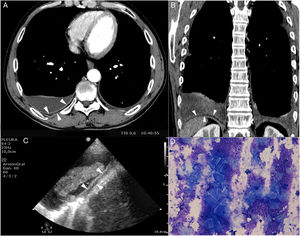
A 47-year-old man with an 8-year history of rheumatoid arthritis was referred for assessment of bilateral (predominantly right-sided) pleural effusion, occupying about 20% of the hemitorax. Both a CT scan and a chest ultrasound showed fat-fluid levels in the pleural space (Fig. 1A–C, arrowheads). A thoracentesis retrieved pseudochylous milky effusion consistent with lymphocytic exudate with cholesterol concentrations of 91 mg/dl, triglycerides 11 mg/dl, and abundant cholesterol crystals (Fig. 1D). A diagnosis was given of pseudochylothorax due to rheumatoid arthritis. Since the patient was asymptomatic, no specific therapeutic measures were taken.
Pseudochylothorax or pleural effusion of cholesterol is an uncommon entity, seen primarily in patients with tuberculosis or rheumatoid arthritis. In a systematic review of 104 cases, these effusions were unilateral (88%) and associated with pleural thickening (80%).1 A cholesterol/triglyceride ratio in pleural fluid of greater than one (sensitivity: 97%) and the presence of cholesterol crystals under polarized light microscope (sensitivity: 90%) are considered pathognomonic.1 Likewise, radiological fat-fluid levels in the pleural space is a rare feature.2
Please cite this article as: Porcel JM, Pardina M, Gatius S. Seudoquilotórax reumatoide. Arch Bronconeumol. 2020;56:666–667.