Cuantificar el grado de cumplimiento de las recomendaciones contenidas en la guía en la práctica clínica publicada en 2009 por la ERS y la ESTS sobre evaluación preoperatoria del riesgo de la resección pulmonar en la actividad asistencial diaria de un hospital terciario.
MétodoEstudio prospectivo observacional. Registro de datos en tiempo real de los pacientes consecutivos remitidos para evaluación desde septiembre de 2009 a diciembre de 2010. Se ha registrado la presencia o ausencia de los estudios incluidos en el algoritmo, sus resultados y, en caso de ausencia de alguna prueba, por qué no se realizó. Se aportan las tasas de mortalidad hospitalaria y de morbilidad cardiorrespiratoria postoperatoria.
ResultadosDe 173 pacientes evaluados, 171 casos fueron resecados, con una mortalidad del 1,2% y una morbilidad cardiorrespiratoria del 11,7%. La tasa de fallos del primer nivel del algoritmo fue del 4,6%, y del segundo nivel (prueba de esfuerzo) del 26%. La ausencia de prueba de esfuerzo se debió a problemas estructurales hospitalarios y a la incapacidad del paciente para realizarla. De los pacientes que se sometieron a esta prueba, 31 alcanzaron un VO2max de 20ml/kg-min o más y fueron intervenidos sin cálculo de los valores de FEV1ppo y DCLOppo; 35 precisaron de dicho cálculo para decidir su operabilidad, y en 2 casos no se recomendó la intervención por inoperabilidad funcional del paciente.
ConclusionesEn el 18,5% de los casos se han encontrado fallos en la aplicación del algoritmo, fundamentalmente por ausencia de la prueba de esfuerzo. La tasa de adecuación al algoritmo debe ser mejorada antes de poder realizar otros estudios de validación.
To quantify the degree of compliance with the recommendations of the clinical practice guidelines published in 2009 by the ERS and the ESTS regarding the preoperative assessment of risk of lung resection in daily clinical practice at a tertiary hospital.
MethodA prospective, observational study of real-time data collected from consecutive patients who had been referred for evaluation from September 2009 to December 2010. We recorded the presence or absence of the recommended studies included in the algorithm, their results and, when a test was missing, the reasons why it was not performed. Hospital mortality and cardio-respiratory morbidity rates are also presented.
Results173 patients were evaluated. In 171 cases, lung resection was performed, with a mortality of 1.2% and a cardio-respiratory morbidity of 11.7%. The failure rate of the first level of the algorithm was 4.6% and for the second level (VO2max test) it was 26%. The absence of exercise tests was mainly due to hospital structural problems and the patients’ inability to perform it. Out of the patients who performed the exercise testing, 31 reached a VO2max of 20ml/kg-min or more and underwent surgery without calculation of FEV1ppo and DCLOppo; 35 patients required the calculation to determine their operability and in 2 cases the intervention was not recommended due to functional inoperability of the patient.
ConclusionsThe validation process found lack of compliance with the proposed algorithm in 18.5% of the cases basically due to the absence of the exercise tests. The rate of adherence to the algorithm recommendations should be improved before performing any other validation studies.
En el año 2009, la European Respiratory Society (ERS) y la European Society of Thoracic Surgery (ESTS) publicaron una guía de práctica clínica (GPC)1, resultado de la colaboración entre especialistas, que contiene las recomendaciones para una correcta y exhaustiva evaluación pretratamiento de los pacientes con carcinoma broncogénico. En especial, se revisaron las evidencias sobre el riesgo de la resección pulmonar, y el resultado se resumió en un algoritmo de evaluación preoperatoria en el que cada punto de decisión está avalado por un grado de evidencia conocido y robusto.
El objetivo de este trabajo es presentar una fase inicial de la validación del proceso de evaluación preoperatorio propuesto, que consiste en cuantificar el grado de cumplimiento de las recomendaciones contenidas en la GPC en la práctica clínica real de un hospital terciario.
MétodoEstudio prospectivo observacional desarrollado entre septiembre de 2009 y diciembre de 2010. Se han registrado en tiempo real los datos de los 173 pacientes consecutivos remitidos para resección pulmonar durante el periodo de inclusión. Los casos procedían fundamentalmente de 6 hospitales que remiten los casos de forma regular para ser intervenidos en nuestro hospital. Por ello, antes de iniciar el estudio se habían consensuado los criterios de evaluación funcional con dichos centros para adaptarlos a las recomendaciones europeas.
A lo largo de todo el tiempo de estudio se consideraron candidatos a la evaluación preoperatoria los pacientes con un índice de Karnosfky superior al 50%, que no presentaran otra patología sistémica con peor pronóstico que el propio tumor y que no mostraron datos concluyentes de irresecabilidad tumoral en los estudios de imagen realizados.
Siguiendo las recomendaciones del algoritmo de decisión1 se establecen 3 niveles de decisión principales: evaluación preoperatoria general, test de esfuerzo y cálculo de los valores previstos postoperatorios de varias variables clave de la evaluación preoperatoria. Para cada nodo de decisión se establecen 2 o 3 salidas, según el nivel en que nos encontremos, que deciden sobre la operabilidad, la recomendación de un tratamiento alternativo a la cirugía o la necesidad de otras pruebas previas a la toma definitiva de decisión, hasta que en el nodo final se recomienda no operar o resecar hasta una cierta extensión pulmonar, según los cálculos realizados.
Detalles de cada uno de los niveles de decisión del algoritmoEstudio preoperatorio generalEl estudio preoperatorio que se consensuó con cada uno de los hospitales de referencia consistió en hemograma, análisis con parámetros de bioquímica general y hepática, estudio de coagulación, electrocardiograma, pruebas de imagen (radiología de tórax y tomografía computarizada [TC] de tórax con contraste) y, si era preciso por las características oncológicas del caso, tomografía por emisión de positrones (PET-scan). Si el paciente presentaba patología cardiológica conocida o sospechada, se realizaba una evaluación cardiológica completa. Respecto a la evaluación funcional respiratoria, los pacientes debían aportar una evaluación de volúmenes funcionales (espirometría basal y tras broncodilatación en valores absolutos y porcentuales para su edad, sexo y altura) y un estudio de difusión pulmonar (DLCO) con datos de difusión de monóxido de carbono ajustados para el valor de la hemoglobina del paciente. En la evaluación de la espirometría el valor clave es el valor de FEV1%, y en el estudio de difusión, la DLCO% ajustada por hemoglobina. Valores superiores al 80% permiten que el paciente sea intervenido sin necesidad de ninguna otra prueba. Si alguno de los 2 valores está por debajo, el paciente precisa una prueba con cálculo del consumo de oxígeno, preferiblemente de alta tecnología, antes de tomar una decisión.
Prueba de consumo de oxígeno (VO2max)Con los datos obtenidos de la evaluación funcional respiratoria se valora, siguiendo el algoritmo de evaluación propuesto1, la necesidad de realizar una prueba de ejercicio de alta tecnología que solo se puede realizar en nuestro hospital y por un único especialista formado para llevarla a cabo. La prueba de adquisición del consumo de oxígeno se desarrolla utilizando un módulo MasterScreen CPX de Jaeger-Vyasis-Healthcare. De esta prueba se obtienen los datos de consumo de oxígeno en valores absolutos (ml/kg-min) y pico (%), que se utilizarán, si es preciso, en los cálculos posteriores, de tal forma que pacientes con valores absolutos iguales o superiores a 20ml/kg-min o con valores pico iguales o superiores al 75% pueden ser intervenidos sin ninguna otra prueba y toleran cualquier tipo de resección. Los pacientes con valores absolutos inferiores a 10ml/kg-min o bien al 35% se clasifican como inoperables por su alto riesgo y se recomienda un tratamiento alternativo. Por último, el grupo de pacientes con valores intermedios necesitan otros cálculos antes de tomar una decisión.
Cálculo de los valores de FEV1%, DLCO% y VO2pico(%) previstos postoperatoriosSegún el algoritmo1, en algunos casos es necesario dar el siguiente paso en la evaluación que se corresponde con el cálculo de los valores previstos postoperatorios de la función pulmonar considerando tanto el volumen (FEV1%) como la difusión (DLCO%), así como de los valores obtenidos en la prueba de esfuerzo: VO2max (ml/kg-min) y el valor del VO2pico(%). Los cálculos se realizan en 2 niveles: primero se calculan los valores previstos postoperatorios para el FEV1% y la DLCO% según la resección propuesta, y si alguno de dichos valores está por debajo del 30%, es necesario entonces calcular el valor del VO2pico(%) y del VO2max. Si finalmente el VO2max estuviera por debajo de 10ml/kg-min o el VO2pico(%) estimado fuera inferior al 35%, de nuevo se recomienda al paciente un tratamiento alternativo.
El cálculo de dichos valores postoperatorios se realiza siguiendo la fórmula publicada por Nakahara et al.2. En dicha fórmula, cada segmento es responsable del 5,26% de los volúmenes registrados. Además, se consideran los segmentos que necesitan ser resecados para una extirpación oncológicamente válida del carcinoma y los segmentos que por broncoscopia están obstruidos por el tumor y, por lo tanto, no intervienen en el intercambio respiratorio.
Variables adquiridasEn este trabajo se ha registrado la presencia o ausencia de los estudios requeridos (FEV1%, DLCO% ajustada por hemoglobina, VO2max (ml/kg-min), VO2 pico(%) y las calculadas: FEV1ppo, DLCO%ppo, VO2picoppo en cada nivel del algoritmo, sus resultados y, si faltara alguna prueba, la causa por la que no se realizó. Se aportan las tasas de mortalidad hospitalaria y de morbilidad cardiorrespiratoria de la serie. Finalmente se aportan los datos de ajuste en cada uno de los niveles de decisión y la tasa final de fallos en la validación de la aplicación del algoritmo.
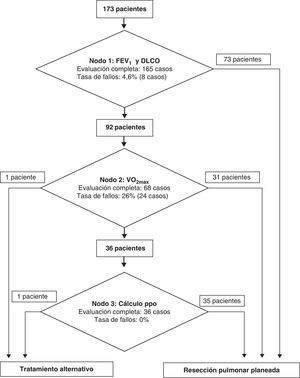
ResultadosDe los 173 pacientes evaluados para la resección pulmonar que cumplían los requisitos básicos, se han intervenido 171. La morbilidad cardiorrespiratoria de la serie es del 11,7%, y la mortalidad, del 1,2% (2 pacientes). Ambos pacientes —de 55 y 75 años, respectivamente— presentaban un carcinoma epidermoide de pulmón y tenían el antecedente común de haber sido tratados de un carcinoma de laringe; uno recibió radioterapia y el otro fue intervenido. En el primer caso el tumor, que nacía en el lobar superior derecho y obstruía completamente el lóbulo, afectaba a la carina principal, por lo que se realizó una neumonectomía derecha con resección de carina traqueal. Funcionalmente el paciente partía de una buena función y no precisó realización de prueba de consumo de oxígeno. El paciente falleció a las 48h, al desarrollar un edema posneumonectomía. El segundo paciente falleció como consecuencia de una insuficiencia respiratoria y cardiaca derecha irreversibles en el contexto de una fibrosis pulmonar de larga evolución que no había precisado tratamiento en ningún momento y que funcionalmente estaba respetado: FEV1% del 102%; DLCO% de 70 y VO2max de 19,8ml/kg-min. Los valores estimados postoperatorios fueron: FEV1%ppo de 74% y DLCOppo de 51,6%. Al paciente se le realizó una lobectomía inferior derecha.
En el primer nodo de decisión se han encontrado un 4,6% de fallos por incumplimiento (8 pacientes) (fig. 1). En un caso no se realizó la espirometría; en 6, el estudio de difusión de CO, y en un caso faltaban ambos parámetros. Sabemos que las pruebas no se realizaron en 8 casos por razones técnicas: i pacientes fueron incapaces de realizar correctamente las exploraciones exigidas, y en el caso restante se desconoce la razón por la que el paciente no realizó ninguna de las 2 exploraciones. Los valores de FEV1% y DLCO% ajustados por hemoglobina fueron suficientes para que 73 pacientes fueran intervenidos sin ninguna otra exploración adicional.
La prueba de esfuerzo —siguiente escalón en el algoritmo de toma de decisiones— se realizó en 68 pacientes de los 92 en los que estaba indicada (26% de fallos). Las causas por las que la prueba no se llevó a cabo fueron: en 14 casos, por razones estructurales hospitalarias; en 6 casos, la prueba estaba contraindicada por razones cardiovasculares; en 3 casos, por imposibilidad para realizarla por limitaciones articulares a nivel de la rodilla, y en el último caso, por la ocurrencia de un cuadro vasovagal que impidió que se pudiera desarrollar el test. Los datos obtenidos de esta prueba nos permitieron intervenir a 31 pacientes sin necesidad de realizar más estudios, un paciente fue reconocido como inoperable por alcanzar un consumo de oxígeno inferior a 10ml/kg-min y en 36 casos fue necesario proseguir con otros cálculos antes de decidir sobre su operabilidad.
Tras realizar los cálculos correspondientes al tercer nodo de decisión, 35 pacientes fueron intervenidos. Un paciente fue considerado inoperable funcionalmente, ya que su consumo pico era inferior al 35%, y se le recomendó un tratamiento alternativo. En este nodo de decisión no se produjeron fallos en la adquisición del cálculo de las variables por las características del nodo.
Esto significa, en resumen, que en el 81,5% de los casos (141/173) se siguieron todas las recomendaciones propuestas en la guía, mientras que el algoritmo se incumplió en el 4,6% (8/173) de los casos en el primer nodo y en el 26% (24/92) de los pacientes que precisaban el cálculo del consumo de oxígeno.
DiscusiónTrabajar con guías de práctica clínica (GPC) significa utilizar la mejor evidencia científica disponible para el beneficio de nuestros pacientes. Pero a pesar de lo que significan, las GPC no se han implantado universalmente y no han dado los frutos esperados en la mejora continua de la calidad asistencial3. Se han descrito fallos en la implantación de las GPC a muchos niveles: extrínsecos a la propia guía (p.ej., de tipo organizativo) o intrínsecos (por ambigüedad, inconsistencia o porque la guía esté incompleta, entre otros)4. Por la importancia que se concede al trabajo habitual con las GPC, se han diseñado herramientas, como por ejemplo el GLIA (GuideLine Implementability Appraisal), para conocer mejor y anticipar los posibles obstáculos en la implantación y el desarrollo de cualquier nueva GPC3. Mediante encuestas internacionales5 se sabe que muchos de los autores de GPC no tienen un programa de mejora continua de la o las GPC creadas y que carecen de personal dedicado específicamente a analizar y divulgar esas GPC. Algunos de ellos piensan que deben ser las unidades receptoras las encargadas de realizar los análisis y las mejoras. Esta es una de las justificaciones para el desarrollo de este trabajo: conocer si en nuestro entorno, con las condiciones generales de que disponemos, podemos desarrollar con suficiente rigurosidad el protocolo recomendado de evaluación preoperatoria. Por lo tanto, no se trata de un estudio de predicción sino solamente de un estudio descriptivo limitado a los pacientes enviados para evaluación. Es muy probable que exista un sesgo de selección previo a la remisión de pacientes por decisiones a otros niveles que se escapan a nuestro conocimiento y a nuestro control.
Sabemos que aplicar la evidencia científica de mayor nivel a la evaluación preoperatoria resulta muy importante, porque el tratamiento quirúrgico del cáncer de pulmón es el que ofrece más posibilidades de curación en estadios precoces, pero a la vez es el que va a condicionar un cambio más importante y más brusco en la calidad de vida del paciente. Es especialmente relevante contar con una herramienta que nos permita distinguir entre los pacientes que pueden presentar complicaciones muy importantes, incluso mortalidad, de los que, pese a su comorbilidad, pueden tolerar el procedimiento1. Según una reciente publicación6, la mortalidad bruta de la resección pulmonar recogida en la base de datos europea de la ESTS, que incluye datos de más de 4.000 pacientes, es del 3%. En nuestra serie, la tasa de mortalidad global es del 1,2%. Es un dato de mortalidad inferior a la de la serie europea, que muestra un 2,9% de mortalidad bruta para los casos intervenidos en España7 y que sugiere que es un algoritmo seguro cuya aplicación puede mantener la mortalidad en tasas muy bajas.
Posiblemente, de los fallos detectados en la aplicación del algoritmo, el que más llama la atención sea la ausencia de pruebas de función pulmonar, que se da en 8 pacientes (el 4,6% de la serie). Los registros de las pruebas de función respiratoria deben cumplir unas normas bien definidas para tener garantías de calidad8, y según un artículo español reciente9, en el que se realiza espirometría a un grupo representativo de población española entre 65 y 85 años, hasta el 10% de estudios pueden no ser técnicamente aceptables. Este es un problema muy importante, pues la base de nuestras estimaciones sobre el riesgo quirúrgico está en las mediciones de los volúmenes espirométricos, concretamente del FEV1%, aun con todas las limitaciones que tiene este parámetro1, y de la DLCO. Es posible que en los casos de imposibilidad técnica para realizar pruebas de función pulmonar válidas, el paciente deba realizar una prueba de esfuerzo como valoración alternativa y objetiva de su riesgo.
El problema detectado más importante ocurre a nivel del segundo nodo de decisión: en cuanto a la prueba de esfuerzo de alta tecnología, solo 68 de 92 pacientes (el 84%) la realizaron. Se considera la prueba más segura para cuantificar el riesgo individual de complicaciones postoperatorias1. Esta técnica, sin embargo, no está disponible en todos los centros donde se realiza cirugía pulmonar. Al revisar las razones por las que no se ha llevado a cabo, destaca que las causas estructurales hospitalarias han sido las responsables de 14 de los 24 fallos, entre ellas, el que solo una persona está entrenada para poder desarrollar e interpretar la prueba, o los problemas técnicos por avería, que impidieron que la prueba se realizara en un tiempo razonable para no alargar indefinidamente el tiempo de espera. Es posible que la solución a este problema esté en la misma GPC1, que reconoce la capacidad de la prueba estandarizada de subir escaleras limitada por síntomas como una alternativa a la prueba de alta tecnología de laboratorio. La discriminación que permite esta prueba puede ayudar a reducir el número de pacientes que necesita la prueba de laboratorio. Sin embargo, esta prueba ha sido criticada por su poca estandarización y por la dificultad para realizarla en un lugar seguro para el paciente.
Otro dato interesante es que la imposibilidad del paciente para realizar la prueba de consumo de oxígeno de alta tecnología también es un factor muy importante, responsable del 41,6% de los fallos en nuestra serie. Respecto a este factor, las contraindicaciones de tipo cardiovascular que presentaron 6 pacientes o las limitaciones articulares de otros 3 enfermos son especialmente relevantes en una población cada vez de mayor edad y, por ello, con más comorbilidad. Resulta muy difícil solventar esta limitación. Es posible que haya que desarrollar nuevas estrategias para poder medir la capacidad de ejercicio del paciente sin poner en riesgo su seguridad realizando pruebas que provocan mucho estrés, como podría ser medir la distancia que recorre andando y la calidad del ejercicio que el paciente realiza diariamente en su vida normal10.
En conclusión, al cuantificar el grado de cumplimiento de las recomendaciones contenidas en la GPC de evaluación preoperatoria del riesgo quirúrgico hemos detectado una tasa de fallos del 18,5% en su aplicación. El 75% de estos fallos se producen en el segundo nodo de decisión por la no realización de la prueba de esfuerzo, debido, sobre todo (58,3% de los casos), a problemas estructurales del hospital.