Hospital admissions due to pneumonia range from 1.1 to 4 per 1000 patients and this figure increases with age. Hospitalization causes a decline in functional status. Physical impairment impedes recovery and constitutes a higher risk of disability and mortality in elderly people.
The objective of this study is to assess the impact of hospital stay in patients with pneumonia related with age.
MethodA total of 116 patients with pneumonia were included in this study, and divided into two age groups: <75 years (n=68) and ≥75 years (n=48). Respiratory function, physical function and psychological and emotional profile were evaluated. Pneumonia severity, nutritional status, independence and comorbidities were also assessed.
ResultsStatistical analyses revealed significant differences between both age groups in pneumonia severity and comorbidities. Significant improvements between admission and discharge were found in lung function in both groups (P<.05), while a significant decrease (P<.05) in strength assessed by dynamometer was found in the ≥75 years group.
ConclusionHospitalization leads to a significant physical impairment in patients admitted for pneumonia. This deterioration increases with age.
Los ingresos hospitalarios por neumonía oscilan entre el 1,1 y el 4 por 1.000 pacientes, aumentando con la edad. La hospitalización provoca un deterioro en el estado funcional. La falta de condición física resultante perjudica la recuperación y pone a los mayores en alto riesgo de discapacidad y de mortalidad.
El objetivo del estudio es evaluar la repercusión de la estancia hospitalaria en pacientes con neumonía en función de su edad.
MétodoSe incluyeron 116 pacientes con neumonía, divididos en dos grupos de edad: <75 años (n=68) y ≥75 años (n=48). Se evaluó la función respiratoria, la función física y el perfil psicoemocional. Además se recogieron como variables la severidad de la neumonía, el estado nutricional, la independencia y las comorbilidades.
ResultadosLos análisis estadísticos revelaron diferencias significativas entre ambos grupos de edad en el grado de la severidad de la neumonía y la presencia de comorbilidades. Se encontraron mejoras significativas (p<0,05) en la función respiratoria en ambos grupos del ingreso al egreso hospitalario. En el grupo ≥75 años se observó una disminución significativa de la fuerza evaluada mediante la dinamometría (p<0,05).
ConclusiónLa hospitalización supone un deterioro físico significativo en pacientes ingresados por neumonía aumentando con la edad.
Various studies1 have shown that hospitalization poses a significant risk to the elderly. Many older patients are confined to their beds with little or no activity, resulting in a decline in their functional status that persists after discharge. Loss of physical form undermines recovery and exposes the elderly to a high risk of impairment and mortality.2
Respiratory diseases currently account for 15.4% of hospital admissions, followed by digestive diseases (12.3%) and cancer treatments (11.3%).3
Respiratory tract infections are very common processes that range from the common cold to pneumonia or pulmonary abscess. Pneumonia, occurring at an incidence of 5.16–6.11 cases per 1000 persons per year,3 is the most common. Mortality rates are high and healthcare costs are elevated.4 Clinical signs and symptoms tend to vary widely, and prognosis often depends on the patient's underlying diseases.
Prospective studies have found that pneumonia is more common in men and in subjects at either end of the age spectrum. It occurs most often during the winter and the risk is exacerbated by factors such as alcohol and tobacco use, malnutrition, uremia, or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).5
Advanced age is also recognized as a risk factor for pneumonia,6 and the number of hospital admissions in patients older than 75 years of age is double that of the population aged between 65 and 74.7
Patients admitted for pneumonia have higher mortality during the year following discharge than those admitted for other reasons, and it has been suggested that inflammation plays a major role in this process. Moreover, some authors, such as Bordon et al., 8 have identified factors such as dementia, liver disease and cancer as predictors of mortality in patients admitted for pneumonia.
The impact of hospitalization9 on the course of various diseases has been studied, but no studies focusing on the effect of hospitalization in pneumonia patients have been identified.
Studies performed in patients with respiratory infection9 have addressed the incidence and causes of the disease, treatments and mortality rates,6 but the impact of hospitalization on these patients has not been assessed.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the impact of hospitalization on patients with pneumonia, depending on their age.
MethodsThis was a prospective study of 116 patients admitted consecutively for pneumonia to the Respiratory Medicine Departments of the Hospital Virgen de las Nieves and the Hospital San Cecilio de Granada between January and May 2014.
Patients with severe cognitive impairment, pleural effusion, pneumothorax or hemoptysis, those who could not perform physical or lung function tests, and isolated patients were excluded. With regard to the type of isolation, patients in airborne isolation units were excluded. The reason for this exclusion was that access to these patients is restricted to prevent contagion and propagation of microbes throughout the hospital.
All patients gave informed consent before inclusion and the study protocol was approved by the ethics committee of both hospitals. The design and objective of this study were registered in the worldwide human clinical studies database, clinicaltrials.gov, under the number NCT02047383.
Subjects received standard medical treatment during the course of the study, in accordance to medical prescription, consisting of oxygen therapy and intravenous antibiotics. They were evaluated on admission and on discharge.
At the start of the study, sociodemographic and anthropometric data were obtained, and pneumonia severity was graded using the CRB-65 scale.10,11 Nutritional status was evaluated using the Mini Nutritional Assessment (MNA) scale,12 dependency according to the Barthel index,13 and co-morbidities using the Charlson index.14
Lung function parameters were also determined, and a physical examination and psychoemotional profiling were performed.
Spirometric testing15 (CareFusion portable spirometer, Micro Spirometer, Basingstoke, UK)16 was used to assess lung function, and respiratory pressures were determined.
Maximum inspiratory pressure and maximum expiratory pressure were used to measure respiratory muscle strength. Maximum inspiratory pressure is the maximum pressure produced by a patient when trying to inhale through a blocked mouthpiece after maximum expiration, and maximum expiratory pressure is the maximum pressure exerted against a blocked mouthpiece, measured during forced expiration after full inspiration17 (Micro-MPM; Sensor-Medico, Yorba Linda, CA, US).
Respiratory symptoms were evaluated using the modified Borg Scale,18 the Leicester Cough Questionnaire and the St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire.
The St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire19 evaluates patient-perceived impact of respiratory tract disease on health status and wellbeing.20
The Leicester Cough Questionnaire evaluates the relationship of cough with quality of life in the previous 24h.21 Total score is from 3 to 21, with a higher score indicating a better quality of life.22
The sit-to-stand test and hand-grip and quadriceps dynamometry were used to determine physical function.
The sit-to-stand test, developed from a previously published protocol,23 records the time taken by the subject to move from a sitting position to standing without using support.23 It has been used in patients with respiratory diseases.23
Muscle tone and hand-grip strength were determined using a dynamometer (TEC-60, Technical Products, Clifton, New Jersey).24
Dynamometry has been used in patients with respiratory diseases.24
Isometric quadriceps strength was measured using a TKK5401 GRIP-D dynamometer. Both legs were evaluated at rest with a knee bend of 60°. Leg dynamometry has been previously used in patients with respiratory diseases.25
Emotional state was determined by reported levels of anxiety and depression during hospitalization and quality of life
Health-related quality of life was evaluated using the EuroQol-5D questionnaire. It provides a multidimensional overview, including physical, social and mental function, and can be applied both in the general population and in specific diseases and types of care.26 The Spanish version was validated by Badia et al.27
This self-administered questionnaire comprises 5 dimensions: mobility, personal care, usual activities, pain/discomfort, and anxiety/depression. It also has a visual analog scale on which patients assess their general health, ranging from 0 (worst imaginable state of health) to 100 (best state of health).28
The hospital anxiety and depression scale29 is used to detect depression and anxiety in hospitalized, non-psychiatric patients. The scale has been validated in Spanish, and shows good internal consistency, external validity, sensitivity, and good specificity.30 Each subscale (anxiety and depression) is scored from 0 to 21.31
This scale has been previously used in studies in respiratory patients.25,32
Statistical AnalysisData analysis was performed using the SPSS statistical software package, version 20.0 for Windows. Variables were presented by mean±standard deviation for continuous variables and percentage for categorical variables. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov test was used to test the normal distribution of quantitative variables. Subjects were divided by age, using 75 years of age as the differential value, since this was the age used in other studies, to form 2 groups, 1 of patients aged ≥75 years and 1 of patients aged <75 years.9
Differences between groups were analyzed using Student's t-tests for the difference between means and the Chi-squared test for categorical variables. Pearson's Chi-squared test was used between qualitative variables. Statistical significance was set at P≤.05 and the confidence interval at 95%.
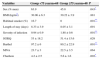
ResultsAfter generating the 2 age groups, their characteristics on admission were analyzed, as shown in Table 1. The <75 years group comprised 68 subjects aged between 35 and 72 years; the ≥75 years group included 48 subjects aged between 75 and 86 years.
Characteristics of Study Subjects (n=116).
| Variables | Group <75 yearsn=68 | Group ≥75 yearsn=48 | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex (% men) | 63.9 | 45.8 | .043* |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 30.06±6.3 | 30.22±3.9 | .881 |
| Habitual smoker (%) | 16.7 | 0 | .001** |
| Length of stay (days) | 8.33±3.9 | 8.05±3.1 | .691 |
| Severity of infection | 0.94±0.9 | 1.88±0.6 | .001** |
| SGRQ | 53±18.2 | 51.4±15.6 | .629 |
| Barthel | 97.2±6 | 80.2±22.9 | .001** |
| MNA | 23.7±3 | 22.5±3.5 | .064 |
| Charlson | 4.2±2.5 | 5.6±1.6 | .003* |
BMI: body mass index; MNA: Mini Nutritional Assessment; SGRQ: St. George's Respiratory Questionnaire.
There were significant differences in sex distribution between the ≥75 years group and the <75 years group (45.8% vs 63.9% men, P=.034). There was a significantly higher proportion of smokers in the <75 years group. Mean length of stay was 8.05±3.1 days in the ≥75 years group, and 8.33±3.9 days in the <75 years group (P=.691). The ≥75 years group had more concomitant diseases and greater dependency, and a higher grade of pneumonia severity.
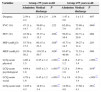
Variables evaluating respiratory capacity are shown in Table 2. Values of respiratory severity variables on admission and on discharge are compared by age group.
Changes in Respiratory Function Between Admission and Discharge.
| Variables | Group <75 years n=68 | Group ≥75 years n=48 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admission | Medical discharge | P | Admission | Medical discharge | P | |
| Dyspnea | 2.59±2.2 | 2.18±2.4 | .154 | 1.47±2.6 | 1±1.5 | .407 |
| FVC (%) | 47.11±14.7 | 50.65±17.2 | .232 | 62.69±7.9 | 75.80±23.4 | .004* |
| FEV (%) | 43.58±16.3 | 35.37±15.3 | .036* | 56.63±16.9 | 62.71±29.9 | .098 |
| MIP (cmH2O) | 53.70±17.2 | 60.15±23.3 | .028* | 43.73±14.7 | 39.27±11.4 | .203 |
| MEP (cmH2O) | 93.50±50.2 | 110.55±50.7 | .028* | 83.67±40.98 | 71.53±31.3 | .099 |
| LCQ-acute physical | 4.66±1.5 | 6.25±1.2 | <.001** | 4.49±1.2 | 5.47±1.4 | <.001** |
| LCQ-acute psychological | 4.64±1.8 | 6.05±1.3 | <.001** | 5.23±1.8 | 5.94±1.5 | .019* |
| LCQ-acute social | 4.78±1.6 | 6.45±1.2 | <.001** | 5±1.8 | 6.24±1.4 | <.001** |
| LCQ-acute total | 14.05±4.3 | 18.83±3.4 | <.001** | 14.66±4.8 | 17.60±4.1 | .001* |
FEV: forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC: forced vital capacity; LCQ: Leicester Cough Questionnaire; MEP: maximum expiratory pressure; MIP: maximum inspiratory pressure.
The ≥75 years group showed significant improvement in forced vital capacity and on all dimensions of the Leicester Cough Questionnaire between admission and discharge. However, in the <75 years group, FEV values decreased significantly between admission and discharge, while respiratory pressures and scores on all dimensions of the Leicester Cough Questionnaire improved significantly.
Variables evaluating the participants’ physical status are shown in Table 3.
Changes in Physical Status Between Admission and Discharge.
| Variables | Group <75 years n=68 | Group ≥75 years n=48 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admission | Medical discharge | P | Admission | Medical discharge | P | |
| Dynam. dominant hand (N) | 274.33±135.1 | 287.32±131.66 | .010* | 164.53±68.7 | 138.00±66.3 | <.001** |
| Dynam. non-dominant hand (N) | 257.76±128.7 | 263.10±134.7 | .362 | 142.76±35.4 | 122.03±53.5 | .001* |
| Dynam. right quadriceps (N) | 96.93±28.3 | 92.36±35.7 | .040* | 79.16±17.5 | 69.06±24.5 | .009* |
| Dynam. left quadriceps (N) | 95.07±31.8 | 85.59±39.2 | .014* | 72.24±23.6 | 60.69±25.2 | .011* |
| STS test(Seconds) | 6.29±2.9 | 7.24±2.9 | <.001** | 2.40±4.9 | 3.00±4.4 | .224 |
Dynam: dynamometry; OLS: One Leg Stance; STS: Sit to Stand.
With respect to changes in physical status between admission and discharge, we found a significant loss of upper and lower limb strength measured by dynamometry in the ≥75 years group (P<.05). In contrast, the <75 years group showed a loss of strength in the quadriceps of both legs, but a significant improvement in hand-grip strength in the dominant hand and in the sit-to-stand test.
Psychoemotional variables are shown by age group in Table 4.
Changes in Emotional State Between Admission and Discharge.
| Variables | Group <75 years n=68 | Group ≥75 years n=48 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Admission | Medical discharge | P | Admission | Medical discharge | P | |
| HAD anxiety | 8.70±5.6 | 7.40±4.9 | .008* | 5.12±4.4 | 3.47±3.8 | <.001** |
| HAD depression | 5.95±4.7 | 5.00±3.8 | .134 | 5.71±3.0 | 6.12±4.2 | .364 |
| HAD total | 16.77±11.5 | 11.27±8.0 | .003* | 10.82±5.7 | 9.59±7.3 | .063 |
| EQ VAS | 53.41±14.3 | 64.32±17.2 | <.001** | 47.65±14.6 | 64.71±17.4 | <.001** |
EQ VAS: EuroQol visual analog scale; HAD: Hospital anxiety and depression scale.
As can be seen, anxiety in both groups decreases significantly between admission and discharge. Moreover, patients’ perception of health status increases in both groups.
DiscussionThe aim of this study was to analyze physical, emotional and functional impairment caused by hospitalization in patients with respiratory infection, and to determine how age may affect this decline. Our results have shown age to be a determinant factor in the decline of patients hospitalized with respiratory infection, with the musculoskeletal system being the most severely affected. However, patients’ psychoemotional state tends to improve between admission and discharge, regardless of age.
Respiratory tract infection is important in the elderly due to its greater incidence and impact. Studies have shown that symptoms of infection present differently in the elderly,33 and rates of hospital admission and death are higher9; therefore, age is a very important variable to take into account when assessing disease course. The groups analyzed in this study showed differences in the grade of pneumonia severity and presence of comorbidities. Both presence of comorbidities and severity were associated with the older group, while the younger group showed less dependency (higher Barthel index scores). These values may be due to the prior presence of predisposing diseases in the lower age group. However, differences in pre-study characteristics between the groups did not determine differences in length of hospital stay.
Physical Decline During HospitalizationPrevious studies have described the impact of hospitalization on patients’ physical status.14 However, none have focused on patients with respiratory infection, nor has the impact of hospitalization by age group been evaluated. This study has shown significant physical impairment in patients admitted for pneumonia.
In the lower age group, pneumonia was also seen to have a significant impact on lung function values at discharge; similar results were previously reported in studies in patients not stratified to age groups.8 Other authors33 have reported a trend towards improved clinical progress in lower age groups after discharge, but this could not be evaluated in our study.
The significant loss of strength in the quadriceps seen during hospitalization (mean 8 days) was also found in other studies in different patient populations.14
Hand-grip strength is an important predictor of functional limitations and impairment. It also correlates with strength in other muscle groups, and therefore is a good indicator of strength in general.34 In this study, we found that patients had a significant loss of strength in their dominant hand.
Hospitalization of elderly patients commonly leads to functional decline, due to inactivity during the stay.1 This may be because patients with respiratory diseases receive oxygen therapy and intravenous serum and antibiotics, restricting mobility even further.
Functional decline during and after hospitalization is an important factor for geriatric subjects becoming more dependent at home, leading to placement in care homes.35
Strength and respiratory muscle resistance are associated with the ability to get about and perform activities of daily living. Respiratory muscle strength is, as such, an important physiological variable that can help prevent functional decline in the elderly and may reduce the risk of morbidity and mortality.36
Sligl et al.37 found that severely limited functional status was the single independent predictor for mortality during the following year. The authors speculated that poor functional status was associated with chronic comorbidity, cognitive impairment, loss of physical condition or malnutrition, and poor physiological response to acute stress, leading to greater impairment.
Our study also found greater physical impairment in the older group. Similar results have been found by other authors, and some have even associated loss of muscle strength with the psychoemotional profile typical of this age group.38
Impact of Hospitalization on Emotional StateOur study showed significant improvements in psychoemotional state between admission and medical discharge, particularly in the younger age group. These results confirm the effect of hospital admission on patients already observed in other studies, which have shown that hospitalization increases levels of anxiety and depression in patients.38 However, the progression of these psychoemotional indicators after resolution of respiratory symptoms was not analyzed in these studies, as we were able to do in ours. This analysis is particularly relevant, since it revealed that the greater the level of anxiety, the greater the risk of re-admission.38
Study Limitations and StrengthsThis study has several limitations that should be taken into account. First, for reasons of sample selection, it was impossible to analyze the potential relationship between clinical decline and pneumonia severity or pneumonia etiology, although grades of severity were evenly distributed between the groups. The second limitation that may have affected our results is that no analytical variable could be included in the evaluation of the impact of pneumonia on muscle strength, which should be included as a possible confounding variable in future studies. Finally, the distribution of the study population was not stratified by sex, although the final distribution found in this study reflects the gender prevalences reported in several other studies.9,39,40 Another limitation of this study is the lack of a long-term follow-up to determine patient progress after discharge.
Clinical RelevanceIn conclusion, our study showed the importance of taking into account patient age when evaluating the impact of hospitalization on pneumonia patients.
Hospitalization caused physical impairment and age is a factor to be taken into account in the hospitalization of patients with respiratory infection, since impairment is most pronounced in the musculoskeletal system. However, psychoemotional state tends to improve between admission and discharge, regardless of age.
The results of this study must be taken into account when developing multidisciplinary therapeutic proposals for avoiding this decline during hospitalization in elderly patients.
FundingThis project was conducted without funding.
Conflict of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Please cite this article as: Martín-Salvador A, Torres-Sánchez I, Sáez-Roca G, López-Torres I, Rodríguez-Alzueta E, Valenza MC. Estudio del deterioro psicofísico y funcional en pacientes ingresados con neumonía. Análisis por grupos de edad. Arch Bronconeumol. 2015;51:496–501.