The aim of this study was to elucidate the impact of pleural lavage cytology positivity on early recurrence in patients operated on non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
MethodsThis is a multicentre prospective cohort study of 684 patients undergoing an anatomical lung resection for NSCLC between October 2015 and October 2017 at 12 national centres. A pleural lavage was performed before and after lung resection. The association between the different predictors of early recurrence and PLC positivity was performed using univariate and multivariate logistic regression models. A propensity score analysis was performed by inverse probability weighting (IPSW) using average treatment effect (ATE) estimation to analyse the impact of PLC positivity on early recurrence.
ResultsOverall PLC positivity was observed in 15 patients (2.2%). After two years, 193 patients (28.2%) relapsed, 182 (27.2%) with a negative PLC and 11 (73.3%) with a positive PLC (p<0.001). Factors associated to early recurrence were adenocarcinoma histology (OR=1.59, 95%CI 1.06–2.38, p=0.025), visceral pleural invasion (OR=1.59, 95%CI 1.04–2.4, p=0.03), lymph node involvement (OR=1.84, 95%CI 1.14–2.96, p=0.013), advanced pathological stage (OR=2.12, 95%CI 1.27–3.54, p=0.004) and PLC positivity (OR=4.14, 95%CI 1.25–16.36, p=0.028). After IPSW, PLC positivity was associated with an increased risk of early recurrence (OR=3.46, 95%CI 2.25–5.36, p<0.001).
ConclusionsPositive pleural lavage cytology was found to be the strongest predictor of early recurrence.
At diagnosis, around 25–35% of non-small cell lung cancers (NSCLC) are limited to the thorax and surgical resection may be considered.1 Despite continuous advances in treatment, the 5-year survival rate for NSCLC remains around 21%,2 with the post-surgical recurrence rate in these patients ranging from 15 to 40%.3,4 Most recurrences occur in the first two years after surgery.5,6 Even for stage I, the post-surgical recurrence rate is 15–30%.7,8 It is therefore important to identify patients at risk of recurrence who could benefit from closer follow-up and complementary treatments.
Pleural lavage cytology (PLC) is the microscopic cellular study obtained from the instillation of saline into the pleural cavity during surgery in patients with NSCLC and no previous pleural effusion. Since Eagan et al. published their results with this procedure in 1984,9 an increasing number of centres have adopted this procedure in their routine practice. A positive PLC, which generally occurs in less than 10% of patients,10–12 appears to be an independent predictor of poor prognosis and overall recurrence. The higher or lower rate of positivity seems to depend on tumour size, pleural invasion, histology, lymph node involvement or lymphovascular invasion.10,12–14 A meta-analysis published in 2010 by the International Pleural Lavage Cytology Collaborators (IPLCC) collected results from 11 centres with 8763 patients.15 Of these, 511 patients (5.8%) had a positive PLC, which was shown to be an independent poor prognostic factor (HR 1.14, p<0.001). It was also concluded that patients with positive PLC should be restaged to a higher T-category up to a maximum of T4. A recently published study observed 5-year recurrence-free survival differences between PLC-positive and PLC-negative patients of 29.7% vs. 75.1% respectively.16 However, the role of PLC positivity in early recurrence in NSCLC patients, defined as recurrence occurring within two years after surgery, has not been studied.
The latest edition of the TNM already contemplates the need to consider patients undergoing lung resection for lung carcinoma with positive PLC as microscopic incomplete resection (R1).17 This would imply assessing complementary treatment strategies in the same way as for patients undergoing surgery for NSCLC with R1. Knowing the status of PLC and applying such treatments could reduce recurrence and long-term mortality in patients who have undergone surgery for NSCLC.
To our knowledge, there are no studies that specifically analyse the cost-benefit of PLC, although we believe that, given the low cost of the technique, it could have a relevant clinical impact in NSCLC patients with PLC positivity. In contrast to what we know about late recurrences, there is no information on the relationship between PLC and early recurrences. Therefore, we conducted a prospective, multicentre study to assess the impact of PLC on early postoperative recurrence after anatomical lung resection in patients with NSCLC.
MethodsThis project was approved by all the ethics committees of the participating centres, obtaining informed consent from the recruited patients to use their clinical data for scientific purposes (approval by the Ethics Committee of the Hospital Arnau de Vilanova in Lérida on 17 August 2015 (CEIC-1449)).
The Spanish Pleural Lavage Study Group (GEELP) of the Spanish Society of Thoracic Surgery (SECT) designed a prospective, multicentre cohort study that included patients undergoing anatomical lung resection for NSCLC between October 2015 and October 2017 in 12 national centres. After the closure of the inclusion period, patients were followed up until October 2019 by standard clinical and radiological protocol at each centre, as well as by review of medical records and/or telephone calls to the patient or relatives.
Patients older than 18 years with NSCLC who underwent anatomical lung resection (lobectomy, pneumonectomy or anatomical segmentectomy) were included. Exclusion criteria were: (1) patients without a final definitive diagnosis of NSCLC, (2) patients who underwent non-anatomic lung resection, (3) patients in whom resection was not complete, (4) patients with significant pleuro-pulmonary adhesions requiring lung manipulation to free the pleural cavity, and (5) patients with confirmed metastatic pleural lesions and/or malignant pleural effusion at the time of access to the pleural cavity.
The outcome variable was early recurrence defined as recurrence occurring in the first two years after surgery at local and/or distant location. Other variables evaluated were demographic (age, gender, smoker), related to the study and clinical staging of NSCLC (location, standardised uptake value [SUV] in positron emission tomography [PET], clinical stage), related to neoadjuvant and adjuvant treatments if administered, surgical (type of resection, surgical approach, surgical extension), pathological (histology, differentiation, tumour size, pleural invasion, vascular invasion, lymphatic involvement, pathological stage, PLC positivity) and those related to recurrence, if any. The edition of the TNM system used was the 7th edition, which was the current edition when the study began. Discrimination was made between well-differentiated (including well-differentiated and moderately differentiated grades) and poorly differentiated (including poorly differentiated and undifferentiated) tumours, early clinical stage (clinical stages I–IIA) and advanced stage (stages IIB–IIIB), and early pathological stage (stages 0–IIA) and advanced pathological stage (stages IIB–IIIB).
Study protocolPleural lavageAfter accessing the thoracic cavity and prior to any manipulation of the lung, 100mL of saline was instilled. Fifty millilitres were drawn (pre-resection sample) and, after completion of lung resection and lymphadenectomy, the second sample (post-resection sample) was obtained in the same manner.
Sample processingThe pre- and post-operative PLC material was separated into two 25mL tubes for each sample, which were centrifuged at 2000rpm for 10min. After centrifugation, the sediment obtained in one of the tubes was decanted and two cytological smears were made and stained with Papanicolaou stain. If a clot had formed in the material from the other tube, it was fixed in formalin and subsequently embedded in paraffin. If no clot had formed, agarose gel was added to generate a cell block (CB), which was also formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded.
Four sections were made from the paraffin-embedded CB. One of them was stained with haematoxylin-eosin. If atypical cells suspicious for malignancy were observed, the remaining sections were immunohistochemically stained for TTF1, in case of adenocarcinoma, or p63 or p40, in case of squamous carcinoma (Fig. 1).
Sample sizeThe required sample size was calculated based on the main objective of the study, i.e. to demonstrate differences in the recurrence rate at two years after surgery according to PLC positivity or negativity. It was assumed that 30% of patients would have tumour progression (relapse, metastasis or exitus) two years after surgery (based on data published in the literature).3,4 The inclusion of 647 patients ensured a statistical power of 80% (beta=0.2) with significance assessed by a Z-test based on two proportions with a type 1 error of 5% (alpha=0.05).
Statistical analysisContinuous variables were expressed as mean and standard deviation or median and interquartile range, as appropriate, and qualitative or categorical variables as frequency and percentage. The Shapiro–Wilks test showed that quantitative variables did not follow a normal distribution. The association between the different predictors of positivity and the positivity of the PLC was analysed using hypothesis testing, with comparison of proportions in the case of qualitative variables (Chi-square, Fisher's exact test) and non-parametric tests (Mann–Whitney U) in the case of quantitative variables. Similarly, risk factors related to early recurrence were analysed. Analyses were performed using univariate and multivariate logistic regression models. The odds ratio (OR) of each variable, its 95% confidence interval (CI) and its p-value were indicated. The significance level was taken as p<0.05 and, in the case of multiple comparisons, the Bonferroni correction was applied.
The association of PLC positivity as a risk factor for early recurrence and clinical, surgical, and oncological variables that could influence the outcome variable (early recurrence) was analysed by two-tailed statistical hypothesis testing, using Mann–Whitney U-tests or Chi-square and standardised mean differences (SMD). Patients with positive PLC with missing variables were imputed using the predictive mean matching (pmm) imputation method. Variables with a p-value<0.2 and/or standardised differences>0.1 were the covariates used to construct the propensity score. The propensity score was estimated using a logit model and the overlap assumption was assessed with a density plot. The effect of the different variables on early recurrence was assessed by inverse probability weighting (IPSW) using average treatment effect (ATE) estimation.
The significant early recurrence variables in the logistic regression model were candidates for constructing a recurrence predictor model, which was selected according to the Akaike information criterion (AIC) value. The adequacy of the model was assessed by the area under the ROC curve and the best cut-off point was calculated by finding the one that maximised sensitivity. The analysis was performed using R software version 4.2.2.
ResultsThe cohort consisted of 684 patients. Pre-pulmonary resection (pre-PR) PLC positivity was obtained in samples from 6 patients (0.9%), and post-pulmonary resection (post-PR) in samples from 13 patients (1.9%), the overall positivity of the cohort being 2.2% (15 patients). Four patients had positivity in both pre- and post-PR PLC (0.6%). The main demographic, staging, surgical and pathological variables between the two groups are summarised in Table 1.
Main characteristics of the study population according to PLC positivity.
| Total | PLC negativity | PLC positivity | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n=684 | n=669 | n=15 | ||
| Age, years | 65.2 (SD±9.65) | 65.2 (SD±9.59) | 65.5 (SD±12.2) | 0.919 |
| Sex | ||||
| Female | 168 (24.6%) | 164 (24.5%) | 4 (26.7%) | 0.822 |
| Male | 516 (75.4%) | 505 (75.5%) | 11 (73.3%) | |
| Smoker | 546 (80.8%) | 533 (80.6%) | 13 (86.7%) | 0.608 |
| Tumour location | ||||
| Central | 212 (31%) | 206 (30.8%) | 6 (40%) | 0.455 |
| Peripheric | 472 (69%) | 463 (69.2%) | 9 (60%) | |
| Tumour SUV in PET | ||||
| SUV<5 | 240 (36.5%) | 238 (37%) | 2(13.3%) | 0.057 |
| SUV>5 | 418 (63.5%) | 405 (63%) | 13 (86.7%) | |
| Clinical stage | ||||
| Initial (I–IIA) | 523 (76.5%) | 516 (77.1%) | 7 (46.7%) | 0.014 |
| Advanced (IIB–IIIB) | 161 (23.5%) | 153 (22.9%) | 8 (53.3%) | |
| Surgical approach | ||||
| Thoracotomy | 361 (52.9%) | 354 (52.1%) | 7 (46.7%) | 0.633 |
| VATS | 321 (47.1%) | 313 (46.9%) | 8 (53.3%) | |
| Histology | ||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 365 (53.4%) | 354 (52.9%) | 11 (73.3%) | 0.125 |
| Others | 319 (46.6%) | 315 (47.1%) | 4 (26.7%) | |
| Tumoral size, mm | 30.6 (SD±20) | 30.3 (SD±19.6) | 45.3 (SD±28.9) | 0.005 |
| Tumoral differentiation | ||||
| Well differentiated | 454 (80.4%) | 451 (81.1%) | 3 (33.3%) | 0.003 |
| Poorly differentiated | 111 (19.6%) | 105 (18.9%) | 6 (66.7%) | |
| Pleural invasion | ||||
| No | 436 (64.8%) | 433 (65.8%) | 3 (20%) | 0.003 |
| Visceral | 210 (31.2%) | 201 (30.5%) | 9 (60%) | |
| Parietal | 27 (4%) | 24 (3.6%) | 3 (20%) | |
| Vascular invasion | ||||
| No | 506 (75.1%) | 499 (75.7%) | 7 (46.7%) | 0.020 |
| Yes | 168 (24.9%) | 160 (24.3%) | 8 (53.3%) | |
| pT | ||||
| pT1–2 | 574 (83.9%) | 564 (84.3%) | 10 (66.7%) | 0.099 |
| pT3–4 | 110 (16.1%) | 105 (15.7%) | 5 (333%) | |
| pN | ||||
| 0 | 500 (73.1%) | 497 (64.3%) | 3 (20%) | <0.001 |
| 1–2 | 184 (26.9%) | 172 (25.7%) | 12 (80%) | |
| Pathological stage | ||||
| Initial (0–IIA) | 498 (72.8%) | 493 (73.7%) | 5 (33.3%) | 0.002 |
| Advanced (IIB–IIIB) | 186 (27.2%) | 176 (26.3%) | 10 (66.7%) | |
Abbreviations: PET, positron emission tomography; PLC, pleural lavage cytology; pN, pathological N descriptor; pT, pathological T descriptor; SUV, standardised uptake value; VATS, video-assisted thoracic surgery.
A univariate and multivariate analysis was carried out in search of factors related to PLC positivity. Significant variables or variables with p<0.2 in the univariate analysis were included in the multivariate analysis, as well as age and sex. Factors associated with overall PLC positivity were poor tumour differentiation and undifferentiation (OR=10.08, 95%CI 1.94–67.98, p=0.009), invasion of the parietal pleura (OR=65.22, 95%CI 4.09–1495.27, p=0.004) and lymph node involvement (OR=12.88, 95%CI 1.95–109.65, p=0.010) (Table 2).
Univariate and multivariate analysis of factors related to PLC positivity.
| Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLC (−) | PLC (+) | p | OR | p | |
| Age, years | 65.2 (SD±9.6) | 65.5 (SD±12.2) | 0.919 | 1.02 (0.94–1.11) | 0.69 |
| Sex | |||||
| Female | 164 (97.6%) | 4 (2.4%) | 0.89 | 2.81 (0.38–60.86) | 0.386 |
| Male | 505 (97.9%) | 11 (2.1%) | |||
| Clinical stage | |||||
| Initial (I–IIA) | 516 (98.7%) | 7 (1.3%) | 0.01 | 1.34 (0.19–7.62) | 0.752 |
| Advanced (IIB–IIIB) | 153 (95%) | 8 (5%) | |||
| Histology | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 354 (97%) | 11 (3%) | 0.129 | 5.39 (1.04–43.23) | 0.065 |
| Others | 315 (98.7%) | 4 (1.3%) | |||
| Tumoral size, mm | 30.3 (SD±19.6) | 45.3 (SD±28.9) | 0.005 | 1 (0.97–1.04) | 0.864 |
| Tumoral differentiation | |||||
| Well differentiated | 451 (99.3%) | 3 (0.7%) | 0.003 | 10.08 (1.94–67.98) | 0.009 |
| Poorly differentiated | 105 (94.6%) | 6 (5.4%) | |||
| Pleural invasion | |||||
| No | 433 (99.3%) | 3 (0.7%) | |||
| Visceral | 201 (95.7%) | 9 (4.3%) | 0.005 | 4.48 (0.75–36.6) | 0.112 |
| Parietal | 24 (88.9%) | 3 (11.1%) | 0.001 | 65.22 (4.09–1495.27) | 0.004 |
| Vascular invasion | |||||
| No | 499 (98.6%) | 7 (1.4%) | 0.016 | 0.86 (0.15–4.54) | 0.862 |
| Yes | 160 (95.2%) | 8 (4.8%) | |||
| pN | |||||
| 0 | 497 (99.4%) | 3 (0.6%) | <0.001 | 12.88 (1.95–109.65) | 0.01 |
| 1–2 | 172 (93.5%) | 12 (6.5%) | |||
| Pathological stage | |||||
| Initial (0–IIA) | 493 (99%) | 5 (1%) | 0.002 | 0.27 (0.03–2.09) | 0.211 |
| Advanced (IIB–IIIB) | 176 (94.6%) | 10 (5.4%) | |||
Abbreviations: SD, standard deviation; PET, positron emission tomography; PLC, pleural lavage cytology; pN, pathological N descriptor; pT, pathological T descriptor; SUV, standardised uptake value; VATS, video-assisted thoracic surgery.
After two years of follow-up, 193 patients (28.2%) relapsed; 182 (27.2%) among those with a negative PLC and 11 (73.3%) among those with a positive PLC (p<0.001). Recurrence in the first year occurred in 104 patients (15.2%), 99 with negative PLC (14.8%) and 5 with positive PLC (33.3%) (p=0.04). There was no difference in the site of recurrence between PLC positive and negative patients (p=0.201). In 11 patients with positive PLC, recurrences were distant in 4 (36%) or loco-regional in 7 (64%). Among 182 patients with negative PLC, recurrences were distant in 80 (44%), loco-regional in 75 (41%) or both in 27 (15%). Univariate and multivariate analysis was performed in search of risk factors related to recurrence in the first two years after surgery. Variables significant or with p<0.2 in the univariate analysis were included in the multivariate analysis, in addition to age and sex. Adenocarcinoma histology (OR=1.59, 95%CI 1.06–2.38, p=0.025), visceral pleural invasion (OR=1.59, 95%CI 1.04–2.4, p=0.03), lymph node involvement (OR=1.84, 95%CI 1.14–2.96, p=0.013), advanced pathological stage (OR=2.12, 95%CI 1.27–3.54, p=0.004) and PLC positivity (OR=4.14, 95%CI 1.25–16.36, p=0.028) were the factors associated with early recurrence (Table 3).
Univariate and multivariate analysis of factors related to early recurrence.
| Univariate analysis | Multivariate analysis | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-recurrence | Recurrence | p | OR | p | |
| Age, years | 65 (SD±10.0) | 65.6 (SD±8.7) | 0.469 | 1 (0.98–1.03) | 0.636 |
| Sex | |||||
| Female | 127 (75.6%) | 41 (24.4%) | 0.207 | 1.45 (0.92–2.31) | 0.113 |
| Male | 364 (70.5%) | 152 (29.5%) | |||
| Tumoral location | |||||
| Central | 142 (67%) | 70 (33%) | 0.062 | 0.67 (0.44–1.03) | 0.067 |
| Peripheric | 349 (73.9%) | 123 (26.1%) | |||
| Tumour SUV in PET | |||||
| SUV<5 | 190 (79.2%) | 50 (20.8%) | 0.001 | 1.45 (0.93–2.27) | 0.104 |
| SUV>5 | 282 (67.5%) | 136 (32.5%) | |||
| Clinical stage | |||||
| Initial (I–IIA) | 386 (73.8%) | 137 (26.2%) | 0.035 | 0.67 (0.38–1.15) | 0.151 |
| Advanced (IIB–IIIB) | 105 (65.2%) | 56 (34.8%) | |||
| Surgical approach | |||||
| Thoracotomy | 242 (67%) | 119 (33%) | 0.004 | 0.78 (0.52–1.16) | 0.216 |
| VATS | 247 (76.9%) | 74 (23.1%) | |||
| Histology | |||||
| Adenocarcinoma | 252 (69%) | 113 (31%) | 0.089 | 1.59 (1.06–2.38) | 0.025 |
| Others | 239 (74.9%) | 80 (25.1%) | |||
| Tumoral size, mm | 29.4 (SD±19.4) | 33.5 (SD±21.3) | 0.016 | 1 (0.99–1.01) | 0.541 |
| Pleural invasion | |||||
| No | 338 (77.5%) | 98 (22.5%) | |||
| Visceral | 131 (62.4%) | 79 (37.6%) | <0.001 | 1.59 (1.04–2.40) | 0.03 |
| Parietal | 16 (59.3%) | 11 (40.7%) | 0.034 | 0.83 (0.29–2.25) | 0.725 |
| Vascular invasion | |||||
| No | 379 (74.9%) | 127 (25.1%) | 0.005 | 1.06 (0.68–1.64) | 0.78 |
| Yes | 107 (63.7%) | 61 (36.3%) | |||
| pN | |||||
| 0 | 393 (78.6%) | 107 (21.4%) | <0.001 | 1.84 (1.14–2.96) | 0.013 |
| 1–2 | 98 (53.3%) | 86 (46.7%) | |||
| Pathological stage | |||||
| Initial (0–IIIA) | 391 (78.5%) | 107 (21.5%) | <0.001 | 2.12 (1.27–3.54) | 0.004 |
| Advanced (IIB–IIIB) | 100 (53.8%) | 86 (46.2%) | |||
| PLC | |||||
| Negative | 487 (72.8%) | 182 (27.2%) | 0.001 | 4.1 (1.25–16.36) | 0.028 |
| Positive | 4 (26.7%) | 11 (73.3%) | |||
Abbreviations: SD, standard deviation; PET, positron emission tomography; PLC, pleural lavage cytology; pN, pathological N descriptor; pT, pathological T descriptor; SUV, standardised uptake value; VATS, video-assisted thoracic surgery.
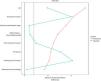
The variables used to construct the propensity score were those most frequently reported in relation to recurrence: adenocarcinoma histology, tumour size, degree of differentiation, visceral and parietal pleural invasion, lymph node involvement, SUV value on PET>5 and pathological stage. Inverse weights were calculated using the ATE estimator. Due to the low number of positive PLCs, some variables were not well balanced, as was the case for pleural invasion (Fig. 2). A double model fit was performed by multivariate analysis (Table 4). PLC positivity was associated with an increased risk of early recurrence (OR=3.46, 95%CI 2.25–5.36, p<0.001).
Multivariate analysis of variables related to early recurrence after propensity score analysis using IPSW with ATE estimator.
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 1.01 | 1.00–1.03 | 0.1 |
| Sex | |||
| Female | |||
| Male | 2.2 | 1.47–3.36 | <0.001 |
| Tumoral location | |||
| Central | |||
| Peripheric | 0.69 | 0.46–1.04 | 0.07 |
| Tumour SUV in PET | |||
| SUV<5 | |||
| SUV>5 | 1.71 | 1.14–2.57 | 0.009 |
| Surgical approach | |||
| VATS | |||
| Thoracotomy | 2.25 | 1.53–3.31 | <0.001 |
| Histology | |||
| Adenocarcinoma | 5.17 | 3.62–7.47 | <0.001 |
| Others | |||
| Differentiation | |||
| Well differentiated | |||
| Poorly differentiated | 1.95 | 1.30–2.92 | 0.001 |
| Pleural invasion | |||
| No | |||
| Visceral | 1.81 | 1.27–2.60 | 0.001 |
| Parietal | 0.26 | 0.13–0.52 | <0.001 |
| Vascular invasion | |||
| No | |||
| Yes | 0.94 | 0.63–1.38 | 0.746 |
| pN | |||
| 0 | |||
| 1–2 | 1.1 | 0.73–1.65 | 0.65 |
| Pathological stage | |||
| Initial (0–IIA) | |||
| Advanced (IIB–IIIB) | 1.7 | 1.10–2.63 | 0.016 |
| PLC | |||
| Negative | |||
| Positive | 3.46 | 2.25–5.36 | <0.001 |
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval; PET, positron emission tomography; PLC, pleural lavage cytology; pN, pathological N descriptor; SUV, standardised uptake value; VATS, video-assisted thoracic surgery.
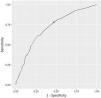
A predictive model for early recurrence was constructed in the patient cohort. The model with the best AIC criterion was the one that included the significant variables in the multivariate analysis: adenocarcinoma histology, pleural invasion, lymph node involvement, advanced pathological stage and positive PLC (AIC=743.5). The area under the ROC curve was 0.70 (95%CI 0.66–0.73). The resulting sensitivity and specificity were 0.75 and 0.54 respectively (Fig. 3).
DiscussionOur main finding was that PLC positivity increased the risk of recurrence in the first two years after surgery in patients who underwent surgery for NSCLC. Likewise, adenocarcinoma histology, lymph node involvement, visceral pleural invasion and advanced pathological stage were associated with the risk of relapse in that period. On the other hand, PLC positivity was related to the degree of tumour differentiation, invasion of the parietal pleura and lymph node involvement.
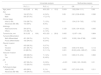
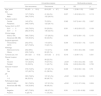
PLC positivity in patients undergoing surgery for NSCLC has been established as a risk factor for mortality and overall recurrence. Positivity rates range from 3 to 6%.10–13,18 Our positivity rate (2.2%) was slightly lower than most of those previously published. Multiple risk factors are associated with PLC positivity. The most frequently referenced are pleural invasion, pathological stage, lymph node involvement and histology, among others (Table 5).11–14,19,20 In our series, factors associated with PLC positivity included the degree of tumour differentiation, involvement of the parietal pleura and lymph node involvement. In a series of 3231 patients, Kaneda et al. observed that pleural invasion of the tumour was one of the factors associated with PLC positivity,12 along with the descriptor pT, pN, histology and pathological stage. Similarly, in the Japanese Joint Committee of Lung Cancer Registry of 4171 patients who underwent PLC with a positivity rate of 5.2% (217 patients),11 the factors related to this result were tumour size, adenocarcinoma histology, advanced pathological stage, and pleural invasion. Another of the most frequently reported factors is lymphatic involvement. In addition to the series by Kaneda et al.,12 other studies such as that of Satoh et al. with 853 patients describe lymph node involvement among the factors related to PLC positivity.19 However, the degree of tumour differentiation has not been published as a risk factor for PLC positivity and, in our series, it was the third most important risk factor.
Factors associated with positivity in PLC in the literature.
| Author/year | n | % PLC + | Factors associated to PLC + |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enatsu et al., 2006 | 1194 | 3.2/4.5a | Pathological stage, pleural involvement, N, lymphatic involvement, vascular involvement, grade of fibrosis, complete resection. |
| Nakagawa et al., 2007 | 1025 | 3.6 | Histology, pathological stage, pleural invasion. |
| Satoh et al., 2007 | 853 | 4.8 | Histology, tumoral location, pathological stage, N, pleural invasion. |
| Kaneda et al., 2012 | 3231 | 4.6 | Histology, pathological stage, T, N, pleural invasion. |
| Kameyama et al., 2014 | 4171 | 5.2 | Tumoral size, histology, pathological stage, pleural involvement. |
| Mazza et al., 2014 | 436 | 3.6 | Sex, histology, T, N, number of positive node stations, pleural involvement. |
Abbreviations: N, N descriptor of TNM; PLC +, pleural lavage cytology positivity; T, T descriptor of TNM.
Several theories attempt to explain the presence of tumour cells in the PLC without pleural effusion. In the case of positive PLC before surgical resection, diapedesis through the subpleural lymphatic vessels21,22 or from the affected lymph nodes and their exfoliation into the pleural cavity,23 as well as direct cell exfoliation of the tumour22 are the most widely accepted theories. In the case of positivity after lung resection, the presence of tumour cells could be due to mechanical causes secondary to tumour manipulation and destruction of lymphatic vessels.24
Most published studies describe overall survival reductions of 25–30% in patients with positive PLC.15,25 Furthermore, a positive PLC has been shown to be a risk factor for long-term recurrence. Thus, in a series of 600 patients with a PLC-positive rate of 4.2%,25 postoperative recurrence among PLC-positive patients was 52% versus 18% among PLC-negative patients. In a retrospective series of 1293 patients with a PLC positivity of 3.9%,26 recurrence-free survival (RFS) was 31.1% in PLC-positive patients versus 75.7% in PLC-negative patients (p<0.001). Fujibayashi et al. observed that positive PLC was associated with worse 5-year RFS among patients with visceral pleural involvement.27 Thus, among patients with pl1 involvement (invasion beyond the elastic layer), the 5-year RFS for those with positive PLC was 22% vs. 60% in those with negative PLC (p=0.002). For patients with pl2 involvement (pleural surface invasion), the 5-year RFS between the two groups was 30.4% vs. 59.7% respectively (p=0.015). A recent published study obtained similar results with 5-year RFS in positive PLC patients of 29.6% vs. 75.1% in negative PLC patients (p<0.001).16 However, to date, the role of PLC positivity on early recurrence has not been investigated. In our work, we found that PLC positivity was one of the most important risk factors for early recurrence, increasing relapse up to 3.46-fold (OR 3.46).
In patients who undergo surgery for NSCLC, the main cause of mortality is recurrence, which generally occurs in the first two years.6 The rate of early relapses (first two years after surgery) in the few and heterogeneous surgical series ranges from 10 to 19%.5,28,29 In the present study it was 28.2% which, although a higher figure, could be justified by the inclusion of patients in stages 0–IIIA. Thus, in the series by Kiankhooy et al.,5 recurrence in the first two years in individuals with T1-T2b was 19%, a figure comparable to that of the patients in our series in stages I–IIA (21.5%). Other series consider early recurrence to be that which occurs within the first year.29 Thus, Kobayashi et al. reported a first-year recurrence rate of 13.4% among patients who underwent surgery for stage I–III NSCLC, similar to that obtained in our series in the same period (15.2%).
There are several published factors related to the risk of early recurrence.5,28,30–32 In our multivariate analysis, adenocarcinoma histology, invasion of the parietal pleura, lymph node involvement, advanced pathological stage and PLC positivity were selected. We then performed a propensity score analysis to specifically study the impact of PLC positivity on early recurrence. Some factors related to recurrence in the first years after surgery such as lymph node involvement, pleural invasion or pathological stage have been previously published. Kawachi et al.,28 in a retrospective series of 402 patients, observed recurrence in the first year after surgery in 21 patients (5.2%), between the first and second year in 22 patients (5.5%) and after two years in 28 patients (7%). The risk factors for recurrence in the first year were the preoperative CEA value, the pT descriptor, the presence of lymphatic permeation, vascular invasion, and pathological stage. Likewise, in the Kobayashi series,29 pathological stage together with C-reactive protein/albumin ratio and vascular invasion were associated with an increased risk of early recurrence. However, PLC positivity has not been studied as a risk factor for early recurrence.
We constructed a predictive model of early recurrence with the significant variables in the multivariate analysis. Our model showed a moderate predictive ability with an AUC of 0.70 and a sensitivity of 75%. Despite the moderate predictive capacity of the model, we believe that our results are generalisable given the multicentre nature of the project in which 12 national centres throughout the country participated. We also believe that the limited exclusion criteria allowed the enrolment of most patients undergoing surgery for NSCLC. It is important to be able to identify and predict which patients have a higher risk of recurrence to assess therapeutic and follow-up strategies. Some studies have investigated the application of complementary treatments in patients who underwent surgery for NSCLC with positive PLC. Although with a small number of patients (n=17),33 Baba et al. observed differences in overall survival at two years between those patients with positive PLC who received intrapleural chemotherapy and those who did not (88% vs. 44%, p=0.004). We think that PLC and subsequent cyto-histological study, as proposed in the latest edition of the TNM, should be established as a criterion for incomplete resection in order to consider complementary treatments. More studies are necessary to evaluate the impact of adjuvant treatments in patients with positive PLC to elucidate their therapeutic and prognostic role. Nowadays, given the paucity of studies on adjuvant treatments in such patients, we should follow these patients more closely. A suggested follow-up schedule in patients with positive PLC could be a clinical and radiological (computed tomography) review every 3 months for the first couple of years.
LimitationsThe main limitation of our study derives from its multicentre nature and the potential variability between pathologists when interpreting PLCs and applying immunohistochemistry techniques. However, the development of a detailed sample processing protocol may have reduced this potential bias. The overall frequency of PLC positivity obtained was low (2.2%), with only 6 patients positive before surgical resection (0.9%) and 13 post-resection (1.9%). Nevertheless, the sample size calculated to detect differences in the early recurrence rate was reached. Finally, although the factors studied are the most representative from a clinical point of view and the most frequently referenced in the literature, there are other factors not considered such as inflammatory or genetic factors that could influence the development of recurrences.
ConclusionOf the risk factors associated with recurrence in the first two years after lung resection for NSCLC, PLC positivity was the most significant, with a 3.46-fold increase in early relapse in the GEELP cohort. Predictors of positive PLC were those related to tumour biology such as degree of differentiation, pleural invasion and lymph node involvement. The identification of risk factors such as PLC may help to define new strategies for follow-up and therapeutic management in patients undergoing surgery for NSCLC.
Authors’ contributionJosé Luis Recuero Díaz: conception, design of the work, acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data for the work, writing-original draft, final approval of the version, and project administration; Sonia Gatius Caldero: conception, design of the work, acquisition, reviewing-original draft, visualisation, final approval of the version, and project administration; Joel Rosado Rodríguez: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Verónica Caamaño Villaverde: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; David Gómez de Antonio: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Eva Tejerina González: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Laura Sánchez Moreno: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; María Martino González: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Milagros Moldes Rodríguez: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Ihab Abdulkader Nallib: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Elena Ramírez Gil: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Irene Amat Villegas: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Marta Genovés Crespo: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Rubén García Ángel: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Cora Sampedro Salinas: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Santiago Figueroa Almánzar: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Amparo Compañ Quilis: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Roser Saumench Perramon: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Guadalupe González Pont: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Íñigo Royo Crespo: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Paula Gambó Grasa: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; José Luis García Fernández: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; José Antonio Jiménez Heffernan: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; José Cerón Navarro: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; Mireia Prieto Rodríguez: acquisition of data for the work, reviewing-original draft and final approval of the version; José Manuel Porcel Pérez: conception, design of the work, analysis and interpretation of data for the work, writing-original draft, final approval of the version, and project administration.
FundingThe GEELP was awarded a grant from the Spanish Society of Thoracic Surgery as the best national research project of 2016.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflicts of interest.
We thank all the local researchers who contributed with patient recruitment and data entry.