Artery embolization (AE) is a safe and useful procedure in the management of massive hemoptysis. The objective of our study was to describe the experience of AE in a tertiary referral center, to characterize angiographic findings at the time of recurrence, and to analyze factors associated with these findings.
Material and methodsObservational retrospective study of patients presenting with life-threatening hemoptysis. All consecutive patients with at least one episode of hemoptysis that required AE during a 13-year period were included. The effects of (i) time to recurrence, (ii) use of coils, and (iii) number of arteries embolized on the likelihood that the recurrence was secondary to recanalization were assessed.
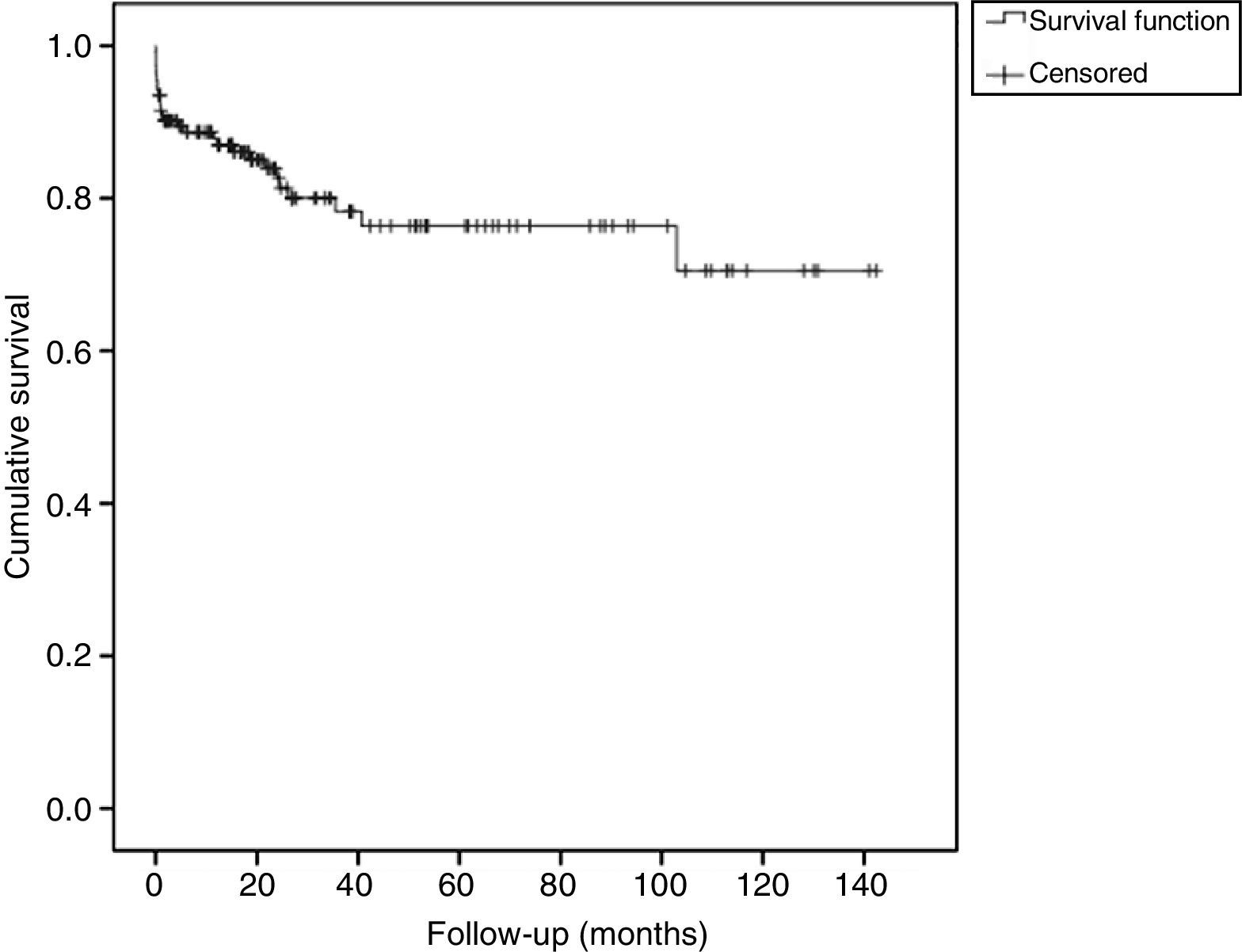
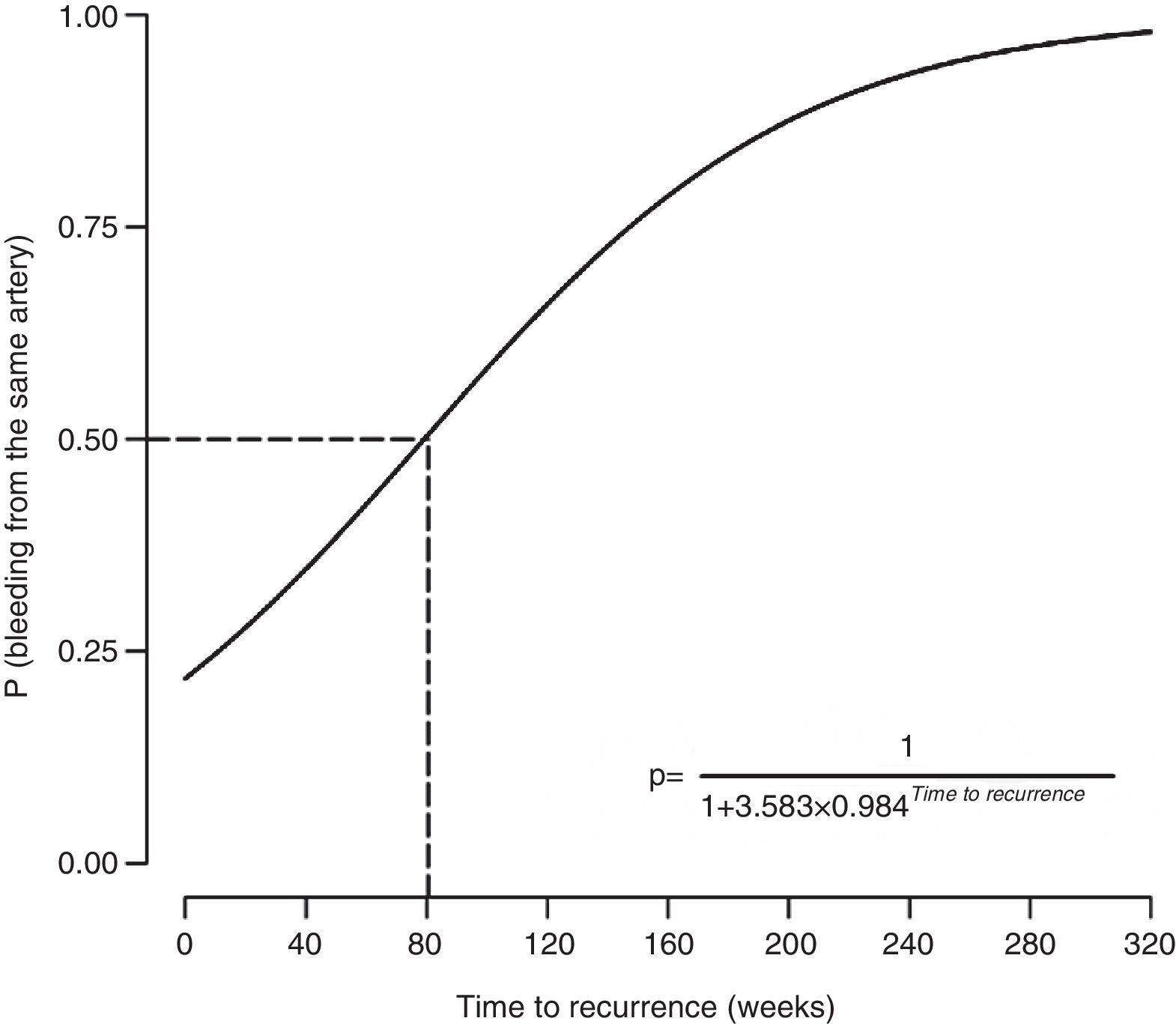
ResultsOne hundred and seventy-six patients were included in the study. Twenty-two patients (12.5%) died due to hemoptysis. Probability of recurrence-free survival at one month was 0.91 (95% CI: 0.87–0.95), at 12 months was 0.85 (95% CI: 0.79–0.91), and after 3 years was 0.75 (95% CI: 0.66–0.83). A longer time to recurrence was associated with a higher probability that the hemorrhage affected the same artery (estimate=0.0157, z-value=2.41, P-value=.016).
ConclusionAE is a safe and useful technique in the management of massive and recurrent hemoptysis. Nevertheless, recurrence after embolization is not uncommon. Recurring hemoptysis due to recanalization is related to time to recurrence, but not to the use of coils or number of arteries embolized.
La embolización arterial (EA) es útil en el tratamiento de la hemoptisis amenazante. El objetivo de este trabajo es describir la experiencia de un centro universitario terciario con la EA como tratamiento de la hemoptisis amenazante, caracterizar los hallazgos angiográficos cuando hay recidivas, y analizar los factores asociados con estos hallazgos.
Material y métodosEstudio observacional retrospectivo en el que se incluyeron todos los pacientes con una EA debido a hemoptisis amenazante durante un periodo de 13 años. Los efectos de: (a) tiempo hasta recurrencia; (b) uso de coils, y (c) número de arterias embolizadas sobre la probabilidad que el sangrado tuviera el mismo origen vascular que en el episodio previo fueron analizados.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 176 pacientes en el estudio. Murieron por hemoptisis 22 pacientes (12,5%). La probabilidad de sobrevivir libre de recidiva al mes fue de 0,91 (IC 95%: 0,87–0,95), a los 12 meses de 0,85 (IC 95%: 0,79–0,91) y a los 3 años de 0,75 (IC 95%: 0,66–0,83). La probabilidad de que la recurrencia fuera debida a una afectación de la misma arteria dependía del tiempo hasta la recurrencia (estimado=0,0157, valor de z=2,41, valor de p=0,016).
ConclusiónLa EA es efectiva en el tratamiento de la hemoptisis, pero las recidivas no son infrecuentes. La recidiva del sangrado por recanalización de la arteria embolizada está relacionada con el tiempo transcurrido hasta la recidiva, pero no con el uso de coils ni con el número de arterias embolizadas.
Since the initial description by Remy et al.,1 arterial embolization (AE) has become a widely used procedure in the treatment of life-threatening and recurrent hemoptysis. Several studies have examined its effectiveness, safety and usefulness.2–10 However, hemoptysis relapse may occur even after embolization in 9.25%–50% of cases.11–24 When this occurs, it is associated with increased risk of mortality.20,22
Recurrence of bleeding after AE has been reported as possibly due to incomplete embolization of vessels, recanalization of previously embolized vessels, revascularization of collateral circulation or progression of the underlying lung disease.12,17,19,23 No studies have examined the relationship between the technical characteristics of the procedure and the risk of recurrence due to recanalization.
The aim of this paper is to describe the experience of our center with AE in the treatment of life-threatening hemoptysis, to analyze the technical characteristics of AE, and to identify factors associated with recurrence due to recanalization.
Material and MethodsStudy SampleThis is a retrospective observational study including 176 patients presenting to a tertiary hospital with life-threatening hemoptysis, who underwent AE. All patients with at least one episode of life-threatening hemoptysis and who had been embolized were consecutively included over a period of 13 years (January 1999–December 2011). Life-threatening hemoptysis was defined as a bleed of at least 200ml in 24h, 100ml a day over 3 consecutive days, or any less severe but life-threatening hemoptysis. The medical records of these patients were reviewed and the following data were collected for analysis: age, gender, etiology of hemoptysis, AE findings, procedure details (embolized arteries, number of embolized arteries, use of coils) and time elapsed between embolizations. In the absence of a more specific diagnosis, the diagnosis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) or bronchiectasis was based on the presence of emphysema or bronchiectasis, respectively, on a computed tomography (CT) scan of the chest. If a new diagnosis was not made, the diagnosis at the time of the second embolization was assumed to be the same as in the previous embolization.
Bronchial Artery EmbolizationAll procedures were performed by two expert interventional radiologists, using the methodology described elsewhere.4 Briefly, the bronchial arteries of both hemithoraces and the non-bronchial systemic arteries of the pathological hemithorax were systematically inspected, and a thoracic aortography was performed. If the study of the bronchial systemic arteries and the branches that would irrigate the lung parenchyma did not reveal the origin of hemoptysis, a study of the pulmonary arteries was performed. The material used for embolization was resorbable, e.g. Spongostan® particles, and non-resorbable, e.g. polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) particles, embospheres and metal coils. For embolization of distal arterial bed, embospheres or PVA particles were systematically used. Metal coils were used for proximal embolization, when catheterization was stable and when permitted by the morphology and size of the artery. If coils could not be used for proximal embolization, Spongostan® particles were used.
Whenever technically possible, all the abnormal vessels that irrigated the affected area were embolized. If pulmonary involvement was not detectable, all the arteries that could be catheterized were occluded. Contraindications for embolization were visualization of the anterior spinal branch or catheter instability. Pulmonary angiography was not routinely performed.
RecurrenceRecurrence was defined as a new episode of life-threatening hemoptysis requiring AE in a patient with previous history of AE. The angiographic findings and factors related to reembolization were collected. Angiographic findings at the time of recurrence were compared with those of the previous episode. In patients with more than one recurrence, each episode was compared with the immediately previous one. It was considered that a relapse was due to recanalization when bleeding occurred in the same artery embolized in the previous intervention.
Statistical AnalysisSPSS version 19.0 (SPSS, Chicago, IL) was used for descriptive and survival analysis. The results of quantitative variables are expressed as mean and standard deviation. Qualitative variables are shown as absolute values and percentages. The survival curve was constructed according to the Kaplan–Meier method. Survival probability is shown with a confidence interval of 95%.
The following relationships were analyzed with four separate mixed-effects logistic models using the package “lme4”25 for R26: (a) time to recurrence, (b) use of coils, and (c) number of embolized arteries, with the probability of the bleeding being caused by recanalization. The regression factor of interest (time to recurrence) was set as a fixed effect, while patient identification was set as a random effect. With this approach, the origin of bleeding “from or not from” the same artery was modeled as a binary result, and the nature of repeated measures of the data was taken into account.
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of our hospital.
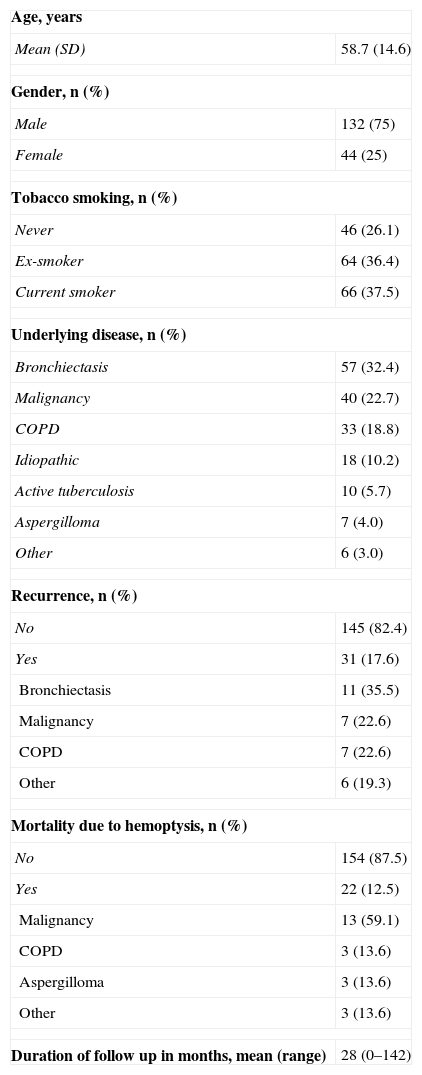
ResultsEtiology of HemoptysisThe characteristics of the 176 patients included in the study are shown in Table 1. The diseases most frequently causing hemoptysis were bronchiectasis, followed by malignancy (primary lung tumor or metastases from other organs), and chronic bronchitis/COPD. Of the 39 patients with malignancy, diagnosis was established prior to embolization in 23 cases (59%).
Characteristics of the 176 Patients Included in the Study.
| Age, years | |
| Mean (SD) | 58.7 (14.6) |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 132 (75) |
| Female | 44 (25) |
| Tobacco smoking, n (%) | |
| Never | 46 (26.1) |
| Ex-smoker | 64 (36.4) |
| Current smoker | 66 (37.5) |
| Underlying disease, n (%) | |
| Bronchiectasis | 57 (32.4) |
| Malignancy | 40 (22.7) |
| COPD | 33 (18.8) |
| Idiopathic | 18 (10.2) |
| Active tuberculosis | 10 (5.7) |
| Aspergilloma | 7 (4.0) |
| Other | 6 (3.0) |
| Recurrence, n (%) | |
| No | 145 (82.4) |
| Yes | 31 (17.6) |
| Bronchiectasis | 11 (35.5) |
| Malignancy | 7 (22.6) |
| COPD | 7 (22.6) |
| Other | 6 (19.3) |
| Mortality due to hemoptysis, n (%) | |
| No | 154 (87.5) |
| Yes | 22 (12.5) |
| Malignancy | 13 (59.1) |
| COPD | 3 (13.6) |
| Aspergilloma | 3 (13.6) |
| Other | 3 (13.6) |
| Duration of follow up in months, mean (range) | 28 (0–142) |
COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Immediate bleeding control was achieved (no recurrence in the first week) in 169 patients (96%). Hemoptysis mortality despite AE was 12.5% (22 patients) (Table 1). Of these, four had required a second embolization. The most frequent causes of bleeding in patients who died were malignancy (59.1%), followed by aspergilloma and COPD, with three cases in each group (13.6%).
One patient (0.6%) had spinal cord ischemia. There were no other serious complications.
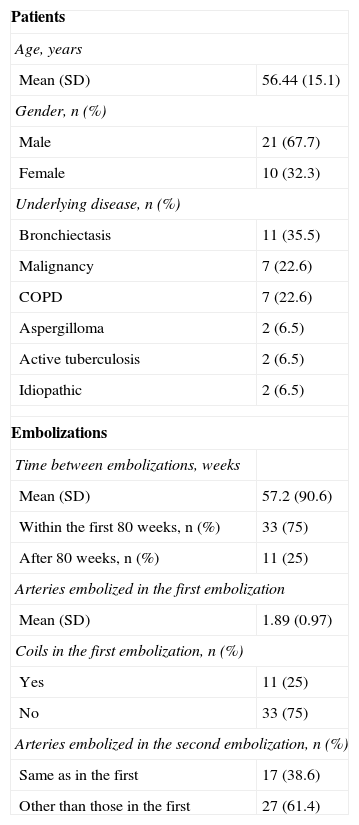
Recurrence of Hemoptysis During Follow-upThirty-one patients presented with recurrent bleeding during the study period. These 31 patients underwent a total of 77 angiograms with AE. The characteristics of these patients and their recurrences are shown in Table 2. The angiographic findings in the second AE, and the characteristics of the previous embolization are described in Table 3.
Characteristics of 31 Patients With Recurrence Included in the Study and Characteristics of the 44 Pairs of Embolizations.
| Patients | |
| Age, years | |
| Mean (SD) | 56.44 (15.1) |
| Gender, n (%) | |
| Male | 21 (67.7) |
| Female | 10 (32.3) |
| Underlying disease, n (%) | |
| Bronchiectasis | 11 (35.5) |
| Malignancy | 7 (22.6) |
| COPD | 7 (22.6) |
| Aspergilloma | 2 (6.5) |
| Active tuberculosis | 2 (6.5) |
| Idiopathic | 2 (6.5) |
| Embolizations | |
| Time between embolizations, weeks | |
| Mean (SD) | 57.2 (90.6) |
| Within the first 80 weeks, n (%) | 33 (75) |
| After 80 weeks, n (%) | 11 (25) |
| Arteries embolized in the first embolization | |
| Mean (SD) | 1.89 (0.97) |
| Coils in the first embolization, n (%) | |
| Yes | 11 (25) |
| No | 33 (75) |
| Arteries embolized in the second embolization, n (%) | |
| Same as in the first | 17 (38.6) |
| Other than those in the first | 27 (61.4) |
SD, standard deviation; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
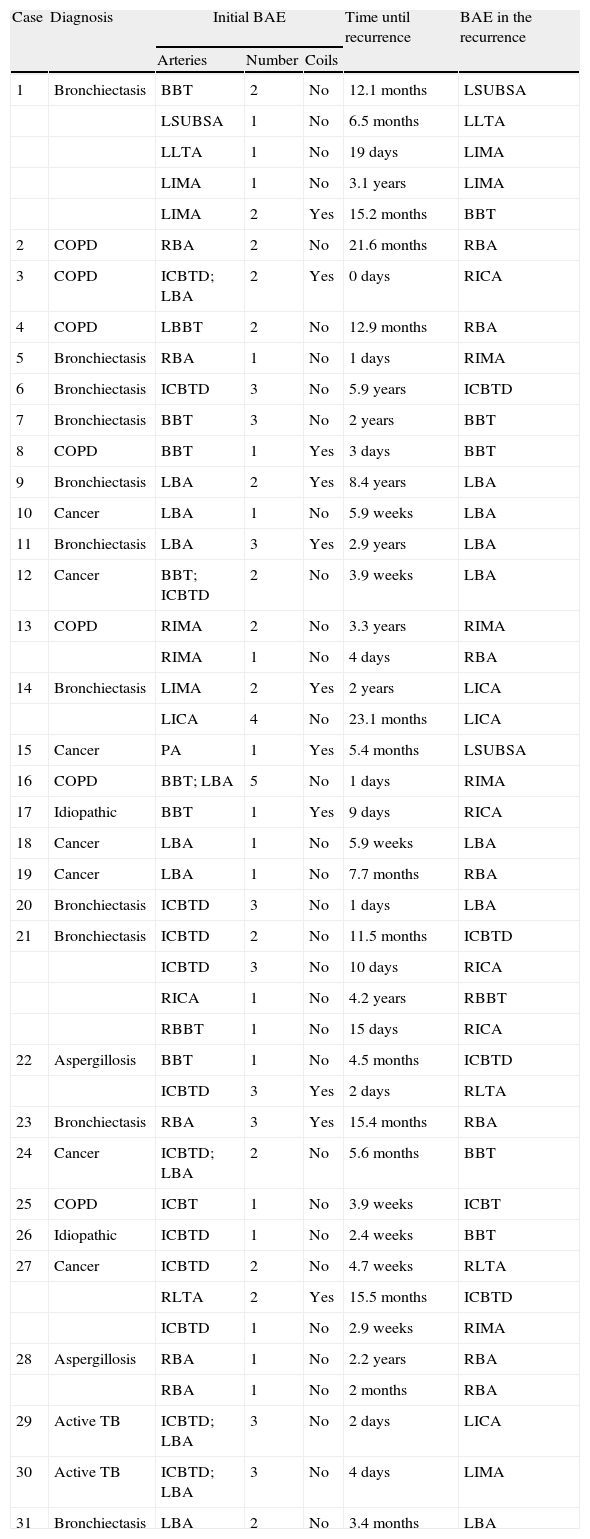
Angiographic Findings in the Second Arterial Embolization, and Characteristics of the Previous Arterial Embolization.
| Case | Diagnosis | Initial BAE | Time until recurrence | BAE in the recurrence | ||
| Arteries | Number | Coils | ||||
| 1 | Bronchiectasis | BBT | 2 | No | 12.1 months | LSUBSA |
| LSUBSA | 1 | No | 6.5 months | LLTA | ||
| LLTA | 1 | No | 19 days | LIMA | ||
| LIMA | 1 | No | 3.1 years | LIMA | ||
| LIMA | 2 | Yes | 15.2 months | BBT | ||
| 2 | COPD | RBA | 2 | No | 21.6 months | RBA |
| 3 | COPD | ICBTD; LBA | 2 | Yes | 0 days | RICA |
| 4 | COPD | LBBT | 2 | No | 12.9 months | RBA |
| 5 | Bronchiectasis | RBA | 1 | No | 1 days | RIMA |
| 6 | Bronchiectasis | ICBTD | 3 | No | 5.9 years | ICBTD |
| 7 | Bronchiectasis | BBT | 3 | No | 2 years | BBT |
| 8 | COPD | BBT | 1 | Yes | 3 days | BBT |
| 9 | Bronchiectasis | LBA | 2 | Yes | 8.4 years | LBA |
| 10 | Cancer | LBA | 1 | No | 5.9 weeks | LBA |
| 11 | Bronchiectasis | LBA | 3 | Yes | 2.9 years | LBA |
| 12 | Cancer | BBT; ICBTD | 2 | No | 3.9 weeks | LBA |
| 13 | COPD | RIMA | 2 | No | 3.3 years | RIMA |
| RIMA | 1 | No | 4 days | RBA | ||
| 14 | Bronchiectasis | LIMA | 2 | Yes | 2 years | LICA |
| LICA | 4 | No | 23.1 months | LICA | ||
| 15 | Cancer | PA | 1 | Yes | 5.4 months | LSUBSA |
| 16 | COPD | BBT; LBA | 5 | No | 1 days | RIMA |
| 17 | Idiopathic | BBT | 1 | Yes | 9 days | RICA |
| 18 | Cancer | LBA | 1 | No | 5.9 weeks | LBA |
| 19 | Cancer | LBA | 1 | No | 7.7 months | RBA |
| 20 | Bronchiectasis | ICBTD | 3 | No | 1 days | LBA |
| 21 | Bronchiectasis | ICBTD | 2 | No | 11.5 months | ICBTD |
| ICBTD | 3 | No | 10 days | RICA | ||
| RICA | 1 | No | 4.2 years | RBBT | ||
| RBBT | 1 | No | 15 days | RICA | ||
| 22 | Aspergillosis | BBT | 1 | No | 4.5 months | ICBTD |
| ICBTD | 3 | Yes | 2 days | RLTA | ||
| 23 | Bronchiectasis | RBA | 3 | Yes | 15.4 months | RBA |
| 24 | Cancer | ICBTD; LBA | 2 | No | 5.6 months | BBT |
| 25 | COPD | ICBT | 1 | No | 3.9 weeks | ICBT |
| 26 | Idiopathic | ICBTD | 1 | No | 2.4 weeks | BBT |
| 27 | Cancer | ICBTD | 2 | No | 4.7 weeks | RLTA |
| RLTA | 2 | Yes | 15.5 months | ICBTD | ||
| ICBTD | 1 | No | 2.9 weeks | RIMA | ||
| 28 | Aspergillosis | RBA | 1 | No | 2.2 years | RBA |
| RBA | 1 | No | 2 months | RBA | ||
| 29 | Active TB | ICBTD; LBA | 3 | No | 2 days | LICA |
| 30 | Active TB | ICBTD; LBA | 3 | No | 4 days | LIMA |
| 31 | Bronchiectasis | LBA | 2 | No | 3.4 months | LBA |
RBA, right bronchial artery; LBA, left bronchial artery; RICA, right intercostal artery; LICA, left intercostal artery; RIMA, right internal mammary artery; LIMA, left internal mammary artery; PA, pulmonary artery; LSUBSA, left subscapular artery; RLTA, right lateral thoracic artery; LLTA, left lateral thoracic artery; BAE, bronchial artery embolization; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; TB, tuberculosis; BBT, bibronchial trunk; RBBT, right bibronchial trunk; LBBT, left bibronchial trunk; ICBT, intercostobronchial trunk; RICBT, right intercostobronchial trunk; LICBT, left intercostobronchial trunk.
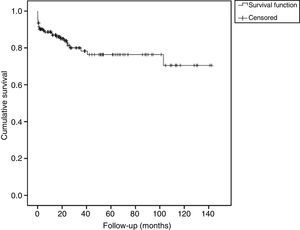
The survival function (without recurrence) of patients during the follow-up is shown in Fig. 1. The probability of recurrence-free survival at one month of follow-up was 0.91 (95% CI: 0.87–0.95). At 12 months this probability was 0.85 (95% CI: 0.79–0.91). The probability of recurrence-free survival at 3 years of follow-up was 0.75 (95% CI: 0.66–0.83).
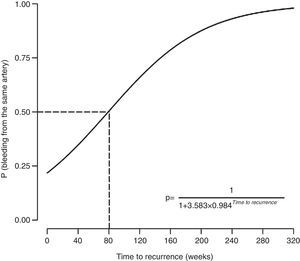
The probability of recurrence being caused by recanalization (i.e. involvement of the same artery) depended on the time to recurrence (estimated=0.0157, z-score=2.41, P=.016). Specifically, a longer time to recurrence was associated with increased probability of bleeding occurring from the previously embolized artery (Fig. 2). The probability of the bleeding source being an artery not previously embolized exceeded 50% when the relapse occurred within 80 weeks of hemoptysis. The probability of the bleeding source being an artery not previously embolized was below 50% when the relapse occurred after 80 weeks of hemoptysis.
There was no significant association between the use of coils or the number of embolized arteries and the angiographic findings (P=.268–.846).
DiscussionThis article describes the experience of a tertiary university hospital treating life-threatening hemoptysis with AE. Our data demonstrate that hemoptysis recurrence due to recanalization is associated with the time to recurrence, and not with the use of coils or the number of embolized arteries. According to this model, the cause of recurrence of hemoptysis within the first 80 weeks after AE would be incomplete embolization, while recurrence after 80 weeks would be secondary to recanalization in most cases.
The described causes of recurrence include progression of the underlying disease, revascularization or recanalization, incomplete embolization, and the occurrence of new blood flow from systemic collaterals. Early re-bleeds have been associated with an incomplete embolization, whereas later hemorrhage is usually due to disease progression.2,12,14,17,19,20 Thus, our study confirms the findings of other groups who included fewer cases of relapse, and adds the 80-week threshold. This 80-week time point could be an important guide for the angioradiology specialist when performing an AE in a patient with recurrence. While the inspection of all vascular territories likely to bleed is strongly recommended, we believe that this information could guide the specialist to initially explore a specific vascular territory. This information would be particularly useful in patients in a life-threatening situation due to hemoptysis, as it would help prioritize which arteries should be studied first. Secondly, a better indication of the bleeding site could help reduce the radiation dose, operative time, and the volume of contrast agent needed for the procedure.27
The etiology of hemoptysis has been associated with the recurrence rate after arterial embolization.13,14,20 Thus, hemoptysis due to tumor disease has higher short- and long-term recurrence rates.14,20 However, one group has reported reasonably good immediate results in patients with malignancy.23
Several studies have explored the likelihood of recurrence in relation to the procedure. Kim et al.21 compared to the results of embolization according to the material used, and found no statistically significant differences in the use of gelfoam, coils, or both, comparing patients with and without recurrence. Mal et al.17 analyzed the results of AE in relation to the interventional radiologist, or the material used for embolization. Brinson et al.16 reported that, in the case of recurrence, the incidence of bleeding from non-bronchial systemic collateral vessels was higher than in the first embolization (75% vs 8%). This is also true in our study, although the difference was not so marked (42% vs 29%). Other authors have analyzed the relationship between the angiographic findings (degree of vascularization) during embolization, and the outcome, and have not found significant differences.13,18,19
Overall, 17.6% of our patients experienced recurrence. The most frequent cause of hemoptysis was bronchiectasis, followed by COPD, active tuberculosis and mycetoma. The recurrence of hemoptysis was due to bronchiectasis in 37.5% of the cases, tumor disease in 25%, and COPD in 18.8%. Differences are detected when our findings are compared with previous series in Spain.9,10 Firstly, our recurrence rate (17.6%) is higher than that reported by Orriols et al.,10 but similar to that found by De Gregorio et al.9 The etiologies most frequently associated with recurrent bleeding, according to Orriols et al.,10 were malignancy and mycetoma, which coincides with the findings in our series. The findings are similar in other series.11–18 These groups agree that the likelihood of recurrence is high, ranging between 9.2511 and 50%.18 Aspergilloma is associated with poor prognosis with respect to both the likelihood of recurrence21–23 and mortality.23
In our study, 75% of recurrences occurred within 80 weeks of surgery, and 61.4% of the arteries embolized in the second procedure were different from those initially embolized. Recurrence occurred when embolization of the vessels involved was not complete, either due to the infiltrative nature of the disease, or because all the arteries involved were not located. If the bleeding site is known, all the anomalous bronchial arteries in the region should be embolized. If the bleeding site is unknown, all the bronchial arteries should be treated. If no abnormal bronchial arteries are detected, an exhaustive search of aberrant bronchial arteries and non-bronchial systemic arteries must be carried out. Failure to treat all the arteries involved increases the number of procedures required to resolve the bleeding,7 as found in our series. When recurrence occurs, mortality increases.22 Therefore, complete embolization and treatment of the causes are crucial to prevent recurrence secondary to the progression of disease.
The mortality rate in our series was 12.5%. Of the patients who died, the etiology of bleeding in 59.1% was malignancy. The mortality rate reported by Orriols et al.10 was 12.3%, similar to our data, and De Gregorio et al.9 reported a mortality at 3 days of 1.7%, well below the rate in the other two reports.
The main limitation of our study is that we performed a retrospective analysis of patients from a single center, which makes it difficult to generalize the results. Furthermore, data on the volume and duration of bleeding could not be recovered from all patients, so this important piece of information has not been included in the analysis. However, one of the strengths of the study is that all patients were clinically followed up in our center after the embolization episode, which means that all further episodes of bleeding or AE have been included in this study.
In summary, AE is an effective technique in the treatment of life-threatening hemoptysis, but recurrences are not uncommon. Hemoptysis recurrence due to recanalization of an embolized artery is related to the period of time until recurrence, but not with the use of coils or the number of embolized arteries.
Authors’ ContributionsIGO and JRM contributed to the study design. CC, JSS, FA and ZS contributed to the clinical data collection. JS, JM and JMM contributed to the angiography review. IGO and JR contributed to the statistical analysis. IGO, JSS, CC, JR, FA, JS, JM, JMM, ZS and JRM contributed to the critical reading of the manuscript.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no financial or personal relationships with people or organizations that could inappropriately influence their work in this article.
Please cite this article as: Garcia-Olivé I, Sanz-Santos J, Centeno C, Radua J, Andreo F, Sampere J, et al. Factores predictores de recanalización arterial en pacientes con hemoptisis amenazante que requieren embolización arterial. Arch Bronconeumol. 2014;50:51–56.