Bronchial asthma is becoming more prevalent in adults. Around 10.2% of the population of Chile reports suspected asthma, with similar rates between men and women.1 The recently developed technique of bronchial thermoplasty (BT) has been shown to be a safe and effective option for the treatment of severe asthma, and improves the quality of life of these patients.2,3
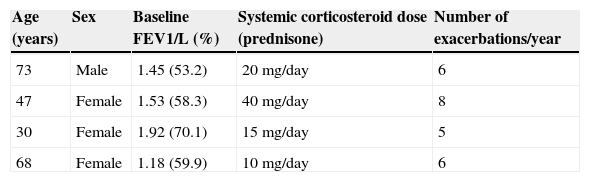
We report the first 4 cases of patients with severe asthma treated with BT in Chile. All were receiving high-dose corticosteroids and inhaled β-agonists (fluticasone or equivalent >1000μg/day), rescue inhalers >3 times a day, leukotriene inhibitors and continuous systemic corticosteroids. Table 1 shows the baseline characteristics of each patient. They all underwent the first 2 sessions of BT on an outpatient basis, and there were no complications. After the third session, all 4 patients had a severe asthma attack and required hospitalization. The first patient was hospitalized for 48h, the second for 6 days, and the third and fourth patients for 7 days each. Patient number 4 also required 3 days of non-invasive mechanical ventilation.
Baseline Characteristics of the 4 Patients Undergoing Bronchial Thermoplasty.
| Age (years) | Sex | Baseline FEV1/L (%) | Systemic corticosteroid dose (prednisone) | Number of exacerbations/year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 73 | Male | 1.45 (53.2) | 20mg/day | 6 |
| 47 | Female | 1.53 (58.3) | 40mg/day | 8 |
| 30 | Female | 1.92 (70.1) | 15mg/day | 5 |
| 68 | Female | 1.18 (59.9) | 10mg/day | 6 |
The interval between treatments for all patients was 4 weeks or more. Baseline forced expiratory volume in 1s (FEV1) before each session remained stable. All patients received 50mg prednisone for 3 days before the procedure, on the day of the procedure and the following day.
BT is a bronchoscopic procedure consisting of 3 sessions of radiofrequency ablation of airway smooth muscle. The right lower lobe is treated during the first session, the left lower lobe during the second, and in the third, both upper lobes are treated. Time between sessions is 4–6 weeks.4
A recent systematic review that included the most relevant randomized clinical trials (AIR, AIR II and RISA) found improvements of 0.28 (0.07–0.50) and −0.15 (−0.4 to 0.10) in AQLQ and ACQ scores, respectively; the hospitalization RR during the treatment period was 3.5 (1.26–9.68) with I2 of 0.0%, and post-treatment RR was 1.12 (0.44–2.85). No improvement was found in the need for rescue medication: −0.68 (−3.63 to 2.28), nor was there any significant change in lung function.4
This is the first report of patients receiving BT in Chile, and the second from Latin America.5 The baseline characteristics of our patients were similar to those previously described (RISA study). However, the need for hospitalization after the third treatment needs to be addressed. The average rate of asthma attacks per year in our patients before the intervention was high, and they required high doses of corticosteroids, factors that could have been related to the need for hospitalization after the third session. However, after the interventions, all our patients went on to have an excellent clinical response. Two of them were able to completely discontinue systemic corticosteroids and the other 2 reduced their dose by half. They all had fewer, less severe exacerbations. These findings should be taken into account in future studies.
FundingNo funding of any type was received for this article.
Conflict of InterestsThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Please cite this article as: Fernández-Bussy S, Labarca G, Caviedes I, Folch E, Majid A. Termoplastía bronquial para el manejo del asma severo: experiencia inicial en Chile. Arch Bronconeumol. 2016;52:52.