43; −0.25]. The next most frequent ADRs were diarrhoea (36.8%), severe in four patients (10.5%), abdominal pain and anorexia (28.9% each), and fatigue (23.7%). Worsening of dyspnoea was reported in 15.8% of patients.
Two patients (5.3%) experienced grade II+ liver enzyme elevation. The first case involved a 78-year-old man treated with nintedanib who received add-on full-dose pirfenidone and two months later developed a grade II liver enzyme elevation. Pirfenidone was subsequently discontinued, and liver function normalized. The patient continued with nintedanib monotherapy. The second case was a 68-year-old woman who had been on pirfenidone, with add-on nintedanib at full initial dosage. She experienced a grade III liver enzyme elevation 22 months after initiation of combination therapy. Following the cessation of both antifibrotic agents, liver function normalized. Both antifibrotics were then reintroduced sequentially, without recurrence of hepatic adverse event.
Twenty-one patients had a dose reduction or treatment discontinuation related to ADRs. In those patients, the main causes for treatment modifications were anorexia (47.6%), diarrhoea (33.3%), weight loss (19.0%) and abdominal pain (9.5%). Nausea and vomiting were associated with dose reduction or treatment discontinuation in only 4.8% of cases.
When comparing the sequences “first-line nintedanib with add-on pirfenidone” (n=20) and “first-line pirfenidone with add-on nintedanib” (n=18), there was no statistical difference in tolerability (as indicated by the need for dose reduction or treatment discontinuation) (Fisher's exact test, p=1.00).
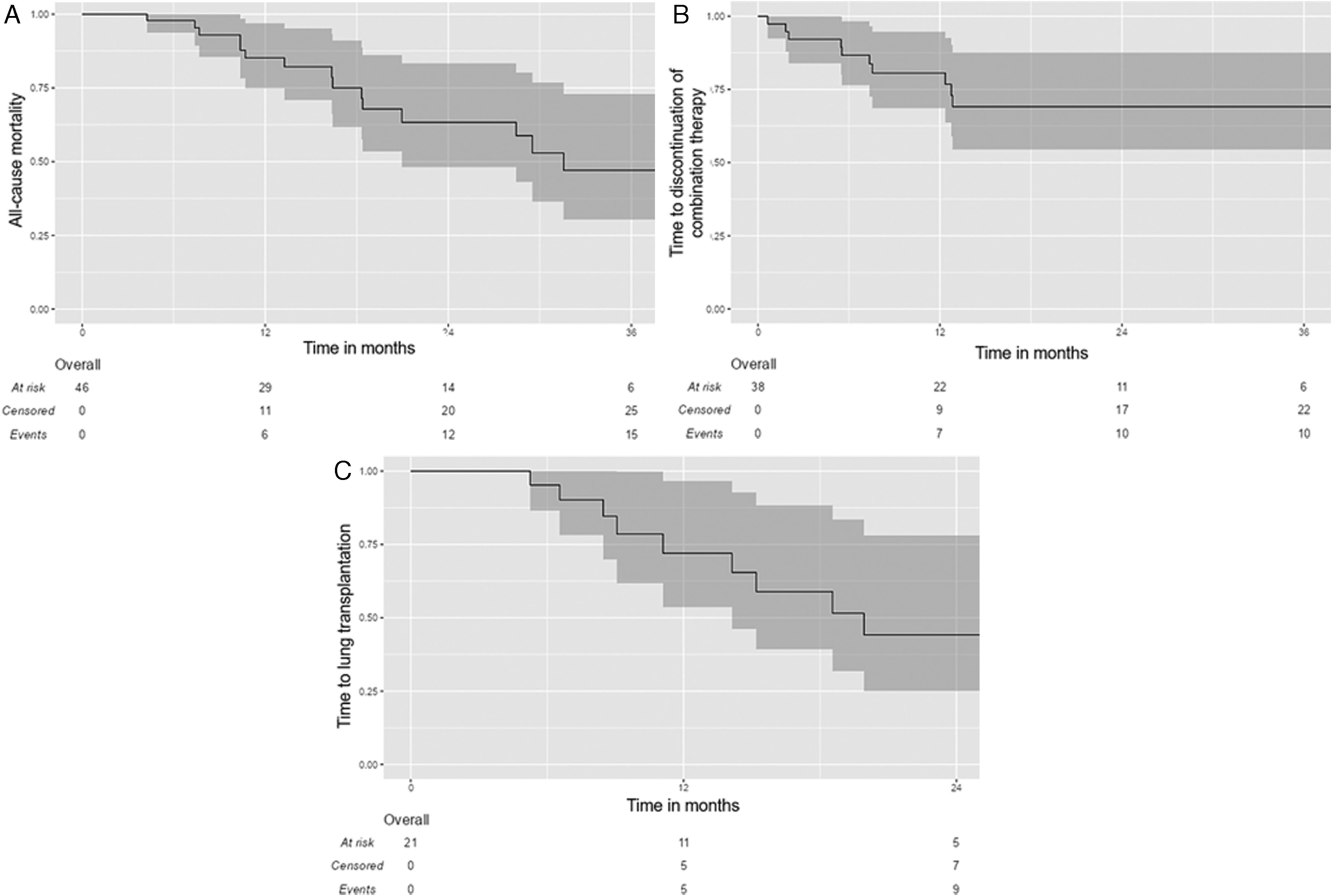
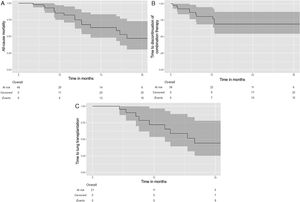
EvolutionPatients were followed for a median duration of 17.4 months [10.4; 29.3]. In the whole population analysis (Fig. 2), the median survival was 28.5 months [16.4, NA], with a five-year survival of 21.7% (95%CI: 8.8–53.4). At the end of follow-up, 16 patients (42.1%) had received combination therapy for less than 12 months, including two patients who were still receiving both medications at the end of the study. Among them, 7 patients (18.4%) received the combination therapy for less than 6 months.
Kaplan–Meier estimates of time to all-cause transplant-free death (A) and time to discontinuation of combination therapy (B) in the whole study population (n=38); and time to lung transplantation (C) in the bridge-therapy subgroup (n=21). Time=0 on the X axis corresponds to the initiation of combination therapy. The shadowed areas represent the 95% confidence interval.
At the time of censoring, 17 patients (44.7%) had continued combination therapy without dose reduction, 11 patients (28.9%) had continued with a dose reduction, and 10 patients (26.3%) had discontinued combination therapy (excluding cessation for death or lung transplantation). Among those who had discontinued the combination therapy, 8 patients had stopped pirfenidone, 2 patients had stopped nintedanib, and none had stopped both antifibrotic therapies. Of 10 patients who discontinued the combination therapy, 5 discontinued during the first 6 months, and 2 discontinued during the subsequent 6 months (e.g. 7/10 during the first year). The median time to combination therapy discontinuation was 6.5 months [2.9; 11.2]. The median duration of exposure to combination therapy was 12.8 months [7.4; 29.0] in the whole population.
Within the subgroup that discontinued the combination therapy, one exacerbation of IPF/PPF occurred while patients were receiving combination therapy (median exposure duration 6.46 months [2.90; 11.20]), versus 5 exacerbations in the period following its discontinuation (median exposure duration 6.54 months [4.59; 11.20]) (p=0.269).
Subgroup analysis of patients listed for lung transplantationIn the subgroup of patients listed for lung transplantation (n=21), eleven patients (52.4%) were transplanted during the study period (Fig. 1). The discontinuation rate of combination therapy was 23.8% in the entire subgroup during the study period (n=5), with no statistically significant difference compared to the discontinuation rate in the overall cohort (26.3%) (p=0.92). Among the eleven lung transplant recipients, the median time from the start of combination therapy to transplantation was 14.2 months [8.76; 19.3]; three patients (27.3%) discontinued combination therapy before the day of transplantation. Patients had bilateral lung transplantation in half of the cases. Five patients died on the waiting list (23.8%).
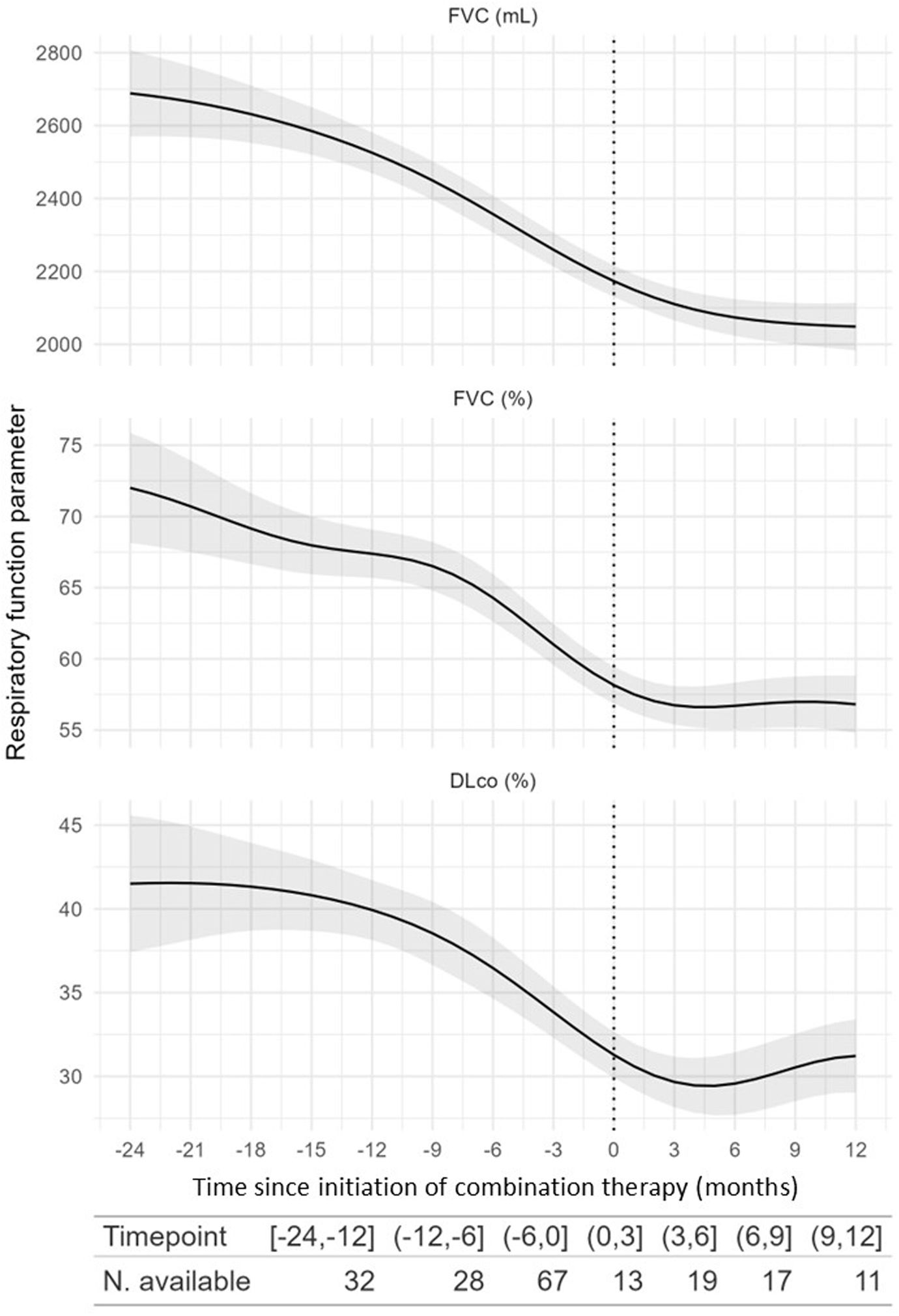
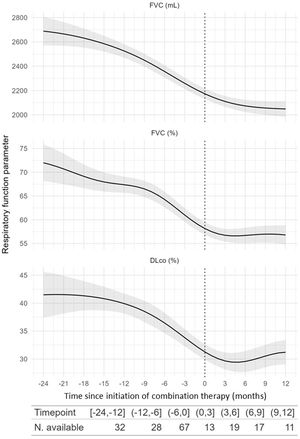
Exploratory analysis of combination therapy efficacyWe evaluated longitudinal changes in FVC, FEV1, DLCO, and 6-minute walk test (6MWT) before and while receiving combination therapy. We found a significant change in the trend in FVC (mL) (p=0.02) (Fig. 3) and FEV1 (mL) (p=0.011), but not in FVC (%) (p=0.6), DLCO (%) (p=0.13), or 6MWT (p=0.4) (Table S1).
Modelling of the evolution of pulmonary function test parameters 24 months before and after combination therapy initiation. The shadowed areas represent the 95% confidence interval. DLCO: diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (expressed in mL/min/mmHg); FVC: forced vital capacity; dashed line: combination therapy initiation.
We reported the outcomes of 38 patients treated with a combination of pirfenidone and nintedanib for IPF or PPF. Upon inclusion, patients exhibited a severe functional impairment (50.0% had a FVC<60%, and mean DLCO was 32% of predicted). Approximately half of the patients received first-line nintedanib, while the other half received pirfenidone. The median duration of initial monotherapy was 25.7 months [15.2; 33.6]. At the initiation of combination therapy, the add-on antifibrotic treatment was administered at full recommended dosages of nintedanib and pirfenidone, in 82.4% and 73.7% of cases respectively.
The safety profile of the combination therapy was consistent with that of the individual antifibrotic drugs. ADRs were observed in 84.2% of patients, and were severe in 28.9%. The most frequent ADRs were weight loss (loss of ≥5% of initial body weight in 52.6% of patients), diarrhoea (36.8%), abdominal pain and anorexia (28.9% each).
For monotherapy, data issued from clinical trial [7,8,26] and real-world studies [27–29] indicate that the incidence of adverse events for nintedanib and pirfenidone were, respectively 4–32% and 5–30% for weight loss, 24–63% and 3–25% for diarrhoea, and 8–29% and 12–17% for anorexia.
As compared to monotherapy, only limited data are available regarding combination therapy of pirfenidone and nintedanib in patients with IPF/PPF. Three clinical trials investigated the use of a combination of nintedanib and pirfenidone in patients with IPF [18,23,25], including one by Vancheri et al. in which patients treated with nintedanib were randomized to receive add-on pirfenidone for 12 weeks versus nintedanib alone [23]. In this study, nintedanib with add-on pirfenidone was not associated with an increased incidence of ADRs or serious ADRs (monotherapy vs combination: 89% vs. 88%, and 3.8% vs. 9.8%, respectively). However, similar to our study, ADRs were the primary reason for discontinuation of combination therapy. These trials did not report any worsening in quality of life among patients undergoing combination therapy [23,25].
Overall, previous trials and real-life studies on combination therapy reported an incidence of ADRs ranging from 71% to 89% (any ADR), with serious ADRs occurring in 4% to 7% of cases. The most common adverse events included diarrhoea (33–49%), anorexia (11–39%), consistent with our findings [18,23–25,30–32].
In our cohort, two patients (5.3%) experienced grade II+ liver enzyme elevation, in line with previous findings [31]. In both cases, the liver function normalized after the interruption of both antifibrotic agents, and both antifibrotics could be reintroduced sequentially, without recurrence of hepatic adverse event.
The incidence of weight loss in our cohort was higher than previously reported for combination therapy (52.6% vs. reported rates of 7–17%) [18,23–25,30–32], and was severe in 23.7%. This could be explained not only by the additive effect from the two antifibrotic combined, but also by the advanced stage of the disease in our patients [33,34]. Tolerability data may also differ between real-life studies and randomized controlled trials due to differences in the rate and nature of comorbidities [23,25], as well as in patient follow-up and management of adverse events. There is also some heterogeneity in the data reported and a lack of precision on the definition of weight loss across studies [31].
The safety profile of combination therapy in our cohort was otherwise consistent with findings from other studies, and in line with that observed with monotherapy. This could be attributed to a selection bias of patients, as patients with poor tolerance to nintedanib or pirfenidone monotherapy were likely not considered for combination therapy. Furthermore, nintedanib and pirfenidone seem to involve different metabolization pathways [35,36]. Data do not suggest significant drug-drug interactions between both antifibrotic treatments [19,23], aside from a potential yet controversial reduction in nintedanib bioavailability when co-administered with pirfenidone [18].
Overall continuation of combination therapy was relatively good, with patients remaining on treatment for a median duration of 12.8 months. Combination therapy was terminated in 26.3% of patients (excluding death or lung transplantation), dose was reduced in 28.9%, and dose was continued unchanged in 44.7% of patients. In the literature, treatment discontinuation rates of monotherapy are reported at 10–21%, dose modification rate of 15–26% and continuation without modification rate of 45–58% [7,8,27–29]. For combination therapy [23–25], previous studies reported rates of 15–49%, 27–43% and 30%, respectively.
Similar to the findings reported by Hisata et al. [24], we observed that the majority of treatment discontinuations for ADRs occurred during the first 12 months. Hisata suggested that physicians were inclined to stop either treatment at the first sign of toxicity, as questions remained about the efficacy and safety of combination therapy. As the first ADR generally occurs shortly after initiation of either nintedanib or pirfenidone [23,37], an early discontinuation of combination therapy would be expected.
Concerning the efficacy of combined treatment, we observed an attenuation in the decline in FVC and FEV1, consistent with previous observations [23–25]. As our study is observational, these results must be taken with caution. The PROGRESSION trial (NCT03939520), an ongoing phase IV trial, is currently evaluating the efficacy and tolerability of a combined therapy of nintedanib and pirfenidone, as compared to unchanged monotherapy, or a switch from one monotherapy to the other, in patients with IPF experiencing disease progression despite first-line antifibrotic therapy.
Antifibrotic drugs reduce the risk of exacerbations of IPF/PPF [9]. Here, we reported the number of exacerbations following discontinuation of combination therapy, however the methodology prevented to derive conclusions on changes in exacerbation rates pre- and post-combination therapy.
In the subgroup of patients listed for lung transplantation and receiving combination therapy, over half (11/21) underwent transplantation during follow-up. Five patients out of 21 (23.8%) discontinued combination therapy among the entire subgroup. We would have hypothesized a better persistence on treatment in the subgroup of patients listed for transplantation due to a possible higher motivation to maintain eligibility, but the rate of treatment cessation in this group was comparable to that of the entire cohort. Secondly, out of 5 patients who discontinued treatment, 4 experienced a >5% reduction in body weight from baseline. Combination therapy may have been discontinued to mitigate further loss of weight as patients prepared for lung transplantation. Interestingly, several studies reported that the continuation of antifibrotics until lung transplantation was safe [38,39].
The limitations of our study include its retrospective design, the limited statistical power due to the small sample size, the absence of comparative arm with monotherapy antifibrotic treatment, and the lack of detailed information about patients’ comorbidities or comedications, which might have influenced clinical outcomes and adverse events. However, the pre-and-post design of the exploratory efficacy analysis allows for a certain degree of comparison against monotherapy regimen. Moreover, since only patients who survived and were not transplanted contributed post-treatment spirometry, and many were already in advanced stages of disease, the apparent slowing of FVC (mL) decline may partly reflect survivor bias and a natural ‘floor effect’, rather than a treatment-specific benefit. As the study population was relatively young and included many patients awaiting lung transplantation, the findings may have limited generalisability to the broader IPF/PPF population.
Despite these limitations, our study has several strengths, including its multicentre, international design. There are limited data on antifibrotic combination therapy in PPF, and this study adds to the emerging evidence in this area.
ConclusionAlthough no new safety signal arose, combination therapy is challenging in real-world setting due to poor tolerability especially weight loss. It can nevertheless be a viable treatment option in some patients, particularly as a bridge to lung transplantation. Further studies are needed to confirm the efficacy of this combined therapeutic strategy.
Take home messageCombining pirfenidone and nintedanib is challenging in real-world setting due to poor tolerability especially weight loss. It can nevertheless be a viable treatment option in some patients, particularly as a bridge to lung transplantation.
Authors’ contributionsCorentin Meersseman: Original Draft Preparation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Review & Editing, Approval.
Elisa Martínez Besteiro: Data acquisition, Investigation, Review & Editing, Approval.
Nicolas Romain-Scelle: Data acquisition, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Review & Editing, Approval.
Bruno Crestani: Data acquisition, Investigation, Review & Editing, Approval.
Sylvain Marchand-Adam: Data acquisition, Investigation, Review & Editing, Approval.
Hilario Nunes: Data acquisition, Investigation, Review & Editing, Approval.
Lidwine Wémeau-Stervinou: Data acquisition, Investigation, Review & Editing, Approval.
Raphael Borie: Data acquisition, Investigation, Review & Editing, Approval.
Rémi Diesler: Data acquisition, Investigation, Review & Editing, Approval.
Claudia Valenzuela: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Review & Editing, Visualization, Supervision.
Vincent Cottin: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal Analysis, Investigation, Resources, Data Curation, Writing, Review & Editing, Visualization, Supervision.
Data sharingThe data supporting the reported results can be obtained from the first author upon reasonable request.
Artificial intelligence involvementArtificial intelligence was not used for this manuscript.
FundingThis work was not funded.
Conflicts of interestAll authors have provided their potential conflicts of interest following the ICMJE guidelines in a file attached to this submission.
Data availability statementData are available for sharing upon reasonable request.