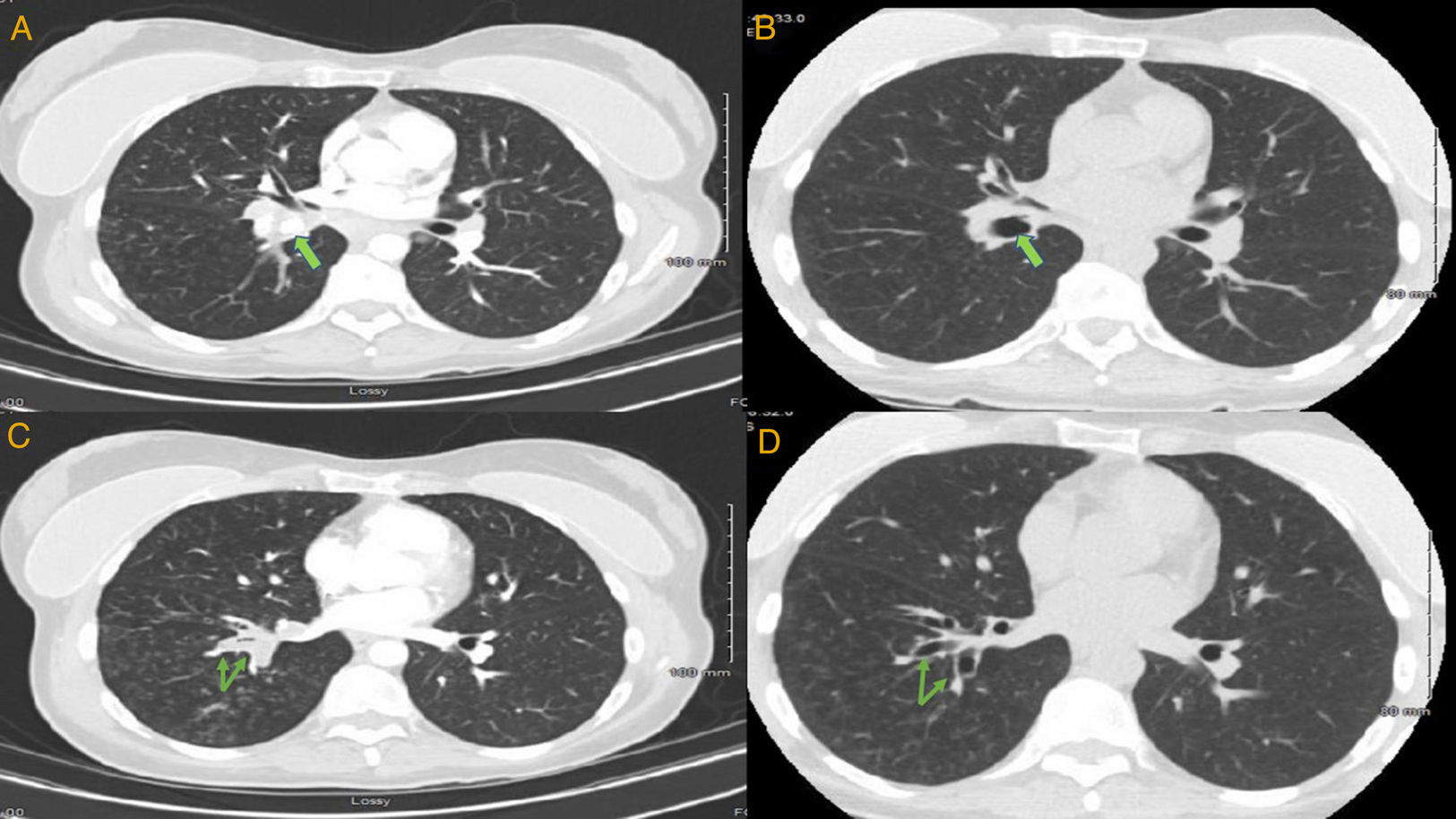
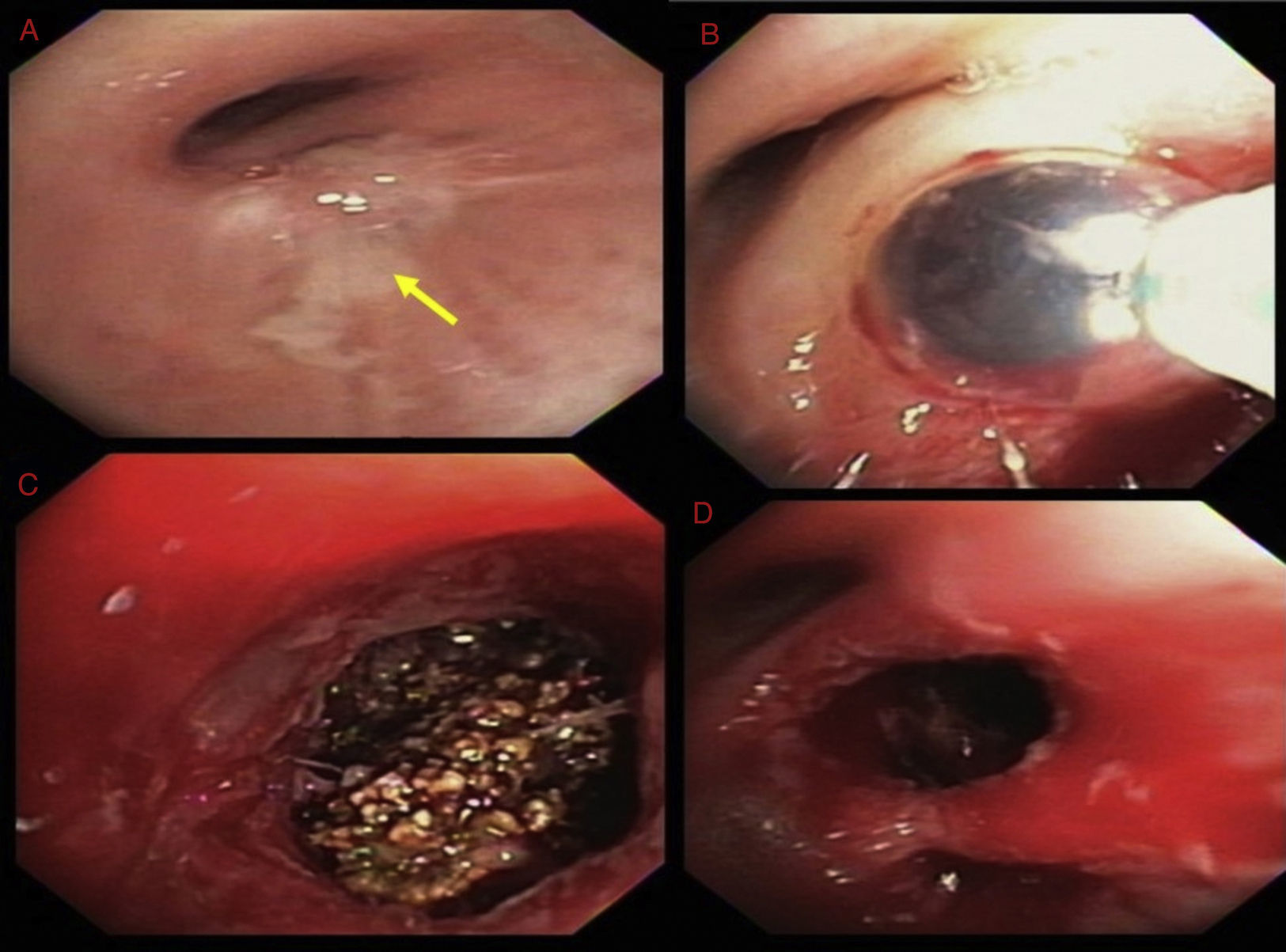
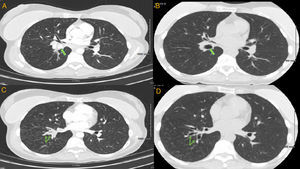
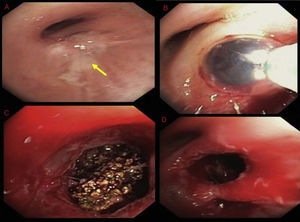
A 45-year-old female presented with a chronic cough. Her symptoms started 20 years back when she was diagnosed with right-sided pneumonia and empyema, requiring surgical decortication. Since then she had regularly been having episodes of coughing and dyspnea, variably treated with antibiotics, steroids and inhalers. However, for the last several weeks, her symptoms had been persistent. Chest CT showed right lower lobe (RLL) bronchiectasis, nodularity and a calcified right hilar lesion, suggestive of a calcified lymph node (Fig. 1, panel A). Bronchoscopy revealed a raised lesion with granulation tissue at the distal end of bronchus intermedius (Fig. 2, panel A). It was causing near complete occlusion of the RLL bronchus. Fogarty balloon catheter was used to dilate the RLL orifice (Fig. 2, panel B). After removal of pus and granulation tissue, a foreign body was noted (Fig. 2, panel C). Rigid bronchoscope and forceps were used to break and retrieve the foreign body. After foreign body's retrieval, patent RLL segments were noted (Fig. 1, panel D). Repeat chest CT showed patent RLL bronchi (Fig. 1, panels B, D) The foreign body appeared to be a fruit seed which the patient likely aspirated 20 years earlier, leading to recurrent post-obstructive pneumonia. Seeds and bones are the most frequently aspirated foreign bodies in adult population.1,2
Chest CT. Panels A, C are cuts from pre-procedure scan. Panels B, D are the same cuts from post procedure scan. Calcified right hilar lesion (arrow, panel A). Collapsed RLL segmental bronchi (arrows, panel C). Post procedure, patent RLL bronchus (arrow, panel B). Post procedure, patent RLL segmental bronchi (arrows, panel D).
Bronchoscopic images. Raised lesion with granulation tissue at the distal end of bronchus intermedius (panel A). Fogarty balloon catheter being used to dilate the RLL orifice (panel B). Foreign body with brown, irregular surface (panelC). Patent RLL segments after retrieval of the foreign body (panel D).