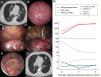
A 62-year-old male diagnosed with vanishing lung syndrome (VLS) presented with a giant emphysematous bulla (21cm×9.4cm×19cm) in the right lung (Fig. 1A). Under medical thoracoscopy, the giant bulla was clearly visualized (Fig. 1B). A 20-ml solution of freeze-dried human fibrin sealant was injected into the bulla cavity through a needle (Fig. 1C), followed by aspiration and sealing using an oval clamp to ensure complete closure (Fig. 1D, E). The entire procedure was completed within 60min. At three months, pulmonary function showed significant improvement with FEV1 increasing from 0.55L to 0.90L and FVC from 1.54L to 2.56L, with chest computed tomography demonstrating near-complete bulla resolution (Fig. 1F). At six months, FEV1 reached 0.91L and FVC reached 2.65L with no evidence of bulla recurrence (Fig. 1G). While surgery remains the conventional treatment for VLS, many high-risk patients are unsuitable surgical candidates [1,2]. Our case demonstrates that medical thoracoscopy with fibrin sealant was successful and represents a potential alternative treatment option for selected VLS patients. This approach uniquely combines direct visualization, precise therapeutic delivery, and mechanical sealing to achieve favorable outcomes with reduced physiological impact compared to conventional surgical approaches.
Medical thoracoscopy with fibrin sealant for vanishing lung syndrome: imaging and 6-month follow-up. (A) Preoperative chest CT scan showing a 21cm×9.4cm×19cm giant emphysematous bulla in the right lung with surrounding atelectasis; (B) Medical thoracoscopy view of the giant bulla before treatment. (C, D) Medical thoracoscopy treatment process of injecting human fibrin sealant into the bulla; (E) Endoscopic view of the bulla after treatment. (F) At the three-month follow-up, a chest CT scan showed near-complete resolution of the bulla. (G) Pre- and post-treatment clinical parameters over 6 months. CAT score=COPD Assessment Test score; PaCO2=arterial partial pressure of carbon dioxide; P/F ratio=arterial oxygen partial pressure divided by oxygen concentration; 6MWD=6-minute walking distance, FVC=forced vital capacity; and FEV1=forced expiratory volume in one second.
F.L. planned the manuscript. L.Z. and K.W. collected clinical data, created the figure, and wrote the manuscript. F.L. revised the manuscript. All authors were involved in the critical reversion of the manuscript and approved it.
Artificial intelligence involvementThe authors used Claude (Anthropic) to assist with language editing, grammar correction, and stylistic improvements of the manuscript. The AI tool was used solely for linguistic enhancement and formatting assistance. All scientific content, clinical interpretations, and conclusions were generated entirely by the human authors. The final manuscript was thoroughly reviewed and approved by all authors.
FundingThis research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare not to have any conflicts of interest that may be considered to influence directly or indirectly the content of the manuscript.