To analyse the frequency, clinical characteristics and survival of patients with lung cancer (LC) who have never smoked in comparison to that in patients who smoke.
Patients and methodsA retrospective study in patients diagnosed with LC by cytohistology between 1999 and 2011. Survival was estimated by the Kaplan–Meier method. The χ2 test was used to estimate the relationship between the variables.
ResultsA total of 2161 patients were diagnosed with LC, 396 (18.3%) of whom had never smoked. The mean age (±standard deviation) in this group was 72.85±10.52 years; 64.6% were women and 35.4% men. According to the cytohistology, 55.6% were adenocarcinoma, 20.5% squamous cell, 15% small cell, 2.7% large cell, and 6.2% other subtypes. The diagnosis was made in advanced stage (iv) in 61.4%, and 14.4% of the patients received surgical treatment. Survival was 12.4%, with no differences between the two groups. In the group of never smokers, women had better survival than men.
ConclusionsOf the patients diagnosed with LC, 18.3% had never smoked. It was diagnosed mainly in women, at advanced stages and the most common histological type was adenocarcinoma. There were no survival differences compared to the group of smokers.
Analizar la frecuencia, las características clínicas y la supervivencia de los pacientes con cáncer de pulmón nunca fumadores comparándolas con los pacientes fumadores.
Pacientes y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de pacientes diagnosticados de cáncer de pulmón mediante citohistología de 1999 al 2011. Se estimó la supervivencia por el método de Kaplan–Meier. Para estimar la relación entre las variables se usó la prueba de χ2.
ResultadosSe diagnosticaron 2.161 pacientes, 396 (18,3%) nunca fumadores. En este grupo la edad media (± desviación estándar) fue de 72,85±10,52, el 64,6% mujeres y el 35,4% hombres. Según la citohistología, el 55,6% eran adenocarcinoma, el 20,5% epidermoide, el 15% de célula pequeña, el 2,7% de célula grande y el 6,2% otros subtipos. El diagnóstico se hizo en estadio avanzado (iv) en el 61,4% de pacientes, y el 14,4% recibieron tratamiento quirúrgico. La supervivencia fue del 12,4%, sin diferencias entre los 2 grupos. En el grupo de nunca fumadores las mujeres tuvieron mejor supervivencia que los hombres.
ConclusionesEl 18,3% fueron pacientes nunca fumadores. Se diagnosticaron mayoritariamente en mujeres, estadios avanzados y estirpe histológica adenocarcinoma. No hubo diferencias de supervivencia con el grupo de fumadores.
Lung cancer (LC) is the leading cause of death from cancer worldwide,1 accounting for 1527000 deaths every year.2 In Spain alone, every year 20401 people die of LC, which is the third most common cause of death after ischaemic heart disease and cerebrovascular disease.3 In Spain, the incidence and mortality of LC continue to rise in women, while in men it reached its peak in the 1990s, and is currently on the decline.4
It is well known that the main causative factor of LC is tobacco use. Indeed, in countries such as the United States, the fall in smoking rates in the population has been accompanied by a reduction in the incidence and mortality of LC.5 However, around 10%–25% of cases of LC occur in never smokers. Even among never smokers, LC remains one of the principal causes of death from cancer6 and in non-smoking women it is the third most common cause of cancer death.7 In recent years this has led to increased interest in other LC risk factors, such as passive smoking, domestic exposure to radon, previous pulmonary comorbidities and genetic or dietary factors.8,9
Recent studies suggest that LC in never smokers (LCNS) is a distinct entity, to be distinguished both epidemiologically and biologically from LC in smokers.10 Furthermore, the rise in the non-smoking population throughout the world justifies the interest in determining how LC behaves in these patients. Accordingly, the aim of our study was to analyse the incidence, clinical characteristics and survival of patients with LCNS in comparison to that in patients who smoke.
Patients and MethodsThis was an observational, retrospective study of a cohort of LC patients, diagnosed between 1 January 1999 and 31 December 2011 in the University Hospital Complex of Orense. All patients with a primary cytohistological diagnosis of LC were included. Case information was collected from the clinical documentation, bronchoscopy and anatomical pathology databases.
We designed a database for the collection of variables, including identification, age, sex, smoking habit, symptoms, comorbidities, fibreoptic bronchoscopy (FB) findings, diagnostic tests, stage, definitive diagnosis, treatment and date of death. The World Health Organisation (WHO) system was used for histological classification.11 Tumour involvement was classified according to the TNM staging system (7th edition) of the International Association for Study of Lung Cancer (IASLC).12 Date of death was obtained from the clinical records, or, if it was not recorded, a telephone call was made to the patient's home or the Death Registry of Galicia. Data were censored on 1 October 2012 (last study day). Never smokers were defined as subjects who had smoked less than 100 cigarettes during their lifetime, and ex-smokers were those who had stopped smoking at least 6 months earlier.13
Statistical AnalysisA descriptive analysis of the data was performed, with quantitative variables expressed as mean±standard deviation. Qualitative variables were provided as absolute frequencies and percentages. The χ2 test was used to determine associations between variables. Survival was estimated using the Kaplan–Meier method and the curves obtained were compared with the Mantel–Haenszel log-rank test. Univariate and multivariate analyses were carried out to identify factors related to death, on the basis of the Cox proportional hazards model. A Cox regression model with p-spline smoothing was estimated for the age variable and for testing the non-linearity of this variable. Statistical significance (P) was set at .05. The Statistical Package for Social Sciences version 15.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL, US) and R Project free software (www.r-project.org/) were used.
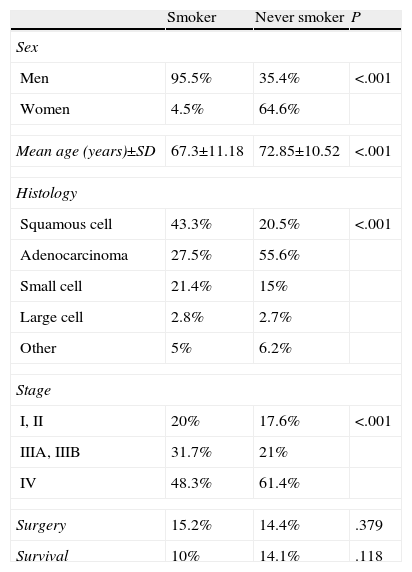
ResultsDemographic CharacteristicsLC was diagnosed in 2161 patients, of which 396 (18%–3%) were LCNS. Of these, 140 (35.4%) were men and 256 (64.6%) women. The principal characteristics of the patients, by smoking habit, are listed in Table 1.
Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics According to Smoking Habit.
| Smoker | Never smoker | P | |
| Sex | |||
| Men | 95.5% | 35.4% | <.001 |
| Women | 4.5% | 64.6% | |
| Mean age (years)±SD | 67.3±11.18 | 72.85±10.52 | <.001 |
| Histology | |||
| Squamous cell | 43.3% | 20.5% | <.001 |
| Adenocarcinoma | 27.5% | 55.6% | |
| Small cell | 21.4% | 15% | |
| Large cell | 2.8% | 2.7% | |
| Other | 5% | 6.2% | |
| Stage | |||
| I, II | 20% | 17.6% | <.001 |
| IIIA, IIIB | 31.7% | 21% | |
| IV | 48.3% | 61.4% | |
| Surgery | 15.2% | 14.4% | .379 |
| Survival | 10% | 14.1% | .118 |
SD: standard deviation; other: adenosquamous, undifferentiated, carcinoid; P: statistical significance of the comparison.
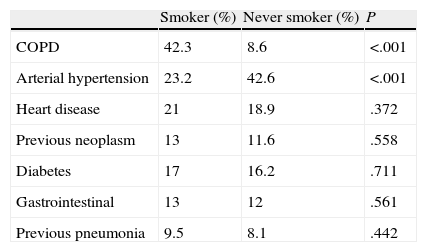
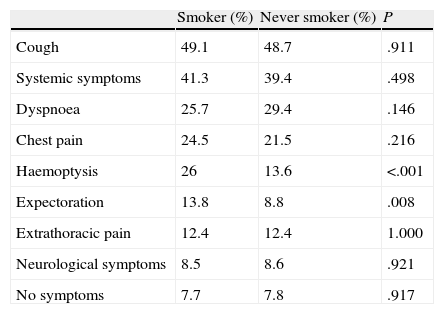
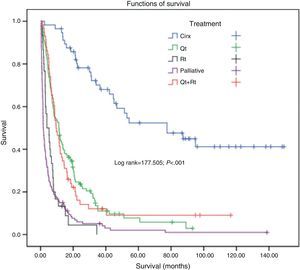
In the LCNS group, the most frequently observed comorbidities were arterial hypertension (42.6%) and heart disease (19%), and in the smokers, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (42.3%) and arterial hypertension (21%) (Table 2). The main symptoms in both groups were cough and systemic symptoms (Table 3). FB was performed in all LCNS patients, and direct and indirect signs of tumour disease were observed under direct vision in 270 (68.2%). LCNS patients were treated with surgery (14.4%), chemotherapy (48.5%), and radiotherapy (23%) and 33.8% were candidates for palliative care only. In 80% of the patients who received radiotherapy, the intent was palliative.
Comorbidities in Smokers and Never Smokers.
| Smoker (%) | Never smoker (%) | P | |
| COPD | 42.3 | 8.6 | <.001 |
| Arterial hypertension | 23.2 | 42.6 | <.001 |
| Heart disease | 21 | 18.9 | .372 |
| Previous neoplasm | 13 | 11.6 | .558 |
| Diabetes | 17 | 16.2 | .711 |
| Gastrointestinal | 13 | 12 | .561 |
| Previous pneumonia | 9.5 | 8.1 | .442 |
COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; P: statistical significance of the comparison.
Symptoms on Presentation of Smokers and Never Smokers.
| Smoker (%) | Never smoker (%) | P | |
| Cough | 49.1 | 48.7 | .911 |
| Systemic symptoms | 41.3 | 39.4 | .498 |
| Dyspnoea | 25.7 | 29.4 | .146 |
| Chest pain | 24.5 | 21.5 | .216 |
| Haemoptysis | 26 | 13.6 | <.001 |
| Expectoration | 13.8 | 8.8 | .008 |
| Extrathoracic pain | 12.4 | 12.4 | 1.000 |
| Neurological symptoms | 8.5 | 8.6 | .921 |
| No symptoms | 7.7 | 7.8 | .917 |
P: statistical significance of the comparison.
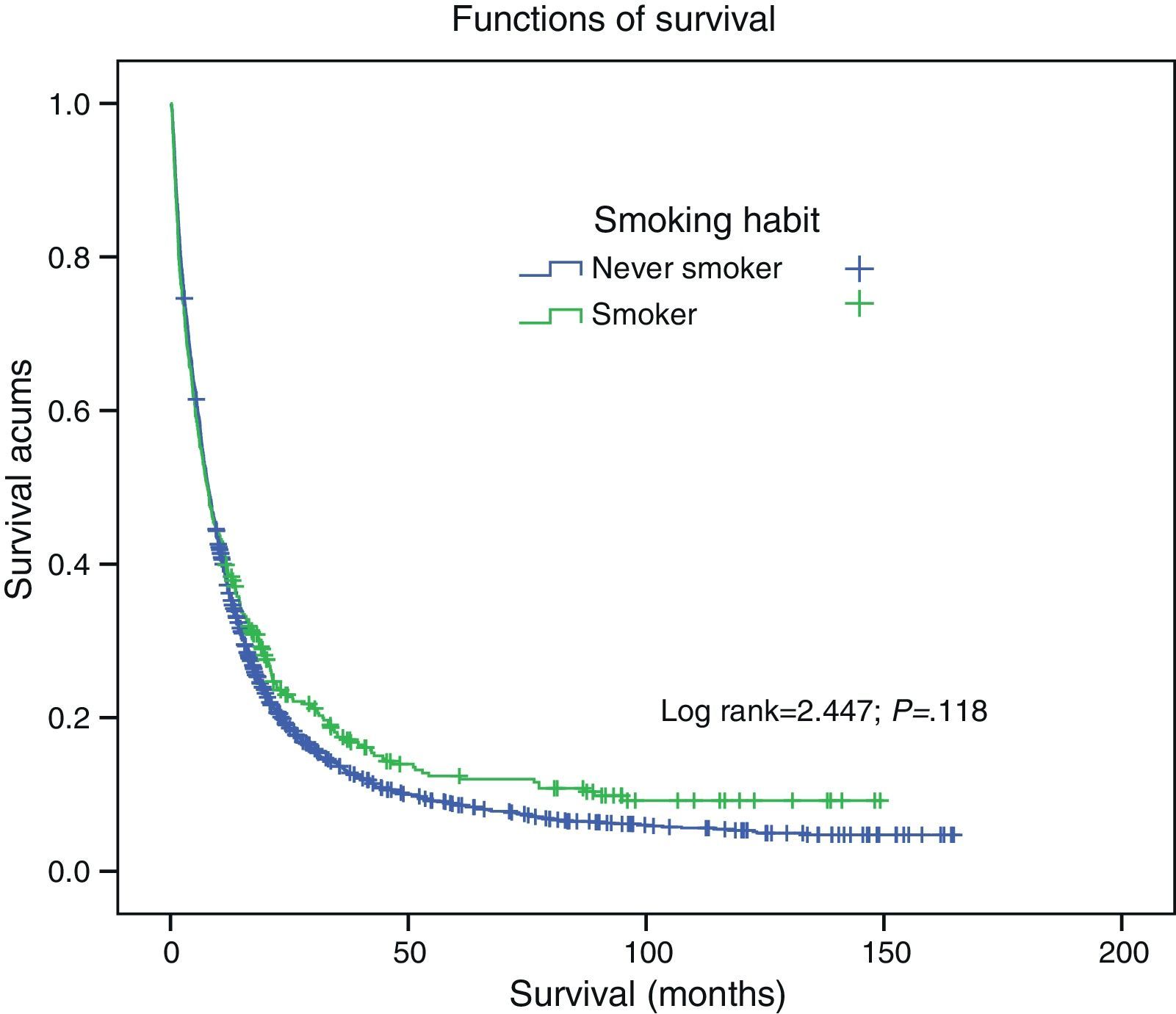
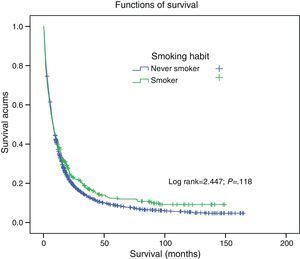
Five-year survival for the overall study population with LC was 9.37%, with a median of 7.8 months (95% CI: 8.1–10.8). Five-year survival in the never smokers group was 12.4% (median: 7.7 months; 95% CI: 9.29–16.5), while in the group of smokers it was 8.69% (median: 7.9 months; 95% CI: 7.37–10.26). There was no significant difference in survival between the 2 groups (log rank=2.47; P=.11) (Fig. 1).
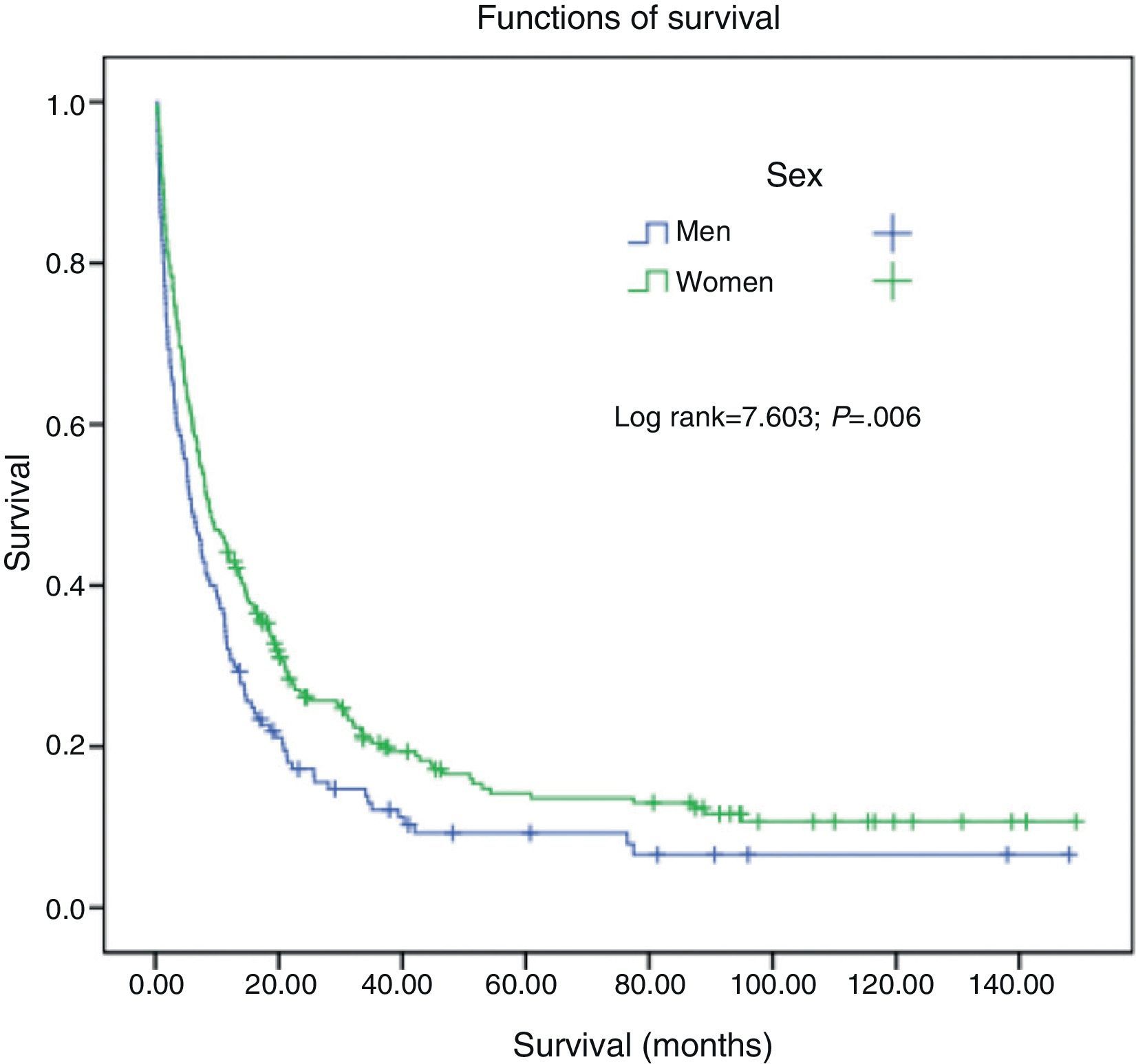
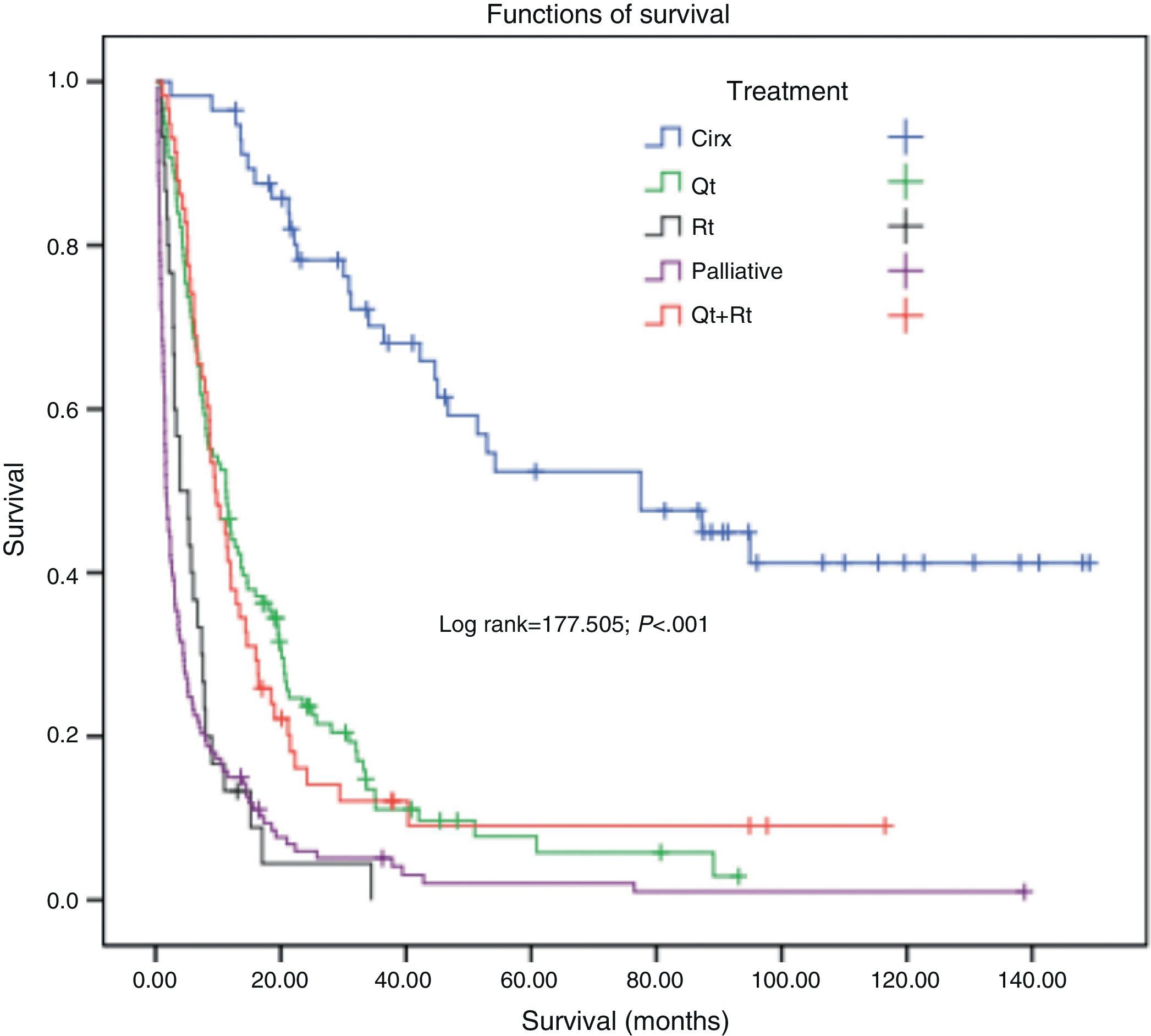
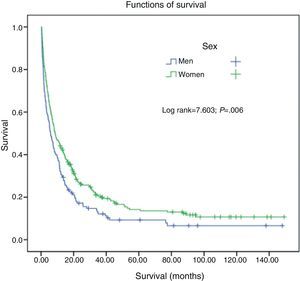
There were significant differences in survival in the never smokers group with regard to sex (log rank=7.6; P=.006) (Fig. 2), histological type (log rank=15.8; P<.001), age (log rank=12.97; P<.001), stage (log rank=69.88; P<.001) and treatment received (log rank 177.5; P<.001) (Fig. 3).
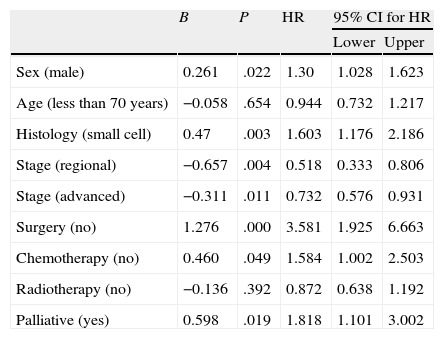
In the Cox multivariate regression analysis, the risk of death in never smokers was significantly greater in cases involving the male sex, small cell subtype, advanced stage and absence of surgical treatment or chemotherapy (Table 4).
Multivariate Analysis of Lung Cancer Prognostic Factors in Never Smokers.
| B | P | HR | 95% CI for HR | ||
| Lower | Upper | ||||
| Sex (male) | 0.261 | .022 | 1.30 | 1.028 | 1.623 |
| Age (less than 70 years) | −0.058 | .654 | 0.944 | 0.732 | 1.217 |
| Histology (small cell) | 0.47 | .003 | 1.603 | 1.176 | 2.186 |
| Stage (regional) | −0.657 | .004 | 0.518 | 0.333 | 0.806 |
| Stage (advanced) | −0.311 | .011 | 0.732 | 0.576 | 0.931 |
| Surgery (no) | 1.276 | .000 | 3.581 | 1.925 | 6.663 |
| Chemotherapy (no) | 0.460 | .049 | 1.584 | 1.002 | 2.503 |
| Radiotherapy (no) | −0.136 | .392 | 0.872 | 0.638 | 1.192 |
| Palliative (yes) | 0.598 | .019 | 1.818 | 1.101 | 3.002 |
B: Cox regression coefficient; HR: hazard ratio; CI: confidence interval; P: statistical significance of the comparison.
Smoking is the main etiological factor for the development of LC. However, LC remains a serious health problem in the never smoker population, in whom the incidence is rising,14 with domestic radon and passive smoking emerging as the principal risk factors.15 In the majority of LC series, 15% of men and about 53% of women have no history of smoking.6 In our study, the percentage of patients with LCNS was 18.3%, with significant differences being observed in terms of sex: 7.7% were men, compared to 76.4% women. This difference coincides with the finding that never smoker females have a higher risk of developing LC than never smoker men,16 which could be explained by other factors, such as genetic predisposition, passive smoking or environmental exposure.
In our series, the most frequent histological strain in smokers was squamous cell carcinoma. In contrast, the never smokers were more often diagnosed with adenocarcinoma. This was found in 55.6% of cases, a rate similar to that of other publications.17 Adenocarcinomas were also more common in women, regardless of their smoking habit.15 Moreover, in the mostly female never smoker population, adenocarcinomas were more common than squamous cell carcinomas.17 Molecular and genetic factors were involved in these histological differences: epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations occur almost exclusively in never smokers, and are more common in women and in adenocarcinomas.18,19 A different K-ras oncogene mutation pattern has also been observed in never smoker patients compared to ex-smokers or active smokers, with significantly more frequent guanine to adenosine transitions in codons 12 and 13 occurring in never smokers.20
It is not clear whether there is a difference between LCNS and LC in smokers with respect to TNM stage at the time of diagnosis. In our study, 51.3% of LCNS patients presented in advanced stage (IV), a significantly higher incidence than in smokers. This phenomenon has also been described in the literature, with frequent reports of patients being diagnosed in more advanced stages.21 One possible explanation for this finding is the more intensive medical follow-up of smokers, who frequently present comorbidities, such as COPD, that require closer clinical and radiological monitoring.
The late diagnosis of LC means that the number of patients who can be treated surgically is low: in our series, 14.4% of the never smokers and 15.2% of the smokers received surgical intervention. On the contrary, 48.5% received chemotherapy. Significant differences have been observed in the response rate to EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors, such as gefitinib, which is higher in never smokers than in smokers with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (36% vs 8%).22 Similar results were observed with erlotinib (24.7% vs 3.9%).23
LC survival is poor, ranging in most series between 6% and 16%.24–26 In our LCNS patients, 5-year survival was 9.37% and no significant differences were observed compared to that in the smoking population. The results in the literature in this area are varied: Nordquist et al.27 reported improved survival in non-smoking patients, while, like us, Toh et al.28 did not find any difference.
One of the most remarkable results of our study is that in never smoker patients, women had better survival than men; in addition, the multivariate analysis showed that the risk of death was higher in the male population. In this respect, the results of the studies are contradictory: some papers report that in LC, female sex is a factor for good prognosis,29 while others describe worse survival and treatment response in women.30 In a previous study carried out by our group,31 no differences were seen in survival between the sexes, although another recent Spanish publication32 describes improved survival in women with LC, with differences depending on the histological type.
Our study has some limitations. Firstly, its retrospective nature meant that no other possible etiological factors, such as radon exposure or passive smoking, thought to be the first and second leading causes of LCNS, respectively,8 were analysed. Our group is now participating in a multicentre study addressing this causative association, and we have seen that in the homes of patients the concentration of domestic radon was threefold higher than in the control population, according to already published preliminary results.9 Secondly, LC with EGFR mutations occurs almost exclusively in never smokers with adenocarcinoma.20 Since the determination of these mutations in our centre is recent, the impact of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors on patient prognosis could not be examined.
To conclude, our study confirms that LCNS has clinical characteristics distinct from those of LC in smokers; it occurs in 18.3% of LC patients, more frequently in women, diagnosis is made in advanced stage and the histological type is predominantly adenocarcinoma. We did not find any significant differences in survival. In our opinion, therefore, this patient group merits further study, with regard to both causative factors and the response to tailored treatment in patients with certain mutation patterns.
Conflict of InterestsThe authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interests.
Please cite this article as: Parente Lamelas I, Abal Arca J, Blanco Cid N, Alves Pérez MT, Dacal Quintas R, Gómez Márquez H, et al. Características clínicas y supervivencia de los pacientes nunca fumadores con cáncer de pulmón. Arch Bronconeumol. 2014;50:62–66.