Lung cancer is one of the most common causes of cancer death in men and women worldwide. Various combinations of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy and immunotherapy are currently used to treat lung cancer. However, the prognosis remains relatively poor due to the higher frequency of tumor mutational burden (TMB). Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 (NFE2L2/NRF2) is often considered a primary regulator of the expression of antioxidant enzymes and detoxification proteins and is involved in cytoprotection. On the contrary, NRF2 is even known to induce metastasis and support tumor progression. Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) plays an important role in negatively regulating NRF2 activity via CUL3-mediated ubiquitinylation and successive proteasomal degradation. Extensive research has shown that the genetic alterations of KEAP1/NFE2L2/CUL3 genes lead to increased expression of NRF2 and its target genes in lung cancer. Thus, these studies provide ample evidence for the dual role of NRF2 in lung cancer. In this review, we discussed the mechanistic insights into the role of NRF2 signaling in therapy resistance by focusing on cell lines, mouse models, and translational studies in lung cancer. Finally, we highlighted the potential therapeutic strategies targeting NRF2 inhibition, followed by the discussion of biomarkers related to NRF2 activity in lung cancer. Overall, our article exclusively discusses in detail the NRF2 signaling pathway in resistance to therapy, especially immunotherapy, and its therapeutic avenue in the treatment of lung cancer.
Globally, lung cancer ranks among the leading causes of cancer-related deaths.1 Small cell lung cancer (SCCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) are the two main types; they account for 15% and 85% of lung cancer cases, respectively. NSCLC is further divided into three major pathological subtypes: adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and large cell carcinoma. NSCLC is currently treated with a variety of surgical, chemotherapeutic, radiation and immunotherapy combinations. The transcription factor NRF2, also called nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor, is encoded by the gene NFE2L2 and is often considered a primary regulator of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in cells.2 Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1) negatively regulates NRF2 activity through Cullin3 (CUL3)-mediated ubiquitylation and subsequent proteasomal degradation. It is well documented that genetic alterations of KEAP1/NFE2L2/CUL3 lead to increased expression of NRF2 and its target genes in human cancers, including NSCLC. As a result, lung tumors develop resistance to chemotherapy, radiotherapy and immunotherapy.3 In this review article, we will discuss how the NRF2 signaling pathway plays an important role in lung cancer by focusing on its function, regulation, and dual roles. In addition, inhibitors that target NRF2 and biomarkers in lung cancer are being discussed.
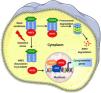
NRF2 signaling pathway in normal cellsUnder normal conditions, NRF2 is integrated into the cytoplasm through binding to its negative regulator KEAP1. KEAP1 has highly reactive thiol groups that act as a sensor for the NRF2 inducers.4 The cysteine residue (Cys151) in the KEAP1-BTB domain is essential for NRF2 activation,5 while Cys288 and Cys297 are crucial for the suppression of NRF2 activity.6 The Kelch domain of KEAP1 mediates the binding of the Neh2 domain to NRF2 and thereby negatively regulates NRF2 transactivation. This interaction between NRF2 and KEAP1 can be well explained by the hinge-latch model.7 According to the hinge-latch model, KEAP1 binds weakly to NRF2 via its DLG motif (latch) and strongly via its ETGE motif (hinge). Two conformations are adopted in this interaction: the open and the closed conformation. When the newly synthesized NRF2 molecule binds to the Keap1 molecule via the ETGE motif, it is in the open conformation. When it subsequently binds to the KEAP1 molecule via the DLG motif, it adopts a closed conformation.8 NRF2 is ubiquitinated by the KEAP1 homodimer CUL3 and then degraded by the 26S proteasome.9 This step occurs mainly through electrophilic compounds and oxidative stress, where some cysteine residues in KEAP1 are oxidized, leading to a reduction in NRF2 ubiquitination. Therefore, stabilized NRF2 accumulates and migrates to the cell nucleus. In the nucleus, NRF2 heterodimerizes with the small Maf protein (sMaf) and binds to the consensus sequence (also known as antioxidant responsive element – ARE) present in the promoter regions of the cytoprotective genes (Fig. 1). NRF2 regulation mediated by KEAP1 is regarded as a canonical mechanism.
NRF2 signaling pathway: under basal condition, KEAP1 controlled NRF2 undergoes Cul3 mediated ubiquitination, leading to the proteosomal degradation of NRF2. Under oxidative stress, the NRF2 dissociates from KEAP1 and enters the nucleus where it heterodimerises with the sMaf proteins and regulates the ARE driven gene expression.
NRF2 is regulated not only by the KEAP1-mediated canonical mechanism but also by non-canonical mechanisms. Dipeptidyl peptidase III (DPP3), p62, p21, and the wilms tumor gene on the X chromosome (WTX), Inhibitor of Apoptosis Stimulating Protein of p53 (iASPP) are examples of proteins that function in a non-canonical manner to disrupt the NRF2-KEAP1 association, results in NRF2 stabilization and increased nuclear translocation and activation.10,11 Furthermore, glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) phosphorylates NRF2 on serine residues of the DSGIS motif, and forms a phosphodegron, ultimately leading to recruitment of the β-TrCP-CUL1-based E3 ubiquitin ligase complex.12
Epigenetic and genetic alterations of KEAP1/NFE2L2 genes in lung cancer patientsGenetic alterations such as mutations and copy number variation of key genes encoding KEAP1 and NRF2 proteins have been reported in NSCLC.13 The mutation present in the KELCH domains in the binding site of NRF2 results in the loss of KEAP1 activity. The gain-of-function mutations in NRF2 more commonly found in several types of squamous cell malignancies, including lung cancer.14–16 A panel of somatic mutations identified in 65 Japanese lung cancer patients confirmed that the loss of KEAP1 function due to mutations increased nuclear accumulation and constitutive activation of NRF2. As a result, upregulation of NRF2 target genes resulted in growth advantages and cisplatin resistance of lung cancer cells.17 Although the nature of NRF2 mutations, which involve direct DNA changes, results in loss of affinity for binding to the KELCH region, the KEAP1 mutations create steric hindrance and gross structural changes in the formation of the NRF2:KEAP1 complex. Additionally, KEAP1 mutations have the ability for epigenetic inactivation. Muscarella et al. found that one-third of the lung tumors had both somatic mutations and loss of heterozygosity in 47 NSCLC tissues, resulting in a higher risk of disease progression.18
Importantly, mutations within the Neh2 domain of the NFE2L2 gene such as ETGE and DLG affect binding affinity to the KELCH domain of KEAP1. As a result, increased NRF2 protein levels are observed in NSCLC. Therefore, the inability to maintain NRF2 protein expression is directly associated with poor prognosis in clinical patients diagnosed with lung cancer.16,19,20 The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) data showed that approximately 30% of human lung cancers harbor mutations in KEAP1 or NFE2L2 genes that ultimately lead to NRF2 stabilization and upregulation of its downstream genes.21,22
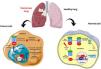
NRF2 signaling pathway in oncogenesisLoss of KEAP1 function leads to defective activation of the NRF2 signaling pathway in NSCLC cells, resulting in resistance to chemotherapeutic agents.13 The inability of KEAP1 to bind NRF2 due to both mutations results in increased NRF2 accumulation and downstream gene transcription. Indeed, constitutive NRF2 activation in human tumor specimens and cell lines increases the expression of genes involved in drug metabolism, thereby maintaining resistance to chemotherapeutic agents, radiotherapy and immunotherapy (Fig. 2).
NRF2 in lung cancer chemotherapy resistanceThe in vitro studies of human cancer cell lines A549, NCI-H292 and LC-AI cells showed that knockdown of NRF2 inhibited cell proliferation and reduced resistance to cisplatin.19,23 Silencing of NRF2 with shRNA or siRNA resulted in inhibition of proliferation of A549 cells with mutated KEAP1 and increased NRF2 levels.24 Furthermore, silencing of NRF2 by RNAi sufficiently reversed resistance to cisplatin in NSCLC cells and improved the sensitivity of A549 to doxorubicin and etoposide.14 Although KEAP1 mutation often increases ARE gene targets by increasing the availability of NRF2, it has also been shown to directly enhance the induction of PPARγ and confer chemoresistance.25 A recent study identified the increased NRF2 and target gene levels with accelerated tumor growth, tumor cell proliferation and migration in lung cancer cell lines A549 and H460 with KEAP1 loss-of-function mutations.26 In addition, NRF2 inhibition with ML385 could inhibit the proliferation of tumor cells with KEAP1 mutation.26 Therefore, all these growth advantages arising from overactivation of NRF2 lead to poor outcomes in lung cancer and make NRF2 an independent prognostic factor for survival analysis of lung cancer patients.27
Interestingly, Satoh et al. focused on the dual role of Nrf2 in lung cancer using a urethane-induced multistep model of Nrf2-deficient mice. In their study, Nrf2-deficient mice showed a relative increase in tumor foci after eight weeks of treatment with urethane. However, Nrf2+/+ mice developed more tumors in Kras-mutant adenocarcinomas in the later stages than Nrf2−/− mice. Indeed, these results suggest that Nrf2 acts as a tumor suppressor at an early stage and as an oncogene at a later stage.28 The same group also showed that the growth of urethane-induced lung tumors is attenuated in Keap1 knockdown mice, thereby avoiding carcinogenesis. On the contrary, when tumor cells from Keap1 knockdown (kd) mice with increased Nrf2 activity were transplanted into nude mice, they showed increased tumorigenicity compared to cells derived from wild-type mice.29 Therefore, it is clear that NRF2 plays a dual role in lung cancer (Fig. 2). A study by Tao et al. tested the NRF2 modulation effects (inhibition by Brusatol or activation by Sulforaphane) in lung cancer using a genetic (conditional KrasG12D oncogene) model in C57BL/6J mice and a chemical (vinyl carbamate) model in A/J mice. Their results suggest that NRF2 activation prevents the initiation of chemically induced cancer but promotes the progression of pre-existing tumors regardless of genetic or chemical etiology.30
In general, NRF2 induces the powerful antioxidant glutathione (GSH) to maintain redox homeostasis in normal cells; However, glutathione also plays an important role in tumor growth and metastasis. NSCLC tumor samples have higher GSH levels and GSH uptake capacity compared to normal lung tissue, and higher plasma GSH levels have been found in patients with NSCLC who have undergone standard chemotherapy.31 In this context, high NRF2 levels in KEAP1-mutant NSCLC increase cell dependence on GSH and also lead to greater radiotherapy resistance through the influence of GSH.32
Overexpression of drug transport proteins is known to promote multidrug resistance in cancers. Importantly, NRF2 regulates the expression of drug transporters and downregulation of NRF2 inhibits the expression of drug transporters and blocks chemoresistance. In fact, NSCLC patients with NRF2/KEAP1 mutations have increased MRP3 levels compared to wild-type patients.33 It's interesting to note that Nrf2 mRNA level can predict chemotherapeutic response and outcomes in NSCLC, and mutant p53 can induce cisplatin resistance via upregulating Nrf2 expression.34
NRF2 in lung cancer radiation therapy resistanceBy producing ROS, radiation therapy can efficiently destroy cancer cells. Nevertheless, certain cancer cells with increased redox and antioxidant capacity can escape the harmful effects of radiation by scavenging ROS, resulting in radioresistance. Intrinsic or acquired radioresistance represents a major obstacle to the clinical outcome of radiotherapy or concurrent chemoradiotherapy in NSCLC.35 To understand the role of Nrf2 in radioresistance, Singh et al. used mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEF) cells and genetically-modified mice models with gain of Nrf2 function (Keap1−/−) and loss of Nrf2 function (Nrf2−/−).32Keap1−/− MEF cells were found to be resistant to ionizing radiation-induced cell death because they had high antioxidant capacity and low levels of endogenous ROS. In comparison, increased sensitivity to γ-irradiation and decreased survival were observed in Nrf2−/− MEF cells and double knockout Keap1−/−; Nrf2−/− cells. The results suggest that elevated Nrf2 levels confer radiotherapy resistance.32 By suppressing the expression of Nrf2 in both the mRNA and protein, 4-(2-Cyclohexylethoxy)aniline (IM3829), an inhibitor of NRF2, has been demonstrated to dramatically enhance the radiosensitivity of human lung cancer cells.36 Similar results were observed for Brusatol, which has been shown to reduce NRF2 protein levels and increase tumor radiosensitivity by promoting NRF2 ubiquitination and degradation in A549 cells.37 However, Brusatol is not a specific NRF2 inhibitor and inhibits both cap-dependent and cap-independent protein translation rather than directly blocking the NRF2 signaling pathway.38
Moreover, A549 NSCLC cells that express NRF2 are more susceptible to radiation-induced apoptosis due to Nrf2-mediated Notch signaling.39 Similarly, the migratory and invasive characteristics of NSCLC cells are inhibited by the combined downregulation of Nrf2 and Notch1.40 According to Binkley et al. Mutations in KEAP1 and NFE2L2 predict local recurrence after radiotherapy but not after surgery in patients with NSCLC. These mutations are associated with approximately half of all local recurrences, and inhibition of glutaminase could allow individual radiosensitization of tumors harboring KEAP1/NFE2L2 mutations.41 Recent in vitro and in vivo studies have shown that co-occurring mutations of STK11 and KEAP1 in KRAS-mutated NSCLC promote tumor growth and confer increased resistance to radiotherapy.42 Another study from three large prospective cohorts involving nearly 1800 patients found that KEAP1/NFE2L2/STK11 mutations are the biomarker of radioresistance in lung cancer patients.43 Recently, NRF2 has been shown to be involved in radioresistance by promoting phosphorylation of replication protein A 32 (RPA32) and cooperates with TOPBP1 to activate the ATR/CHK1 signaling pathway. NRF2 may play a role in DNA damage response independent of its antioxidant role.44
NRF2 in immunotherapy resistanceImmune checkpoint blockade (ICB) is a new targeted treatment that has the potential to stimulate durable immune responses against different kinds of tumors, including lung cancer. NSCLC has a high tumor mutation burden (TMB), which is thought to trigger an antitumor response and serve as a biomarker of favorable responses to ICB.45 Although ICB improves the survival of a significant number of patients with this disease, primary resistance affects a significant number of patients with advanced NSCLC.46
The influence of NRF2 activation on tumor immunity has recently attracted more attention, both in terms of immune cell activation and cancer-intrinsic activation. Interestingly, loss of KEAP1 has been shown to be due to an immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment, leading to a deficiency of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) and Natural Killer (NK) cells in mice with lung cancer, suggesting a link with NRF2 hyperactivity and immune evasion.47 LKB1 activates the AMPK and KEAP1/NRF2 signaling, which increases the expression of PD-L1 in NSCLC.48
A large database study found that the patients with KEAP1-NFE2L2 mutations who underwent ICIs had shorter OS than wild type and that KEAP1-mutant NSCLC is associated with higher TMB.49 It indicates ICIs may not be beneficial for NSCLC patients with KEAP1-NFE2L2 mutations despite high TMB. A subset of lung adenocarcinomas resistant to immunotherapy is identified by coexisting alterations in KEAP1, PBRM1, SMARCA4, and STK11. Compared to single mutant and wild-type tumors, tumors with co-mutations showed worse survival rates. Lung adenocarcinomas in which these mutations coexist are characterized by an immunologically cold phenotype.50 Anti-PD-L1 therapy extends survival of patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma with low NRF2 signature. According to in vivo modeling, NRF2 activation is a key oncogenic driver that promotes aggressive lung adenocarcinoma by interacting with STK11 loss and KRAS activation.48 In contrast, a clinical study showed that KEAP1 mutant tumors have very low PD-L1 expression despite a worse clinical outcome, suggesting that there must be multiple mechanisms by which NRF2 activation contributes to immune evasion in cancer.51
Analysis using single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) revealed that tumors with KEAP1 mutations exhibit high tumor associated marcophage (TAM) levels, exhausted CD8+ T cells, and are linked to a poor prognosis for patients.52 Patients with lung adenocarcinomas who have KEAP1 mutations exhibit low levels of antigen presentation genes and chemokines resulting lower TILs and cytotoxic T lymphocytes in the tumor immune environment.53 Recent work showed that the loss of KEAP1 decreased tumoral CD8+ cells and increased M2 macrophages via stabilization of EMSY, which suppresses the type I interferon response and promotes immune evasion.54 It has been reported that STK11 and KEAP1 are poor prognostic factors in patients receiving ICIs. In Hispanic NSCLC patients receiving ICIs, STK11 and KEAP1 mutations are linked to a poor overall survival.55 A comprehensive examination of cancer types, including lung cancer, shows that low HLA-I, IFNγ and lymphocyte levels are associated with increased NRF2 activity and the stromal populations of lung squamous cell carcinomas are responsible for the negative relationship between NRF2 and immune cells.56 Antitumor CD8+ T cells and CD103+ DCs are inhibited by KEAP1 mutations in lung cancer. In tumors with KEAP1 mutations, immune evasion is caused by hyperactivation of NRF2. Inhibiting glutaminase may increase the susceptibility of KEAP1 mutant tumors to immunotherapy.57 In addition, Baird and Yamamoto found that NRF2-activated cells were significantly immunoedited, allowing the cancer cells to evade immune screening and promote the progression of malignant neoplasms. This immune surveillance reduces antigen presentation by the MHC-I complex, associated with downregulation of activating ligands for NK cells or reduces the antitumor activity of cytotoxic T cells.58 Taken together, all of these studies suggest that NRF2 contributes to immunosuppression in cancer through multiple mechanisms.
NRF2 in tumor cell metabolismNRF2 also plays a significant role in controlling tumor cell metabolism. Hyperactive NRF2 promotes cell proliferation by inducing metabolic reprogramming that redirects glucose and glutamine into anabolic pathways, particularly with sustained activation of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K)–AKT signaling.59 The gain of NRF2 signaling promotes tumorigenesis through an autoregulatory feedback loop involving miRNA-dependent regulation of pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) and histone deacetylase 4 (HDAC4).60 Briefly, NRF2 also modulates microRNAs to mediate pro-survival processes. In lung cancer, Singh et al.60 further investigated the effects of Nrf2 on the PPP and the tricarboxylic acid cycle and discovered that activation of NRF2 reduced miR-1 and miR-206 expression and resulted in an increase in metabolic gene expression in the pathway. Our recent genome-wide ChIP-Seq global study also found that NRF2 directly regulates genes involved in PPP along with focal adhesion pathways in A549 NSCLC cells.61 The genes associated with the focal adhesion pathway can promote glucose consumption, lipogenesis and glutamine dependence, ultimately leading to the promotion of tumor growth.62
To shed light on the metabolic features of NRF2-activated lung cancers, Saigusa et al. have performed targeted global metabolomic (G-Met) analyses and metabolomic (T-Met) analyses of NSCLC cells along with exome and transcriptome analyses.63 Interestingly their results identified the genes involved in metabolism and production of lipid mediators that help NRF2-activated cancer cells to escape antitumor immunity.63 Our previous study on the A549 microarray data also identified the key genes involved in metabolic pathways including porphyrin and chlorophyll metabolism, glycolysis/gluconeogenesis, PPP, drug metabolism and others.64
To support the in vitro evidence of NRF2's role in metabolic reprogramming, researchers have also focused on in vivo studies. For instance, Best et al. demonstrated that the Keap1f/f/Ptenf/f mice enable the formation of LUAD and the reprogramming of PPP.47 On the other hand, Keap1 mutant mice developed LUAD tumors with increased levels of Taldo1, an enzyme that provides ribose-5-phosphate for nucleic acid synthesis and NADPH for lipid biosynthesis.65 Lung adenocarcinoma patients who have mutational activation of the NRF2 pathway experience poor prognosis and tumor immunosuppression due to the upregulation of kynureninase, which mediates tryptophan metabolism.66
Therapeutic strategies to target NRF2It has been increasingly recognized that more attention needs to be paid to therapeutic strategies to target NRF2 in cancer. Global research efforts are being directed toward the development of NRF2 inhibitors (Fig. 3). The following is a list of NRF2 inhibitors that have been well studied.
Procyanidin: Procyanidins are condensed tannins prepared from Cinnamomi cortex extract. It has shown to suppress Nrf2 expression and enzymatic activities of its targeted genes such as NQO1 and UGT in human lung cancer A549 cells.67
Luteolin: It is a flavonoid present in food plants and vegetables that can potently inhibit NRF2 both in vitro and in vivo on A549 NSCLC cells and A549 tumor xenograft cells grown subcutaneously in athymic nude mice.68
Trigonelline: It is an alkaloid that is abundant in various plant sources such as garden peas, coffee beans, hemp seeds, oats and fenugreek seeds. A study by Arlt et al. showed that trigonelline blocks Nrf2-dependent proteasome activity of PDAC cell lines (MiaPaca2, Panc1 and Colo357) that have high basal NRF2 activity. Remarkably, the submicromolar doses of trigonelline efficiently suppressed NRF2 nuclear accumulation and proteasome activity, abolishing their protective effects in vitro and in vivo.69
Brusatol: Brusatol, a quassinoid plant extract from Bruceajavanica, traditionally used in Chinese medicine for treating various diseases, including cancer amoebic dysentery, and malaria.70–72 Ren et al. showed that brusatol was able to strongly potentiate the cytotoxic effects of cisplatin in a variety of cancer cell lines and A549 NSCLC xenografts by upregulating the ubiquitination of NRF2 and its subsequent degradation.73
Chrysin: The study, which focuses on the potential antitumor activity of chrysin, was found to reduce NRF2 mRNA and protein levels and chemosensitize multidrug-resistant HCC-derived cells (Bel-7402/ADM) to doxorubicin by inhibiting HO-1 expression due to the down regulation of the PI3K/AKT/ERK pathways.74
Oridonin: It is a bioactive diterpenoid present in Rabdosiarubescens, has been proved to possess potent anticancer effects.75–77 Oridonin suppresses Nrf2-mediated antioxidant signaling pathways in vitro and in vivo and shows pro-apoptotic effects by activating PPAR-γ in osteosarcoma.78
Convallatoxin: It is a cardenolide glycoside extracted from Convallaria majalis and the stem bark of Antiaristoxicaria represses NRF2 activity by activating its negative regulator GSK-3β and sensitizes A549 cells to 5-fluorouracil-mediated cell death by promoting apoptosis.79
Halofuginone: Halofuginone is a synthetic derivative of febrifugin and suppresses NRF2 protein accumulation in A549 cells harboring the KEAP1 gene mutation and in human esophageal cancer cells (KYSE70) harboring the NRF2 gene mutation. Interestingly, Halofuginone not only decreases NRF2 protein accumulation but also the expression of its downstream target genes.80
Plumbagin: Plumbagin, a naphthoquinone compound found in the root of the medicinal plant Plumbagozeylanica. Combined treatment of plumbagin and brusatol showed synergistic effects in reducing cell proliferation and viability by inhibiting the NRF2 activity in ECC1 cells.81
Triptolide: Triptolide is a diterpenoid epoxide derived from Tripterygium wilfordii. It dramatically reduced Nrf2 expression and transcriptional activity in NSCLC and liver cancer cells, resulting in chemosensitivity to antitumor activity both in vitro and in a lung xenograft tumor model.82
Small molecule inhibitors: ML385, a small molecule inhibitor, binds to the Neh1 domain of NRF2, disrupts the binding of the MAFG-NRF2 protein complex and prevents the expression of its downstream target gene in NSCLC cells.83 A recent study discovered R16, a small molecule NRF2 inhibitor that specifically binds to KEAP1 mutants and repairs the disrupted KEAP1/NRF2 interactions to restore the mutants’ NRF2 inhibitory function.84
Other strategies: Directly targeting NRF2 using inhibitors is considered the primary approach to treating NRF2-dependent lung cancer. It may be beneficial to develop other strategies to suppress the downstream effectors. One of these strategies is glutamine inhibition. KEAP1 mutant tumors are glutamine dependent and rely on exogenous glutamine. In KEAP1 mutant lung cancer, targeting glutamine with its antagonist DRP-104 clearly demonstrated suppression of tumor growth and enhanced response to checkpoint blockade.85 Another strategy is to reposition the drug mitomycin C in order to inhibit downstream genes of the NRF2 signaling pathway. It has been demonstrated to inhibit most of the NRF2 target genes for PPP enzymes, NQO1, and cytochrome P450 reductase.86 Synthetic lethality with geldanamycin and its derived HSP90 inhibitors has also become another approach to inhibit NRF2 activity.87
NRF2 and its target genes as biomarkers in lung cancerNRF2 activity is upregulated in lung cancer, mainly through increased NRF2 and its downstream gene expression due to KEAP1/NFE2L2 gene mutations. Increased NRF2 activity also occurs due to KEAP1 gene deletions or NRF2 amplification in lung cancer patients. These genetic alterations were identified through large-scale, high throughput sequencing in lung cancer patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). Approximately 17% of TCGA patients with lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD)22 have KEAP1 mutations, while 27% of TCGA patients with lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC)21 have both KEAP1 and NFE2L2 mutations. Therefore, analysis of NRF2 target genes based on patient stratification with these mutations allows us to identify novel genes, biomarkers, and therapeutic targets in lung cancer. Current knowledge of NRF2 and KEAP1 mutations in lung cancer suggests that resistance to cancer treatments is responsible for the poor prognosis associated with increased expression of NRF2 and its target genes. Cescon et al. identified a gene expression signature in LUSC patients with activation of the NRF2 signaling pathway and reported that these patients have less benefit from adjuvant cisplatin/vinorelbine chemotherapy.88 A meta-analysis study by Qian et al. identified the NRF2-associated molecular signature (NAMS) as a prognostic gene signature in NSCLC using NRF2 knock down A549 NSCLC cell microarray data.89 Similarly, our previous study using NRF2 knock-down A549 NSCLC cell microarray data identified a set of NRF2 regulated genes known as the NRF2-regulated metabolic gene signature (NRMGS) involved in cancer metabolism and act as prognostic biomarkers in LUAD.64 Furthermore, our recent multi-omics study identified potential prognostic biomarkers that strongly correlated with the NRF2 activity in KEAP1-mutated TCGA-LUAD patients and named them KEAP1 Mutation Specific Gene Cluster (KMSGC).90 Interestingly, Kerins and Ooi identified a comprehensive catalog of somatic NRF2 mutations in different tumor types to identify the prognostic biomarkers in NRF2-mutated cancers.91 Similarly, a distinct set of NRF2-cancer target genes which containing ARE sequences have been reported in several NRF2-mutated human cancers.92 More recently, we found several NRF2-regulated prognostic biomarkers in KEAP1 mutations associated with KEAP1 hypomethylated TCGA LUAD patients.93 Using TCGA data, MacLeod et al. reported an AKR biomarker panel with four members of the aldo-keto reductase (AKR) superfamily in both LUSC and LUAD.94 Therefore, comprehensive characterization and exploration of different NRF2-related gene sets would be a better approach for prognostic and diagnostic evaluation in lung cancer patients.
ConclusionInduction of NRF2 activity by its activators remains a classic and viable approach to prevent chronic diseases, including cancer, in which inflammatory and oxidative stress contribute to the pathogenesis. In addition, in the last two decades, many studies have shown that hyperactivation of NRF2 promotes the growth and proliferation of cancer cells and increases the chemoresistance and radioresistance of cancer cells. Furthermore, NRF2-mediated metabolic reprogramming could also serve as a potential therapeutic target in lung cancer. NRF2 overactivation can be caused by multiple mechanisms in cancer cells, with tremendous implications for tumor biology. Therefore, inhibiting NRF2 activity in fully malignant cells could be a useful strategy for cancer treatment. Many studies have identified NRF2 inhibitors, but none have been successful in clinical trials to date. However, these inhibitors may not be very selective, which could cause them to interact with other downstream signaling pathways and cause negative effects. Some recent studies have discovered small molecules that show promising inhibitory effects on NRF2, but they need further research and optimization. Indirect approaches to inhibit downstream NRF2 processes would also be helpful.
To address patient resistance to immunotherapy, a more comprehensive investigation is required to gain a mechanistic understanding of the effects of NRF2 on immune functions in NSCLC. Finally, understanding the oncogenic profile of NRF2 is crucial for safe and efficient cancer treatment. However, the effects vary depending on the stage of cancer.
Ethical approvalNot applicable.
FundingThis study was supported by the Sri Shankara Cancer Foundation and Meg Steels.
Authors’ contributionsAll authors contributed to the study's conception and design. The literature search was performed by SR, TP, VM, DV and SJV. The first draft of the manuscript was written by SR, AN and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript
Consent to participateNot applicable.
Consent to publishNot applicable.
Conflict of interestsThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Data availabilityNot applicable.
The authors thank the Sri Shankara Cancer Foundation for the facilitation of this manuscript. The authors thank Servier Medical Art for the use of the figure templates provided by Servier, licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 Unported License.