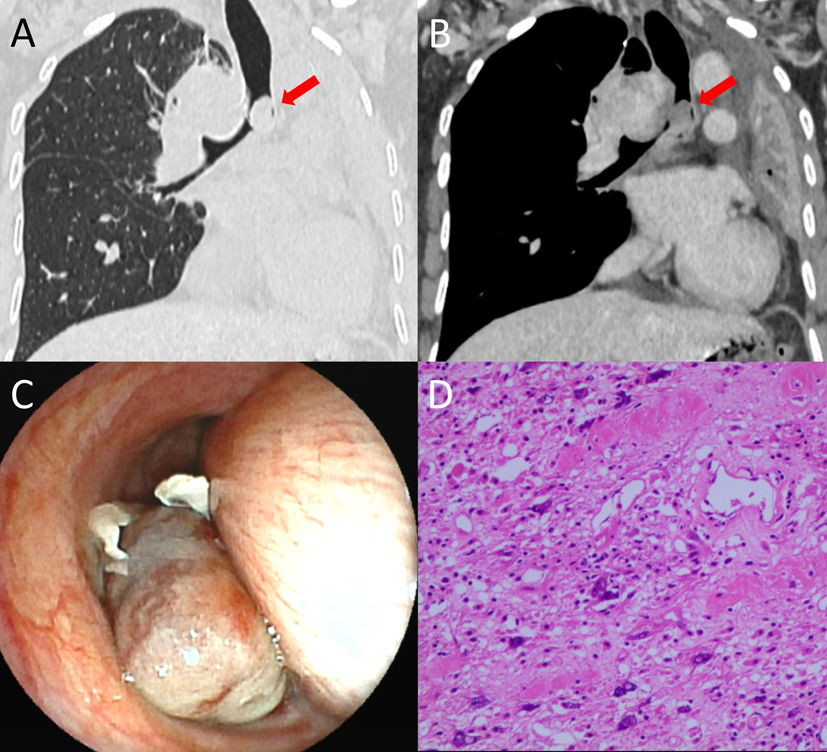
A 56-year-old female was evaluated due to persistent cough and wheezing lasting over one month. Chest CT (Fig. 1A, B) revealed a nodular soft tissue density lesion, measuring approximately 10mm×14mm, within the left main bronchus, which exhibited mild enhancement post-contrast. Obstructive atelectasis was observed in the left lung. A lobulated soft tissue mass, measuring approximately 43mm×61mm, was identified below the carina and demonstrated marked enhancement post-contrast. Bronchoscopy (Fig. 1C) demonstrated complete obstruction of the left main bronchus by a neoplasm, with significant extrinsic compression causing narrowing of the right main bronchus. Histopathological examination (HE and IHC, Fig. 1D) of the bronchoscopic biopsy specimen revealed findings consistent with liposarcoma. Bronchial liposarcoma is a malignant tumor originating from primitive mesenchymal tissue, specifically adipocyte precursor cells, within the bronchial or tracheal wall. While liposarcoma represents a relatively common subtype of soft tissue sarcoma (approximately 20%), its primary occurrence within the bronchi or trachea is exceptionally rare, constituting an infrequent type of primary endobronchial malignancy [1,2]. It is most frequently diagnosed in adults aged 40–60 years. Clinical manifestations primarily result from bronchial lumen obstruction, with cough being the most common symptom, followed by dyspnea or wheezing secondary to airway narrowing.
Chest CT (A, B) revealed a nodular soft tissue density (arrows) within the left main bronchus demonstrating mild enhancement after contrast administration. A lobulated soft tissue mass was observed below the carina, showing marked enhancement post-contrast. Bronchoscopy (C) demonstrated complete obstruction of the left main bronchial lumen by a neoplasm and significant extrinsic compression causing stenosis of the right main bronchus. Microscopically (D), heterogeneous cellular density, cellular pleomorphism, nuclear pleomorphism (variation in nuclear size and shape), and abundant cytoplasm were noted.
Q.P.Z. contributed to the conception, the acquisition, the literature search and preparing the figures; B.L.L. contributed to drafting the text and approved the manuscript.
DeclarationNever used any artificial intelligence tools or technologies to assist in generating the paper.
FundScience and Technology Program of Jiangxi Provincial Health Commission (No. 202511053).
Conflict of interestThe authors disclose no conflicts.