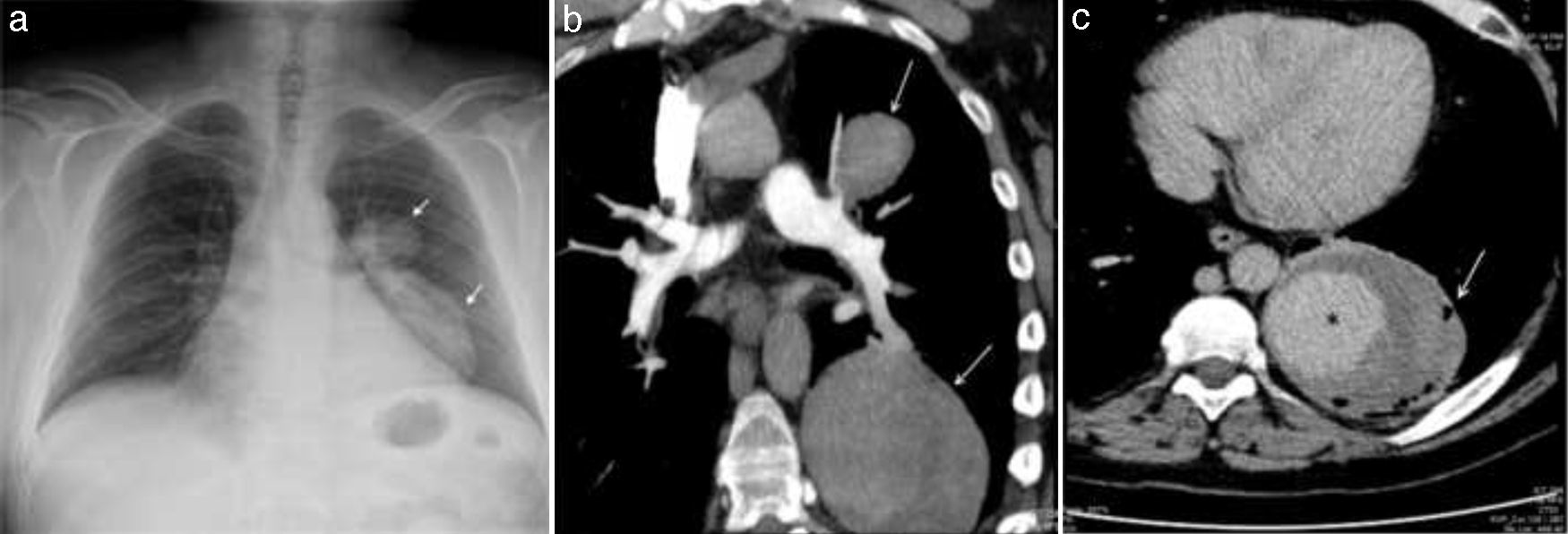
A 54-year-old man diagnosed with Behçet's Disease (BD) 5 years previously at another hospital was admitted to our center with massive hemoptysis. The chest X-ray showed bilobular, smooth edged opacity localized in the left hilar and paracardiac region that not conceal heart contours (Fig. 1a, arrow). Computerized tomography pulmonary angiography showed 2 lesions originating from the upper and lower branches of the left pulmonary artery, their central zones filled with contrast material, at early phase of imaging (Fig. 1b, arrow). Contrast filling was enhanced at late phase of the imaging (Fig. 1c, asterisk). The periphery of the lower lesion was less opaque, with small air bubbles (Fig. 1c, arrow). The signs suggested thrombosed pseudoaneurysms ruptured into the bronchus. The patient was diagnosed with a rupture of pulmonary artery aneurysm (PAA) and high dose glucocorticoid and cyclophosphamide pulse therapy was started.
The chest X-ray showed opacity localized in the left hilar and paracardiac region (a, arrow). Computerized tomography pulmonary angiography (CTPA) showed 2 lesions, originating from upper and lower branches of the left pulmonary artery (b, arrow). Contrast filling was enhanced at late phase of imaging (c, asterisk), with small air bubbles at the periphery of the lower lesion (c, arrow).
BD is a multi-system inflammatory disorder, classified as vasculitis. PAA represent the major complication of pulmonary BD and has a poor prognosis, being associated with massive hemoptysis.1 Medical treatment with immunosuppressive agents is preferred over surgery because a recurrent aneurysm or fistula at the anastomotic site is a common complication after surgical resection.2
Please cite this article as: Seyhan EC, Gunluoglu MZ, Erol C. Ruptura intrabronquial de un aneurisma de arteria pulmonar en un paciente con enfermedad de behçet. Arch Bronconeumol. 2017;53:29.