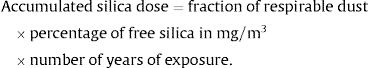Silicosis is one of the occupational respiratory diseases most commonly encountered in our setting. It is caused by inhalation of crystalline silica that triggers a fibrotic response in the lung parenchyma. It presents as diffuse interstitial disease and clinical expression ranges from asymptomatic forms to chronic respiratory failure. Diagnosis is based on clinical history and radiological findings. There is no effective treatment, and once diagnosed, the patient must avoid all sources of occupational exposure. In these guidelines, the clinical, radiological, and functional aspects of silicosis are reviewed, and strategies for diagnosis, monitoring, and classification of patients are proposed, along with recommendations regarding the occupational implications of this disease.
La silicosis es una de las enfermedades respiratorias de origen ocupacional más frecuentes en nuestro entorno. Está ocasionada por inhalación de sílice cristalina que desencadena una respuesta fibrótica en el parénquima pulmonar. Se presenta como una enfermedad intersticial difusa y su expresión clínica es variable, existiendo desde formas asintomáticas hasta la insuficiencia respiratoria crónica. El diagnóstico está basado en la historia clínica y los hallazgos radiológicos; no tiene un tratamiento efectivo, y cuando se diagnostica precisa que el paciente sea apartado de toda fuente de exposición laboral. Esta normativa repasa aspectos clínicos, radiológicos y funcionales, sugiriendo también estrategias de diagnóstico y seguimiento para la clasificación de los pacientes, y recomendaciones para las implicaciones laborales de esta enfermedad.
Silcosis is a diffuse pulmonary interstitial disease characterized by a fibrotic response in lung parenchyma caused by continual inhalation of crystalline silica (SiO2). It is one of the primary pneumoconioses–diseases caused by inhalation of mineral dust–and its presentation, clinical course, and severity are variable. No effective treatment is available, so prevention and early diagnosis are essential if this disease is to be controlled. Silicosis has been known since ancient times, and while there have been some improvements in prevention, it continues to be a global public health problem, and one of the most common occupational respiratory diseases in our setting. Because it has been classified as an occupational disease, physicians have the additional responsibility of assessing the work capacity of affected patients. These guidelines, which review the basic aspects of the disease and standardize diagnostic methodology, treatment, and prevention, are aimed at pulmonologists and doctors attending patients with potential exposure to silica.
EpidemiologyNo reliable figures are available on the population exposed to silica inhalation, so the real prevalence of the disease is unknown. However, epidemiological relevance can be estimated from databases such as the CAREX registry. In 2000, this registry recorded 3.2 million individuals exposed to silica in the European Union. In Spain in 2004, 1.2 million workers, particularly in the construction sector, were exposed to this risk.1
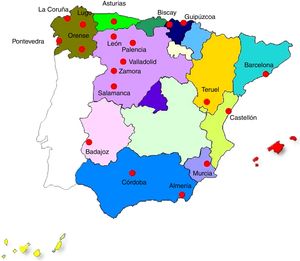
In Spain, varying prevalences have been reported from cross-sectional studies conducted in industries where there is a risk of silica inhalation: 47.5% in granite quarries in El Escorial (1990),2 6% in underground fluorite mines in Asturias (1993),3 6% in the slate industry in Galicia (1994),4 and 6% in granite works in Extremadura.5 In the annual reports of the National Silicosis Institute, the disease is listed as occurring in most of the autonomous communities of Spain, although data from some regions are not available6 (Fig. 1). Since 2008, the number of new diagnoses has increased in industries other than coal mining, such as granite, slate, and artificial silica conglomerate works. This phenomenon may reflect changes in the incidence of the disease or factors derived from socioeconomic circumstances (Table 1).
New Diagnoses of Silicosis.
| Year | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | 375 | 264 | 224 | 151 | 115 | 134 | 165 | 220 | 256 | 166 |
Silicosis is caused by the inhalation of crystalline silica, including quartz (the most abundant in nature), cristobalite, and trimidite.
Sources of exposure are almost exclusively occupational (Table 2) and are numerous, as silica is found in varying proportions in many minerals.
Main Occupations With Exposure to Crystalline Silica.
| Excavations in mines, tunnels, quarries, underground galleries Quarrying, cutting and polishing siliceous rock Dry cutting, grinding, sieving and manipulation of minerals and rock Manufacture of silicon carbide, glass, porcelain, earthenware and other ceramic products Manufacture and maintenance of abrasives and detergent powders Foundry work: cast shakeout, sprue removal and blast cleaning Milling work: polishing, filing products containing free silica Sandblasting and grinding Pottery industry Handling quartz conglomerates and ornamental stone Dental prostheses |
In principle, anyone working in processes involving earth works or products containing silica, such as building or masonry and cement work can be exposed to silica. In our setting, we see a high proportion of quarry workers and ornamental stone cutters (granite and slate). Moreover, in recent years, cases of silicosis have been described in artificial stone workers exposed to dust generated from the handling of quartz conglomerates widely used in interior decoration, kitchens, and bathrooms that have a crystalline silica content of between 70% and 90%.7 Environmental exposure to respirable crystalline silica may be significantly higher in the vicinity of industrial sources of dust, such as quarries and sand works, and cases of non-occupational silicosis have been reported in communities living close to such places.8
Silicosis Risk FactorsIntensity of ExposureThe risk of developing silicosis is closely linked to the accumulated exposure of an individual to crystalline silica during their working lifetime. Exposure can be calculated as follows:
The following factors must be taken into account when calculating exposure:
- -
Fraction of respirable dust: dust with particles of a size that can reach alveolar units (5μm particles: 30%; 1μm particles: 100%). Particles larger than 10μm are deposited in the upper airways by impaction.
- -
Emission limit values (ELV): these are reference values indicating safe levels of exposure. If they were always respected, the vast majority of workers exposed during their lifetime would avoid adverse health effects.9 Legislation on respirable dust limits varies between countries; in Spain, they are regulated by Order ITC/2585/2007 of 30 August 2007, approving the complementary technical instruction 2.0.02 on “Protection of workers from dust, with respect to silicosis in extractive industries”,10 which states:
- a)
The concentration of free silica in the respirable fraction of dust will not exceed 0.1mg/m3 (in the case of cristobalite or trimidite, this value will be reduced to 0.05mg/m3).
- b)
The concentration of respirable dust will not exceed 3mg/m3.
However, several studies have found that a limit of 0.05mg/m3 does not provide sufficient protection from silicosis,11 nor is there a limit that can be considered safe and risk-free, so all reduction in exposure will reduce the risk of disease.
Furthermore, occupational characteristics affect intensity of exposure. Dust with high concentrations of dry, recently fractured silica is more harmful: sand blasters, for example, produce fine particles that, if inhaled, can cause acute, accelerated forms of silicosis.12
Individual FactorsIt is important to remember that while exposure is significant, it is not entirely determinant, many workers do not fit the dose–response pattern. Some individuals are particularly sensitive to low doses, while others can tolerate high exposure levels.13 The susceptibility of a subject to the disease is associated with the build-up and persistence of inhaled dust in the body, due to inefficient defense systems and clearance mechanisms that may be affected by genetic or other factors, such as smoking or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or other respiratory diseases. Some risk factors for disease progression have been identified, including high levels of exposure, previous history of tuberculosis, and profuse opacities on imaging studies.
Clinical FormsSeveral forms of the disease can be identified from the clinical, radiological and functional data. These are classified as chronic silicosis (simple, complicated, and interstitial pulmonary fibrosis), accelerated silicosis and acute silicosis (Tables 3 and 4).
Clinical Forms of Silicosis.
| Clinical form | Time of exposure | Radiology | Symptoms | Lung function |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Simple chronic | >10 years | Nodules <10mm | None | Normal |
| Complicated chronic | >10 years | Masses >1cm | Dyspnea, Cough | Obstructive or restrictive changes, variable severity |
| Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis | >10 years | Diffuse reticulonodular pattern | Dyspnea, Cough | Restrictive changes with reduced diffusion capacity |
| Accelerated | 5–10 years | Rapidly progressing nodules and masses | Dyspnea, Cough | Rapidly deteriorating lung function (FVC and FEV1) |
| Acute | <5 years | Bilateral acinar pattern similar to alveolar proteinosis | Dyspnea | Generally restrictive changes with reduced diffusion capacity |
Silicosis Prevention.
| Primary prevention | Monitor levels of respirable dust Recommend personal protection measures |
| Secondary prevention | Monitor exposed workers Smoking cessation Monitoring for tuberculosis infection |
| Tertiary prevention | Avoid exposure to dust inhalation Report cases, recommend occupational disease assessment Monitoring for tuberculosis infection Treatment of airflow limitation and respiratory failure |
The simple and complicated chronic forms are the most common, appearing generally 10–15 years after exposure. Symptoms range from the asymptomatic simple chronic silicosis detected in a radiological examination to complicated silicosis that most frequently presents with dyspnea and cough. The classic radiological sign of simple silicosis is a bilateral diffuse nodular pattern (opacities <1cm), with greater upper lobe and posterior involvement. The simple form may progress to complicated silicosis (defined as presence of opacities >1cm) in a process of nodular conglomeration, parenchymal retraction and paracicatricial emphysema. In more severe cases, there is extensive structural breakdown with formation of fibrotic masses, respiratory failure, and chronic cor pulmonale. This progression from simple to complicated silicosis is a consequence of a complex interaction between intensity and duration of exposure and the genetic susceptibility of the subject.14
In interstitial pulmonary fibrosis, the main symptom is dyspnea. Radiological findings are very similar to those of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). Not much information is available on this form of the disease, but a recent study reported an incidence of 11% of pneumoconiosis cases with radiological findings interpreted as IPF.15
Accelerated SilicosisThis is an intermediate entity between the acute and the chronic forms that generally appears after a period of exposure of 5–10 years and progresses more often and more rapidly to complicated forms.16,17
Acute Silicosis or SilicoproteinosisAcute silicosis is generally caused by massive exposure. It is similar to alveolar proteinosis, and presents with dyspnea, weight loss and progressive respiratory failure.18 Bilateral perihilar consolidations similar to alveolar proteinosis are seen on chest X-rays, and high resolution computed tomography (HRCT) reveals ground glass opacities or air space consolidations.
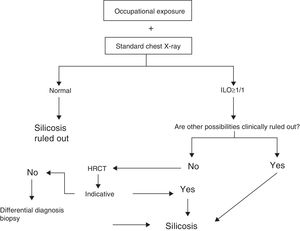
DiagnosisDiagnosis of silicosis is based on the concurrent appearance of the following criteria:
- 1
Occupational history of crystalline silica exposure
- 2
Characteristic radiologic findings as follows: simple chest X-ray with profusions ≥1/1 (see ILO classification)
- 3
Other possible diseases ruled out.
An occupational history must be obtained to estimate accumulated exposure to silica dust. Occasionally job changes can make it difficult to obtain an accurate occupational history, but at least the following should be included18:
- -
Prior and current working activity, recording time of exposure to crystalline silica.
- -
Detailed description of job.
- -
Technical protective measures (use of waterjet cutter, ventilation, dust extraction) and individual precautions (masks).
- -
Measurement of respirable dust, in order to determine accumulated exposure risk (when this information is available).
This examination is essential for the diagnosis of silicosis and for evaluating possible progression. The International Labor Office (ILO) has established a classification coding radiological changes in a reproducible format.19
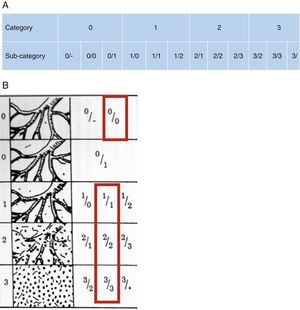
ILO Classification (see online version for full description)The classification contains five sections:
- 1
Technical quality of radiographs: 1: good, 2: acceptable, 3: poor, and 4: unacceptable.
- 2
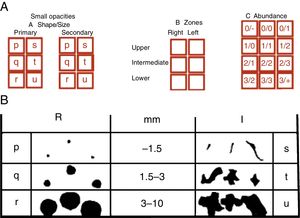
Parenchymal alterations: size, profusion, shape and site (Figs. 2 and 3)
- •
Small opacities: Small opacities are described according to profusion, affected zones of the lung, shape and size.
- •
Large opacities: A large opacity is defined as an opacity having the longest dimension exceeding 10mm. There are 3 categories: A, B, and C.
Fig. 2.(A) In the ILO reading, reference must be made to the shape and size of lesions, expressed in 2 letters and to lesion profusion, expressed in 2 numbers. The zone of the lung in which the lesions are located must also be indicated. (B) Figure shows small opacities, both round (R) and irregular (I) and nomenclature according to shape and size.
- •
- 3
Pleural abnormalities.
- 4
Symbols, for recording additional coded findings.
- 5
Comments, not included above.
The latest version of the ILO, published in 2011, introduced the use of digitized images in the evaluation of silicosis. Twenty-two standard digitized images are provided and the technical features required by the radiological equipment and requirements for reading radiographs are specified: images must be viewed on medical-grade flat-screen monitors designed for diagnostic radiology at least 21 inches (54cm) per image, with a maximum luminance ratio of 250candelas/m2 and a maximum pixel size of 210 microns. Resolution must be at least 2.5 linear pairs per millimeter.
Ruling Out Other DiseasesAdditional examinations may be required for differential diagnosis in certain cases (Fig. 4).
Complementary TestsLung Function TestsThese tests are used in diagnosis and follow-up of patients to detect lung involvement, support the diagnosis of severity in each case, and guide future occupational choices.
Spirometry is the main technique for testing lung function. Findings may range between normal values and obstructive or restrictive patterns with marked decreases in FEV1 and FVC. Observational studies in large series of patients have shown that loss of lung function with reduced FVC and FEV1 is associated with the magnitude of exposure, extent of radiological lesions and history of tuberculosis (moderate grade of evidence).20,21 Spirometry is performed at the time of diagnosis and at check-ups for the evaluation of possible functional deterioration22,23 (consistent recommendation).
Diffusion capacity is affected in the complicated forms of the disease and is sensitive to the presence of fibrosis.14 Static lung volumes can demonstrate a reduction in total lung volume associated with radiological involvement. These examinations are performed in patients with complicated silicosis or if abnormalities are detected on standard spirometry (consistent recommendation).
Pulse oximetry and arterial blood gases are useful for establishing severity, since they can detect respiratory failure (PaO2<60mmHg with SpO2<90%) in the more advanced cases.
Exercise studies do not appear to provide relevant data in asymptomatic patients, but they can be useful in selected cases for the objective measurement of exercise capacity14 (low evidence level, consistent recommendation).
Other Radiological ExaminationsHigh Resolution Computed Tomography (HRCT)Typical HRCT findings include small nodules that may be calcified, generally in upper and posterior fields in centrilobular and subpleural sites. If subpleural nodules coalesce, they adopt a pseudoplaque morphology. Progressive massive fibrosis (PMF) masses generally have spiculated borders and are associated with surrounding bullous emphysema. They have the density of soft tissue and may show inner areas of calcification or lower density due to necrosis. Lung architecture and vascular anatomy distortion may also be observed. Hilar and mediastinal lymphadenopathies are also seen in 40% of cases.24,25
Although HRCT has been shown in comparative studies to be more sensitive than chest X-ray in the diagnosis of silicosis, the lack of clear standards for HRCT reading and the risk of increasing false positives in the diagnostic process mean that this examination is not recommendable for silicosis screening26–28 (moderate level of evidence, consistent recommendation).
With regard to the role of HRCT in the diagnosis of silicosis, it should be added that systematic use of this technique in this and other diseases may have more disadvantages than advantages. Diagnostic criteria for silicosis are based on an occupational history and characteristic radiological signs, and the available data were derived from cohort studies in which the diagnostic tool used was chest X-ray.
The generalized use of HRCT may lead to the detection of pulmonary nodules of uncertain significance that could prevent reaching a definitive diagnosis and may only add confusion. Moreover, from an occupational point of view, in accordance with current guidelines, a worker may not be eligible for disability allowance, although on the basis of these results, his/her company might declare that they are unfit for work. Taking into account all these aspects, and in view of the available knowledge, we believe that an HRCT should be limited to the following cases:
- 1
Chest X-ray reveals very profuse nodular opacities with a tendency to coalesce, since in this situation, HRCT could detect early stage fibrotic masses.
- 2
Atypical radiological signs for the differential diagnosis of other diseases.
Silicosis is an incurable, chronic, progressive disease. It can cause morbidity, disability and death, depending on its severity. There is still no effective treatment for reversing lesions or slowing its advance, so efforts remain focused on the 3 levels of prevention:
Primary PreventionPrimary prevention consists of maintaining respirable dust levels within the legal limits. This strictly technical measure is beyond the responsibility of the physician, and, moreover, currently acceptable silica limits do not completely eliminate the risk of disease.
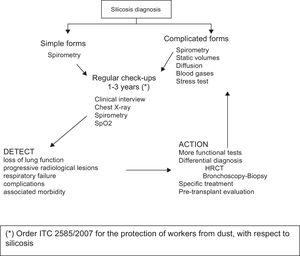
Secondary PreventionSecondary prevention is aimed at diagnosing early stage disease and preventing complication. Workers exposed to silica inhalation should be followed in a health monitoring program, with regular assessment of clinical history, spirometry and chest X-rays, at intervals determined by years of accumulated exposure, according to the protocol approved by Order ITC/2585/2007 for the protection of workers from dust, with respect to silicosis. When complicated pneumoconiosis is diagnosed, diffusion capacity and static lung volumes are determined. Regular check-ups are performed every 1–3 years, depending on the clinical form, functional involvement and radiology. Milder cases can be seen less often (Fig. 5). Screening for additional cases should also be encouraged in industries in which this disease is diagnosed.
The role of silica in cancer and the probable synergy with tobacco in the development of COPD in exposed subjects makes smoking cessation a particularly important objective in this group of patients (consistent level of recommendation). As chronic respiratory disease sufferers, silicosis patients are candidates for Streptococcus pneumoniae and annual influenza vaccination (high quality evidence, consistent recommendation).
Tertiary PreventionWhen silicosis has been diagnosed, all exposure to silica must be avoided to prevent disease progression29 (moderate quality evidence, consistent recommendation). Any tuberculosis infection must be detected and treated according to standard procedures.30
Obstructive ventilatory deficit is a very common situation in complicated silicosis. Treatment of this disorder, even in the presence of respiratory failure, is similar to that recommended for COPD patients.29
Sometimes transplant is the only alternative in younger patients with severe disease. Although there are no specific indications for this option in silicosis patients, available data show similar survival rates to patients with COPD or other diffuse interstitial diseases31.
The Role of the Pulmonologist in the Evaluation of Occupational DisablementOccupational RelocationThe first medical prescription when silicosis is diagnosed is to cease exposure. If the patient is an active worker, this must be reported to the occupational risk prevention department and the individual should be moved to a position without risk of exposure. If such a position is unavailable, the patient must be considered unfit for their current job.
Occupational Disease DeclarationAs this is an occupational disease, listed in group IV of Annex I of the Royal Decree 1299/2005, 10 November 2006, on occupational diseases, it must be entered officially in the ad hoc registry available in the regional social security (INSS) offices (CEPROSS). This declaration is generally made by the ATEEPP mutual assurance company, which collaborates with the social security department responsible for the protection and insurance of occupational incidents. If the patient is not covered by this plan (i.e., is unemployed or retired), the department responsible for this procedure is the medical inspection unit of the regional INSS office. The person responsible for reporting the diagnosis is the Primary Care physician, after receiving the diagnosis from the pulmonologist.
Disablement AssessmentThe assessment of permanent occupational disablement, if applicable, is the responsibility of the INSS regional office. The patient may ask to be assessed by the Disablement Assessment Team of the INSS regional office. This team will determine the appropriate degree of disability on the basis of the medical reports submitted and in accordance with applicable legislation.
This assessment is only undertaken in cases with a definitive diagnosis of silicosis; this, according to law, requires a chest X-ray showing ILO classified profusions ≥1/1.
The information required in the pulmonologist's report for these purposes is the following:
- a.
Clinical form of the disease (simple or complicated silicosis and ILO classification, or diffuse interstitial fibrosis).
- b.
Any permanent respiratory functional impairment, irrespective of whether derived from a disease other than silicosis. If other than silicosis, that disease must be specified.
- c.
Possible concomitancy of silicosis with active or residual pulmonary tuberculosis must be declared, since the regulations specify different occupational disablement categories for each of these situations.
The basic pulmonology examinations required are posteroanterior and lateral chest X-rays (interpreted according to the ILO classification) and spirometry. Other complementary test results will be provided, depending on the specific circumstances of the patient.
Social Repercussions (see full version online)A diagnosis of silicosis has a profound impact on the social and working life of a patient, since, unlike other diseases, it rules out any chance of continuing to work in jobs with a risk of silica exposure irrespective of functional involvement, so for this reason the diagnosis must be robust.
Magnetic Nuclear Resonance and Positron Emission Tomography (See Online Version)Pathology (See Online Version)Other diseases associated with the inhalation of crystalline silica and complications (see online version).
Supplementary data associated with this article can be found, in the online version, at http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.arbr.2014.07.002.
Please cite this article as: Fernández Álvarez R, Martínez González C, Quero Martínez A, Blanco Pérez JJ, Carazo Fernández L, Prieto Fernández A. Normativa para el diagnóstico y seguimiento de la silicosis. Arch Bronconeumol. 2015;51:86–93.