Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is characterized by high morbidity and mortality, with physical inactivity being a major contributor to poor outcomes. This study aims to identify subgroups of inactive COPD patients by analyzing reported barriers to physical activity and the perceived impact of inactivity on their disease.
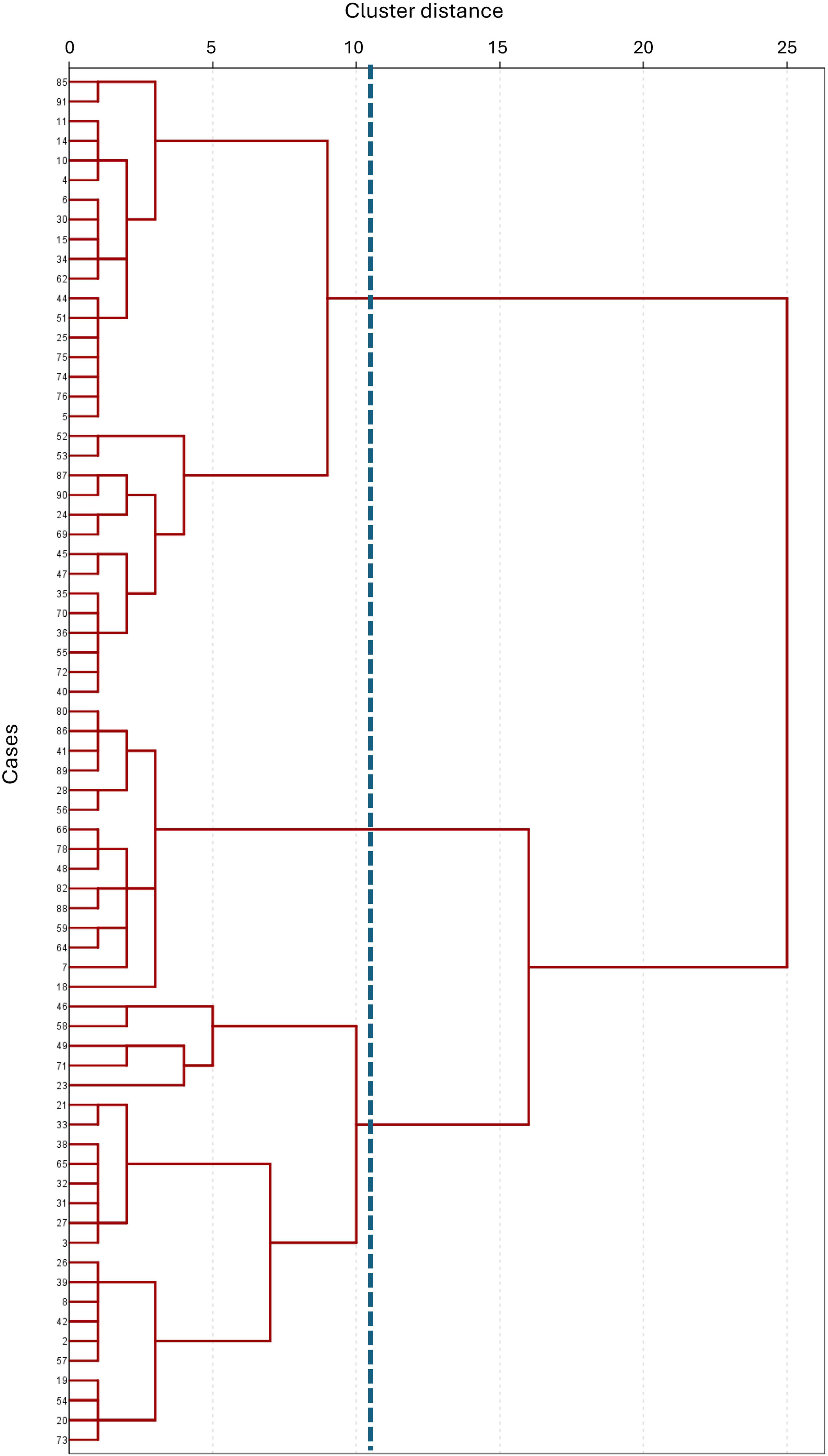
MethodsIn 91 consecutive stable COPD patients, physical activity was measured using a SenseWear armband and the SAQ-COPD questionnaire, to define inactivity as a physical activity level <1.69. Clinical and functional assessment included measurement of lung volumes, diffusing capacity, muscle strength, six-minute walk test and progressive cardiorespiratory exercise test. Cluster analysis was performed based on patients’ responses to the profile and impact sections of SAQ-COPD questionnaire.
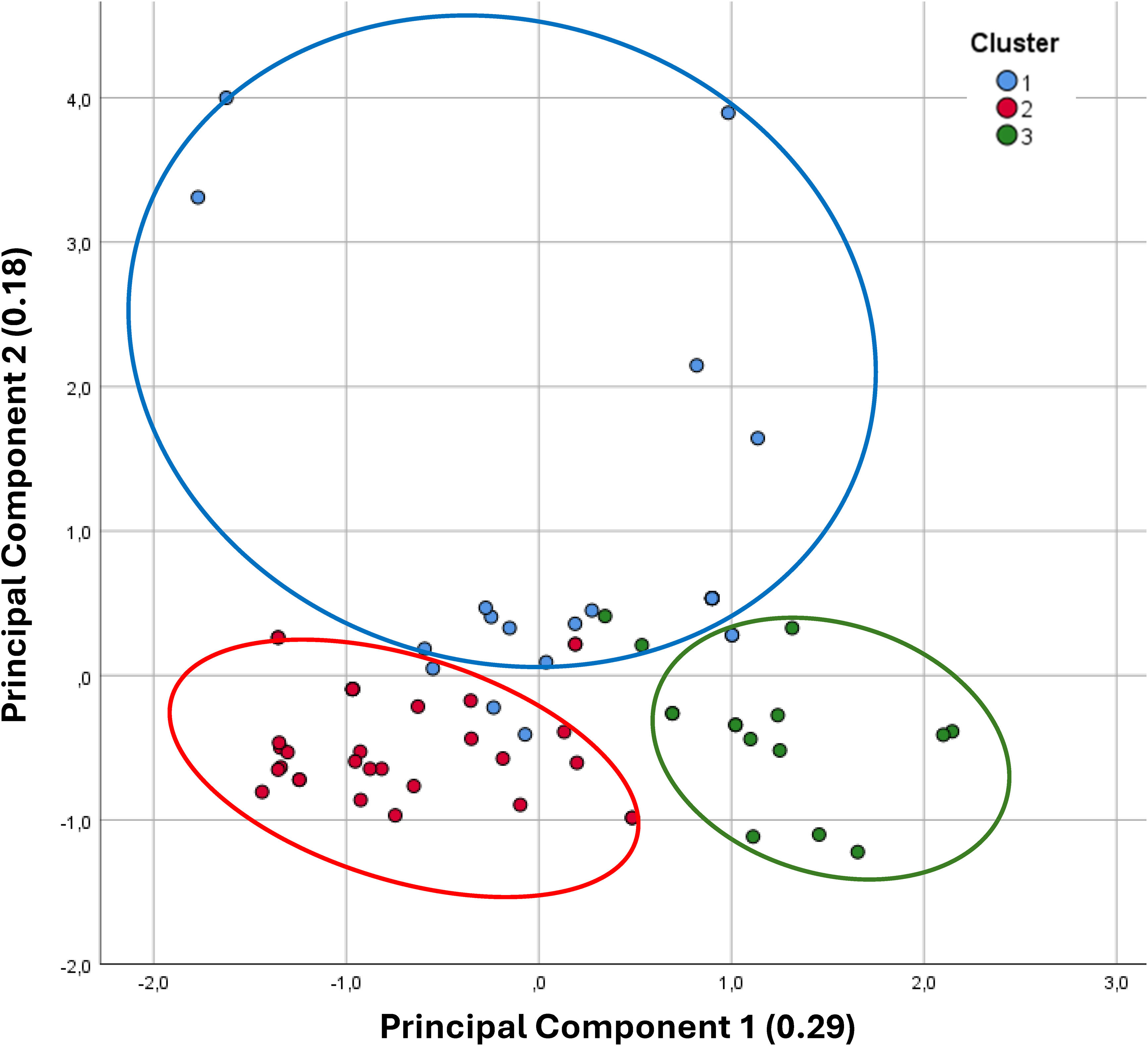
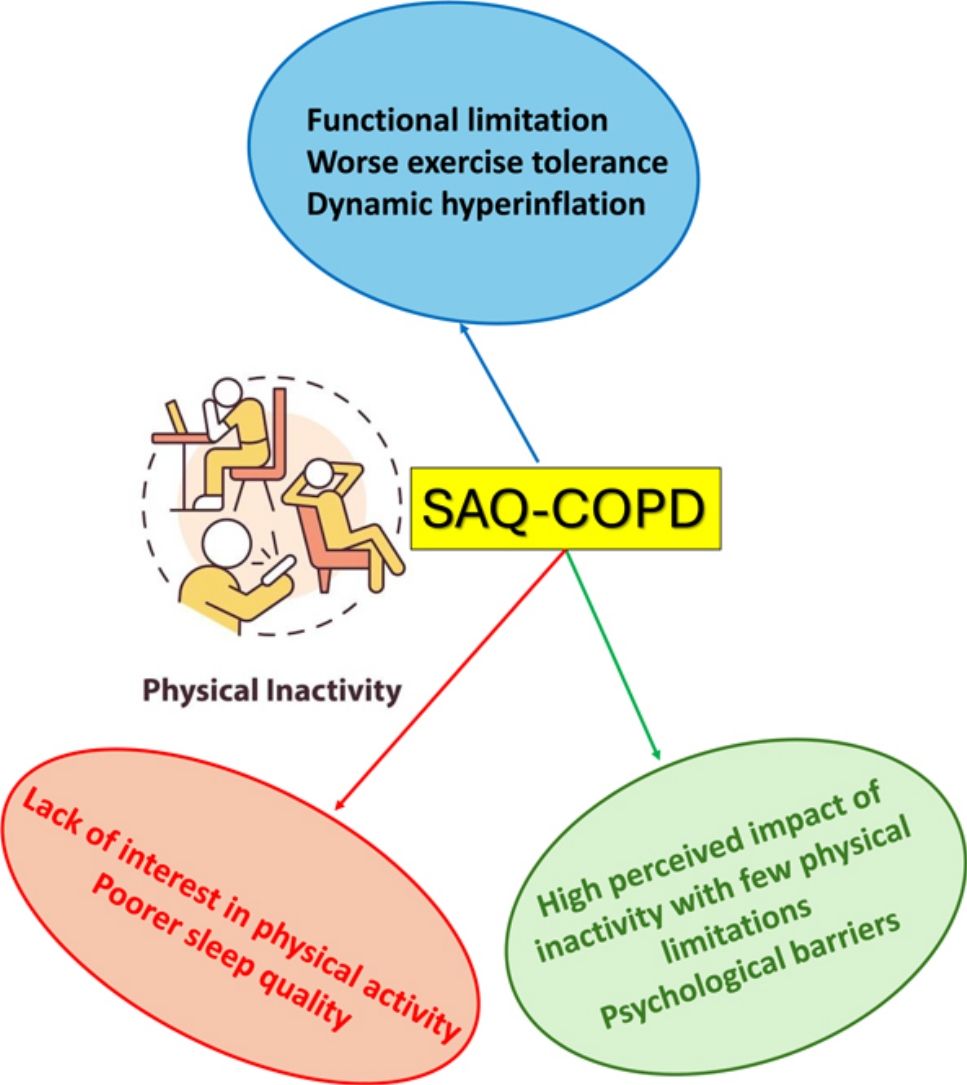
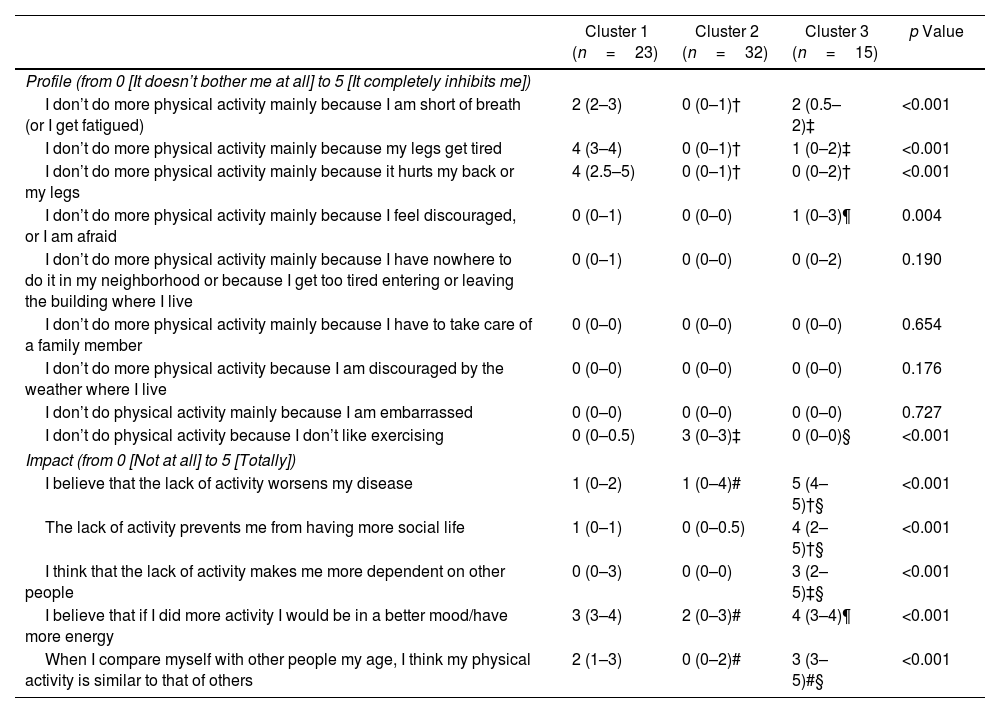
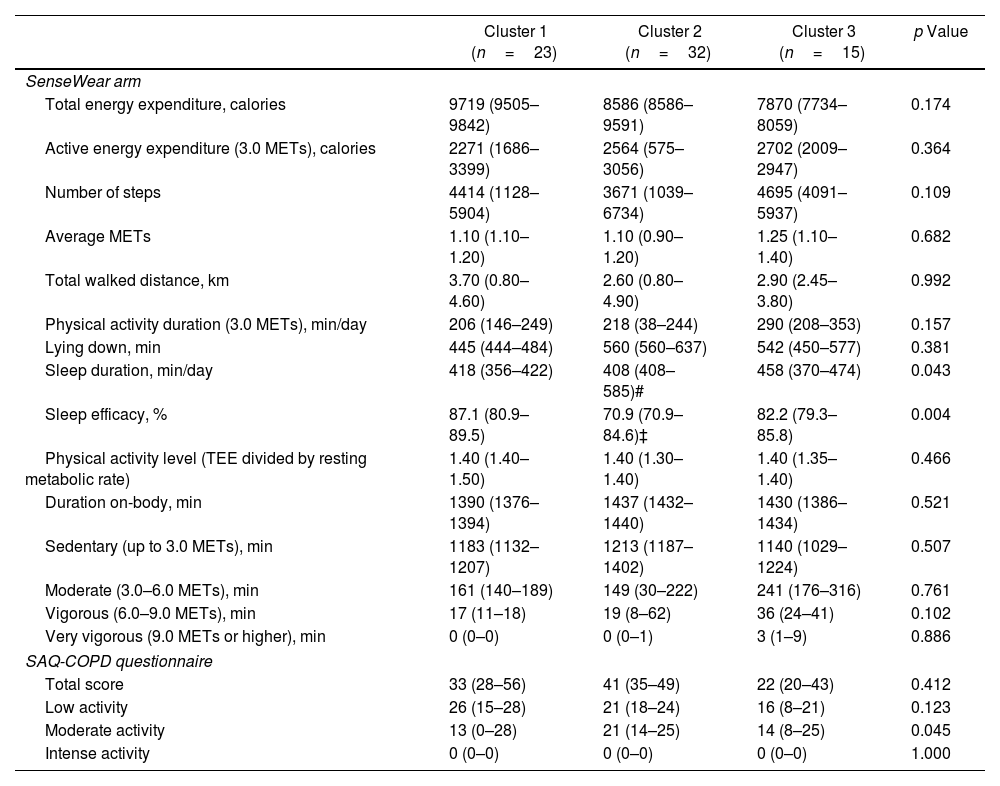
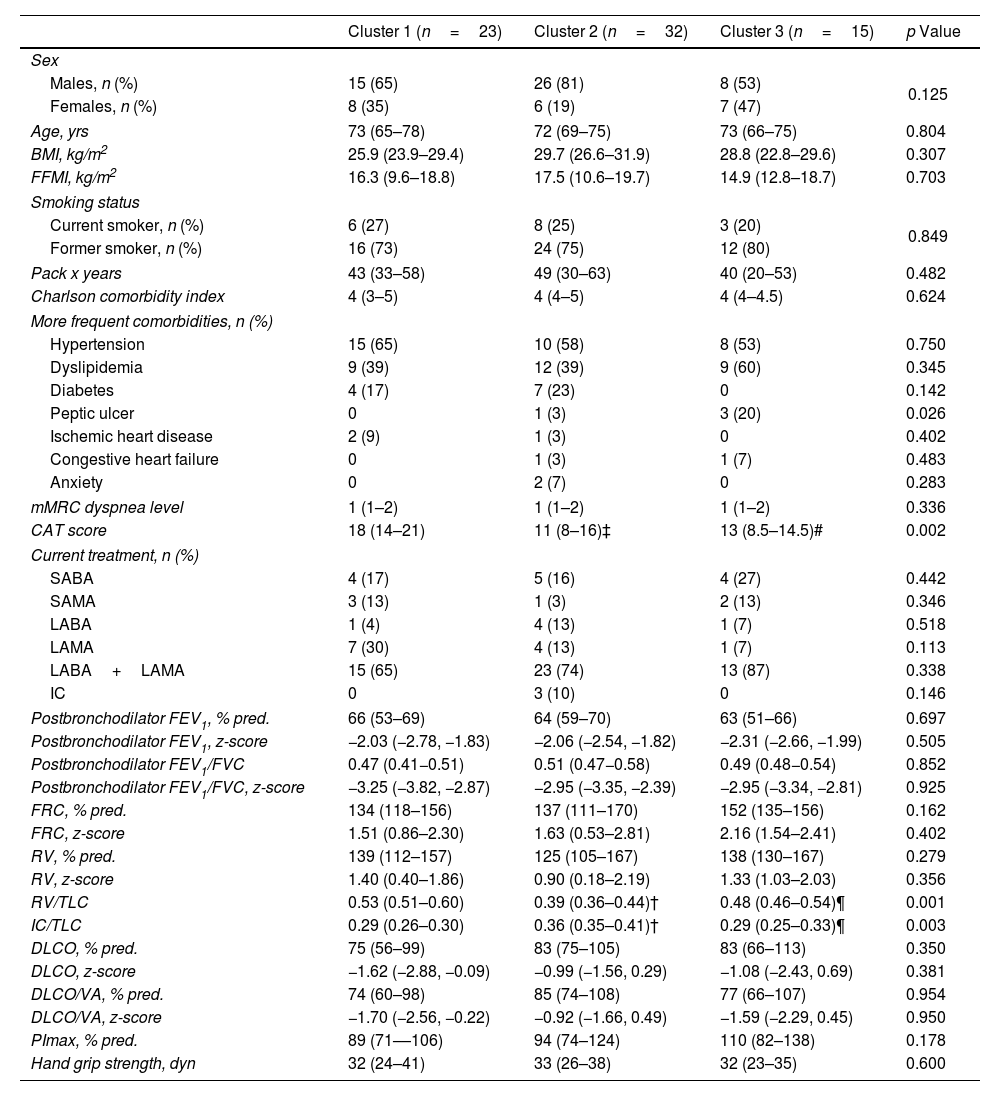
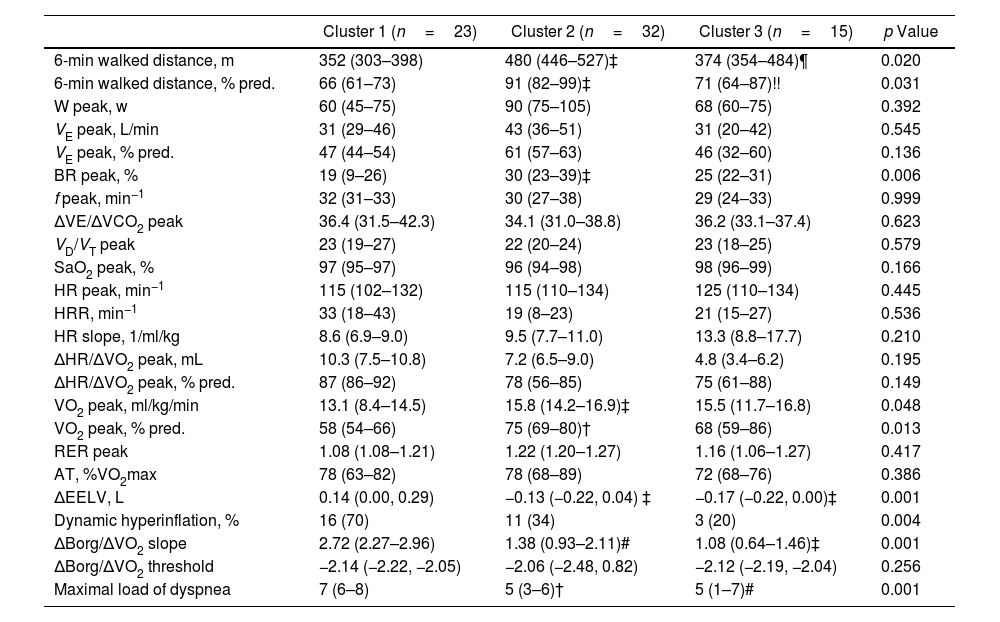
ResultsIn 70 inactive COPD patients, three distinct clusters were identified: Cluster 1 showed significant functional limitations, particularly dyspnea and leg fatigue, alongside worse exercise tolerance and dynamic hyperinflation. Cluster 2 displayed few functional limitations but reported a lack of interest in physical activity as the primary reason for inactivity, with poorer sleep quality observed. Cluster 3 exhibited a high perceived impact of inactivity despite reporting fewer physical limitations, with psychological factors such as fear and discouragement acting as primary barriers. Factor analysis revealed two principal components: perceived impact of inactivity and limiting factors for exercise.
ConclusionThese findings highlight the heterogeneity among inactive COPD patients and emphasize the need for tailored interventions targeting both physical and psychological barriers. SAQ-COPD questionnaire may be a useful instrument for this individualized assessment of inactive COPD patients.