Expanding TNM staging system for lung cancer with the addition of new prognostic factors could enhance patient stratification and survival prediction. The goal of this study is to assess if TNM prognosis capacity could be improved by incorporating other pathological characteristics of surgical specimen.
MethodsWe retrospectively reviewed lung cancer resections, stages I–II, performed between January 1st 2010 and May 1st 2019. We collected clinical variables and pathological characteristics, including vascular, lymphovascular and perineural invasion, STAS, necrosis and stromal features. Mortality and recurrence-free survival were assessed with univariable and multivariable Cox analysis. We explored how these factors would modify the TNM Harrel's index.
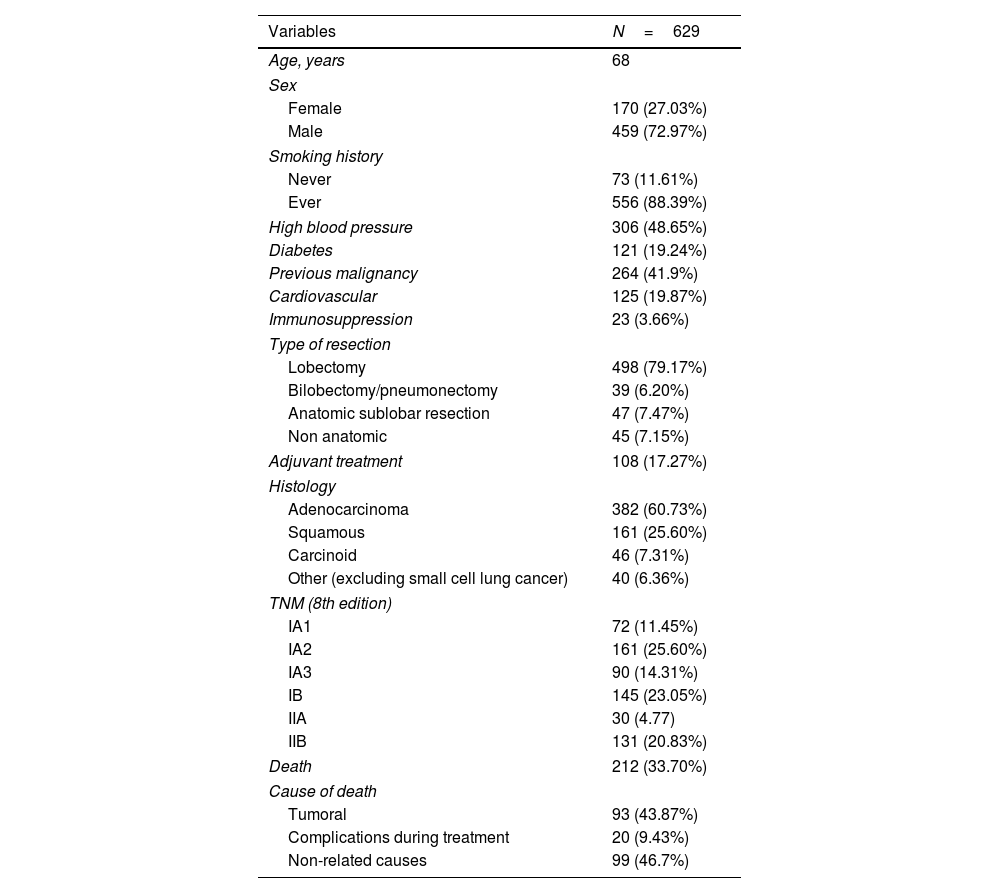
Results629 tumors were analyzed. Median overall survival was 53.9 months. Median recurrence-free survival was 47.6 months. Specific survival at 3, 5 and 10 years was 90, 83 and 74%. Recurrence-free survival at 3, 5 and 10 years was 76, 70 and 65%.
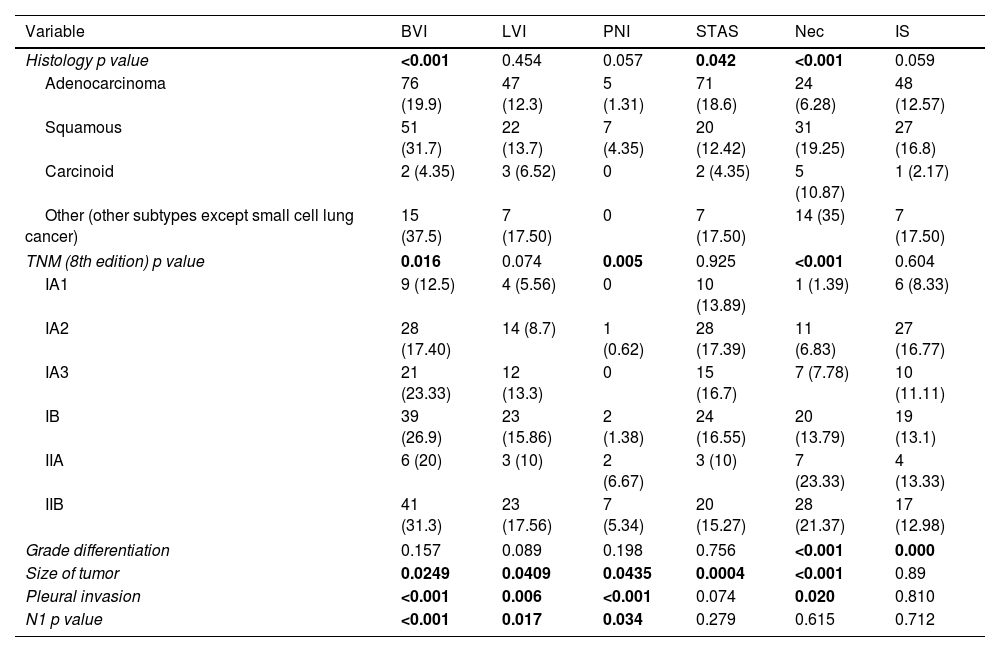
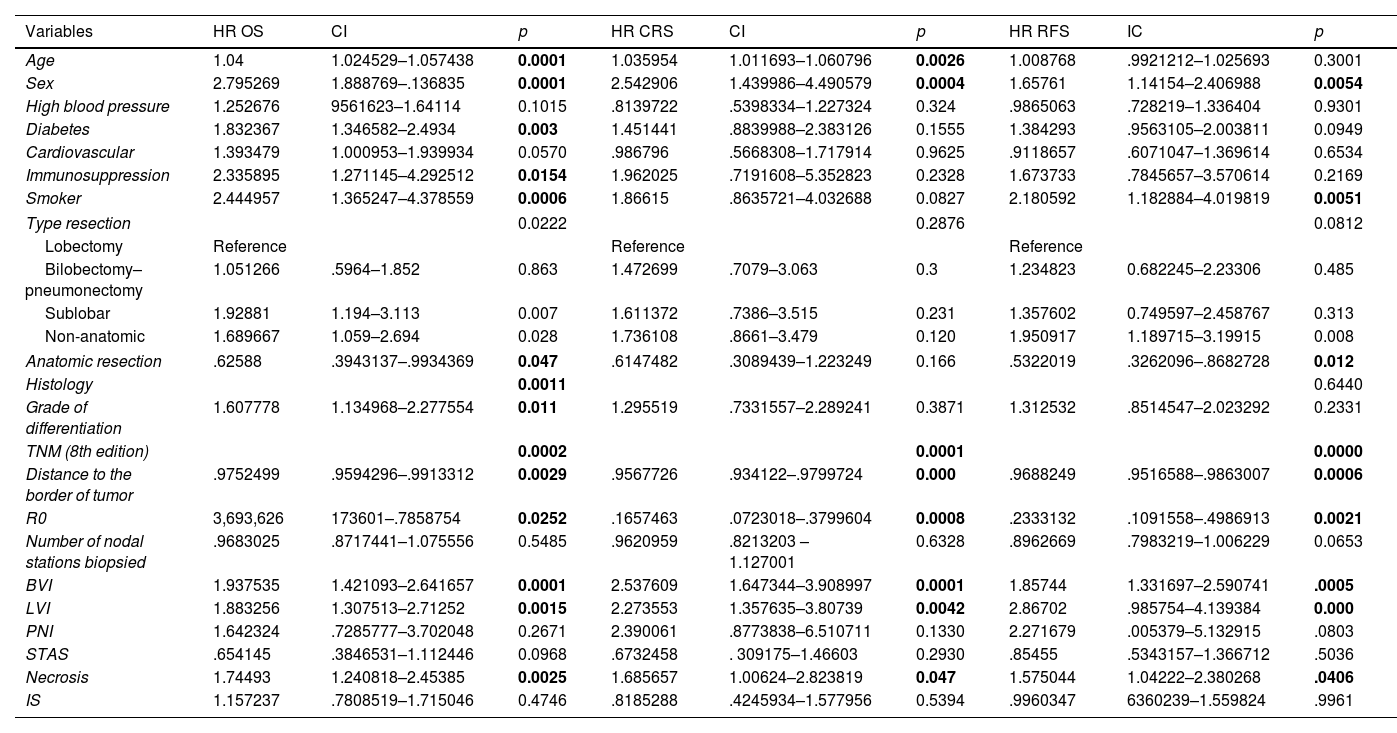
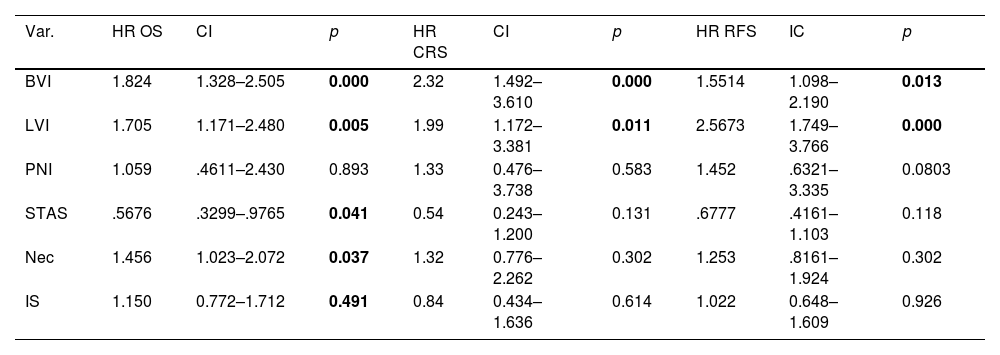
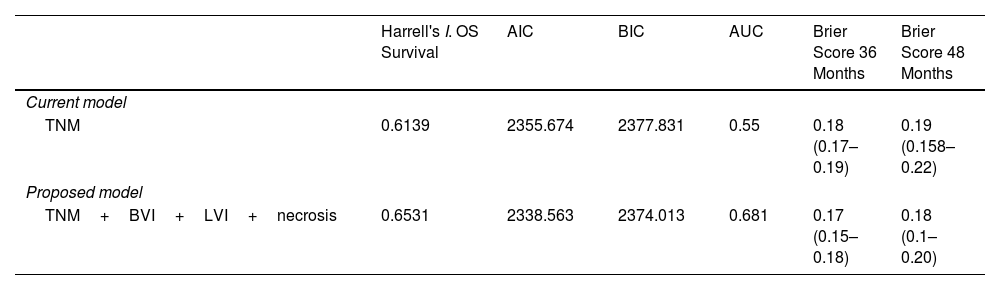
The multivariable analysis showed that overall survival was significantly related to TNM classification (p<0.0002), vascular infiltration (HR 1.93, CI 1.42–2.64, p<0.0001), lymphovascular invasion (HR 1.88, CI 1.30–2.71, p<0.0015) and necrosis (HR 1.74, CI 1.24–2.45, p<0.0025). Harrell's index for TNM was 0.6139. Adding vascular, lymphovascular invasion and necrosis, it increased up to 0.6531.
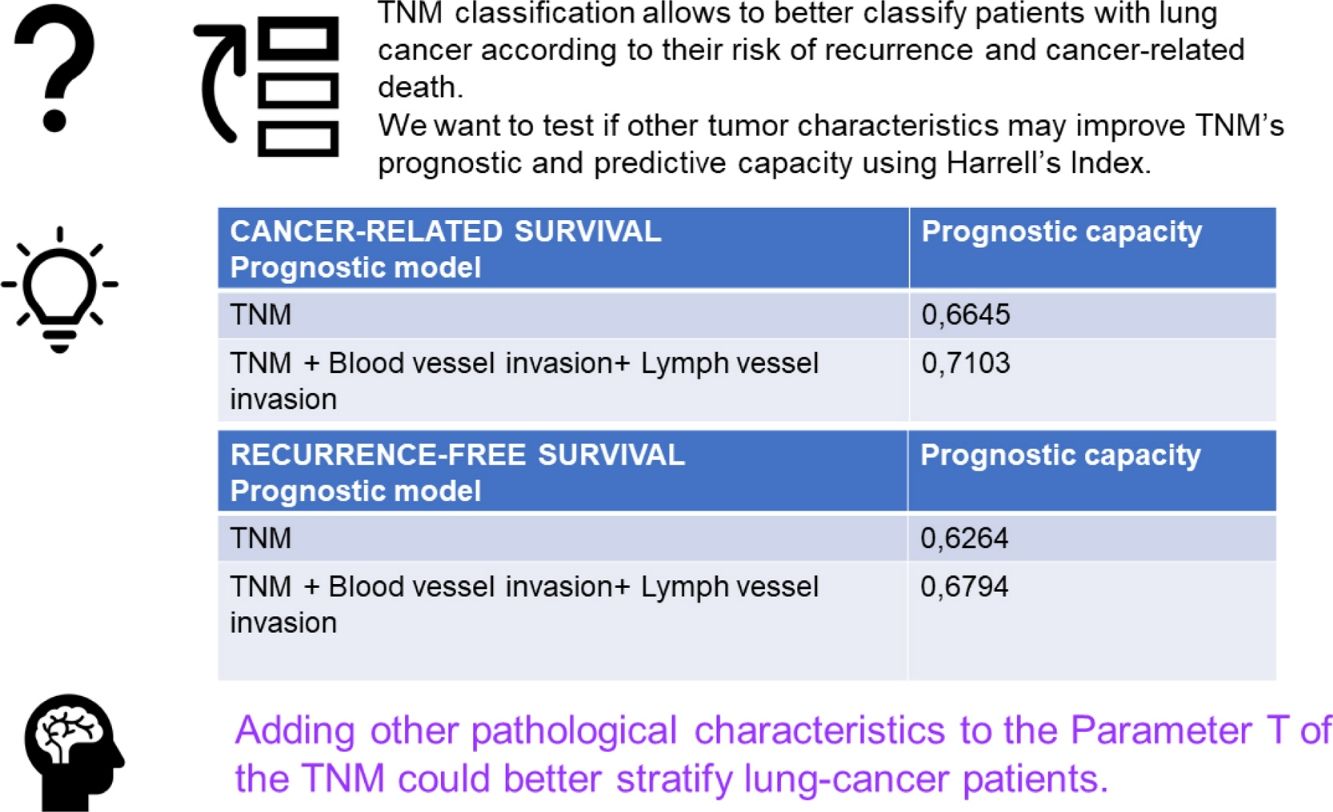
The multivariable analysis showed that specific survival was significantly related to TNM classification (p<0.001), vascular infiltration (HR 2.23, CI 1.44–3.46, p<0.001) and lymphovascular invasion (HR 1.85, CI 1.09–3.13, p<0.021). Harrell's index for TNM was 0.6645. Adding vascular and lymphovascular invasion, it increased up to 0.7103. Recurrence-free survival was related to TNM, vascular infiltration (HR 1.48, CI 1.05–2.09, p<0.023) and lymphovascular invasion (HR 2.40, CI 1.64–3.50, p<0.001). Harrell's index for TNM was 0.6264. Adding vascular and lymphovascular invasion, it increased up to 0.6794.
ConclusionsIncluding vascular and angiolymphatic invasion in the staging system classification could better stratify patients at risk of recurrence and tumor-related death.