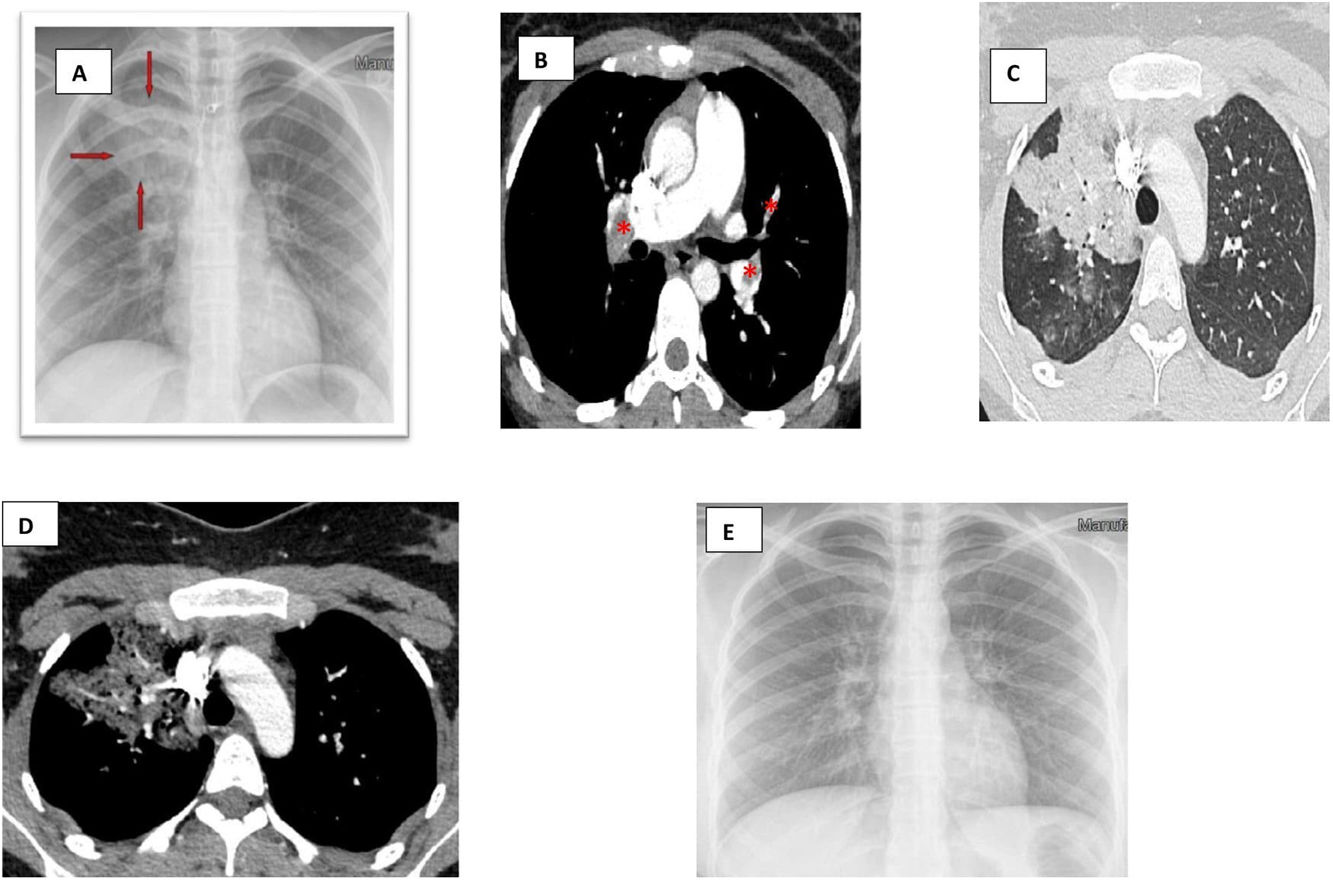
A 20-year-old woman, non-smoker, was admitted to our department presenting sudden onset of dyspnea. Her medical history included oral contraceptive use three months ago. Basic laboratory tests showed elevated D-dimers levels. Chest radiograph demonstrated pulmonary infiltrates in the right upper field (Fig. 1A). Further imaging evaluation using CTPA showed filling defects in both main pulmonary arteries, all lobar and segmental arterial branches except in right upper lobe arteries as well as ground glass opacities in the right upper lobe (Fig. 1B–D). These findings were compatible with pulmonary embolism and associated focal pulmonary edema. No signs of right/left cardiac dysfunction were found on transthoracic echocardiography. The patient was treated with rivaroxaban for 3 months. Complete resolution of alveolar infiltrates was noted after 5 days of anticoagulation treatment (Fig. 1E).
(A) An admission chest radiograph showing pulmonary infiltrates (red arrows) in the right upper lung field. (B) A CT pulmonary angiography demonstrating filling defects in both main pulmonary arteries (red asterisk). (C) A CT pulmonary angiography demonstrating filling defects in lobar and segmental arterial branches. (D) A CT pulmonary angiography demonstrating ground glass opacities in the right upper lobe without filling defects in right upper lobe arteries. (E) A chest radiograph performed on the 5th day of hospitalization showing complete resolution of the focal pulmonary edema.
Focal or diffuse pulmonary edema arising from pulmonary embolism is an uncommon complication.1,2 The precise mechanism of this rare entity is still unclear; however, hyperperfusion with microvascular damage as well as the release of humoral factors (proinflammatory cytokines, thromboxanes, and other mediators of inflammation) thus leading to disrupted permeability of pulmonary microvasculature with excess transudate into the alveoli could explain the development of focal alveolar edema in pulmonary regions with patent pulmonary arteries.
FundingThe authors received no financial support for the research and/or authorship of this article.
Conflict of interestsThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest in the publication of this article.