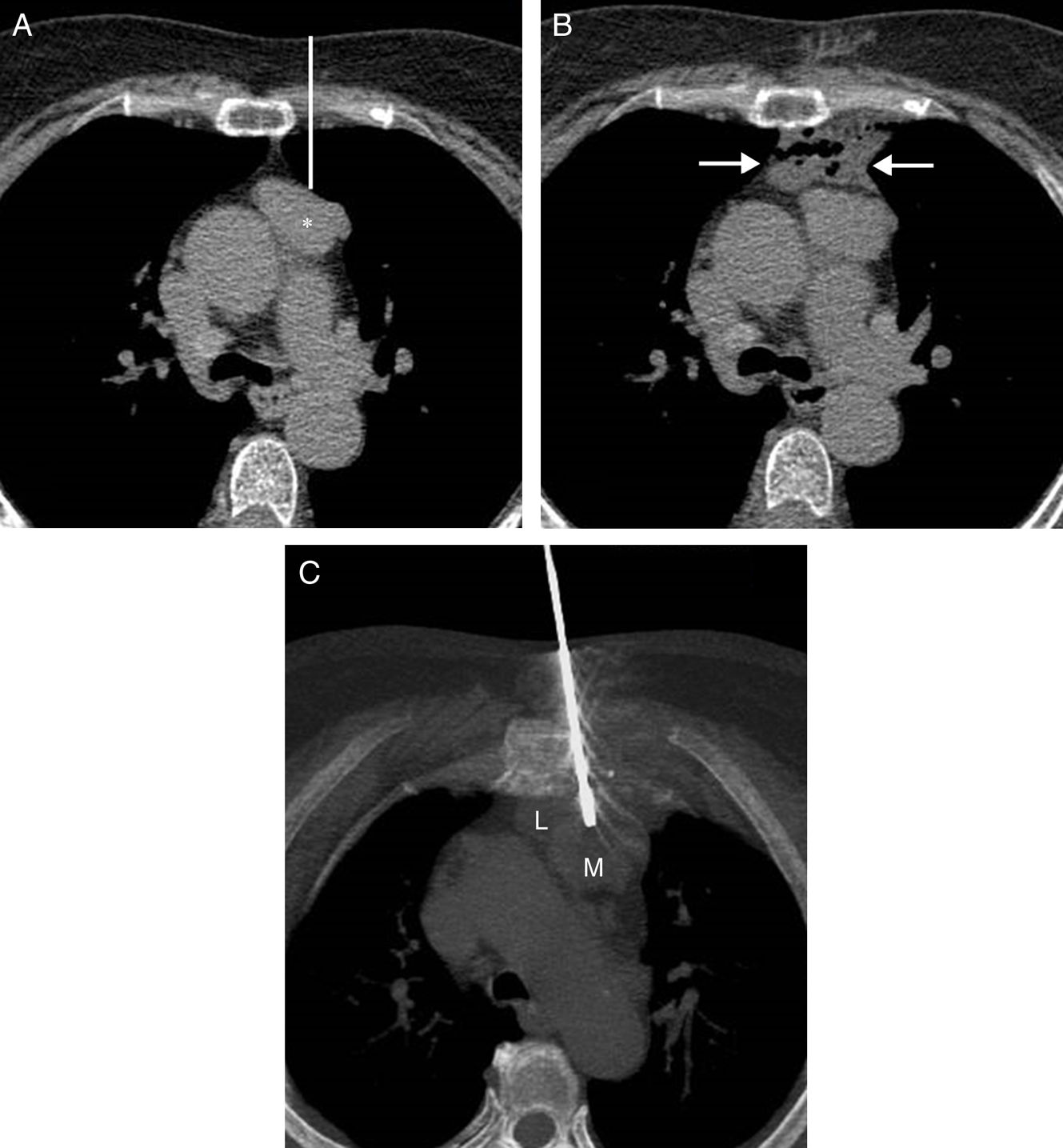
We report the case of a 73-year-old woman with no significant clinical history, in whom an anterior mediastinal mass was detected incidentally. Image-guided core needle biopsy (CNB) of the mass was performed, but the theoretical trajectory of the biopsy needle was interrupted by the pulmonary parenchyma of the left upper lobe between the anterior chest wall and the mediastinal mass (Fig. 1A). To avoid puncturing the pleural surface and the pulmonary parenchyma with the biopsy needle, we used an intramuscular needle to instill 100ml saline into the scant fatty tissue of the patient's anterior mediastinum, thus creating a collection of fluid (Fig. 1B), which provided a safe approach route, avoiding perforation of either the pleura or the left lung. The biopsy needle was then inserted between the left internal mammary vessels and the left lateral edge of the sternum, traversing the previously created fluid collection (Fig. 1C). Histological material was collected that confirmed the diagnosis of thymoma, World Health Organization classification type A. Cytological diagnosis of thymomas using fine needle aspiration can be difficult to interpret, so histological material retrieved by CNB is preferable, although this technique is often accompanied by a higher rate of complications (pneumothorax, lung bleeds).1,2 Hydrodissection with saline is a simple technique that creates a safe access route for the histologic diagnosis of anterior mediastinal masses.
(A) Axial chest CT image showing an anterior mediastinal mass (asterisk). The white line indicates the theoretical path of the biopsy from the anterior chest wall to the mediastinal mass, traversing the pleural surface and the left pulmonary parenchyma. (B) Axial chest CT image showing the creation of a small fluid collection (arrows) between the anterior chest wall and the mediastinal mass. (C) Axial maximum intensity projection CT image of chest showing the biopsy needle crossing the fluid collection (L) and penetrating the mediastinal mass (M).
Please cite this article as: Gorospe Sarasúa L, Almeida-Aróstegui NA, Arrieta P. Biopsia con aguja gruesa de timoma en mediastino anterior: creación de ruta de acceso segura mediante hidrodisección. Arch Bronconeumol. 2018;54:388.