It is not known whether clinical practice guidelines for the treatment of COPD exacerbations with short courses of systemic corticosteroids (SC-SCS) are followed in clinical practice.
MethodProspective, observational cohort study in patients admitted due to severe COPD exacerbation. The primary endpoint was the percentage of patients who received SC-SCS as treatment for severe exacerbation (doses of 200–300mg for 5–6 days). Secondary variables were percentage of patients with duration or reduced dose, dose in the first 24h, days of intravenous systemic corticosteroids (SCS), and duration of hospital length of stay (LOS). Simple linear regression was performed with LOS as a dependent variable and multivariate analysis with factors associated with LOS.
Results158 patients were evaluated. 4.4% (7) patients received SC-SCS, 8.7% received a reduced dose and duration was reduced in 15.8%. The median dose and duration of SCS were 602.5mg (200–1625) and 14 (4–36) days, respectively. We observed an association between days of SCS and LOS (P<.001) and doses of intrahospital SCS and LOS (P<.001). Factors associated with LOS were doses of intrahospital SCS received (0.01 [95% CI: 0.007–0.013]; P<.001), days of steroid treatment (0.14 [95% CI: 0.03–0.25], P=.009) and PAFI (pO2/FiO2 ratio) at admission (−0.012 [95% CI: −0.012 to -0.002], P=.015).
ConclusionsThe SCS schedules used in routine clinical practice are longer and administered at a higher dose than recommended, leading to a longer hospital stay.
Se desconoce si en la práctica clínica habitual se siguen las recomendaciones de las guías de práctica clínica con respecto al tratamiento de las exacerbaciones de la EPOC con pautas cortas (PC) de corticoesteroides sistémicos (CS).
MétodoEstudio de cohortes, prospectivo y observacional en pacientes que ingresan por una agudización grave de su EPOC. La variable principal fue porcentaje de pacientes que recibían PC de CS como tratamiento en la exacerbación grave (dosis acumulada total de 200 a 300mg y una duración de 5-6 días). Las variables secundarias fueron porcentaje de pacientes con duración o dosis corta, dosis en las primeras 24horas, días de CS intravenosos y duración de la estancia hospitalaria (EH). Se realizó regresión lineal simple con días de estancia hospitalaria como variable dependiente y análisis multivariante con factores asociados a estancia hospitalaria.
ResultadosSe evaluaron 158 pacientes; 4,4% (7) pacientes recibieron una PC de CS. El 8,7% recibió un tratamiento corto y el 15,8% una duración reducida. La mediana de dosis y duración de CS fue 602,5mg (rango intercuartílico: 430-850) y 14 (rango intercuartílico: 4-36) días respectivamente. Observamos asociación entre más días de CS y una mayor EH (p<0,001) y una mayor dosis de CS intrahospitalaria e incremento de EH (p<0,001). Los factores asociados con EH fueron dosis de CS intrahospitalaria recibida (0,01 [IC 95%: 0,007-0,013]; p<0,001), días de tratamiento esteroideo (0,14 [IC 95%: 0,03-0,25]; p=0,009) y PAFI (cociente pO2/FiO2) al ingreso (–0,012 [IC 95%: –0,012 a –0,002]; p=0,015).
ConclusionesLas pautas de CS empleadas en la práctica clínica habitual son más prolongadas y a una mayor dosis que las recomendadas, asociando una mayor estancia hospitalaria.
The natural history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by intermittent episodes of exacerbation. Exacerbations are associated with an accelerated loss of lung function,1 poorer quality of life2 and greater mortality,3 associated mainly with more severe exacerbations requiring hospitalization.4 Optimal management of severe exacerbations is essential if prognosis is to improve. Hospital treatment of COPD exacerbations (COPDE) includes the use of oxygen, antibiotics, bronchodilators, and systemic corticosteroids (SCS). SCS are useful for improving lung function and symptoms, improving the 30-day treatment failures rate, and reducing hospital stay.5 However, no benefit in terms of mortality has been demonstrated, and the use of SCS is associated with increased side effects, the most frequent being hyperglycemia.5
At present, almost all COPD clinical management guidelines recommend the use of SCS in severe exacerbations. However, the recommendations vary to some extent in terms of the appropriate dose and duration of treatment. Thus, while the GOLD 20136 guidelines recommended 30–40mg prednisone daily for 10–14 days, the NICE guidelines7 proposed a slightly shorter duration (7–14 days), and the 2012 edition of the Spanish COPD guidelines8 recommended treatment with oral prednisone 0.5mg/kg/day or equivalent until clinical improvement, with suspension of the treatment as soon as possible, preferably before 7–10 days. Following publication of the REDUCE study,9 a randomized clinical trial which showed that a 5-day regimen produced similar rates of new exacerbations at 6 months, similar mortality and less exposure to corticosteroids as a 14-day regimen (37.2% versus 38.4%; P=NS), GOLD 20146 included a recommendation for a 5-day course of 40mg prednisone/day, and repeated the same recommendation in the recent update.10 The Spanish COPD guidelines updated in 201411 include the REDUCE data, and support the use of short 5-day courses, but only in exacerbations which do not require hospitalization, even though over 90% of the patients included in the REDUCE study were hospitalized.12
Despite these recommendations, very little is known about the patterns of use of corticosteroids (dose and duration) in routine clinical practice. Our hypothesis is that, in the real world, practices vary widely, and the dose and duration of SCS are usually greater than those recommended in the clinical guidelines, and that this may impact on the duration of hospital stay.
Materials and MethodsStudy Design and ParticipantsThis was a prospective, observational cohort study in patients seen in a tertiary hospital (Hospital Universitario de A Coruña), with a catchment area of 540000 inhabitants. The study was conducted between 1 July 2013 and 1 August 2015, and was approved by the Galician Clinical Research Ethics Committee (CREC).
We included patients older than 40 years, with a history of smoking, COPD diagnosis prior to admission defined according to the GOLD criteria (FEV1/FVC<0.7 post-bronchodilator), and a diagnosis of COPDE. Patients who were taking chronic SCS were excluded, as were those who did not receive SCS during hospitalization, and those with no history of smoking. Only the first admission was analyzed among patients who were readmitted.
ObjectivesThe primary study objective was to determine the percentage of patients receiving short course of SCS in the treatment of acute COPDE. A short course was defined as a cumulative dose 200–300mg prednisone or equivalent over 5–6 days. Secondary variables were the percentage of patients with a SCS duration of 5–6 days, percentage of patients with a cumulative dose of 200–300mg prednisone, dose given in the first 24h, days of intravenous SCS, and duration of hospital stay.
Data CollectionPatients were seen by the usual medical team in each department, and data were collected by the investigators. Data were collected from patients admitted to the respiratory medicine hospital ward and to one of the internal medicine wards. Demographic (age, sex, smoking status, and immunizations), laboratory and clinical data were collected from the patients. Comorbidities were assessed and the Charlson index was calculated. Functional status was evaluated using the Barthel index. COPD severity was determined from spirometric values, baseline dyspnea scale (mMRC), COPD assessment test (CAT), and exacerbation history. The severity of the current episode was assessed by calculating dyspnea, eosinopenia, consolidation, acidosis, and atrial fibrillation. Treatments received by all patients were recorded. With regard to SCS, the type, dose, duration and route of administration were recorded. Prednisone doses were used as a reference for the calculation of equivalent doses of other SCS. Finally, data on hospitalization were recorded, including days of hospital stay, resources used (ICU admission and need for mechanical ventilation), and in-hospital mortality.
Statistical AnalysisQuantitative data are expressed as mean and standard deviation and qualitative data as frequencies. Quantitative data that did not follow a normal distribution are expressed as median and interquartile range. The association between hospital stay and duration of steroid treatment and cumulative dose were evaluated using the Spearman rank correlation. Simple linear regression with days of hospital stay as the dependent variable was used to study the degree of correlation. Multivariate linear regression was performed with factors associated with hospital stay: variables with a P-value of <.05 in the univariate analysis were incorporated into this model. All statistical analyses were performed using a digital statistical program (Stata for Mac O.S., version 13.0; Statacorp Inc., USA). Values were considered significant if P<.05.
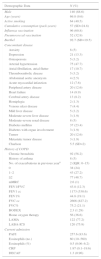
ResultsPatient CharacteristicsA total of 179 patients were analyzed, of whom 21 were withdrawn from the study (6 for chronic use of corticosteroids, 11 who did not receive corticosteroids, and 4 non-smokers). The final cohort consisted of 158 patients, 88.6% of whom were men. Mean age was 69.8 (standard deviation, 9.5) years. Patient characteristics are shown in Table 1.
Baseline Patient Characteristics.
| Demographic Data | N (%) |
|---|---|
| Male | 140 (88.6) |
| Age (years) | 69.8 (9.6) |
| Active smoking | 64 (40.5) |
| Cumulative consumption (pack-years) | 57 (SD=24.8) |
| Influenza vaccination | 96 (60.8) |
| Pneumococcal vaccination | 52 (32.9) |
| Barthel | 92.7 (SD=19.5) |
| Concomitant disease | |
| Anxiety | 8 (5) |
| Depression | 21 (13.3) |
| Osteoporosis | 5 (3.2) |
| Arterial hypertension | 75 (47.7) |
| Atrial fibrillation, atrial flutter | 17 (10.7) |
| Thromboembolic disease | 5 (3.2) |
| Abdominal aortic aneurysm | 4 (2.5) |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 12 (7.6) |
| Peripheral artery disease | 20 (12.6) |
| Heart failure | 14 (8.9) |
| Cerebral artery disease | 13 (8.2) |
| Hemiplegia | 2 (1.3) |
| Venous ulcer disease | 7 (4.4) |
| Mild liver disease | 5 (3.2) |
| Moderate-severe liver disease | 3 (1.9) |
| Moderate-severe renal disease | 8 (5) |
| Diabetes mellitus | 37 (23.4) |
| Diabetes with organ involvement | 3 (1.9) |
| Tumor | 20 (12.6) |
| Metastatic tumor disease | 3 (1.9) |
| Charlson | 5.5 (SD=2) |
| History of COPD | |
| Chronic bronchitis | 92 (58.2) |
| History of asthma | 8 (5) |
| No. of exacerbations in previous yeara | 2 (IQR: 0–15) |
| 0 | 38 (24) |
| 1–2 | 43 (27.2) |
| ≥2 | 77 (48.7) |
| mMRC | 2.6 (1) |
| FEV1/FVC | 43.8 (12.3) |
| FEV1 cc | 1173 (530.6) |
| FEV1% | 44.8 (19.1) |
| FVC cc | 2666 (827.2) |
| FVC% | 75.2 (21.1) |
| BODEX | 2.3 (1.29) |
| Home oxygen therapy | 56 (36.6) |
| LAMA | 122 (77.2) |
| LABA-ICS | 120 (75.9) |
| Current admission | |
| PAFI | 257.6 (83.6) |
| Eosinophils (no.) | 60 (10–560) |
| Eosinophils (%) | 0.5 (0.06–6.2) |
| CRP | 1.97 (0.1–19.6) |
| DECAF | 1.3 (0.96) |
CI: inhaled corticosteroid; CRP: C-reactive protein; DECAF: DECAF score (Dyspnea, Eosinopenia, Consolidation, Acidemia and atrial Fibrillation); FEV1: forced expiratory volume in the first second; FVC: forced vital capacity; LABA: long-acting beta-2 agonist; LAMA: long-acting muscarinic agonist; PAFI: ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen.
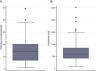
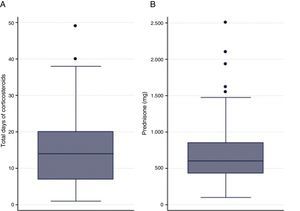
Only 4.4% of the cohort (7 patients) received a short course of SCS; 8.7% (13) received an SCS dose of between 200 and 300mg; and in 15.8% (24) the duration of administration was 5–6 days. Mean SCS dose was 602.5mg (interquartile range [IQR]: 430–850), and the median duration of SCS was 14 days (IQR: 7–20) (Fig. 1). Median duration of intravenous SCS was 4 days (IQR: 2–7) (Fig. 1). Median length of hospital stay was 9 days (IQR: 7–12.5) (Table 2).
SCS Dose and Duration.
| Variable | Median (Interquartile Range) |
|---|---|
| SCS dose in first 24h | 125 (100–150) |
| SCS dose during hospitalization | 510 (370–695) |
| SCS dose on discharge | 45 (0–175) |
| Total SCS dose | 602.5 (430–850) |
| Intravenous steroid dose | 4 (2–7) |
| Total days of steroid administration | 14 (7–20) |
| Days of hospital stay | 9 (7–12.5) |
SCS: systemic corticosteroid.
SCS dose in milligrams of prednisone.
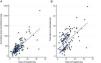
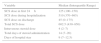
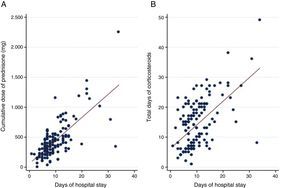
A positive association was observed between the dose of SCS and hospital stay (P<.001) (rho=0.48) and days of SCS and hospital stay (P<.001) (rho=0.49) (Fig. 2). The multivariate analysis showed that a greater length of hospital stay was independently associated with a higher dose of SCS during admission after adjustment for other clinical variables, such as days of steroid treatment and PaFi (hazard ratio pO2/FiO2) at admission (Table 3).
Multivariate Analysis of the Association of Hospital Stay and Intrahospital Dose of Corticosteroids.
| Variable | Coefficient | SD | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intrahospital dose of SCS (mg prednisone) | 0.01 | 0.001 | <.001 |
| Total days of SCS administration | 0.14 | 0.05 | .009 |
| PAFI | −0.012 | 0.005 | .015 |
PAFI: ratio of partial pressure arterial oxygen and fraction of inspired oxygen; SCS: systemic corticosteroid.
The dose and duration of treatment with SCS in COPD exacerbations in clinical practice are much higher than those recommended in clinical practice guidelines, and are associated with increased hospital stay. Treatment with SCS in patients admitted to hospital with severe exacerbation of COPD is a practice that is clearly widespread in hospitals. Indeed, the AUDIPOC study13 showed that more than 90% of the patients who had been admitted for COPDE received treatment with SCS.
This unquestionable evidence on the use of these drugs prompts us to ask whether they might be less beneficial in some subgroups, such as patients with low eosinophil levels14–16 and patients whose exacerbation is clearly caused by infection,17 or if the efficacy of high doses administered by inhalation would be comparable to that of systemic administration.18
In this study, we observed that instead of the recommended dose of 200mg (40mg/day for 5 days), patients in clinical practice were receiving 3 times this amount. This could be explained in several ways: (a) a delayed switch to oral treatment; (b) doses of corticosteroid used in asthma being transferred to COPD; and (c) the risk of adrenal crisis due to an abrupt withdrawal. It is interesting to note that more than 50% of the recommended dose is administered in the first 24h, a period during which the patient is generally treated in the emergency department. In addition, we found that the recommended short duration of administration (5 days) is almost is tripled in clinical practice. Despite evidence that oral administration of steroids is not inferior to intravenous administration,19 and that this is the route of choice in some guidelines,6,10 we found in this study that the average time to switch to oral administration was 5 days. Delays in the switch to oral administration, whether for corticosteroids or antibiotics, would require the patient to remain hospitalized for intravenous administration, thus extending hospital stay. It is important to remember that patients receiving corticosteroids are at risk of hyperglycemia. Excessive exposure to corticosteroids, whether from excessively high doses or prolonged duration of treatment, may cause hyperglycemia,20 and concomitant hyperglycemia can also prolong hospital stay. Accumulated doses of corticosteroid can also cause musculoskeletal effects which may become a problem as the frequency of exacerbations increases. The most worrying of these effects are fractures, infections and other metabolic changes.21
This study has a number of limitations that should be mentioned. The most obvious is that its single-center design prevents any generalization of our conclusions. However, we suspect that our observations hold true for other centers, or that the situation is even be worse than our findings suggest. In the AUDIPOC study, for example, 72% of patients who received corticosteroids during admission continued to receive them on discharge, compared to 52% in our series. A second limitation is that the study was conducted under conditions of routine clinical practice, and some of the study investigators were directly involved in the clinical management of these patients, a situation which may have generated some bias when deciding on the recommended dose and treatment duration. Moreover, the patients were not classified by phenotypes, so we cannot be sure, but merely suspect, that patients with asthma-COPD overlap behave differently. Finally, while we found an independent association between the duration of hospital stay and the dose and duration of steroids, many other factors which might have a direct effect on clinical practice were not analyzed, such as social considerations, hospital inefficiencies, continued care after discharge, etc.
In summary, this study shows that systemic corticosteroid regimens used in clinical practice in the treatment of severe exacerbations of COPD are administered for much longer periods and at higher doses than recommended, a practice that has a direct impact on hospital stay. More studies are needed to confirm how generalized this practice is in our setting and to determine the possible medium- and long-term consequences.
Conflict of InterestsThe authors state that they have no conflict of interests.
Please cite this article as: Marcos PJ, Nieto-Codesido I, de Jorge Dominguez-Pazos S, Huerta A, Márquez E, Maiso A, et al. Tratamiento con esteroides sistémicos en agudización grave de enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica: empleo de pautas cortas en práctica clínica habitual y relación con la estancia hospitalaria. Arch Bronconeumol. 2017;53:611–615.