Alveolar-pleural fistulas (APF) are a clinical entity that represents a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge.
ObjectiveThe objective of this work is to design a diagnostic algorithm for the anatomical detection of APF in patients who are not candidates for surgical treatment.
MethodProspective non-randomized study of 47 patients. Diagnostic procedures were performed: (a) prior to bronchoscopy: computed axial tomography (CT) and implantation of electronic pleural drainage system (EPD) and (b) endoscopic: endobronchial occlusion (EO) by balloon, selective endobronchial oxygen insufflation (OI) (2l) and selective bronchography (BS) (instillation of iodinated radiological contrast using continuous fluoroscopy).
ResultsThe sample was predominantly male (81%). The diagnostic methods revealed: (a) Determination of the anatomical location of APF by CT in 15/46 patients (31.9% of sample), and variations in the pattern (intermittent or continuous air leak) and quantification after drug administration sedatives using EPD, (b) endoscopic: anatomical determination of APF was achieved in 57.1, 81 and 63.4% respectively using EO, OI and BS. The combination of the diagnostic tests allowed us to determine the anatomical location of the APF in 91.5% of the sample. No complications were recorded in 85.1% of cases.
ConclusionsThe diagnosis of APF by flexible bronchoscopy is a useful method, with an adequate safety and efficacy profile. The proposed diagnostic algorithm includes the use of EPD and performing a CT scan. Regarding endoscopic diagnosis: in case of continuous air leak, the first option is OE; and if the leak is intermittent, we recommend endobronchial OI, with BS as a secondary option (respective sensitivity 81% vs 63.4% and complications 8.1% vs 7.3%).
Alveolar-pleural fistulas (APF) are a clinical entity characterized by communication between the lung parenchyma or peripheral bronchus and the pleural space1 that involve a change in physiological pressure.2 An APF that exceeds 5 days’ duration is called a persistent air leak (PAL).3
The etiology of PALs is linked, in most cases, to underlying diseases or iatrogenesis. The definitive diagnosis of APF combines the existence of PAL,3 clinical suspicion (fever and/or persistent pneumothorax) and the results of complementary diagnostic tests.
APFs represent a diagnostic and therapeutic challenge in that establishing their exact location is an essential step to achieving anatomical closure. In a non-negligible number of cases, computed axial tomography (CT)4 fails to identify APF. Currently, flexible bronchoscopy (BF) indicated in the diagnosis3 and treatment of APF, does not have an established diagnostic algorithm that allows the localization of APF.
Our main objective was to design a diagnostic algorithm based on the premise that it could increase and improve the detection of APF location in patients who were not candidates for surgical treatment.
Material and methodsSelected population and inclusion–exclusion criteriaWe present a prospective non-randomized study of 47 patients with clinical suspicion of APF and presence of PAL, recruited between February 2018 and April 2023. The CT images and the endoscopic procedures performed were recorded and included in our analysis.
The inclusion criteria were: patients over 18 years of age with persistent air leak ≥5 days (refractory to conventional treatment with pleural drainage) and contraindication for surgery (comorbidities or lack of patient consent). The exclusion criteria were: central bronchopleural fistula, primary pneumothorax with indication for surgery, pregnant women and/or presence of contraindications for bronchoscopy with sedation (recent ischemic heart disease [4 weeks] and/or severe coagulation disorders).
Some of the patients recruited during part of the inclusion period were included in a post-marketing monitoring study carried out by the Spanish Ministry of Health.5 The present study has been approved by the ethics committee of the Hospital Clínico Universitario de Valladolid (PI 23-3229).
Procedure prior to bronchoscopyThe first step was performing a helical CT scan including the entire thoracic cavity, using collimations between 0.625 and 1.5mm with rotation time: 0.5s, pitch: 1, 120kV and dose modulation technique. The images were analyzed using multiplanar reconstructions (axial, coronal, sagittal and oblique) and minimum intensity projection (MinIP) techniques, evaluating with a lung window (length: −600, width: 1500 Hounsfield units (HU) and with mediastinal window (length: 30, width: 400HU).
Although bibliographic reports4 suggest that CT scan images can display the presence of an APF through direct (identification of a fistulous tract between the pleural space and the lung parenchyma) after analysis of the images acquired in lung window (technical specifications: level, −600 Hounsfield unit (HU); width, 1500HU) and indirect signs (presence of air bubbles despite no direct visualization of the fistulous tract or parenchymal diseases predisposing the development of a pneumothorax of secondary etiology); in our study only the visualization of the fistulous tract between the pleural space and the lung parenchyma/peripheral bronchus (direct sign4,6,7) was considered in our study as a radiological diagnosis of APF.
Protocol for using endothoracic drainage and management of PALAfter the clinical–radiological diagnosis of PAL, a Thopaz® electronic pleural drainage (EPD) system (Thopaz-System, Medela AG, Baar, Switzerland) was implanted for continuous monitoring of PAL (ml/min). This allowed us to know the quantification and pattern of the PAL,8 before, during and after the procedure. The aspiration used was −8cm of H2O.
Endoscopic diagnostic methods- a)
Endobronchial balloon occlusion
The initial endoscopic approach was performed using a 1.4mm double lumen balloon specifically designed for endobronchial use (Olympus®, Germany), through the working channel (2.8mm diameter) of the flexible bronchoscope with sequential occlusion of the various lobar bronchi.9–11 This was the initial approach in all clinical situations that allowed it, excluding patients with intermittent air leak. We considered the location of the APF to be identified when the EPD recorded 0ml/min.
- b)
Selective endobronchial oxygen insufflation (OI)
The second diagnostic test consisted of systematically and selectively oxygen insufflation (OI) into the bronchial subsegments with suspected APF in its most distal portion. Selective insufflation of low oxygen flows, at 2L per minute was carried out through the working channel of the therapeutic bronchoscope – like methodology described by Vial et al.12 in another entity – with continuous monitoring of the flow recorded in the EPD. We considered the location of the APF to be identified when the EPD recorded a flow rate of ≥250ml/min in intermittent air leaks or a flow rate of ≥500ml/min in persistent air leaks of a continuous nature.
- c)
Selective bronchography
The third diagnostic test, excluding those with documented personal allergies, was the performance of selective bronchography (SB) by instillation of non-ionic, monomeric, triiodinated, water-soluble iodinated radiological contrast (Omnipaque® 300mg I/ml, dissolved in physiological saline at a 1:2 ratio).
The contrast was selectively installed into the lobar bronchi using continuous fluoroscopy, through a 90cm-long radiopaque catheter (Combicath®, 2.8mm diameter). Visualization and in situ review of the images made it possible to determine and diagnose the location of the APF. Due to the radiological trace of iodinated contrast in the lung parenchyma, only the lobar bronchi suspected of inhabiting the anatomical location of the APF were analyzed after the two aforementioned tests.
Patients with clinical complications after the endoscopic procedure were treated according to existing protocols in the intensive care/intermediate respiratory care units based on their symptoms.
Statistical analysisThe data were entered into a database and statistically analyzed using SPSS (IBM Corp. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 29.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp). Continuous variables were described as mean±standard deviation (SD) in case of normal distribution or as median and range if the distribution was non-normal. Qualitative variables were described using absolute and relative frequencies (percentages).
To study the association between qualitative variables, the Chi square test was used, with Yates’ correction and Fisher's exact test when the conditions required it. In the case of quantitative variables, the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was used to determine the normality of the distributions. To study the differences between independent means, the parametric or non-parametric statistical tests required by the application conditions were used (Student's t or Mann–Whitney U in the case of two categories; ANOVA with Bonferroni's post hoc test or Kruskal's H–Wallis for comparisons of more than two categories). Finally, the relationship between quantitative variables was analyzed using the Pearson (in parametric conditions) or Spearman (in non-parametric conditions) correlation tests.
ResultsCharacteristics of the patientsA total of 47 patients were recruited: 38 (81%) men and 9 women (19%). The mean age was 64 years old (minimum, 42; maximum, 94; SD, 11 years).
In our study, the most prevalent comorbidities were: infectious diseases, 53.1%; lung neoplasms, 23.4%; pulmonary emphysema, 14.8% and diffuse interstitial lung disease (DILD) in 3 patients (0.38%).
Use of endothoracic drainage system with digital measurement (EPD)40 patients with thoracic drainage were connected to EPD (85.1%). The pressure was set at −8cm H2O. Connection to EPD was not possible in 7 patients (14.9%) due to the absence of electronic endothoracic drainage (N=4); it was also not possible in patients with a previous thoracostomy (n=3). Of the 35 patients with continuous air leak prior to the procedure, 31 could be quantitatively determined by the EPD system. The mean PAL value was 1189.35ml/m (SD 1507.24ml/min).
Variations were observed in the absence/presence of discharge, specifically in the amount present after beginning the procedure and administering general anesthesia with subsequent invasive mechanical ventilation or deep sedation in monotherapy with propofol (1189.35±1507.245ml/m vs 390. 79±768.29ml/m respectively). The non-parametric Wilcoxon test for two related samples demonstrated statistical evidence of differences between both variables (p=0.000).
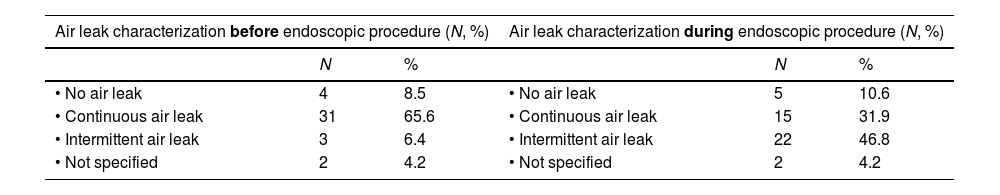
Table 1 reveals the modification in the pattern of persistent air leak after the administration of general anesthesia or deep sedation. A significant increase in intermittent air leaks (6% vs 45.8%), a decrease in continuous air leaks (65.6 vs 31.9%) and changes to the quantification in ml/min of the output were observed.
Changes in the persistent air leak pattern after general anesthesia or deep sedation administration in patients with electronic pleural drainage (N=40).
| Air leak characterization before endoscopic procedure (N, %) | Air leak characterization during endoscopic procedure (N, %) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | ||
| • No air leak | 4 | 8.5 | • No air leak | 5 | 10.6 |
| • Continuous air leak | 31 | 65.6 | • Continuous air leak | 15 | 31.9 |
| • Intermittent air leak | 3 | 6.4 | • Intermittent air leak | 22 | 46.8 |
| • Not specified | 2 | 4.2 | • Not specified | 2 | 4.2 |
- a)
CT
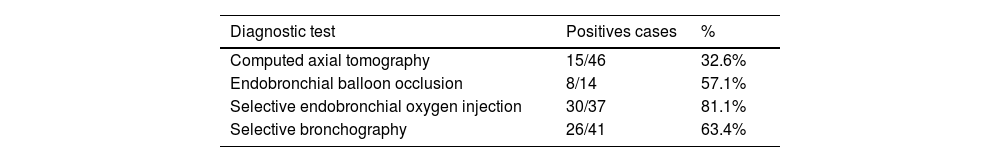
CT was performed in all patients except one, due to important clinical instability, which limited transfer to the radiology service. Their analysis demonstrated absence of anatomical location of the APF in 29 patients (61.7%), anatomical location of APF in 15 (31.9%) and suspicion of the location, without exact anatomical determination in 2 cases (4.3%).
- b)
Use of occlusion balloon
35 patients had continuous PAL prior to the procedure; however, this leak pattern (essential for performing the occlusion balloon test) decreased to 15 cases after the induction of anesthesia/sedation.
In 14 of these 15 patients, a balloon was used as an endobronchial occlusion test, which achieved anatomical determination of APF in 8/14 patients (57% of continuous PAL). We were not able to use this method with one patient due to severe respiratory failure.
- c)
Endobronchial oxygen insufflation (OI)
The selective endobronchial OI test was performed in 37 patients (78.7% of the sample), allowing the anatomical location of the APF to be identified in 30 patients (30/37; 81%).
Of the 10 patients who did not receive the OI test, 4 were not connected to EPD. In all other cases, APF was located by other diagnostic tests, and the OI test was not performed.
- d)
Selective bronchography
A selective bronchography (SB) diagnostic test was performed in 41 patients (87.2% of the sample). Non-performance was due to: impossibility of using fluoroscopy (3 patients) or/and documented allergy to iodinated contrast (3 patients). In 26 patients (63.4%), visualization of the anatomical location of the APF was achieved.
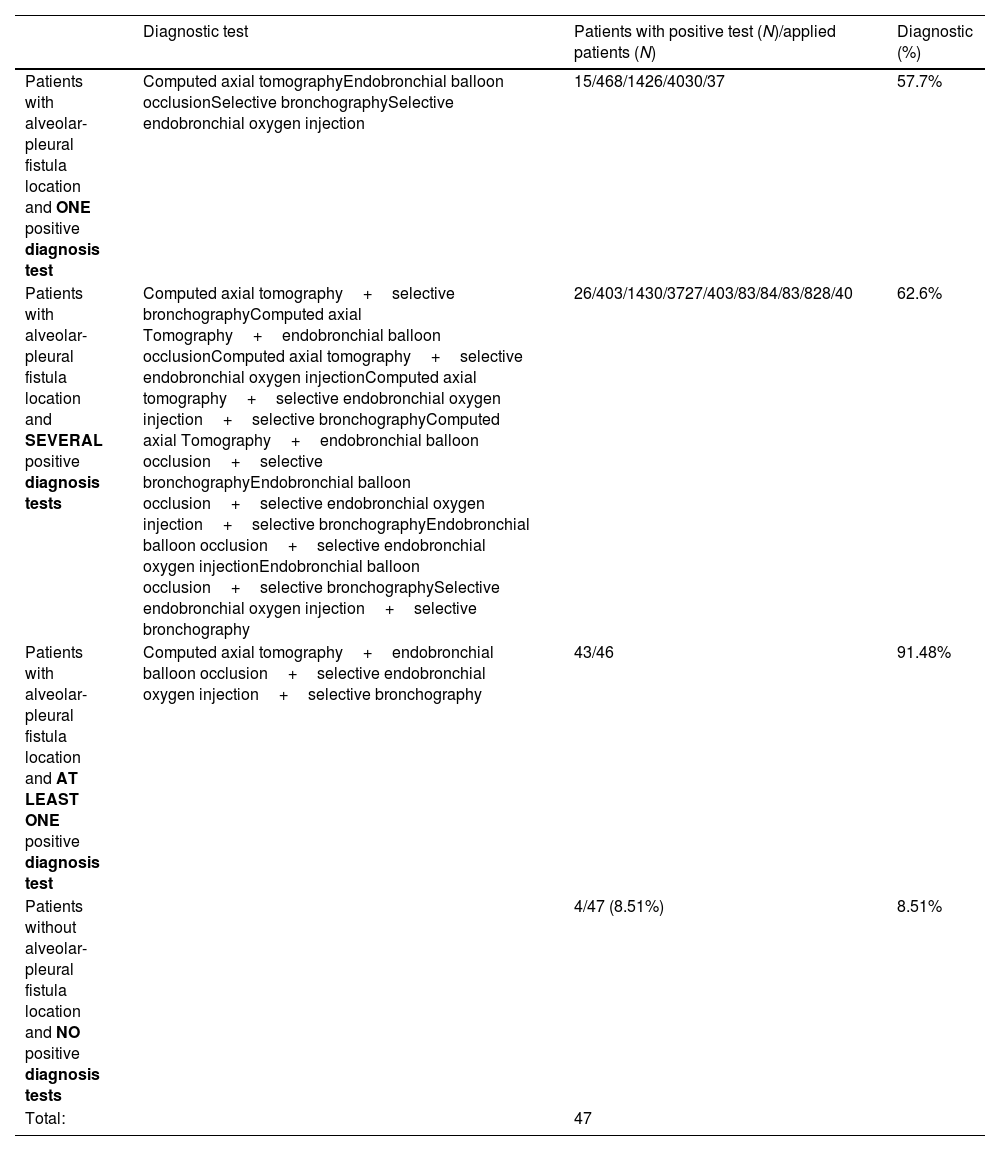
Sensitivity of individual and collective diagnostic testsTable 2 reflects the sensitivity of each diagnostic test applied. The combination of diagnostic tests allowed us to determine the anatomical location of the APF in 43 patients (91.5% of the sample). The diagnostic profitability for the application of each test is shown in Table 3.
Diagnostic profitability for the application of each test.
| Diagnostic test | Patients with positive test (N)/applied patients (N) | Diagnostic (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patients with alveolar-pleural fistula location and ONE positive diagnosis test | Computed axial tomographyEndobronchial balloon occlusionSelective bronchographySelective endobronchial oxygen injection | 15/468/1426/4030/37 | 57.7% |
| Patients with alveolar-pleural fistula location and SEVERAL positive diagnosis tests | Computed axial tomography+selective bronchographyComputed axial Tomography+endobronchial balloon occlusionComputed axial tomography+selective endobronchial oxygen injectionComputed axial tomography+selective endobronchial oxygen injection+selective bronchographyComputed axial Tomography+endobronchial balloon occlusion+selective bronchographyEndobronchial balloon occlusion+selective endobronchial oxygen injection+selective bronchographyEndobronchial balloon occlusion+selective endobronchial oxygen injectionEndobronchial balloon occlusion+selective bronchographySelective endobronchial oxygen injection+selective bronchography | 26/403/1430/3727/403/83/84/83/828/40 | 62.6% |
| Patients with alveolar-pleural fistula location and AT LEAST ONE positive diagnosis test | Computed axial tomography+endobronchial balloon occlusion+selective endobronchial oxygen injection+selective bronchography | 43/46 | 91.48% |
| Patients without alveolar-pleural fistula location and NO positive diagnosis tests | 4/47 (8.51%) | 8.51% | |
| Total: | 47 |
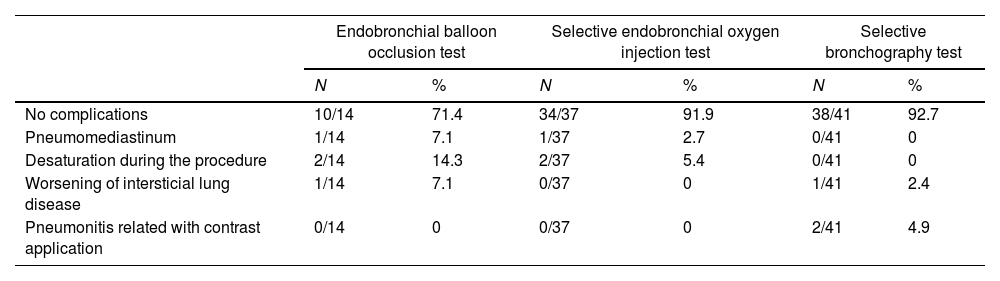
40 patients (85.1%) did not present complications during the procedure. The only complication, independent of the diagnostic test used, was desaturation (defined as that which limited the bronchoscopic procedure) in two patients.
One patient presented a complication associated with OI: development of pneumomediastinum after the simultaneous application of the occlusion balloon and oxygen insufflation in the distal region. Despite having been resolved during the procedure, precautions should be taken to avoid this complication and its associated risks.
On the other hand, two patients undergoing SB developed a clinical picture compatible with pneumonitis possibly related to the application of contrast, although no association was found between the dose of contrast administered and the presence of complications (p-value>0.202). Table 4 shows the complications associated with each diagnostic method.
Complications associated with each diagnostic method.
| Endobronchial balloon occlusion test | Selective endobronchial oxygen injection test | Selective bronchography test | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | % | N | % | N | % | |
| No complications | 10/14 | 71.4 | 34/37 | 91.9 | 38/41 | 92.7 |
| Pneumomediastinum | 1/14 | 7.1 | 1/37 | 2.7 | 0/41 | 0 |
| Desaturation during the procedure | 2/14 | 14.3 | 2/37 | 5.4 | 0/41 | 0 |
| Worsening of intersticial lung disease | 1/14 | 7.1 | 0/37 | 0 | 1/41 | 2.4 |
| Pneumonitis related with contrast application | 0/14 | 0 | 0/37 | 0 | 2/41 | 4.9 |
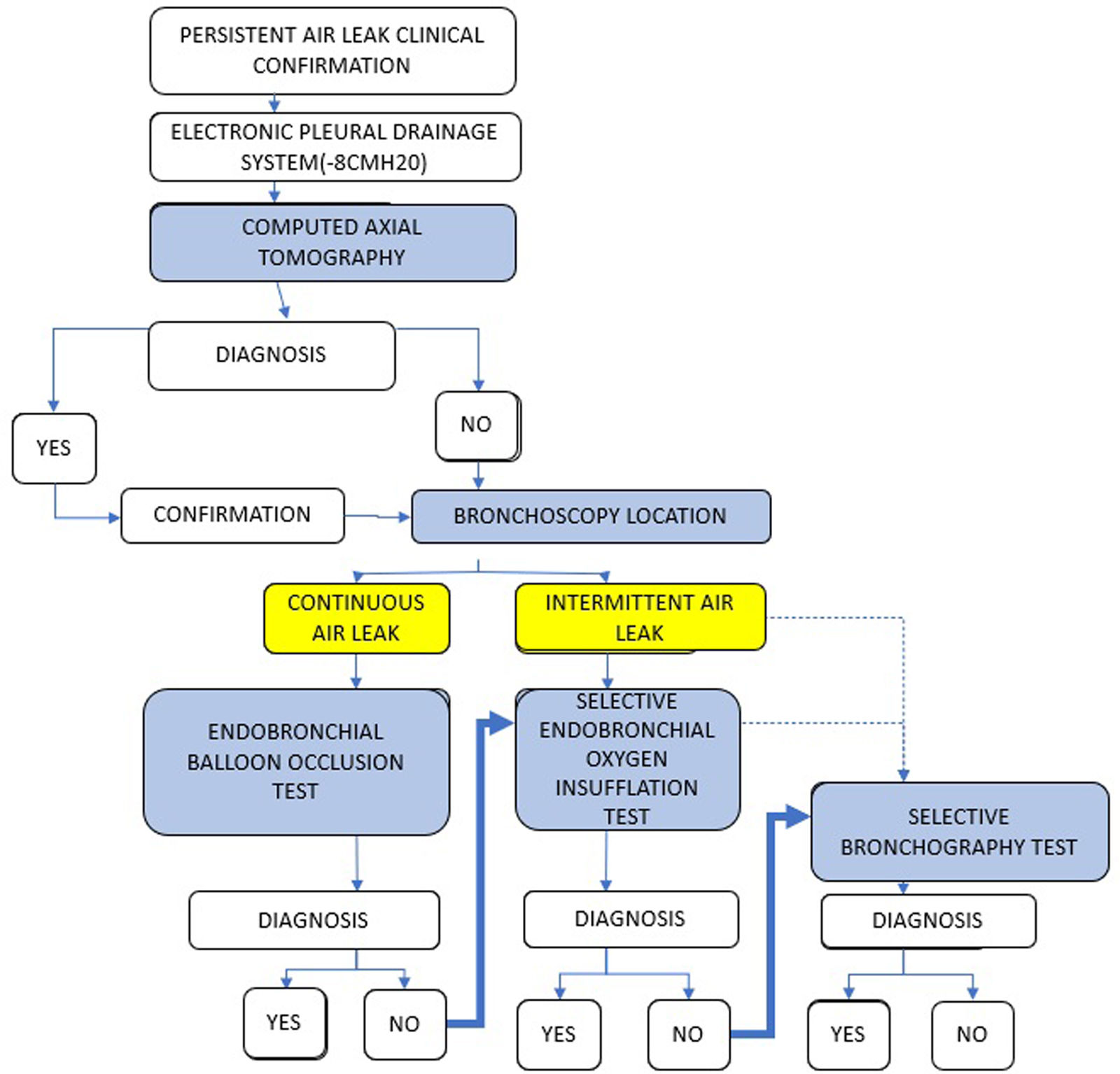
After clinical confirmation of the existence of a PAL, we recommend the use of EPD for close monitoring and categorization. CT would be the first diagnostic test to perform, as it allows anatomical localization prior to confirmation by endoscopic methods. The endoscopic determination of APF must consider whether it is continuous or intermittent, as well as possible variations in behavior after the induction of the sedation/anesthesia required for the procedure.
- a)
An endobronchial balloon occlusion test is the primary approach to addressing a continuous air leak. If it is not possible to perform one; if an anatomical determination is not achieved; or if more detailed anatomical confirmation is required, another diagnostic test should be considered.
- b)
In case of intermittent leak or cessation of PAL after induction of sedation/anesthesia, an endobronchial OI test should be considered, due to the high sensitivity demonstrated (81%) and low percentage of complications (8.1%).
- c)
If it is not possible to perform one; if the anatomical determination of the APF is not achieved; or if more detailed anatomical confirmation is required, a BS may be performed, due to the sensitivity demonstrated in our series (63.4%) and the low percentage of complications. (7.3%).
The proposed diagnostic algorithm is shown in Fig. 1.
DiscussionClosing APFs involves knowing their exact anatomical location.13 Despite the widespread use of CT as a diagnostic tool, the radiological identification of the fistulous tract in APF has a moderate success rate (33–64.7%)4,7,14 similar to that obtained in our study sample (32.6% of cases).
The systematic use of EPD systems is an excellent method for monitoring PAL that allows us to know the severity (ml/min), its behavior (persistent/intermittent nature) and the real-time quantification of the impact of balloon occlusion, during the procedure with an objective evaluation.
The use of EPD has expanded in recent years. Two studies report its use: Dooms et al.9—prospective population of 10 patients with PAL of postsurgical etiology (aspiration pressure of −8cm H2O)—and Firlinger et al.15—retrospective study in 13 patients affected by primary and secondary pneumothorax (without specification of the aspiration pressure used). In our study, the use of EPD was collected prospectively, with a suction pressure of −8cm H2O, in 40 patients affected by PAL of diverse etiologies.
The balloon occlusion test was described by Ratliff et al.11 and, despite the absence of a published algorithm, it is standardized.16 The interpretation of this diagnostic test may be controversial in the case of air leak assessment quantitatively using EPD, since the articles that address its use have presented disparate results.9,15 Dooms et al.9 consider the determination of APF location to be complete when the EPD recording is less than 20ml/min, while Firlinger et al.15 consider a detected flow less than 100ml/min or a decrease greater than 50% in the previously recorded flow to be necessary for diagnosis. In our study, when it was possible to perform the balloon test, determination of the location of the APF was considered adequate when the EPD recording was 0ml/min. The lower profitability of this test in our results compared to other studies could be due to the high incidence in our series of documented PALs lower than 100ml/min.
However, despite the existence of PAL observed in clinical practice, several authors affirm the impossibility of determining its anatomical location, with percentages varying from 9.4 to 24%.17,15,18–20 In our study, balloon occlusion was superior with a percentage of 43%.
The possibility of performing other diagnostic tests to determine the anatomical location of APF has been raised, limited to case series experiences. Van Zeller et al.,21 Tian et al.22 and Vial et al.12 described the use of methylene blue, Chartis® system and OI, respectively.
Referencing the diagnostic method of Vial et al.12 in our sample—despite the fact that his population comprised two patients affected by central bronchopleural fistulas of post-surgical etiology—OI was used for multiple purposes: (1) to artificially reproduce the air leaks that had temporarily ceased after administering sedation/anesthesia (debit 0ml/min in the measurement in the EPD), (2) to obtain their quantification and (3) to select the most probable lobar segmental bronchus for the location of the APF in order to then perform a selective bronchography.
After performing the diagnostic method using endobronchial balloon occlusion, which is the most used in the literature,15,17–20 we propose performing other tests:
- a)
First, endobronchial OI through systematic analysis of suspected bronchial subsegments. Its performance in 37 patients allowed us to establish the anatomical location of the APFs in 30 patients (81.1%) with a low percentage of associated complications.
- b)
Second: the BS allowed us to determine the anatomical location of the APF in 26 patients of the 41 in whom it was performed (63.4%), with a low percentage of associated complications. The use of this technique for the anatomical diagnosis of APF has not been described in the available literature.
Despite the previous encouraging results for the exact anatomical determination of APF, three limitations were found in its use not described in the literature:
- 1)
Contrast injection can limit the interpretation of a second BS during the same procedure, due to remains of contrast present in the parenchyma. As a result, the use of BS must be thorough and selective (segmental bronchus suspected of being affected).
- 2)
Protection: adequate planning of individual radiological protection and the endoscopy room is necessary.
- 3)
In our study, two patients manifested clinical-gasometric alterations—without previous explanation—which we attributed to the use of endobronchial iodinated contrast. These patients were diagnosed with pneumonitis secondary to the use of contrast agents (PC). There are no recommendations in our references regarding toxicity derived from the use of endobronchial iodinated contrasts. The two patients who presented this clinical entity experienced clinical, oximetric and radiological improvement in the hours that followed the start of empirical treatment.
However, the impossibility of applying all tests to each of the patients in our population due to their unique clinical situations must be taken into account as a limitation of the study.
Finally, we must remember that the anatomical determination of AFP is the fundamental step before treatment. At present, the endoscopic approach is considered a less invasive alternative for patients with a high perioperative risk and a first-line “urgent therapeutic need”.15 The bibliographic evidence shows a wide heterogeneity of therapeutic methods with good clinical results – success effectiveness rate between 50 and 100% in case series with a description of more than five cases13,15,23 and a broad therapeutic arsenal in continuous technological improvement (Watanabe Spigots, tissue glues, thrombotic agents and unidirectional endobronchial valves).15–18,20,23–25
ConclusionsSuccess in the anatomical localization of the APF highlights the possibility of applying endoscopic treatment to reduce the high morbidity and mortality associated with this clinical entity.
The diagnosis of APF by flexible bronchoscopy is a useful method, with an adequate safety and efficacy profile. The application of the proposed diagnostic algorithm, based on the combination of imaging and endoscopic tests, allowed the anatomical detection of APF in 91.5% of cases.
In our sample, the individual profitability of CT in the anatomical detection of APF was 32.6%. In the case of endoscopic methods, it was 57.1%, 81.1% and 63.4% with the balloon occlusion test, endobronchial OI, and selective bronchography test, respectively.
FundingThis research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Contribution of each authorB.V. and C.D. conceived of the presented idea. C.D. and J.M.M. verified the analytical methods.
All authors provided critical feedback and analysis. They also discussed the results and contributed to the final manuscript.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare not to have any conflicts of interest that may be considered to influence directly or indirectly the content of the manuscript.
Declaration of AI and AI-assisted technologiesArtificial intelligence involvement has not been employed for this work.