Bronchiectasis is one of the most common comorbidities in severe asthma. However, the mechanisms by which asthma promotes the development and progress of this condition are not well defined. This study aimed to analyze the inflammatory phenotypes and quantify the expression of proinflammatory and remodeling cytokines in asthma patients with and without bronchiectasis.
MethodsThe study sample comprised individuals with severe asthma and bronchiectasis (group AB, n=55) and a control population of individuals with severe asthma without bronchiectasis (group AC, n=45). Induced sputum samples were obtained and cell types determined by differential cell count. Proinflammatory and bronchial remodeling cytokines (IL-8, neutrophilic elastase, TGFβ1, VEGF, IFN-γ, TNF-α, and GM-CSF) were analyzed by immunoassay in sputum supernatant.
ResultsNeutrophilic inflammation was the primary phenotype in both asthma groups. Higher levels of TGFβ1, VEGF and IFN-γ were observed in asthma patients with bronchiectasis (group AB) than in controls (group AC) (15 vs 24pg/ml, p=0.014; 183 vs 272pg/ml, p=0.048; 0.85 vs 19pg/ml, p<0.001, respectively). Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) levels were significantly lower in the AB group than in the AC group (1.2 vs 4.4pg/ml, p<0.001). IL-8, neutrophil elastase and TNF-α did not present significant differences between the groups.
ConclusionsRaised levels of TGFβ1 and VEGF cytokines may indicate airway remodeling activation in asthma patients with bronchiectasis. The type of inflammation in asthma patients did not differ according to the presence or absence of bronchiectasis.
Asthma is a heterogeneous airway disease with multiple phenotypes.1 The condition is severe in only a minority of patients (5%–10%) but the rate of comorbidities in this cohort is high, and the worldwide socioeconomic burden of severe asthma is heavy.2 Airway inflammation is another important factor, and a cluster study3 identified both eosinophilic and neutrophilic inflammation as severe asthma subtypes.
One of the most frequent comorbidities in severe asthma is bronchiectasis. Bronchiectasis may mimic asthma symptoms, resulting in poor asthma control, persistent clinical symptoms and difficult disease management.4,5 The role of the innate immunity pathway seems to be relevant in the pathogenesis of bronchiectasis; the associated inflammation is predominantly neutrophilic, with elevated levels of interleukin-8 (IL-8).6
Although severe asthma and bronchiectasis frequently coexist, it is uncertain whether a cause–effect relationship exists between these two conditions. Bronchiectasis in asthma may be related to the disease itself or it may be a concomitant finding that has another known or unknown cause. In severe asthma, airway remodeling is commonly associated with changes including epithelial damage, ciliary dysfunction, goblet cell hyperplasia and fibroblast differentiation, and, as a result, the formation of extracellular matrix components.7 Cytokines, chemokines and growth factors released from inflammatory and structural cells in the airway, in particular cytokines transforming growth factor-beta 1 (TGFβ1) and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), are believed to play a pivotal role in the development of remodeling.8 These structural changes may contribute to the permanent destruction of normal airways, leading to progressive airway narrowing and mucus plugging of the bronchial lumen and facilitating the formation of bronchiectasis.
However, the mechanisms by which asthma promotes the development of bronchiectasis are not well defined. Identifying bronchiectasis in severe asthma patients and achieving a better understanding of the inflammatory phenotypes and the underlying mechanisms are therefore of key importance in precision medicine.9 To our knowledge, no data on these issues are currently available.
This study aimed to analyze the inflammatory phenotypes and to quantify the expression of proinflammatory and remodeling cytokines in asthma patients with and without bronchiectasis.
Material and MethodsStudy Population and DesignWe performed a cross-sectional case–control study in a cohort of 269 patients with asthma attending a specialized asthma unit in 2018.10 After excluding patients with known causes of bronchiectasis (n=12: 8 with Churg-Strauss syndrome, 2 with allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis, and 2 with post-tuberculosis sequelae) and patients with non-severe asthma (n=120), 137 were diagnosed with severe asthma, and, of these, bronchiectasis was confirmed in 71.10
The clinical history of these 137 patients was reviewed, and data were collected on diagnosis, asthma severity, time since disease onset, the frequency and cause of exacerbations and treatment. The Asthma Control Test (ACT)11 was administered. All patients underwent forced spirometry, laboratory tests, and sputum induction. At the time of performing these tests, it was confirmed that the patients had not had an exacerbation during the previous month. All patients were assessed for suspected clinically significant bronchiectasis, IgG levels, IgG subclasses, antinuclear antibodies (ANA), extractable nuclear antigen (ENA), antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA), anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs), rheumatoid factor, and cystic fibrosis to rule out other possible etiologies of bronchiectasis. Sputum was obtained in 55 patients with severe asthma and bronchiectasis (group AB) and in 45 patients with severe asthma without bronchiectasis (group AC). The study population finally comprised all patients in whom sputum samples were obtained.
The study was approved by the hospital Ethics Committee (PR(AG)50/2019). All patients provided written informed consent prior to participation.
Asthma Diagnosis and SeverityThe diagnosis of asthma was made according to GINA1 guidelines and was based on clinical symptoms plus 1 or more complementary tests. All patients had shown reversible airway obstruction on bronchodilator testing, a positive methacholine challenge test, or variability >20% in the peak flow recording. The definition of severe asthma was also based on the GINA guidelines, i.e., patients taking steps 4 and 5 of medication consisting of at least 400μg of inhaled corticosteroids (budesonide or equivalent doses) plus a long-acting beta-2 agonist.1
Bronchiectasis Diagnosis and SeverityBronchiectasis was identified following the Spanish Society of Pulmonology and Thoracic Surgery (SEPAR) recommendations.12 Morphological characteristics of the condition, including bronchodilation, bronchial wall thickening, dilation type, and lobe extension, were reviewed and assessed according to the modified Reiff score13 in 6 lobes (18 points in total). Scores of 1–6 were considered mild, 7–12 moderate, and ≥13 severe. The FACED parameter14 was used to evaluate patients’ clinical status.
High-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) was performed with 1mm slices at 10mm intervals in maximum inspiration. All imaging features of bronchiectasis were interpreted by two pulmonologists working independently. For controversial images, an expert radiologist was consulted and the final decision was made. The degree of inter-observer agreement was assessed using the Kappa statistic.
Pulmonary Function TestIn all patients, forced spirometry was performed prior to sputum induction. Spirometry was performed using a MasterLab instrument (MasterLab, Jaeger, Germany), according to European Respiratory Society (ERS) and American Thoracic Society (ATS) guidelines.15 The reference values proposed by the ERS were used.16
Sputum Induction and ProcessingInduced sputum was obtained using an ultrasonic nebulizer (OMRON, Hoofddorp, Netherlands) with an output of 1ml/min at room temperature. All patients were instructed to blow their nose and to rinse their mouth thoroughly to minimize saliva contamination. The test was completed by inhalation of a stepwise hypertonic solution (3%, 4% and 5%) during 7min of mouth breathing keeping the nosed clipped. A deep cough and expectoration were indicated after each exposure to facilitate the acquisition of the sputum sample. In all cases, the induction procedures were only performed if forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) was more than 1.5l. The total induction time did not exceed 30min. Sputum samples obtained were processed immediately using the previously standardized protocol.17
Atopy and Smoking StatusPatients were considered atopic if they had at least one positive prick test for any of the common environmental allergens. Non-smokers were patients who had never smoked, and ex-smokers were those who had not smoked for at least 6 months. The number of pack-years was calculated in all cases.
Definition of Eosinophilic and Neutrophilic InflammationThe type of inflammation was determined by the sputum differential cell count.18 The neutrophilic phenotype was defined by the presence of ≥65% neutrophils and <3% eosinophils; the eosinophilic phenotype by ≥3% eosinophils and <65% neutrophils; the mixed phenotype by the presence of ≥3% eosinophils and ≥65% neutrophils; and the paucigranulocytic phenotype by both <3% eosinophils and <65% neutrophils.
Quantification of Biomarkers in Sputum SupernatantInflammatory and proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IFN-γ, GM-CSF, Bio-Rad Lab, Inc; IL-8, R&D Systems, Inc), airway remodeling-related cytokines (TGFβ1 and VEGF, R&D Systems, Inc), and PMN elastase (Invitrogen) were measured. All the above cytokines were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Since IL-5 and IL-13 levels were undetectable in our pilot test, these two biomarkers were not analyzed in the later assay.
Statistical AnalysisStatistical analysis was performed using Stata version 15.1 (StataCorp; Texas; USA). Variable normality was tested by the Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Categorical variables are presented as n (%), and continuous variables as means (SD) or medians (p25, p75) according to data distribution. Comparisons between groups were performed using the chi-square test for qualitative variables or the Fisher exact test, as appropriate. Student's t-test or the Wilcoxon rank-sum test was used to compare continuous variables between groups depending on the normal or non-normal distribution of the data. The significance of correlations was evaluated by determining Spearman rank correlation coefficients. A p-value <0.05 was considered statistically significant.
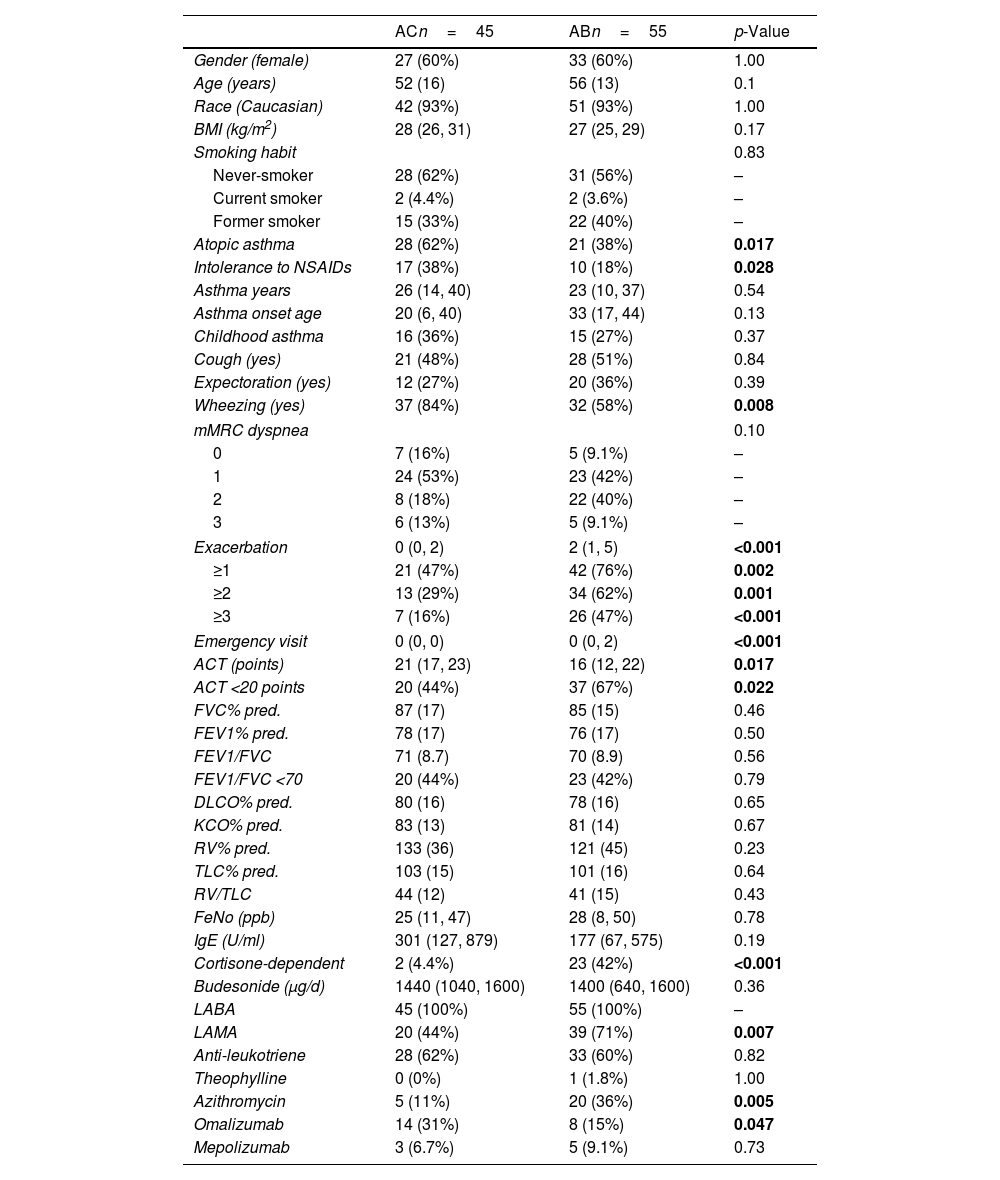
ResultsThe sociodemographic characteristics and functional data of the patients finally included in the study are shown in Table 1. Female patients were more numerous in both groups. Mean ages were 52 years for the AB group and 56 for AC group. Patients in the AC group had greater intolerance to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) than the AB group (38% vs 18%, p=0.028) and more atopic asthma (62% vs 38%, p=0.017). Subjects in the AB group presented more asthma exacerbations (median 2 vs 0 courses, p<0.001). Furthermore, patients in the AB group had worse asthma control than the AC group (ACT: 16 vs 21, p=0.017). No significant differences were observed with regard to lung function. A larger proportion of patients was considered to be oral corticosteroid-dependent in the AB group (42% vs 4%, p<0.001). These patients were also more likely to be receiving LAMA (77% vs 44%, p=0.007) and azithromycin (36% vs 11%, p=0.005).
Sociodemographic, Clinical Data and Questionnaires.
| ACn=45 | ABn=55 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender (female) | 27 (60%) | 33 (60%) | 1.00 |
| Age (years) | 52 (16) | 56 (13) | 0.1 |
| Race (Caucasian) | 42 (93%) | 51 (93%) | 1.00 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28 (26, 31) | 27 (25, 29) | 0.17 |
| Smoking habit | 0.83 | ||
| Never-smoker | 28 (62%) | 31 (56%) | – |
| Current smoker | 2 (4.4%) | 2 (3.6%) | – |
| Former smoker | 15 (33%) | 22 (40%) | – |
| Atopic asthma | 28 (62%) | 21 (38%) | 0.017 |
| Intolerance to NSAIDs | 17 (38%) | 10 (18%) | 0.028 |
| Asthma years | 26 (14, 40) | 23 (10, 37) | 0.54 |
| Asthma onset age | 20 (6, 40) | 33 (17, 44) | 0.13 |
| Childhood asthma | 16 (36%) | 15 (27%) | 0.37 |
| Cough (yes) | 21 (48%) | 28 (51%) | 0.84 |
| Expectoration (yes) | 12 (27%) | 20 (36%) | 0.39 |
| Wheezing (yes) | 37 (84%) | 32 (58%) | 0.008 |
| mMRC dyspnea | 0.10 | ||
| 0 | 7 (16%) | 5 (9.1%) | – |
| 1 | 24 (53%) | 23 (42%) | – |
| 2 | 8 (18%) | 22 (40%) | – |
| 3 | 6 (13%) | 5 (9.1%) | – |
| Exacerbation | 0 (0, 2) | 2 (1, 5) | <0.001 |
| ≥1 | 21 (47%) | 42 (76%) | 0.002 |
| ≥2 | 13 (29%) | 34 (62%) | 0.001 |
| ≥3 | 7 (16%) | 26 (47%) | <0.001 |
| Emergency visit | 0 (0, 0) | 0 (0, 2) | <0.001 |
| ACT (points) | 21 (17, 23) | 16 (12, 22) | 0.017 |
| ACT <20 points | 20 (44%) | 37 (67%) | 0.022 |
| FVC% pred. | 87 (17) | 85 (15) | 0.46 |
| FEV1% pred. | 78 (17) | 76 (17) | 0.50 |
| FEV1/FVC | 71 (8.7) | 70 (8.9) | 0.56 |
| FEV1/FVC <70 | 20 (44%) | 23 (42%) | 0.79 |
| DLCO% pred. | 80 (16) | 78 (16) | 0.65 |
| KCO% pred. | 83 (13) | 81 (14) | 0.67 |
| RV% pred. | 133 (36) | 121 (45) | 0.23 |
| TLC% pred. | 103 (15) | 101 (16) | 0.64 |
| RV/TLC | 44 (12) | 41 (15) | 0.43 |
| FeNo (ppb) | 25 (11, 47) | 28 (8, 50) | 0.78 |
| IgE (U/ml) | 301 (127, 879) | 177 (67, 575) | 0.19 |
| Cortisone-dependent | 2 (4.4%) | 23 (42%) | <0.001 |
| Budesonide (μg/d) | 1440 (1040, 1600) | 1400 (640, 1600) | 0.36 |
| LABA | 45 (100%) | 55 (100%) | – |
| LAMA | 20 (44%) | 39 (71%) | 0.007 |
| Anti-leukotriene | 28 (62%) | 33 (60%) | 0.82 |
| Theophylline | 0 (0%) | 1 (1.8%) | 1.00 |
| Azithromycin | 5 (11%) | 20 (36%) | 0.005 |
| Omalizumab | 14 (31%) | 8 (15%) | 0.047 |
| Mepolizumab | 3 (6.7%) | 5 (9.1%) | 0.73 |
Continuous variables are expressed as mean (SD) or median (p25, p75); categorical variables in n (%). Significant p-values are shown in bold font.
AC: asthma without bronchiectasis; AB: asthma with bronchiectasis; BMI: body mass index; HAD: Hospital Anxiety and Depression Score; HADa: HAD anxiety score; HADd: HAD depression score (anxiety and depression were defined using a cut-off value of 7 points: ≤7 normal; ≥8 abnormal); mini-AQLQ: mini Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire; LABA: long-acting beta-agonists; LAMA: long-acting muscarinic antagonist; mMRC: modified Medical Research Council; NSAIDs: nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs.
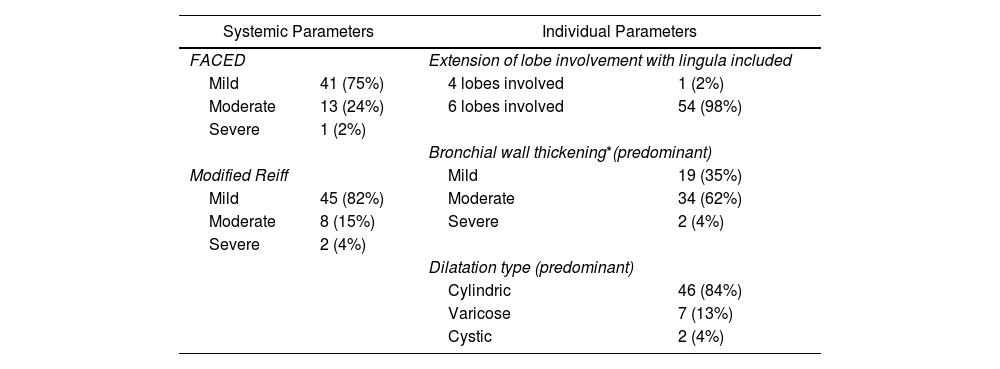
Regarding the severity of the 55 patients with bronchiectasis (AB group), 75% were classified as mild according to FACED and 82% according to the modified Reiff criteria. Fifty-four patients (98%) had widespread bronchial dilation involving all six lobes. Ninety-seven per cent of patients exhibited either mild or moderate bronchiectasis. The predominant dilation type was cylindrical (84%) (Table 2). Kappa values (and overall agreement %) for the lobe extension, bronchial dilation, bronchial wall thickening, and dilation type were 0.50 (98%), 0.68 (87%), 0.71 (87%), and 0.75 (93%) respectively. Potentially pathogenic bacteria were identified in 11 subjects (20%) with bronchiectasis (AB group), including Pseudomonas aeruginosa (3 cases), Haemophilus influenzae (2), Streptococcus pneumoniae (2), and Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Moxarella catarrhalis and Pseudomonas putida (1 each).
Assessment of Bronchiectasis in Radiological and Clinical Parameters.
| Systemic Parameters | Individual Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| FACED | Extension of lobe involvement with lingula included | ||
| Mild | 41 (75%) | 4 lobes involved | 1 (2%) |
| Moderate | 13 (24%) | 6 lobes involved | 54 (98%) |
| Severe | 1 (2%) | ||
| Bronchial wall thickening*(predominant) | |||
| Modified Reiff | Mild | 19 (35%) | |
| Mild | 45 (82%) | Moderate | 34 (62%) |
| Moderate | 8 (15%) | Severe | 2 (4%) |
| Severe | 2 (4%) | ||
| Dilatation type (predominant) | |||
| Cylindric | 46 (84%) | ||
| Varicose | 7 (13%) | ||
| Cystic | 2 (4%) | ||
Left column: systemic parameters. Right column: individual parameters.
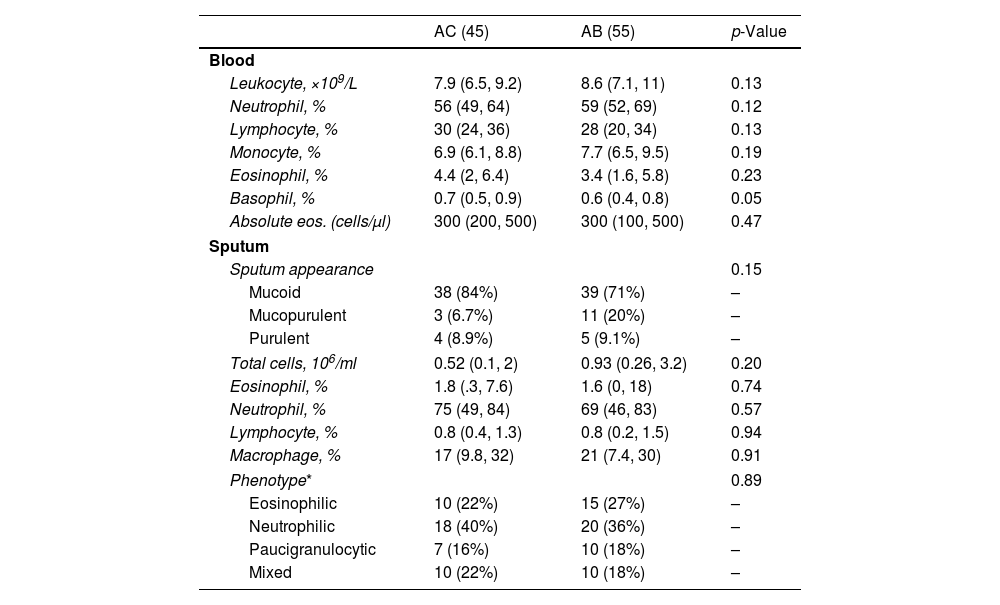
Of the 55 asthma subjects with bronchiectasis (AB group), the airway inflammatory phenotype based upon induced sputum leukocyte differential cell count was neutrophilic in 20 (36%), eosinophilic in 15 (27%), paucigranulocytic in 10 (18%), and mixed inflammation in 10 (18%). Neutrophilic inflammation also predominated in the AC group (40%) (Table 3). No differences were observed in eosinophils and neutrophils either in peripheral blood or in the sputum sample.
Inflammatory Profile and Phenotype in Patients With Bronchiectasis (AB) and Without Bronchiectasis (AC).
| AC (45) | AB (55) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Blood | |||
| Leukocyte, ×109/L | 7.9 (6.5, 9.2) | 8.6 (7.1, 11) | 0.13 |
| Neutrophil, % | 56 (49, 64) | 59 (52, 69) | 0.12 |
| Lymphocyte, % | 30 (24, 36) | 28 (20, 34) | 0.13 |
| Monocyte, % | 6.9 (6.1, 8.8) | 7.7 (6.5, 9.5) | 0.19 |
| Eosinophil, % | 4.4 (2, 6.4) | 3.4 (1.6, 5.8) | 0.23 |
| Basophil, % | 0.7 (0.5, 0.9) | 0.6 (0.4, 0.8) | 0.05 |
| Absolute eos. (cells/μl) | 300 (200, 500) | 300 (100, 500) | 0.47 |
| Sputum | |||
| Sputum appearance | 0.15 | ||
| Mucoid | 38 (84%) | 39 (71%) | – |
| Mucopurulent | 3 (6.7%) | 11 (20%) | – |
| Purulent | 4 (8.9%) | 5 (9.1%) | – |
| Total cells, 106/ml | 0.52 (0.1, 2) | 0.93 (0.26, 3.2) | 0.20 |
| Eosinophil, % | 1.8 (.3, 7.6) | 1.6 (0, 18) | 0.74 |
| Neutrophil, % | 75 (49, 84) | 69 (46, 83) | 0.57 |
| Lymphocyte, % | 0.8 (0.4, 1.3) | 0.8 (0.2, 1.5) | 0.94 |
| Macrophage, % | 17 (9.8, 32) | 21 (7.4, 30) | 0.91 |
| Phenotype* | 0.89 | ||
| Eosinophilic | 10 (22%) | 15 (27%) | – |
| Neutrophilic | 18 (40%) | 20 (36%) | – |
| Paucigranulocytic | 7 (16%) | 10 (18%) | – |
| Mixed | 10 (22%) | 10 (18%) | – |
Continuous data are expressed as median (p25, p75); categorical variables appear in n (%).
AC: asthma without bronchiectasis; AB: asthma with bronchiectasis.
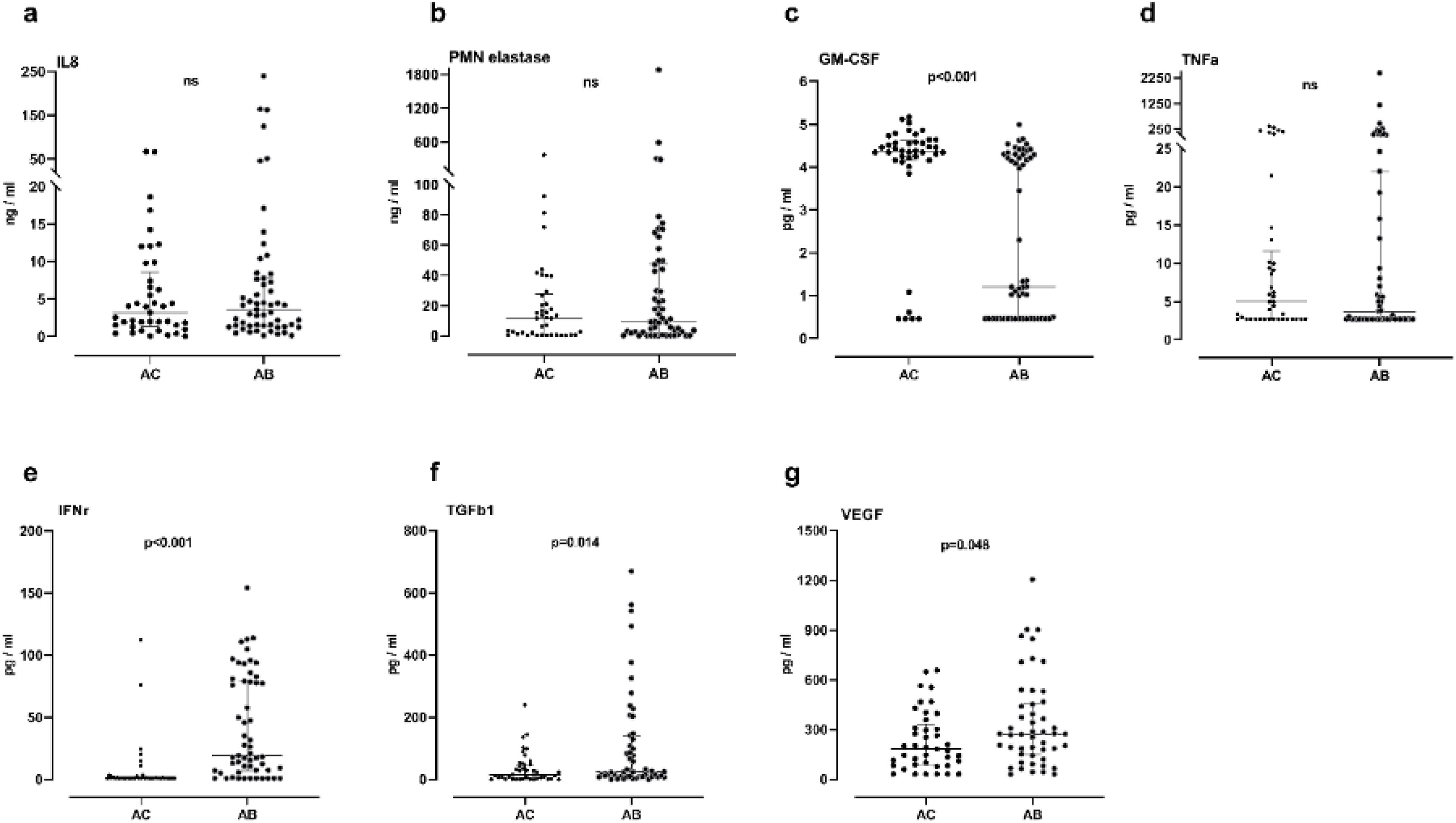
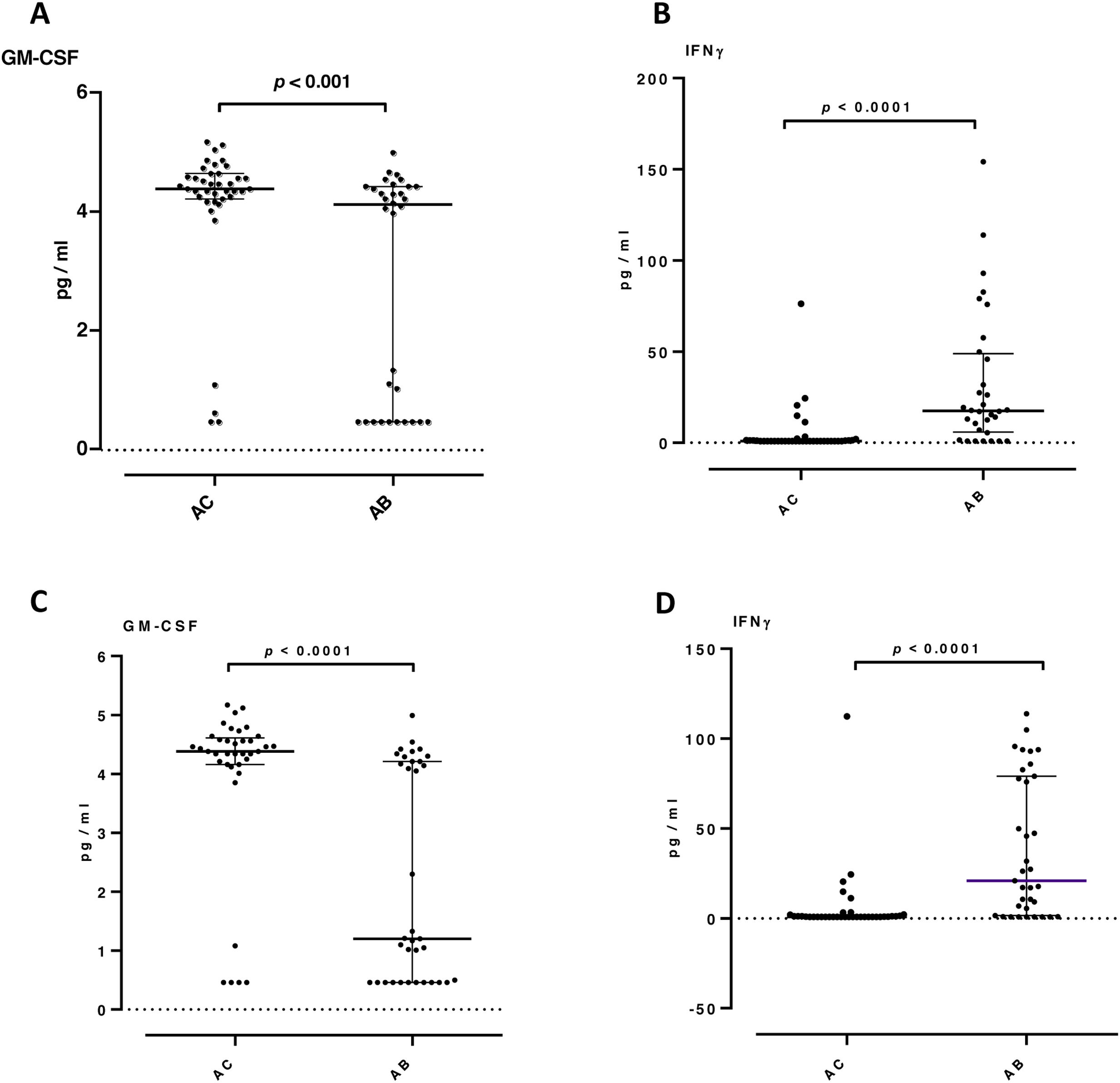
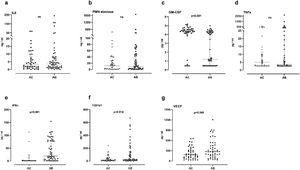
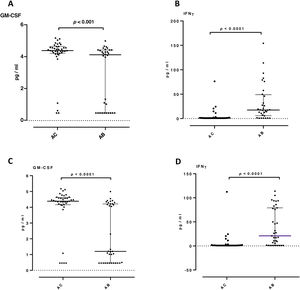
In sputum samples, higher levels of TGFβ1, VEGF and IFN-γ were observed in the AB group than in the AC group (24 vs 15pg/ml, p=0.014; 272 vs 183pg/ml, p=0.048; 19 vs 0.85pg/ml, p<0.001 respectively). Granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) levels were significantly lower in the AB group (1.2 vs 4.4pg/ml, p<0.001). Levels of IL-8, neutrophil elastase and TNF-α did not show significant differences between the groups (Fig. 1). In the AB group, we observed that patients who took oral corticosteroids and/or azithromycin had higher levels of TGFβ1 compared to patients who were not taking these medications (p=0.042 and <0.0001, respectively). Furthermore, in patients who were not taking oral corticosteroids and/or azithromycin, the AB group maintained higher levels of IFN-γ (p<0.0001) and lower levels of GM-CSF (p<0.001) compared with the AC group (Fig. 2). No significant differences were observed for the rest of the biomarkers analyzed by treatment.
Proinflammatory and airway remodeling cytokines. (A) Interleukin-8 (IL-8); (B) human neutrophil elastase; (C) granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF); (D) tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α); (E) interferon-gamma (IFN-γ); (F) transforming growth factor-beta 1; (G) vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Data expressed as median and interquartile range. AC: without bronchiectasis; AB: with bronchiectasis.
Proinflammatory and airway remodeling cytokines in patients not taking oral corticosteroids and/or azithromycin: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) (A and C) and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) (B and D). A and B patients not chronically taking oral corticosteroids. C and D patients not taking azithromycin. Only statistically significant biomarkers are shown. Data expressed as median and interquartile range. AC: group without bronchiectasis; AB: group with bronchiectasis.
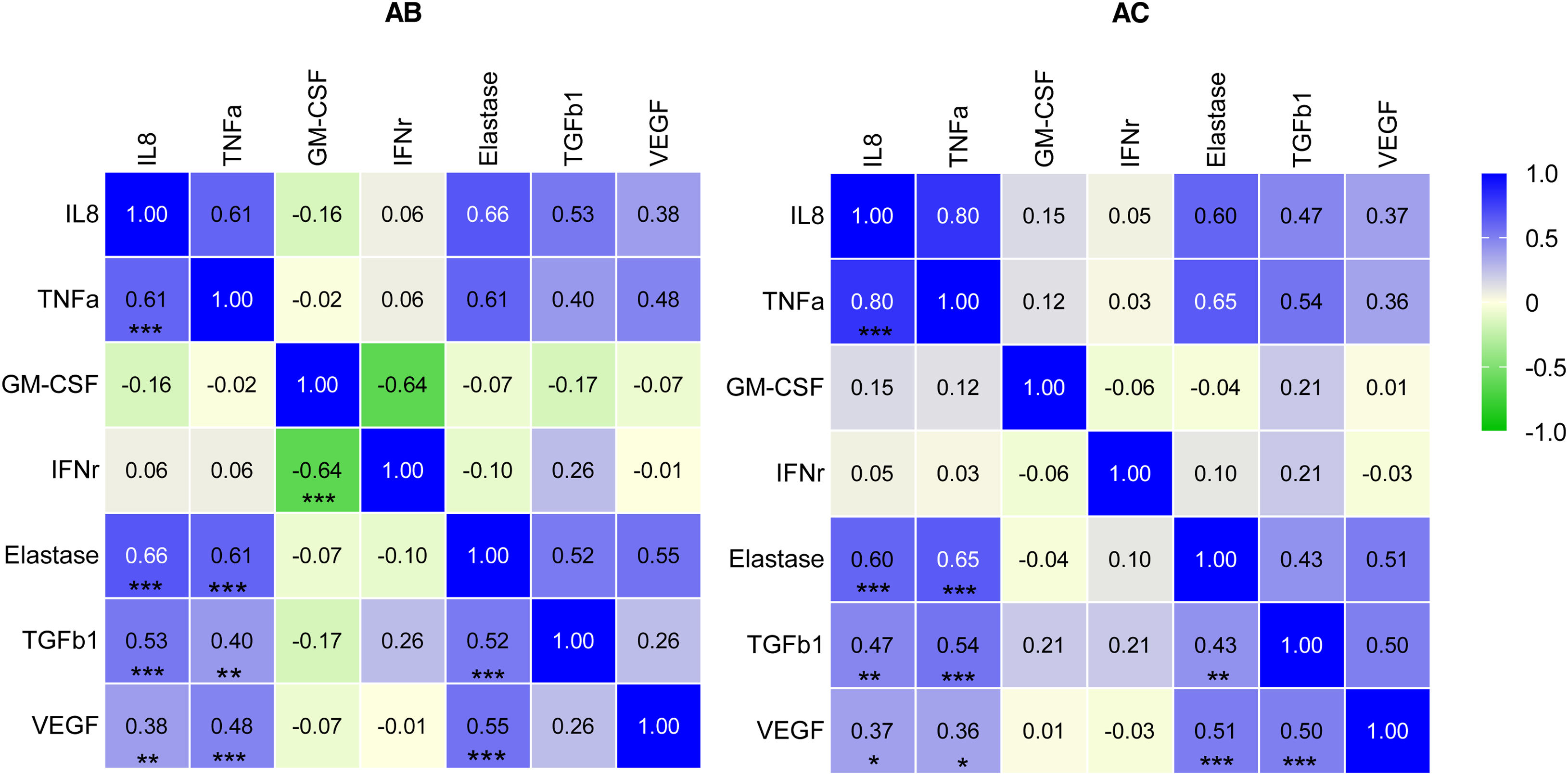
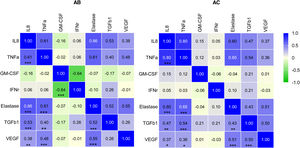
As shown by the correlation matrix (Fig. 3), there was a moderate positive correlation between IL-8, TNF-α, neutrophil elastase, TGFβ1 and VEGF levels regardless of the presence of bronchiectasis. IFN-γ presented a negative correlation with GM-CSF in the AB group (rs=−0.64, p<0.001). A moderate correlation was observed between TGFβ1 and VEGF in the AC group (rs=0.50, p<0.001).
Spearman-correlation matrix of the cytokines studied. Each colored square represents the correlation between two cytokines. Red indicates a strong positive correlation, and green a strong negative correlation. Significant p-values are marked in the lower triangle. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001. AC: without bronchiectasis; AB: with bronchiectasis.
In this study we identified increased levels of key mediators implicated in airway remodeling from the airways of individuals with asthma and bronchiectasis, including TGFβ1 and VEGF. The study demonstrates that the inflammatory phenotype of patients does not differ depending on the presence or absence of bronchiectasis.
VEGF and TGFβ1 are both considered essential in the airway remodeling process.7,8 The increase in TGFβ1 in the cohort of severe asthma patients with bronchiectasis in the present study may reflect a greater degree of asthma severity. In fact, TGFβ1 is a major mediator involved in proinflammatory responses and fibrotic tissue remodeling within the asthmatic lung, and its role has been highlighted in severe eosinophilic asthma in comparison with mild to moderate patients and healthy controls.19 Similarly, VEGF is a potent stimulator of vascular angiogenesis, promoting the development of bronchial microvasculature in asthma.8 Increased expression of VEGF was found to be correlated with a higher degree of airway narrowing and airway vascular permeability. In this context, the bronchial wall thickening in bronchiectasis may be the consequence of a complex proinflammatory and inflammatory action with the involvement of VEGF. Moreover, VEGF plays an important role in Th2 inflammation-inducing eosinophilic inflammation, mucous metaplasia, subepithelial fibrosis, myocyte hyperplasia, dendritic cell activation, and airway hyperresponsiveness via IL-13-dependent and independent mechanisms.20 Overall, the increases in these two cytokines in this study may reflect airway remodeling in severe asthma with bronchiectasis. The differences observed in TGFβ1 and VEGF depending on whether or not the patients were taking oral corticosteroids and/or azithromycin may be due to the modulating effect of these drugs but we cannot rule out that these patients had alterations in these biomarkers due to more serious disease, given that they needed more medication.
GM-CS levels were found to be lower in the sputum of severe asthma patients with bronchiectasis. GM-CSF (also known as CSF2) is a multifunctional inflammatory mediator. Together with IL-5, it partially modulates the Th2 pathway, promoting the accumulation and survival of eosinophils in allergic inflammation in asthma subjects.21 The role of GM-CSF in the priming, activation and survival of neutrophils has also been reported.22 Neutrophilic inflammation is widely recognized in bronchiectasis. As primary components of the innate immune cell system, neutrophils are primary mediators of the rapid innate host defense, reacting immediately against airway infection. In an in vitro study, Ruchaud-Sparagano et al.23 suggested that GM-CSF significantly improves neutrophil phagocytic capacity in blood in patients with idiopathic bronchiectasis. Furthermore, a study in mouse models confirmed that GM-CSF maintains normal pulmonary physiology and resistance to local infection, and plays an essential role in host defenses.24 GM-CSF may also have a critical role in mediating the Th2 allergic inflammation pathway.25 In our study, the lower levels of this cytokine may have led to an impairment of the neutrophil function in asthma patients with bronchiectasis. In this context, we must note that our bronchiectasis patients presented more exacerbations, a finding that may be related to the diminished response of neutrophils driving a vicious circle that would favor the appearance of new episodes of bronchiectasis. Further studies of these CSF subtypes in well-characterized asthma phenotypes are now required to strengthen our understanding of the immunological mechanism.
Interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) is a marker of Th1 pathway inflammation. Increased expression of this cytokine has been demonstrated in severe asthma in comparison to mild and moderate asthma.26 Duvall et al.26 found that severe asthma patients had high ratios of Th1-enriched CD4+ T cells to natural killer (NK) cells in bronchoalveolar lavage liquid compared with non-severe asthma patients and heathy controls. Moreover, studies conducted in children have shown severe asthma to be associated with higher production of IFN-γ in bronchoalveolar lavage cells. In house dust mite-sensitized mouse models of asthma, IFN-γ seems to contribute to epithelial disruption if the T cell myeloid IL-10 axis is blocked.27 Moreover, IFN-γ seems to suppress the function of the secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor (SLPI), a protein that exhibits antimicrobial activity and is thought to play a critical role in mucosal defense.28 The secretory leukocyte protease inhibitor was inversely correlated with IFN-γ expression.29 The balance between proteolytic enzymes (proteases, including elastases) and their inhibitors (proteinase inhibitors) also can be an underlying mechanism of bronchiectasis.6 Overexpression of these cytokines may reflect major Th1 pathway inflammation with an increased risk of altering the normal physiological defense mechanism and proteolytic effect.
In this study, no differences were found in the inflammatory phenotype of severe asthma patients with and without bronchiectasis. However, there was a neutrophil-predominant inflammatory phenotype in both groups, and almost 80% of subjects presented granulocytic inflammation (eosinophilic, neutrophilic or mixed). Indeed, both eosinophilic and neutrophilic forms of inflammation represent a common subset of severe asthma.3,30,31 In the Severe Asthma Research Program (SARP) study, Moore et al.32 found that severe asthma patients expressed high levels of eosinophils and neutrophils in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid, and that neutrophilic and mixed granulocytic forms were associated with a more severe asthma phenotype. Similarly, in the U-BIOPRED hierarchical clustering study,33 the authors identified three clusters in which cluster 2 was characterized by the highest neutrophil level, cluster 1 comprised mainly subjects with eosinophilic inflammation mediated by IL-13/Th2 signature and ILC2, and cluster 3 consisted mostly of patients with paucigranulocytic inflammation and a high expression of mitochondrial oxidative stress and aging gene signatures. In any case, eosinophilic, neutrophilic and mixed granulocytic forms of inflammation were clinically associated with a high degree of airway obstruction.33 More recently, the ISAR (International Severe Asthma Registry) study34 observed a variability in the phenotype, noting that patients with severe asthma present both an eosinophilic and a neutrophilic phenotype, with geographic variability. The study defined neutrophilia as fewer than 300 eosinophils in blood. With this definition, 48.5% of patients presented an eosinophilic phenotype, although this percentage could vary depending on inflammation markers in sputum. In this regard, studies comparing sputum inflammation in patients with asthma and bronchiectasis are scarce. Simpson et al.35 examined sputum toll-like receptor (TLR) protein expression in neutrophilic asthma and a small cohort of bronchiectasis patients. They found that both patients with neutrophilic asthma and patients with bronchiectasis showed increased expression of the receptors TLR2 and surfactant protein A, and proposed that activation of the innate immune inflammation pattern is common to these two entities. Moreover, in patients with bronchiectasis, increased levels of sputum proteolytic enzymes such as neutrophil elastase and matrix metalloproteinase have been observed.36 Nevertheless, although bronchiectasis is usually associated with neutrophilic inflammation6,37 when asthma is also present, the inflammation may also be eosinophilic or mixed (neutrophilic–eosinophilic).38 In this context, Tsikrika et al.39 demonstrated that the presence of significant neutrophilic inflammation is mainly related to greater bronchial destruction on HRCT and lower bronchodilator reversibility, while the presence of a high percentage of sputum eosinophils is characterized by greater bronchodilator reversibility. In our study, no significant correlations were found between sputum eosinophils, neutrophils and parameters related to the radiological features of bronchiectasis.
This study has three main limitations that should be mentioned. Firstly, this was a single-center study carried out at a clinic specializing in severe asthma. Larger studies should now be carried out in different settings to corroborate the data obtained. Secondly, we stress that all subjects were taking standard asthma medication, including inhaled corticosteroid therapy. This may have affected the sputum differential cell percentage, since corticosteroids can promote the apoptosis of eosinophils, although they seem to be insensitive to neutrophils in severe asthma.40 Thirdly, the heterogeneity of both asthma and bronchiectasis makes it difficult to know which of the two diseases begins first. In the present study, the marked bronchial hyperresponsiveness and/or reversible airflow obstruction, along with the exclusion of all possible causes of the origin of the bronchiectasis, suggest that bronchiectasis was secondary to asthma, although we cannot rule out other options. Finally, cytokines associated with the Th2 inflammatory pathway (i.e., IL-5 and IL-13) could not be detected in our pilot study, and so their roles and possible interactions with the non-Th2 inflammation may be underestimated.
In conclusion, increased levels of TGFβ1 and VEGF cytokines may indicate airway remodeling activation in asthma patients with bronchiectasis. No differences were observed in the inflammatory phenotypes of asthma patients with and without bronchiectasis. These results highlight the potential significance of non-invasive methods of assessing airway inflammation. It remains to be seen whether these tools will help to define different disease phenotypes in the future and whether they can provide clinically relevant information regarding disease prognosis and response to treatment.
Conflict of InterestsX. Muñoz reports personal fees from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, GlaxoSmithKline, Novartis, Teva, Mundifarma, Chiesi, Faes, outside the submitted work. The other authors have no competing interests to declare.
The study was partially supported by FIS PI15/01900 (Fondo Europeo de Desarrollo Regional (FEDER) and Fundacio Catalana de Pneumología (FUCAP)).