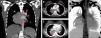
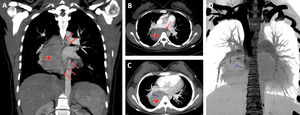
A 18-year-old female presented for evaluation of recurrent cough and hemoptysis. A giant pulmonary sequestration mimicking a paravertebral mass was detected in computed tomography (Fig. 1A–D).
Coronal (A) and axial (B) CT scans show a giant pulmonary sequestration (star) feeding by systemic arteries (red arrows). Maximum intensity projection (MIP) axial CT scan (C) also reveals that the pulmonary sequestration was drained by the pulmonary vein (blue arrow) of the right lower lobe. Coronal volume rendering negative MIP image shows clearly the drainage vein (blue arrow). RPA, right main pulmonary artery; RPV, right main pulmonary vein.
Pulmonary sequestration is a rare congenital lung anomaly. It is defined by nonfunctional lung tissue originating from the normal bronchopulmonary system and bleeding from the aberrant systemic artery. Pulmonary sequestration is classified as extralobar and intralobar. About three quarters of the cases are localized in the left lower lobe. In rare cases, it can mimic a benign or malign thoracic lesions.1,2 Detecting pulmonary sequestration before surgery is very important to prevent serious intraoperative complications.