Ingestion of foreign bodies is a common occurrence across all age groups, typically arising from accidental events or inquisitive behavior. While many instances result in uneventful passage through the gastrointestinal tract, certain cases may present therapeutic challenges, especially when the foreign body becomes lodged or migrates to unexpected locations.1,2
The migration of an ingested foreign body into the posterior mediastinum is a rare and challenging scenario, requiring careful consideration and specialized intervention. In this case presentation, we aim to discuss the clinical nuances, diagnostic challenges, and the role of minimally invasive surgical techniques as well as the importance of a careful anamnesis in addressing such unique and intricate cases.
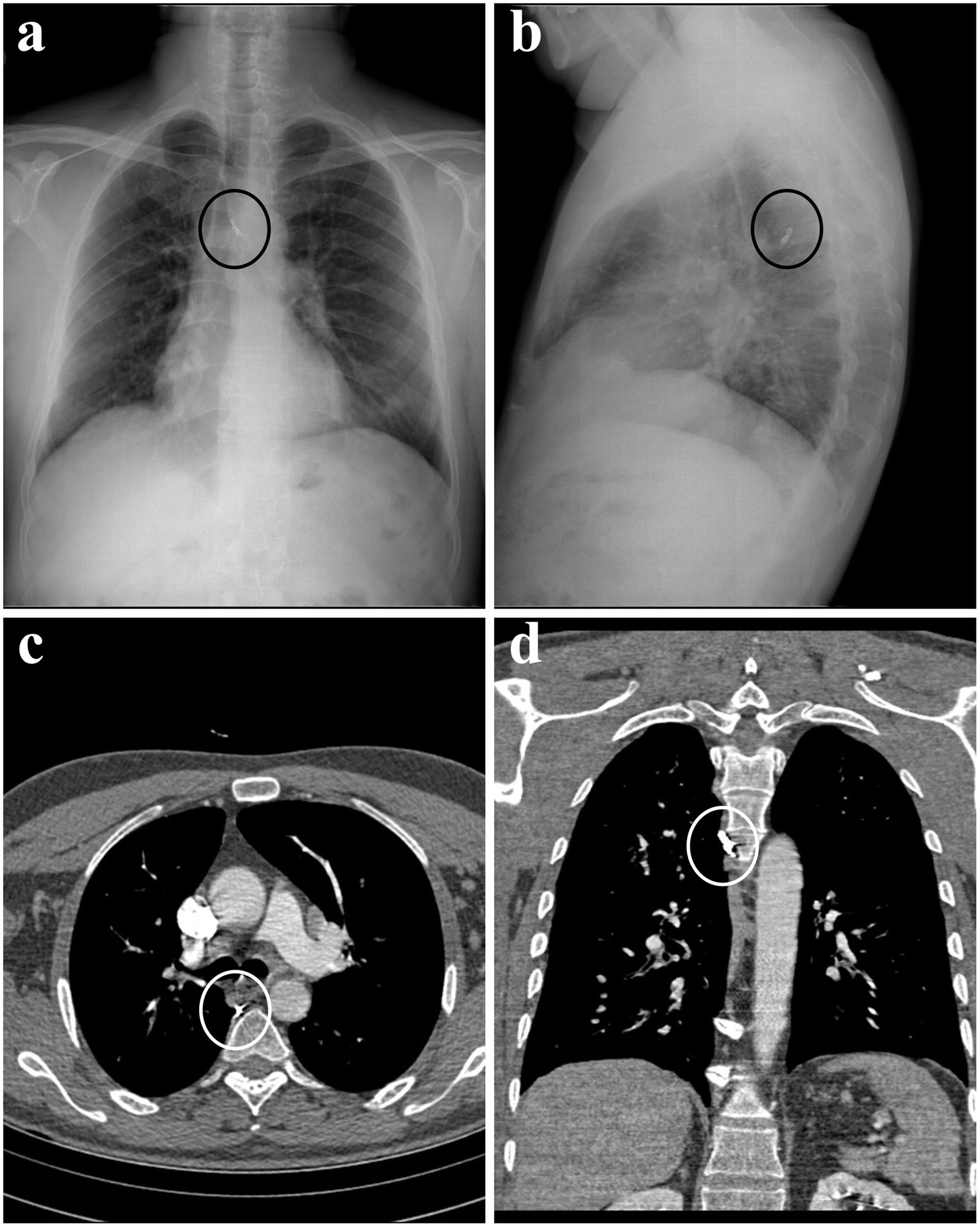
Case ReportA 45-year-old male applied to our department complaint with blood in sputum for 1 week. Physical examination was normal. There was no feature in his medical history other than 20 pack-years of smoking. Chest X-ray and computed tomography (CT) scans revealed the opacity in the posterior mediastinum, suggestive of a metallic foreign body (Fig. 1).
When the anamnesis was detailed due to these radiological findings, it was seen that he had a history of getting a piece of dishwashing scourer in his mouth while eating soup approximately 2 weeks ago. The patient's psychiatric history absence and the presence of eyewitnesses led to the realistic evaluation of this medical history. In the light of these data, surgery was planned with the preliminary diagnosis of a foreign body transesophageally migrated into the posterior mediastinum. Preoperative fiberoptic bronchoscopy was performed, revealing remnants of clots; however, no active hemorrhage was observed.
Surgical intervention was planned due to the likelihood of continued migration of the foreign body, the history of hemoptysis in the patient, and the potential for the foreign body to cause infection.
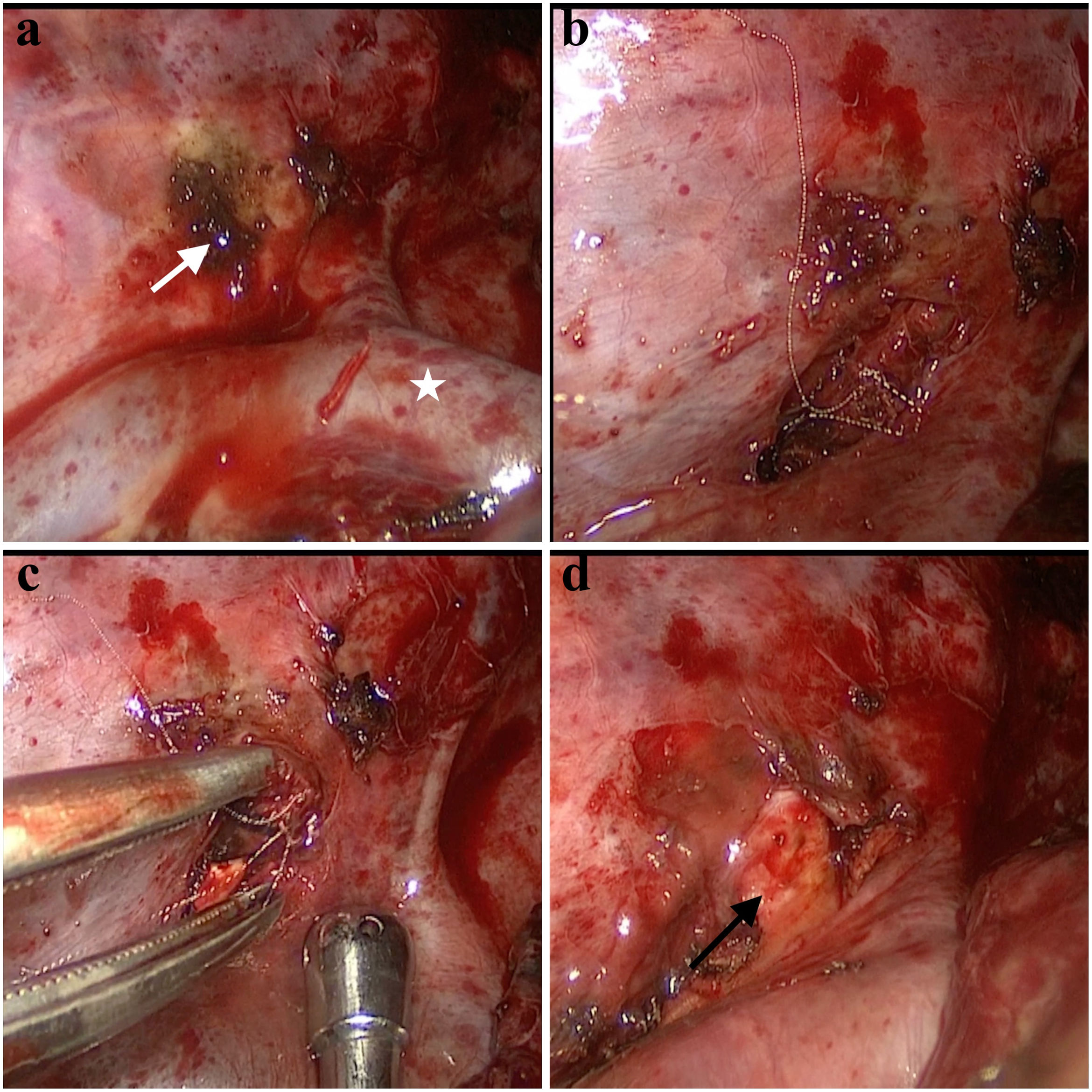
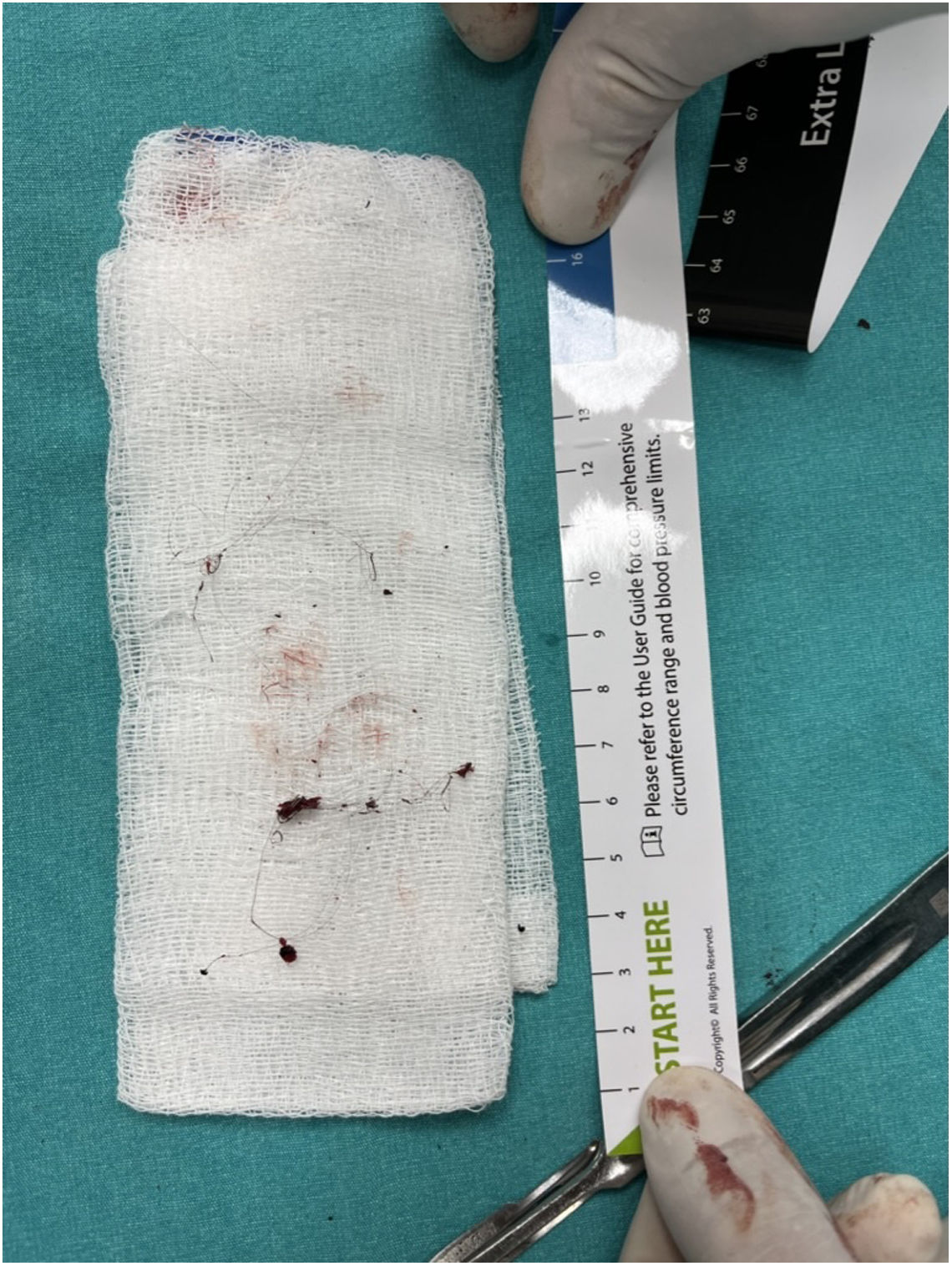
Right sided video-assisted thoracic surgery was performed. Pleural adhesions were removed with blunt and sharp dissections. The area between the azygos vein and the vertebral body was dissected. The sympathetic chain was identified and preserved. The foreign body, consisting of a thinly curved metal material, was completely removed (Figs. 2 and 3). The adjacent esophageal segment was dissected, and air was administered through a nasogastric tube and an underwater leak test was performed. No air leakage was observed in the esophagus. Intraoperative X-ray radiography was performed due to the possibility of a residual foreign body. No residual foreign body was observed. The operation was completed without any complication.
This figure shows intraoperative images in stages. The area indicated by the white arrow in (a) is the area where the lung parenchyma is adhered, and the foreign body is removed from underneath. (b and c) The folded wire piece of a metal dish sponge. (d) The vertebral body after the complete removal of the foreign body is shown with a black arrow.
The postoperative period was uneventful. The thorax tube was terminated on the 3rd postoperative day and the patient was externalized.
DiscussionThe presented case of transesophageal migration of an ingested foreign body into the posterior mediastinum sheds light on the intricate nature of such incidents and emphasizes the need for a comprehensive understanding of atypical migration patterns.
Ingested foreign objects, especially if these objects have pointed ends, can migrate to neighboring areas along the digestive tract. The cases of needles migrating to deep cervical tissues, omentum, and liver after ingestion are documented in the literature. The common characteristic of these cases is that patient history, potential complications, and treatment approaches are generally well-defined.3–5 A history of psychiatric illness or suicidal attempts is frequent and surgery, often preferred as laparotomy or laparoscopy, is commonly chosen due to intra-abdominal migration. However, the posterior mediastinum, being an uncommon location for lodged foreign bodies, demands heightened vigilance in diagnosis and treatment planning.6,7 Standard imaging modalities may not always capture the exact location or provide sufficient information for planning a surgical approach.
In our case, there was also a history of hemoptysis as a confusing symptom. We attributed this to the inflammation induced by the foreign body in the surrounding lung parenchyma. The supporting evidence for this includes increased opacity in the relevant region of the lung parenchyma on CT and, intraoperatively, significant parenchymal adhesions formed in the posterior mediastinal region where the foreign body had lodged.
In our case, the successful application of video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) exemplifies the adaptability of minimally invasive techniques in addressing such complexities. VATS not only allows for precise visualization but also minimizes the invasiveness of the procedure, contributing to a quicker recovery for the patient.
Collaborative efforts are crucial for accurate diagnosis, risk assessment, and the formulation of an effective treatment strategy. Additionally, ongoing advancements in imaging technologies and surgical methodologies play a pivotal role in enhancing our capabilities to manage such intricate cases.
Informed ConsentA written informed consent was obtained from patient.
Authors’ ContributionsIdea/concept, design, writing the article and literature review: G.B.; data collection, control/supervision, critical review: S.K.
FundingThe authors received no financial support for the research and/or authorship of this article.
Conflict of InterestThe authors declared no conflicts of interest.