Cystic fibrosis (CF) patients commonly have chronic lung infections and frequent exacerbations caused by a range of bacteria, including Pseudomonas aeruginosa (P. aeruginosa) and Achromobacter xylosoxidan, requiring multiple cycles of antibiotics such as piperacillin/tazobactam. This combination has been associated in the literature with increased bone marrow toxicity, and it should be used with caution.1
We report 2 cases of CF patients, presenting with fever and myelotoxicity caused by piperacillin/tazobactam administered for P. aeruginosa infection, who required a switch to another antibiotic.
The first patient was a 20-year-old man with CF genotype F508del/F508, colonized with methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and P. aeruginosa. He was admitted for a respiratory exacerbation, with increased cough, greenish expectoration, weight loss, and worsening lung function, manifesting as forced vital capacity (FVC) 2950ml (53%), forced expiratory volume in 1second (FEV1) 1885ml (42%), and FEV1/FVC 63.90. Treatment was started with intravenous piperacillin/tazobactam 4/0.5g every 8hours, and tobramycin 400mg/24h. The patient was discharged after 10 days to complete treatment at home. He was readmitted 7 days later with fever, myalgia, and epigastralgia. Clinical laboratory tests showed anemia (hemoglobin 11.3g/dl) and leukopenia (2940/mm3), with a normal blood smear. Piperacillin/tazobactam was switched to ceftazidime, while the aminoglycoside was maintained, leading to an improvement in laboratory parameters.
Our second case was a 23-year-old man with CF genotype F508del/unknown mutation with the following lung function status: FVC 2950ml (60%); FEV1: 1670ml (42%); and FEV1/FVC (56.56%); along with chronic P. aeruginosa bronchial infection. In view of symptoms of respiratory infection and functional decline, treatment was started with piperacillin/tazobactam 4/0.5g/8h and tobramycin 400mg/24h. On day 17 of treatment, he developed fever (39.5°C) with no other accompanying signs. Clinical laboratory tests revealed anemia (hemoglobin 12.5g/dl), thrombocytopenia (96,000/mm3) (Table 1), coagulation changes (prothrombin activity 56% and cephalin time 41.6 s), and hepatic involvement (GOT 170U/l, GPT 51U/l, GGT 24U/l, and LDH 1462U/l). Piperacillin/tazobactam was switched to levofloxacin. On day 4 after admission, the patient's platelet count (165,000/mm3), coagulation parameters (prothrombin activity 102% y and cephalin time 29.6s), and liver function (GOT 18U/l, GPT 27U/l, GGT 19U/l, LDH 285U/l) improved.
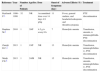
Adverse Reactions Associated With Piperacillin/Tazobactam in Cystic Fibrosis.
| Reference | Year | Number of Patients | Age/Sex | Dose | Onset of Symptoms (day) | Adverse Effects (%) | Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reichardt P.1 | 1996–1998 | 32 | NR | Accumulated dose over 14 days 4.9g/kg | 11 | Fever, general malaise, and headacheLeukopenia and thrombocytopenia | PTZ discontinuation |
| Bandara M.3 | 2010 | 1 | 39/F | 4.5g iv every 6h | 7 | Hemolytic anemia | Transfusion, steroids, iv immunoglobulin, PTZ discontinuation |
| Zanetti R.C.2 | 2013 | 1 | 19/F | NR | 13 | Hemolytic anemia | Transfusion, inmunoglobulina iv, PTZ discontinuation |
| Marik P.E.4 | 2013 | 1 | 24/M | NR | 15 | Hemolytic anemia | Transfusion, steroids, inmunoglobulina iv, PTZ discontinuation |
F: female; iv: intravenous; M: male; NR: not reported; PTZ: piperacillin/tazobactam.
Several papers have been published on the adverse effects of piperacillin/tazobactam in CF patients. For reasons that are still unclear, these events seem to be more common in CF than in the general population.3 Risk factors include a high accumulative dose of antibiotics in a short period of time and prolonged treatments (>10 days).1–3 Haptene-induced hemolytic anemia4 has been reported to respond well to intravenous immunoglobulin.2 Leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, fever, and hypersensitivity reactions that range from pruritis and skin rash to anaphylactic shock5 have also been reported, but no cases of coagulation changes or liver toxicity have been published.
In our experience, CF patients show increased adverse effects to piperacillin/tazobactam, so they should be used with caution in this population. One of our patients, who was a frequent exacerbator (requiring ≥2 intravenous antibiotics/year),6 received piperacillin/tazobactam in an attempt to improve results obtained with previous antibiotic combinations. We conclude that this drug may be considered for use in second-line treatment, but it is inadvisable to use it for periods longer than 14 days. High doses should also be avoided, even for short periods of time.
Conflict of InterestsThe authors state that they have no conflict of interests.
Please cite this article as: Diab Cáceres L, Marcos MC, Girón Moreno RM. Fibrosis quística y piperacilina tazobactam: reacciones adversas. Arch Bronconeumol. 2015;51:664–665.