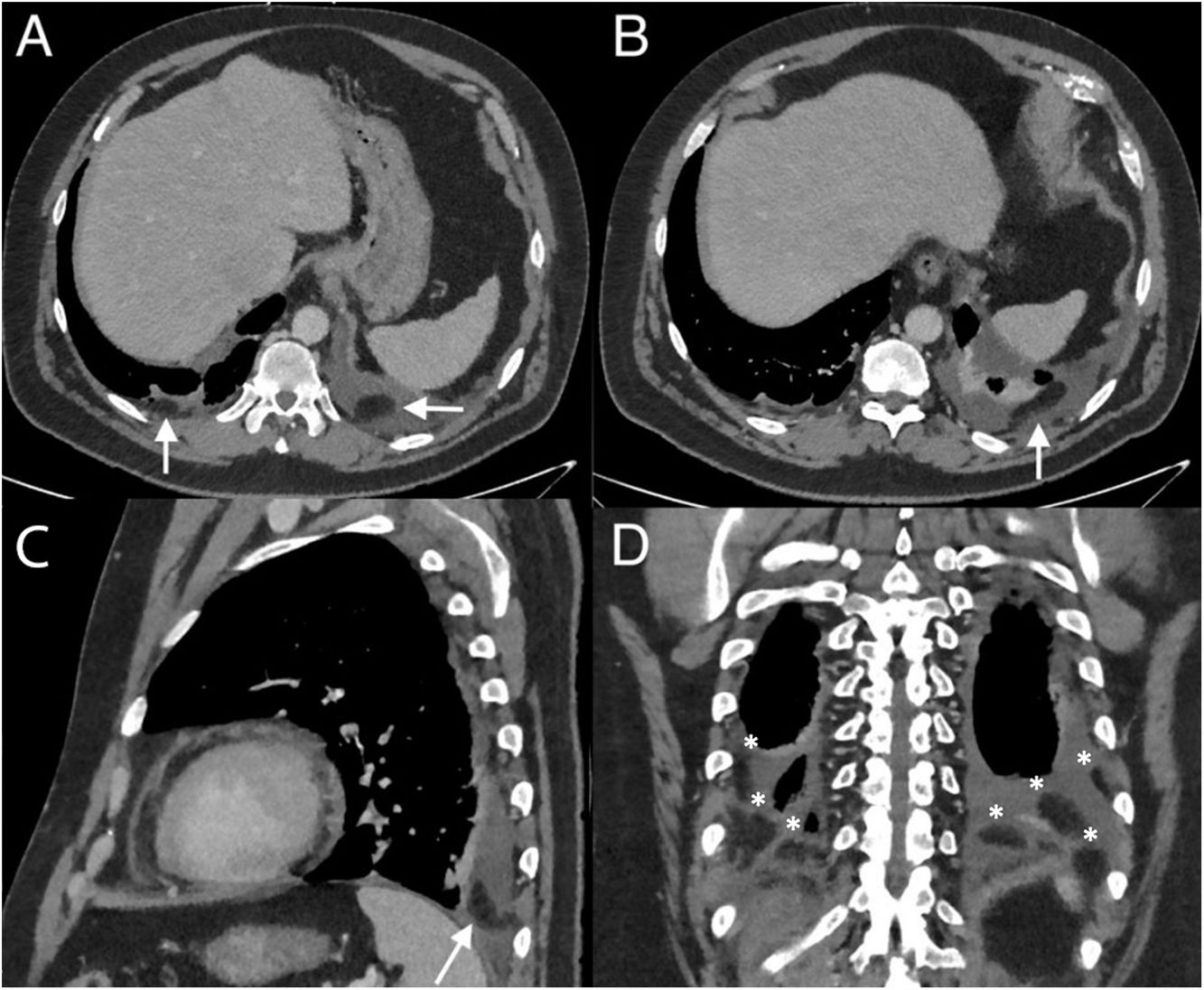
A CT requested for ruling out malignancy in a 51-year-old male with hemopericardium showed multiple bilateral well-defined homogeneous pedunculated fat attenuating lesions arising from the posterior parietal pleura (Fig. 1) floating in a small bilateral pleural effusion. A diagnosis of multiple bilateral pleural appendages was made.
Contrast-enhanced portal venous phase CT scan. (A and B) Axial views. Right and left pleural effusion and pleural appendages (arrows). (C) Sagittal view. Left pleural effusion and a pleural appendage (arrow). (D) Coronal view. Multiple bilateral pleural appendages floating in pleural effusion (*).
Pleural appendages are pedunculated outpouchings of extrapleural fat covered by parietal pleura that project into the thoracic cavity. The term was coined due to their similarity with colonic epiploic appendages. Their pedunculated shape with long thin stalks may explain epipericardial fat necrosis and thoracoliths, just as epiploic appendages undergo epiploic appendagitis and cause calcified peritoneal loose bodies. Without pneumothorax and pleural effusion, they are indistinguishable from normal extrapleural fat. Their reported prevalence in moderate/severe pneumothorax is 49.5%, usually located at the cardiophrenic angle and measuring 10–70mm in length.1
The differential diagnosis must be made with pleural lipomas and liposarcomas. Pleural lipomas are benign fatty tumors with smooth contours and obtuse margins with the pleural surface. At least a quarter of their circumference is in contact with the pleura. In contrast to pleural appendages, pleural lipomas are clearly visible without pleural effusion or pneumothorax and are rarely pedunculated. As for liposarcomas, contrast-enhanced MRI plays a key role in demonstrating post-contrast enhancement and invasion of adjacent structures.2
Conflict of InterestsThe authors state that they have no conflict of interests.