Lung disease is the major cause of death among cystic fibrosis (CF) patients, affecting 80% of the population. The impact of extracorporeal circulation (ECC) during transplantation has not been fully clarified. This study aimed to evaluate the outcomes of lung transplantation for CF in a single center, and to assess the impact of ECC on survival.
MethodsWe performed a retrospective observational study of all transplanted CF patients in a single center between 1992 and 2011. During this period, 64 lung transplantations for CF were performed.
ResultsFive- and 10-year survival of transplanted patients was 56.7% and 41.3%, respectively. Pre-transplantation supplemental oxygen requirements and non-invasive mechanical ventilation (NIMV) do not seem to affect survival (P=.44 and P=.63, respectively). Five- and 10-year survival among patients who did not undergo ECC during transplantation was 75.69% and 49.06%, respectively, while in those did undergo ECC during the procedure, 5- and 10-year survival was 34.14% and 29.87%, respectively (P=.001). PaCO2 is an independent risk factor for the need for ECC.
ConclusionsThe survival rates of CF patients undergoing lung transplantation in our hospital are similar to those described in international registries. Survival is lower among patients receiving ECC during the procedure. PaCO2 is a risk factor for the need for ECC during lung transplantation.
La enfermedad pulmonar es la principal causa de mortalidad en el 80% de los pacientes con fibrosis quística (FQ). La influencia de la circulación extracorpórea (CEC) no está completamente establecida. Los objetivos son evaluar los resultados del trasplante pulmonar por FQ en un solo centro y la influencia de la CEC sobre la supervivencia de estos pacientes.
MétodosEstudio observacional retrospectivo de todos los pacientes afectados de FQ trasplantados en un solo centro entre 1992 y 2011. En este período se han realizado 64 trasplantes pulmonares por FQ.
ResultadosLa supervivencia de los pacientes trasplantados a los 5 y 10 años fue del 56,7 y el 41,3%, respectivamente. El requerimiento de oxígeno suplementario previo al trasplante no parece afectar a la supervivencia (p=0,44), al igual que los pacientes que se trasplantaron con ventilación mecánica no invasiva (p=0,63). La supervivencia a los 5 y 10 años para los pacientes que no se trasplantan con CEC es del 75,69 y el 49,06%, respectivamente, mientras que los que se trasplantan bajo CEC tienen un supervivencia a los 5 y 10 años del 34,14 y el 29,87%, respectivamente (p=0,001). La PaCO2 es un factor de riesgo independiente para la necesidad de CEC.
ConclusionesLos pacientes con FQ trasplantados pulmonares en nuestro centro tiene una supervivencia similar a la descrita por los registros internacionales. Los pacientes trasplantados bajo CEC tienen una menor supervivencia. La PaCO2 es factor de riesgo de necesidad de CEC durante el trasplante pulmonar.
Cystic fibrosis (CF), which occurs in 1 out of 5500 births, is the most common genetic disease in Caucasians.1
Lung disease is the main cause of death in 80% of patients and the only intervention that has been shown to improve the survival of patients with advanced lung disease is lung transplantation (LT).2
As sequential bilateral LT becomes more common and surgical techniques improve, the use of extracorporeal circulation (ECC) in LT has declined.
Studies that evaluate the impact of ECC in LT are limited to the most prevalent diseases: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and pulmonary fibrosis (PF).3,4
The main objective of this study was to evaluate the LT outcomes in CF and long-term survival in a single center. Secondary objectives were to evaluate the impact of ECC on survival and to identify factors that may determine the need for this therapy.
MethodsThis was a retrospective observational study conducted in all CF patients receiving lung transplants in the Hospital Vall d’Hebron (Barcelona, Spain) between April 1, 1992 and September 30, 2011. During that period, 64 LTs were performed for CF in our center.
Transplant recipients were followed up until September 2014, so the minimum follow-up, unless patients died earlier, was 3 years.
ECC was applied during the procedure at the discretion of the surgical team, according to the criteria listed below, previously published in the literature5:
- 1.
Scheduled: for correction of cardiac defects during transplantation.
- 2.
Technical difficulties during the surgical procedure: cardiac or pulmonary lesions, impossibility for lung collapse, etc.
- 3.
Cardiac dysfunction and right ventricular failure.
- 4.
Hyperacute graft dysfunction or pulmonary edema after implantation of the first lung.
- 5.
Cardiac index <2L/min/m2.
- 6.
Mixed venous oxygen saturation <60%.
- 7.
Arterial oxygen saturation <85%.
- 8.
Mean pulmonary artery pressure >50–60mmHg.
- 9.
pH<7.00.
Prolonged mechanical ventilation (MV) was defined as MV administered for more than 21 days.6
Absolute frequencies and percentages were used to describe nominal variables. Quantitative variables were compared using the χ2 test or Fisher's test as needed. Survival was calculated using the Kaplan–Meier test. Since the probability of requiring ECC can differ among individuals and the factors that lead to the requirement of ECC may also affect survival, a propensity score analysis was used to control for the possibility of confounding factors.
Stata 13.1 software was used for the statistical analysis.
ResultsMean age was 20.7±8 (r: 9–49) years. Twenty-six (40.6%) patients were included in the pediatric LT program (0–17 years), with a mean age of 13.9 (r: 9–17) years. The other 38 patients were from the adult LT program (18–49 years), with a mean age of 35.3 (r: 18–49) years.
Of the 64 LTs, 33 (51.5%) were male and 31 (48.5%) were female, yielding a male/female ratio of 1.06/1.
Mean body mass index (BMI) was 16.9±2.7 (r: 10–22.9) kg/m2. According to the WHO classification,7 25 patients had severe malnutrition.
Mean time on the waiting list was 9.3±8.5 (r: 0–34) months. For the pediatric transplant group, the mean wait was 9 (r: 0.7–34.7) months, and for the adult group it was 10.5 (r: 0.1–30.2) months.
With regard to oxygen needs prior to LT, 51 (79.6%) patients used chronic home oxygen therapy, and 13 (20.3%) patients required non-invasive mechanical ventilation (NIMV). Mean time using oxygen therapy before the LT was 15.9±21.4 (r: 1–96) months.
At the time of inclusion in the waiting list for LT, patients had median PaO2 values of 63 (r: 27–85) mmHg and PaCO2 43.5 (r: 30–84) mmHg. Pulmonary function test (PFT) values (%) for FVC were 38.4±14 (r: 14–82) and FEV1 26±10 (r: 13–60). Mean distances on the 6-minute walk test (6MWT) were 323±111 (r: 72–636) m.
LT recipients received MV for a mean period of 10 days (r: 1–60 days). Twelve patients (18.7%) required prolonged MV. Mean intensive care unit (ICU) stay was 17.7±16.7 (r: 1–90) days.
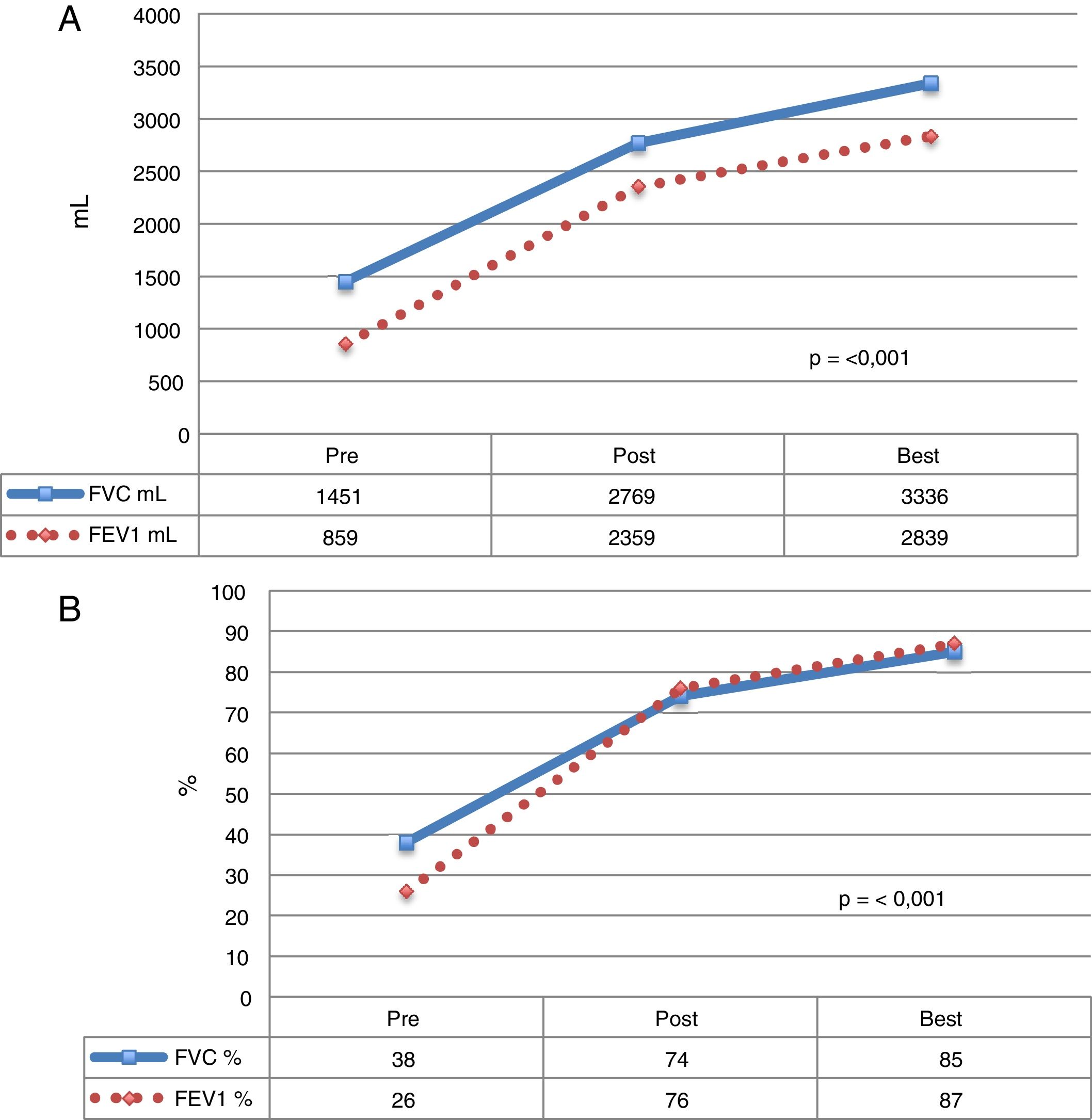
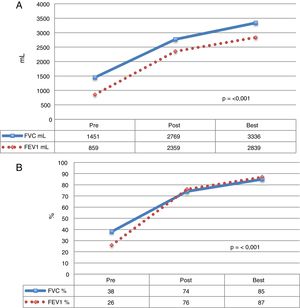
Mean time to achieve best lung function was 41.1 (r: 1.7–167.5) months post-LT (Fig. 1).
Functional parameters of CF patients who received LT. The mean of each value before LT, during the postoperative period, and the best mean values achieved during follow-up. (A) Values expressed as milliliters (ml). (B) Values expressed as percentage according to weight and height of each patient. FEV1: forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC: forced vital capacity.
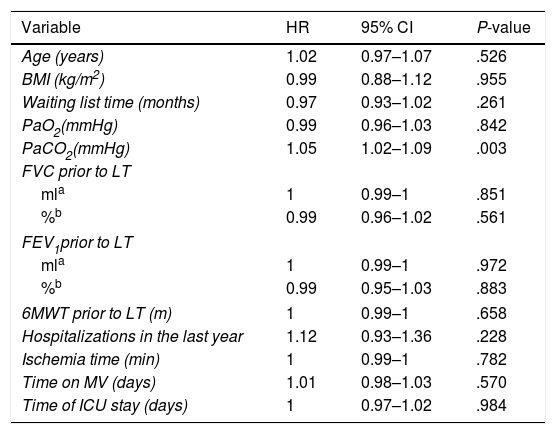
The only variable identified in the univariate analysis that increased the probability of death was preoperative PaCO2 (HR: 1.05; 95% CI: 1.02–1.09) (Table 1).
Univariate Analysis of Risk Factors for Mortality According to the Cox Proportional Hazards Method.
| Variable | HR | 95% CI | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 1.02 | 0.97–1.07 | .526 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.99 | 0.88–1.12 | .955 |
| Waiting list time (months) | 0.97 | 0.93–1.02 | .261 |
| PaO2(mmHg) | 0.99 | 0.96–1.03 | .842 |
| PaCO2(mmHg) | 1.05 | 1.02–1.09 | .003 |
| FVC prior to LT | |||
| mla | 1 | 0.99–1 | .851 |
| %b | 0.99 | 0.96–1.02 | .561 |
| FEV1prior to LT | |||
| mla | 1 | 0.99–1 | .972 |
| %b | 0.99 | 0.95–1.03 | .883 |
| 6MWT prior to LT (m) | 1 | 0.99–1 | .658 |
| Hospitalizations in the last year | 1.12 | 0.93–1.36 | .228 |
| Ischemia time (min) | 1 | 0.99–1 | .782 |
| Time on MV (days) | 1.01 | 0.98–1.03 | .570 |
| Time of ICU stay (days) | 1 | 0.97–1.02 | .984 |
6MWT: 6-minute walk test; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; BMI: body mass index; FEV1: forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC: forced vital capacity; HR: hazard ratio; PaO2: partial pressure of oxygen; PaCO2: partial pressure of carbon dioxide; VM: mechanical ventilation.
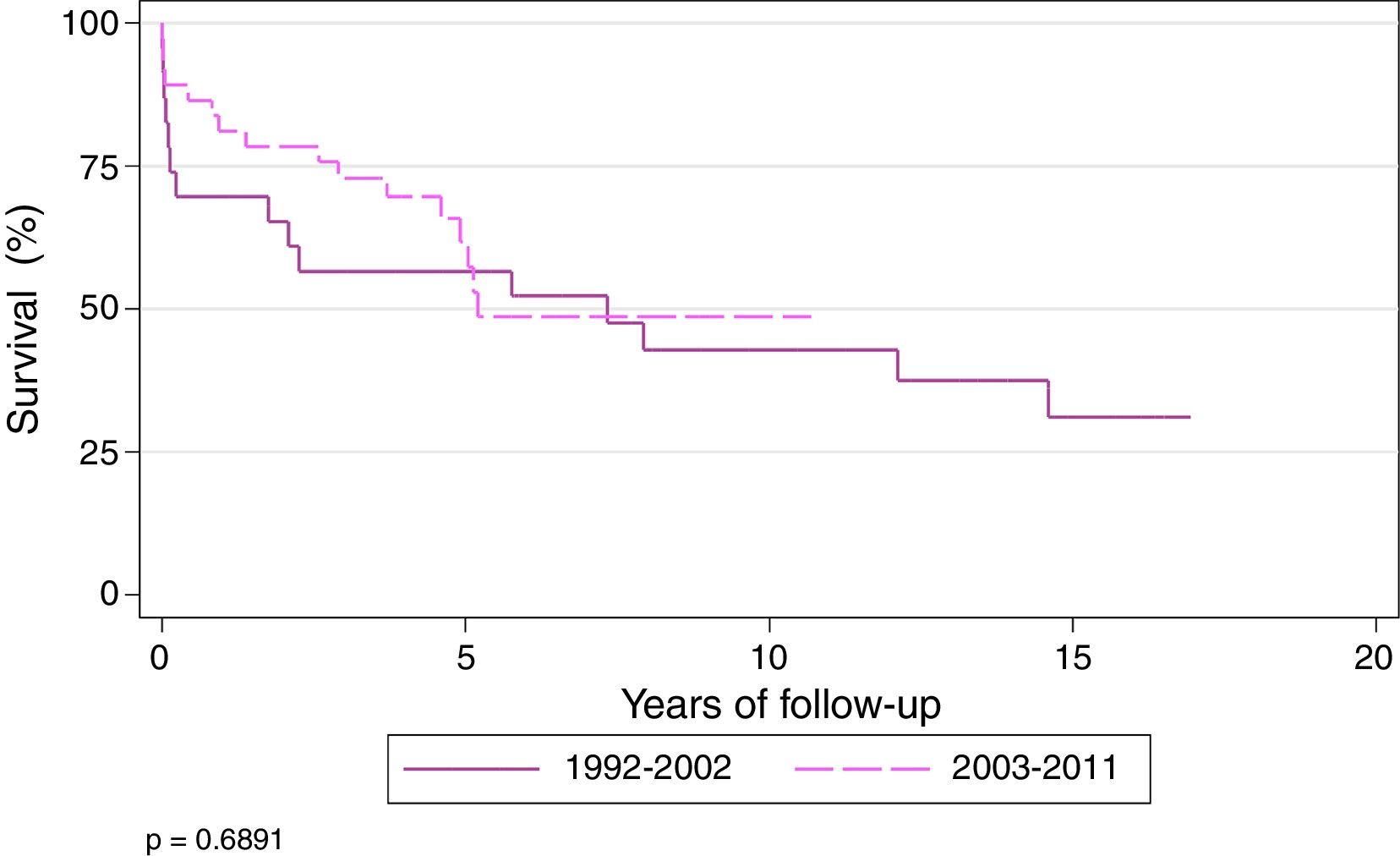
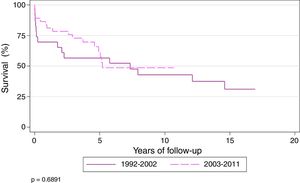
Actuarial survival (Kaplan–Meier) of patients transplanted for CF at 1, 3, 5, and 10 years was 71.8%, 62.4%, 56.7%, and 41.3%, respectively, with a median survival of 5.7 years. Patients were divided into 2 time periods: 1992–2002 and 2003–2011. Survival at 1, 3, 5, and 10 years was 61.5%, 50%, 50% and 37%, respectively, for transplanted patients during the first period, and 78.9%, 70.9%, 60%, and 42%, respectively, during the second period (P=.68). Median survival for the second period was 7.3 years (Fig. 2).
At the end of the study, the longest survival post-transplantation was 17 years, observed in 1 patient.
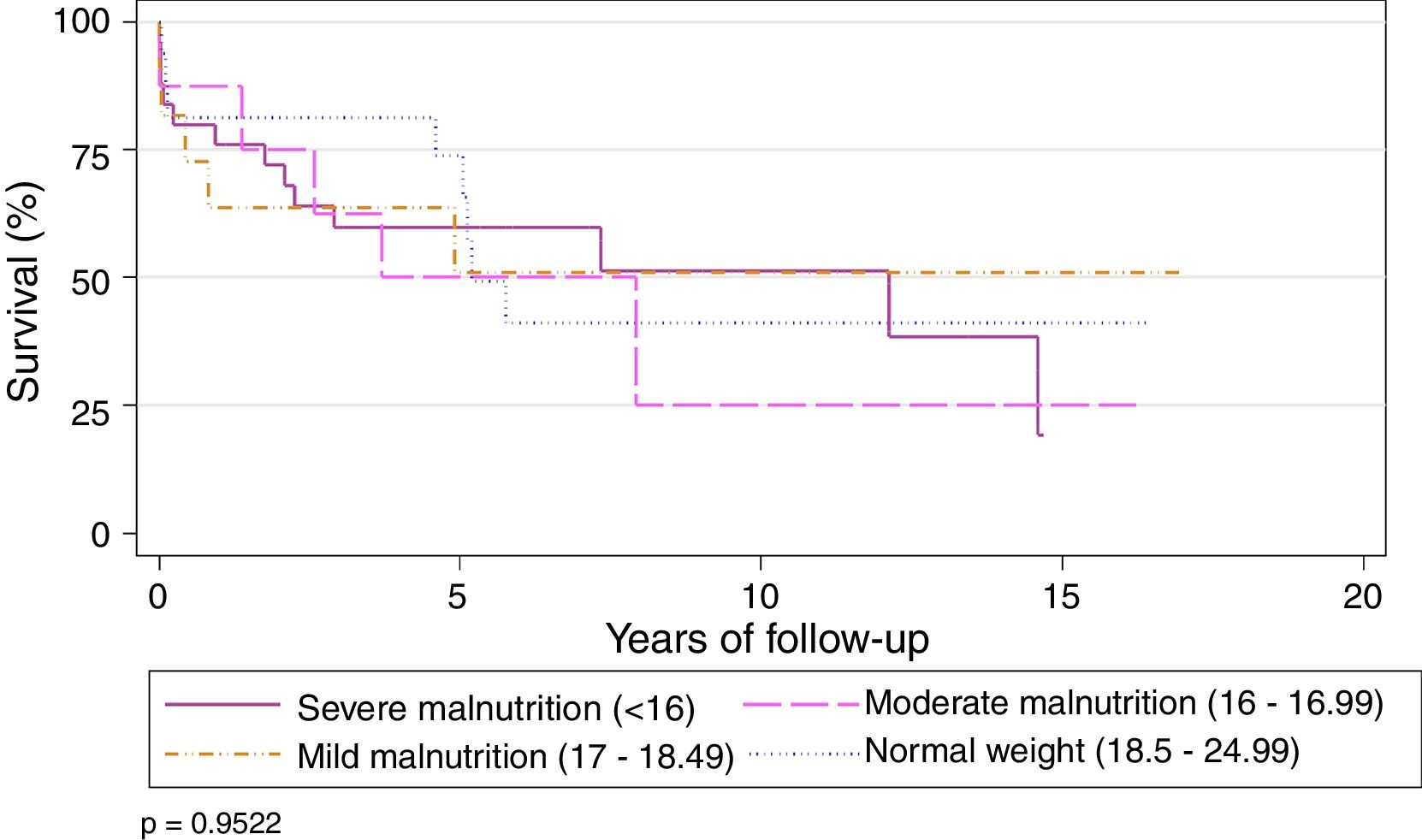
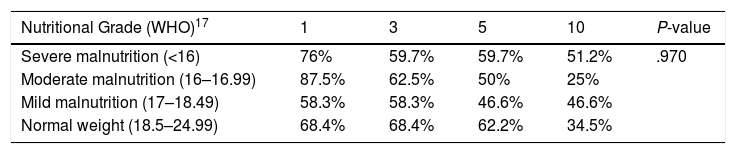
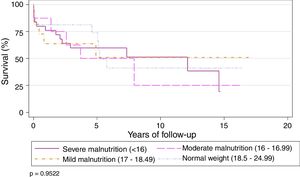
Preoperative BMI did not seem to significantly affect the overall survival of the series. Survival stratified by grades of malnutrition was similar, with a slight, non-significant improvement in the group with severe malnutrition, 5 years after the LT (Table 2) (Fig. 3).
Actuarial Survival by Different Nutritional Grades.
| Nutritional Grade (WHO)17 | 1 | 3 | 5 | 10 | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severe malnutrition (<16) | 76% | 59.7% | 59.7% | 51.2% | .970 |
| Moderate malnutrition (16–16.99) | 87.5% | 62.5% | 50% | 25% | |
| Mild malnutrition (17–18.49) | 58.3% | 58.3% | 46.6% | 46.6% | |
| Normal weight (18.5–24.99) | 68.4% | 68.4% | 62.2% | 34.5% |
WHO: World Health Organization.
Patients who were receiving oxygen therapy at the time of the intervention showed 1, 3, 5, and 10-year survival rates of 72.5%, 60.7%, 53.8%, and 38%, respectively, compared to 69.2%, 69.2%, 69.2%, and 55.3%, respectively, among patients who did not require supplemental oxygen (P=.44).
No differences were found between patients receiving NIMV and those not receiving this therapy. Survival of transplanted patients receiving NIMV at 1, 3, 5, and 10 years was 69.2%, 53.8%, 43%, and 43%, and 72.5%, 64.7%, 60.1% and 42.1% in patients not receiving NIMV, respectively (P=.63).
Twenty-nine patients (45.3%) were operated under ECC, with a mean extracorporeal support time of 198±115 (r: 53–410) min.
Of the 51 patients who were receiving home oxygen therapy, 25 (49%) required extracorporeal support during surgery (P=.351). Of the 13 patients receiving NIMV at the time of LT, 9 required ECC during the intervention (P=.052).
At the time of LT, patients who needed ECC during surgery had mean PaO2 58.2mmHg and PaCO2 53.7mmHg. Although PaO2 values were lower in patients who needed ECC, the result were not statistically significant (P=.291). In contrast, PaCO2 appears to be a factor that determines the need for ECC (P=.018).
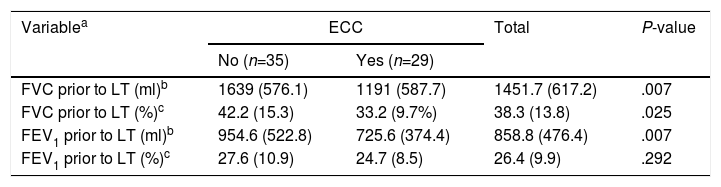
All PFT variables determined before LT appear to affect the need for ECC, with the exception of FEV1% (Table 3).
Comparison of Pulmonary functions test by need of ECC.
| Variablea | ECC | Total | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No (n=35) | Yes (n=29) | |||
| FVC prior to LT (ml)b | 1639 (576.1) | 1191 (587.7) | 1451.7 (617.2) | .007 |
| FVC prior to LT (%)c | 42.2 (15.3) | 33.2 (9.7%) | 38.3 (13.8) | .025 |
| FEV1 prior to LT (ml)b | 954.6 (522.8) | 725.6 (374.4) | 858.8 (476.4) | .007 |
| FEV1 prior to LT (%)c | 27.6 (10.9) | 24.7 (8.5) | 26.4 (9.9) | .292 |
ECC: extracorporeal circulation; FEV1: forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC: forced vital capacity.
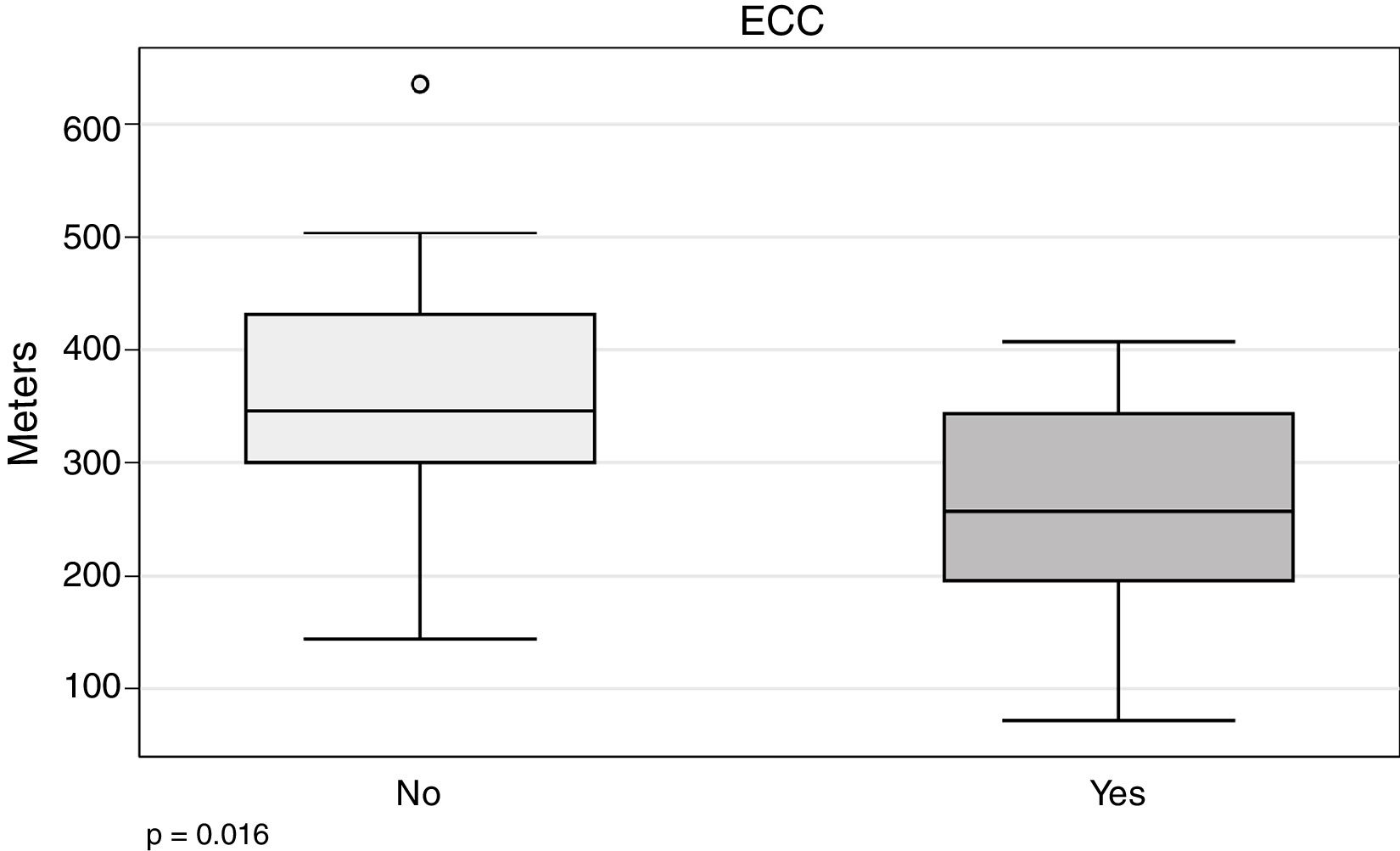
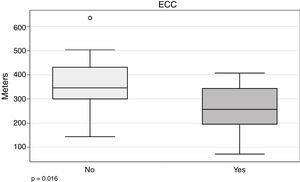
In our series, the 6MWT appears to be related with the need for ECC (266.5±94.7 vs 352.4±109m; P=.016) (Fig. 4).
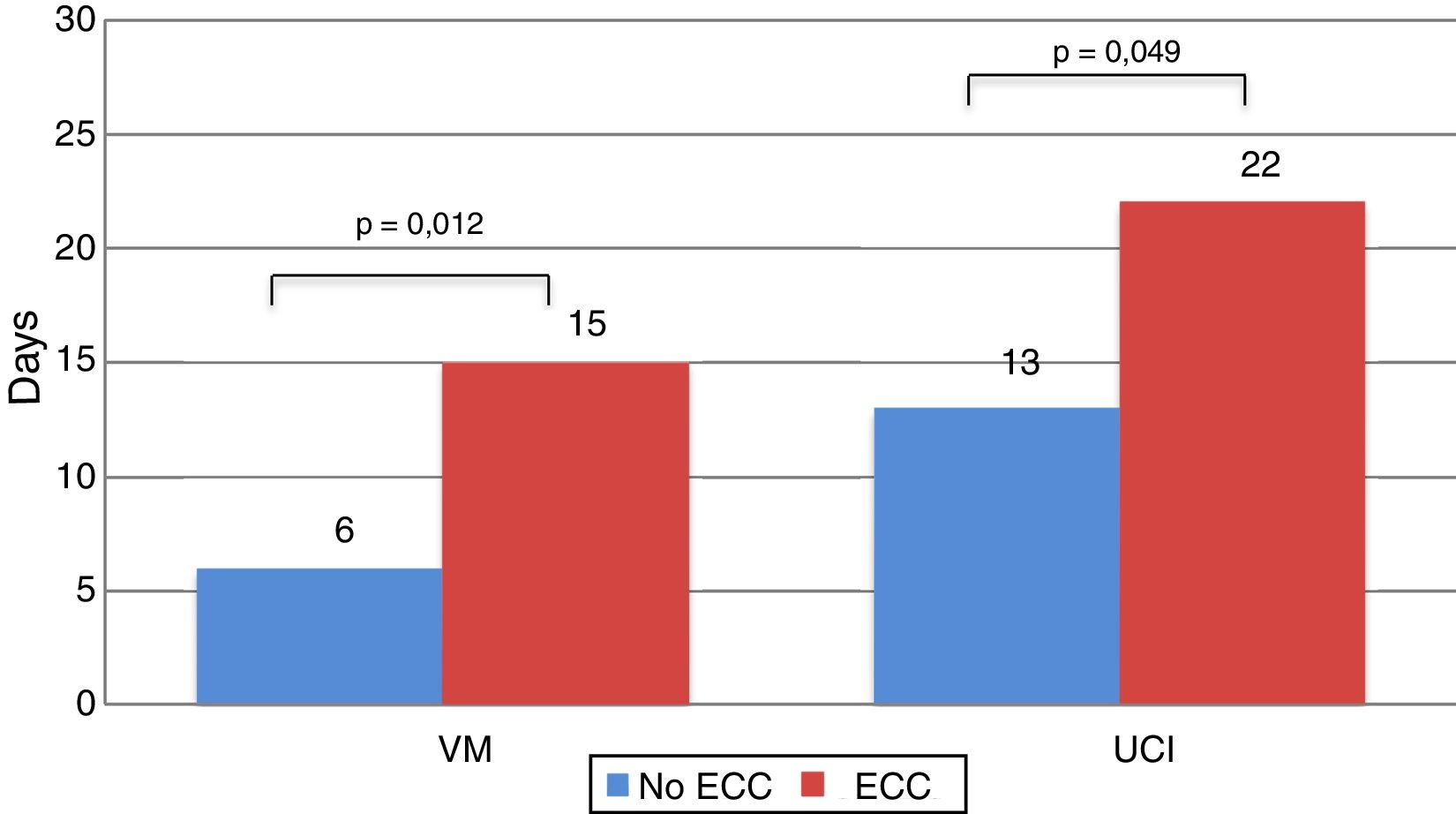
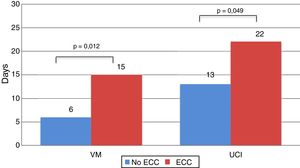
Recipients who needed ECC during the intervention spent more time on MV (15.29±16.81 vs 6.19±8.72 days; P=.012), and more time in the ICU (22.56±20.20 vs 13.77±12.19 days; P=.049) (Fig. 5).
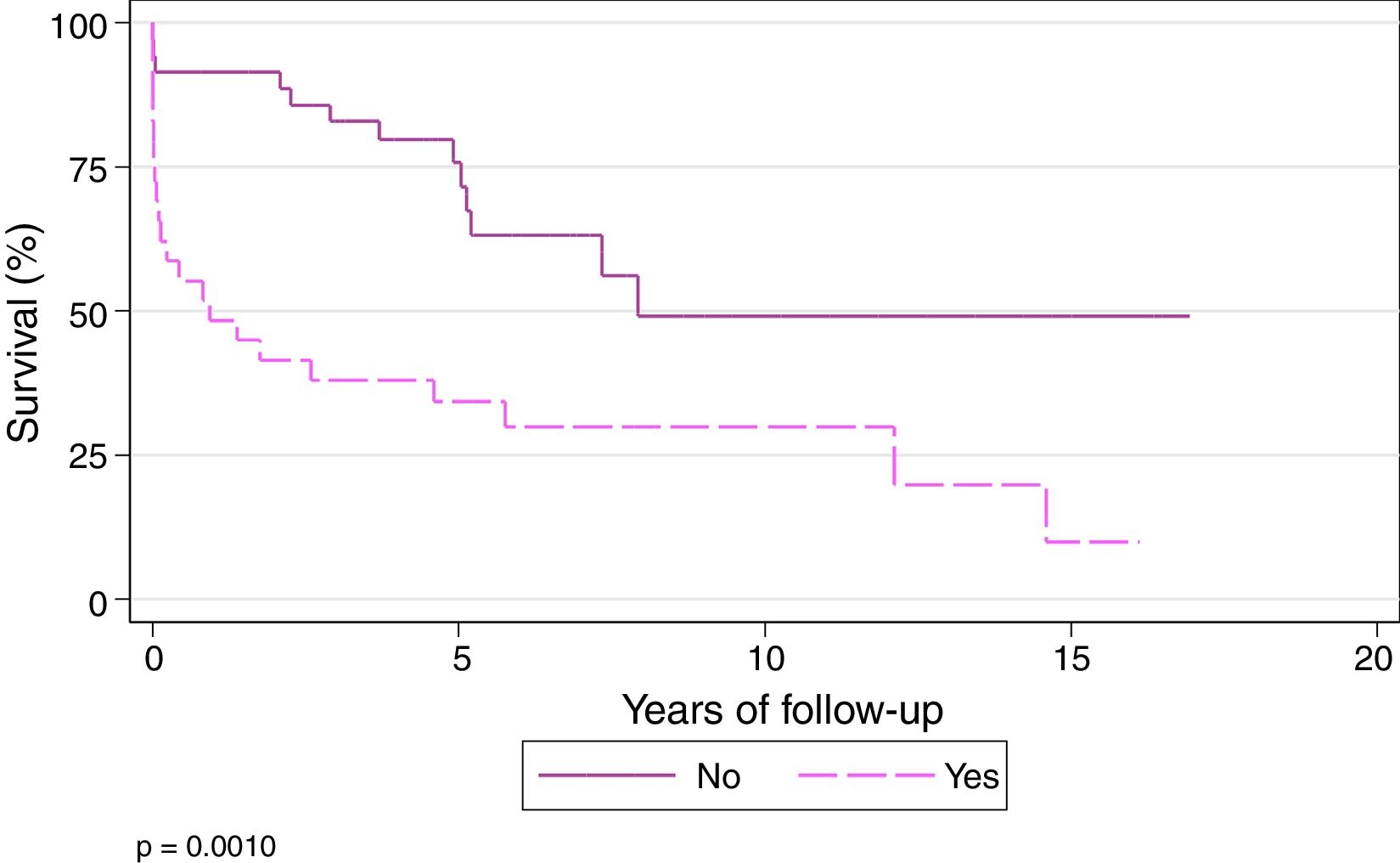
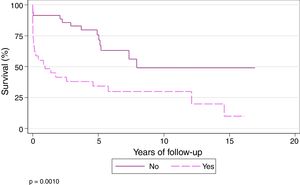
Survival at 1, 3, 5, and 10 years among patients who did not undergo ECC during the transplantation procedure was 91.43%, 82.86%, 75.69%, and 49.06%, respectively, while 1, 3, 5, and 10-year survival in those who underwent ECC during the procedure was 48.28%, 37.93%, 34.14%, and 29.87%, respectively (P=.001) (Fig. 6).
Four statistically significant variables were identified in the univariate analysis and subsequently used to calculate the propensity score (Table 4).
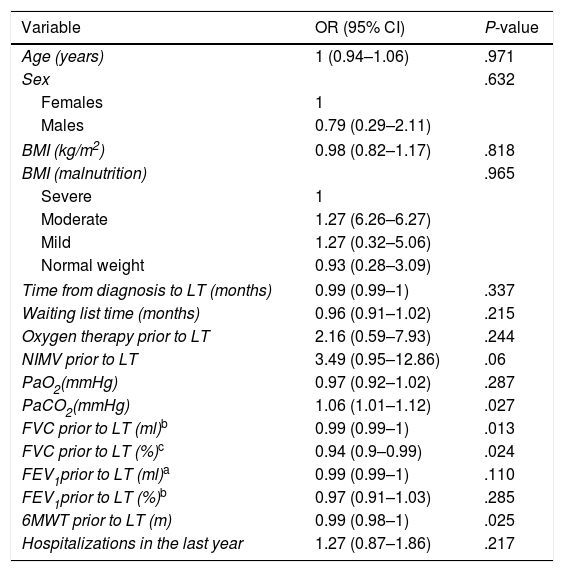
Univariate Analysis of Risk Factors for ECC According to the Cox Proportional Hazards Method.
| Variable | OR (95% CI) | P-value |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 1 (0.94–1.06) | .971 |
| Sex | .632 | |
| Females | 1 | |
| Males | 0.79 (0.29–2.11) | |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 0.98 (0.82–1.17) | .818 |
| BMI (malnutrition) | .965 | |
| Severe | 1 | |
| Moderate | 1.27 (6.26–6.27) | |
| Mild | 1.27 (0.32–5.06) | |
| Normal weight | 0.93 (0.28–3.09) | |
| Time from diagnosis to LT (months) | 0.99 (0.99–1) | .337 |
| Waiting list time (months) | 0.96 (0.91–1.02) | .215 |
| Oxygen therapy prior to LT | 2.16 (0.59–7.93) | .244 |
| NIMV prior to LT | 3.49 (0.95–12.86) | .06 |
| PaO2(mmHg) | 0.97 (0.92–1.02) | .287 |
| PaCO2(mmHg) | 1.06 (1.01–1.12) | .027 |
| FVC prior to LT (ml)b | 0.99 (0.99–1) | .013 |
| FVC prior to LT (%)c | 0.94 (0.9–0.99) | .024 |
| FEV1prior to LT (ml)a | 0.99 (0.99–1) | .110 |
| FEV1prior to LT (%)b | 0.97 (0.91–1.03) | .285 |
| 6MWT prior to LT (m) | 0.99 (0.98–1) | .025 |
| Hospitalizations in the last year | 1.27 (0.87–1.86) | .217 |
6MWT: 6-minute walk test; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; BMI: body mass index; FEV1: forced expiratory volume in 1 second; FVC: forced vital capacity; NIMV: non-invasive mechanical ventilation; OR: odds ratio; PaCO2: partial pressure of carbon dioxide; PaO2: partial pressure of oxygen.
These statistically significant variables all corresponded to lung function prior to LT: PaCO2 (OR: 1.06; 95% CI: 1.01–1.12), FVC (ml) (OR: 0.99; 95% CI: 0.99–1), FVC % (OR: 0.94; 95% CI: 0.9–0.99) and, finally, the 6MWT (OR: 0.99; 95% CI: 0.98–1).
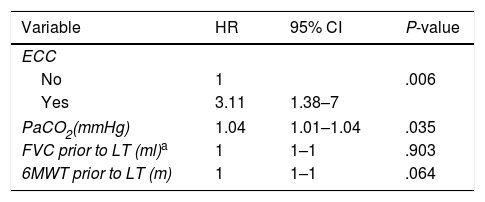
A logistic model was developed with the variables that were significant in the univariate analysis to calculate the probability of needing ECC during LT. In the multivariate study, these variables predicted a 3-fold chance of requiring ECC during LT, compared to the other parameters analyzed (Table 5).
Multivariate Analysis of ECC Risk Factors. Final Cox's Proportional Hazards Regression Model With Statistically Significant Variables in the Univariate Analysis.
| Variable | HR | 95% CI | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECC | |||
| No | 1 | .006 | |
| Yes | 3.11 | 1.38–7 | |
| PaCO2(mmHg) | 1.04 | 1.01–1.04 | .035 |
| FVC prior to LT (ml)a | 1 | 1–1 | .903 |
| 6MWT prior to LT (m) | 1 | 1–1 | .064 |
6MWT: 6-minute walk test; 95% CI: 95% confidence interval; FVC: forced vital capacity; HR: hazard ratio; PaCO2: partial pressure of carbon dioxide.
Most publications on patients transplanted for CF show similar results according to age.8–12
One of the larger series of CF patients that included 176 transplant recipients found that slightly more recipients were female (51.7%).13
BMI results in our series are very similar to those published in an Italian study of 55 CF patients undergoing LT (BMI 17.3±2.1kg/m2).14
Snell et al.15 reported a series of 45 CF transplant recipients and concluded that women with a BMI <18kg/m2 had a greater risk of mortality within 1 year of inclusion in the LT waiting list.
In our study, we divided recipients into BMI groups defined according to the WHO nutritional classification,7 and found no differences in mortality, regardless of the patient's nutritional status (P=.92).
Mean time on the LT waiting list in our series was 9.3±8.5 (r: 0–34) months. This is similar to waiting list times published in the literature, which range from 6.8 to 47 months.12,14–19
When we analyzed the need for oxygen therapy prior to transplantation, we found that 79.6% of recipients used oxygen therapy before LT. It should be pointed out that, in addition to blood gases criteria, oxygen therapy was indicated in patients presenting desaturation during exertion (to improve work of breathing and increase exercise capacity) and saturations below 90% during more than 10% of the nocturnal recording. In some cases, oxygen therapy was used to provide symptomatic improvement of respiratory failure, even in the absence of hypoxemia.20
In their paper on the effect of healthcare insurance coverage on LT for CF, Merlo et al.16 reported that 72.8% of patients in the United Kingdom received oxygen therapy prior to LT, a result that rises to 83.8% in the United States of America.
In our series, 20.3% of our patients required NIMV before LT. Madden et al. published one of the largest series evaluating the use of NIMV in CF patients. Mean time of administration of NIMV among patients on the LT waiting list was 61 (r: 1–600) days. These authors reported that NIMV improved hypoxia but did not correct hypercapnia.21
With regard to mean spirometric values, we recorded FVC and FEV1 values of 38.4% and 26%, respectively, similar to those published in the literature.9,16,22–25
In a Spanish series, pre-LT FVC and FEV1 values were 40% and 20%–30%, respectively. The authors reported that mean FVC and FEV1 values achieved during follow-up were >80% and 80%, respectively.26
The mean distance of 323m walked by our patients on the 6MWT was very similar to other series.9 Vizza et al.22 concluded that distance walked on the 6MWT is an independent risk factor for mortality on the LT waiting list: their patients who died prior to LT walked a mean distance of 343m.
Lung recipients in our study received MV for a mean of 10 (r: 1–60) days, and 12 (18.7%) patients required prolonged MV. Hadem et al. studied prolonged MV in 690 LT recipients, including 179 CF patients, and found that almost 12% of CF patients received long-term MV (>21 days).27
In our series, mean ICU stay during the postoperative period after LT was 17.7±16.7 (r: 1–90) days. Although the stay in the ICU has not been differentiated between the group of children and that of adults, the results are similar to that presented in other series, with stay averages of 20±19 days for children and 10±9 days for adults.26
Although overall survival in our series was similar to that of other published series,9,26 it is lower than reported by the international registry. However, when the “era effect” is applied, median survival improves for transplantations performed between 2003 and 2011.28
A total of 45.3% of our patients were operated under ECC, while rates among other centers range between 6.89% and 69%.18,23,26,29–33 In our series, mean extracorporeal support time was 198±115 (r: 53–410) min, similar to ECC times during LT published in the literature.34
The Newcastle group published a series of 259 patients who underwent single-lung transplant for various diagnoses; ECC was used in 20.5% of patients. They found that MV was not influenced by the use of ECC (P=.15): patients who needed ECC received MV for a mean of 31.3 (r: 6.2–78.3) hours. However, they did find a significant difference with respect to ICU stay, with a mean length of stay of 5.2 days for the ECC group and 2.8 days for the non-ECC group (P≤.01).3 Similar results were reported in another study, which found a longer ICU stay in patients who required ECC (5.2 vs 2.8 days for those who did not need ECC, P=<.01).35
In our series, survival at 1, 3 and 10 years was 91.43%, 82.86%, and 49.06%, respectively, in patients who were operated without ECC, while in patients transplanted under ECC, 1, 3, and 10-year survival was 48.28%, 37.93% and 29.87%, respectively (P=.001).
Many studies have evaluated survival of transplant recipients according to ECC, but almost all investigated patients with COPD or PF.
One study of 50 patients transplanted for COPD evaluated the influence of ECC on mortality, and found that 1 and 3-year survival of patients who underwent ECC was 85.7% and 64.3%, respectively.4
Our study identifies 3 factors that may be considered risk factors for ECC during LT for CT: pre-procedure PaCO2, FVC, and 6MWT.
Although we did not analyze the factors that might determine waiting list mortality, lung function values might play an important role in pre-LT risk stratification.
A study of CF patients who were candidates for cardiopulmonary transplant evaluated various parameters that might affect survival on the waiting list. The 2 variables identified by this study were FEV1 and PaCO2. Patients with FEV1 values greater than 17% have half the risk of dying on the waiting list as patients with values less than 17% (RR 0.47, 95% CI: 0.23–0.97). As for PaCO2, the authors found that the relative risk of mortality on the waiting list was 1.44 (95% CI: 1.17–1.77) for every 7mmHg increase in PaCO2.36
Ciriaco et al. also evaluated the risk variables for LT candidates with CF. When they compared patients who were transplanted and those who died while on the waiting list, FEV1 (21.2% vs 16.5%, P=.02) and 6MWT (391.8 vs 290.1m, P<.02) were the most significant variables. They also mentioned the importance of the PaCO2, although this result did not reach statistical significance (46 vs 54mmHg, P=NS).12
A multicenter study was conducted with the aim of defining pre-LT risk factors for mortality in a series of 343 CF patients waitlisted for LT. The results showed that FEV1≤30% (HR 6.8; 95% CI: 2.4–19.3, P<.01) and PaCO2≥50mmHg (HR 6.9; 95% CI, 1.5–32.1, P=.01) were risk factors for mortality.37
Although studies have assessed the impact of 6MWT on patients with coronary disease and during the postoperative period after cardiac surgery,38–40 no publications were found that associate this parameter with the need for the ECC during LT. Nor did we find any publications that associated PaCO2 and FVC with a risk for requiring ECC during LT.
As transplant programs have advanced, new care strategies have been introduced, such as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), which is currently one of the most important kinds of extracorporeal support, not only during the surgical procedure itself, but also as a bridge to LT and during the postoperative period. The impact of ECMO on the survival of transplanted CF patients has yet to be analyzed.
One of the most important limitations of our series, apart from its retrospective nature, is the small number of patients, and, accordingly, our results must be interpreted with caution. Another limitation is the heterogeneity of the study patients, as we included both pediatric and adult CF patients with LT. In an attempt to resolve this limitation, we used statistical techniques such as the propensity score to achieve more homogeneous comparisons between the patients. Another important limitation of our study is the lack of data on the causes of early mortality in the ECC patient group. This information would have helped identify the causes of limited short-term survival among this group.
In conclusion, survival among lung transplant recipients with CF in our hospital is similar to that described by the international registries, although patients in whom ECC was used during the procedure appear to have lower survival. PaCO2 was identified as an independent risk factor for the need for ECC during LT.
Conflict of InterestsThe authors state that they have no conflict of interests.
Please cite this article as: Jauregui A, Deu M, Romero L, Roman A, Moreno A, Armengol M, et al. El trasplante pulmonar en la fibrosis quística y la influencia de la circulación extracorpórea. Arch Bronconeumol. 2018;54:313–319.