The systematic use of bibliometric indicators in the evaluation of research has given rise to the publication of in-depth studies on the advantages and disadvantages of each of these indicators. The most widely used indicator, the impact factor (IF),1 has been frequently criticized for its many limitations, such as inclusion of citations of articles that are not included in the denominator of the calculation formula (editorials, letters, etc.), an analysis period of only 2 years, the inclusion of self-citations and the lack of evaluation of the quality of the origin of the citation or the risk of manipulation, among others.2–5
A recently proposed new parameter, the SCImago Journal Rank (SJR) index, has been readily accepted and adopted. It uses for its calculations citations from the Scopus database (Elsevier).2 The SJR corrects many of the factors criticized in the IF,2 since it includes more journals, covers a longer period for including citations (3years), and limits self-citations. More importantly, it weighs citations according to the importance of the journal where they were published, using an algorithm similar to that of Google PageRank®.
To compare the results of both indexes (IF and SJR) in specialized respiratory system journals, the values for 2012 were analyzed. The journals are listed under the category Respiratory System of the Journal Citation Reports® for the IF calculation and under the category Pulmonary and Respiratory Medicine of SCImago for the calculation of the new index. These indexes were obtained from the official websites of the Web of Science (at http://www.accesowok.fecyt.es/), which includes the Journal Citation Reports®, and the SCImago Journal & Country Rank (http://www.scimagojr.com/). The latter is available on free access. The classification order of the journals for each index was reviewed and the possible correlation between both indicators was evaluated using Spearman's test.
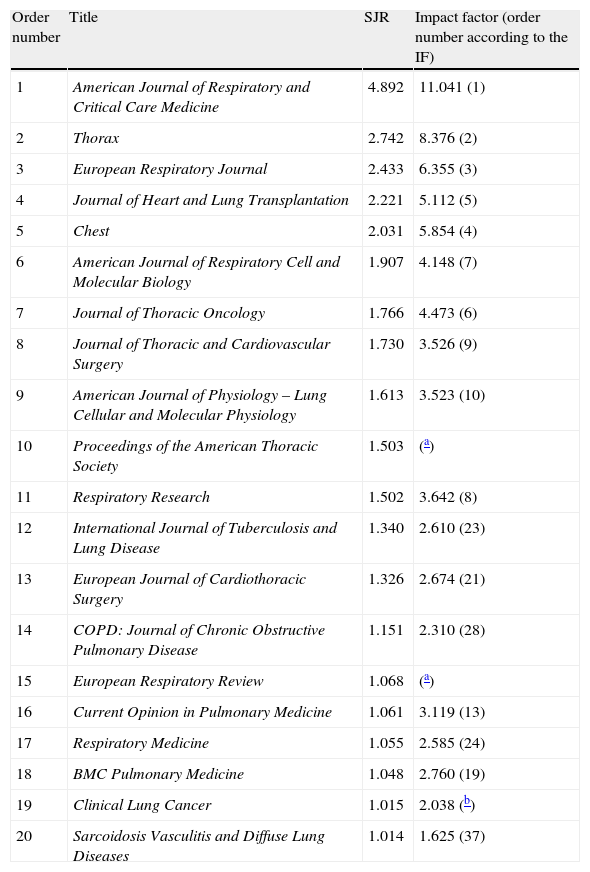
The Journal Citation Reports® includes 50 specialized respiratory system journals and the SCImago Journal & Country Rank includes 98. In general, it was found that the top journals occupy similar positions in both classifications, as seen in Table 1, which lists the top 20 journals according to the SJR with their equivalent position in the IF. There was a very high correlation between the indicators for journals in this category (r=0.94; P<.001).
Respiratory System Journals With the Highest Score on the SCImago Journal Rank and the Corresponding Impact Factor Value.
| Order number | Title | SJR | Impact factor (order number according to the IF) |
| 1 | American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine | 4.892 | 11.041 (1) |
| 2 | Thorax | 2.742 | 8.376 (2) |
| 3 | European Respiratory Journal | 2.433 | 6.355 (3) |
| 4 | Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation | 2.221 | 5.112 (5) |
| 5 | Chest | 2.031 | 5.854 (4) |
| 6 | American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology | 1.907 | 4.148 (7) |
| 7 | Journal of Thoracic Oncology | 1.766 | 4.473 (6) |
| 8 | Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery | 1.730 | 3.526 (9) |
| 9 | American Journal of Physiology – Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology | 1.613 | 3.523 (10) |
| 10 | Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society | 1.503 | (a) |
| 11 | Respiratory Research | 1.502 | 3.642 (8) |
| 12 | International Journal of Tuberculosis and Lung Disease | 1.340 | 2.610 (23) |
| 13 | European Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery | 1.326 | 2.674 (21) |
| 14 | COPD: Journal of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease | 1.151 | 2.310 (28) |
| 15 | European Respiratory Review | 1.068 | (a) |
| 16 | Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine | 1.061 | 3.119 (13) |
| 17 | Respiratory Medicine | 1.055 | 2.585 (24) |
| 18 | BMC Pulmonary Medicine | 1.048 | 2.760 (19) |
| 19 | Clinical Lung Cancer | 1.015 | 2.038 (b) |
| 20 | Sarcoidosis Vasculitis and Diffuse Lung Diseases | 1.014 | 1.625 (37) |
SJR, SCImago Journal Rank; IF, impact factor.
Our data reveal that use of the SJR index does not significantly change the classification of respiratory system journals compared to the IF. Moreover, its calculation methods address the main limitations attributed to IF, including nuances, such as citation weighting, that may improve the characterization of the journals. All these aspects, added to the fact that SCImago Journal & Country Rank is free access, lead us to believe that SJR may be at present be considered not only as a complement but also as an alternative to the IF.
Please cite this article as: García-Pachón E, Arencibia-Jorge R. Comparación del factor de impacto y el índice SCImago Journal Rank en las revistas del sistema respiratorio. Arch Bronconeumol. 2014;50:308–309.