Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) is the most prevalent lung cancer worldwide,1 being adenocarcinoma the most frequent. The diagnosis and treatment includes molecular tests to detect mutations in the gene for epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) or rearrangements in the gene for anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK), for which there are targeted treatments in stages IIIB and IV, specifically erlotinib or gefitinib.2 In Colombia, there is limited information about these mutations.
A regional study reported a prevalence of 24.8% for EGFR mutations, placing our country between the prevalences reported in Asian and European populations. Another research found an incidence of 3.8% of EML4-ALK fusion gene in a small sample of patients.3,4 In Colombia, the population is diverse; information regarding lung cancer related mutations is limited5,6. We describe the mutational and clinical characteristics of patients with NSCLC in a high complexity center in Cali, Colombia, and report the clinical experience concerning follow-up and treatment of our patients.
We developed a cohort study of patients diagnosed with NSCLC. ALK and EGFR mutations, risk-factor association, adherence to follow-up and survival probability within 90 and 180 days were collected and analyzed. A total of 114 patients diagnosed with NSCLC between June 2013 and February 2016 were included. Patients who were referred for genetic testing were excluded. Medical records were revised at the time of diagnosis, at three and six months. The type of treatment, presence of metastases, change in TNM staging, presence of toxicity due to TKI and death were registered.
EGFR gene mutations were analyzed in the cobas® z 480 platform for the automatic detection and amplification of 42 mutations. The expression of protein kinase, was explored using Ventana ALK (D5F3) and processed in the BenchMark ULTRA® automated platform. 54 patients were tested for the presence of both mutations and 57 for the EGFR gene only, since the implementation of EML4-ALK mutation started in 2014.
Quantitative variables were summarized using measures of central tendency and qualitative variables with relative and absolute frequencies. The calculation of the overall survival was performed via the Kaplan–Meier method. The end-point was death from any cause. Associations between ‘mutation’ and the independent variables ‘age’, ‘history of smoking’ and ‘gender’ were tested through a regression analysis. The measures of magnitude are presented as odds ratios (OR) with their respective 95% confidence intervals.
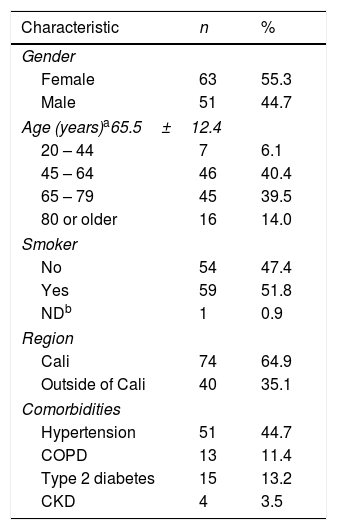
Demographic and clinical characteristics of all the patients are shown in Table 1. Mean age was 65±12y, ranging from 24 to 88 years of age. 55% were women and 52% had a history of smoking. The most common comorbidity was arterial hypertension with 45%, followed by type 2 diabetes with 13.2%. At the time of diagnosis, 72.8% had stage IV cancer according to the TNM classification system. The most frequent histological type was adenocarcinoma with 80.7%, followed by the large cell cancer with 9.6%. The most commonly used diagnostic techniques were fibrobronchoscopy and surgery, each representing 40.3%.
Demographic and clinical characteristics of patients with NSCLC at Fundación Valle del Lili.
| Characteristic | n | % |
|---|---|---|
| Gender | ||
| Female | 63 | 55.3 |
| Male | 51 | 44.7 |
| Age (years)a65.5±12.4 | ||
| 20 – 44 | 7 | 6.1 |
| 45 – 64 | 46 | 40.4 |
| 65 – 79 | 45 | 39.5 |
| 80 or older | 16 | 14.0 |
| Smoker | ||
| No | 54 | 47.4 |
| Yes | 59 | 51.8 |
| NDb | 1 | 0.9 |
| Region | ||
| Cali | 74 | 64.9 |
| Outside of Cali | 40 | 35.1 |
| Comorbidities | ||
| Hypertension | 51 | 44.7 |
| COPD | 13 | 11.4 |
| Type 2 diabetes | 15 | 13.2 |
| CKD | 4 | 3.5 |
Of the 111 patients tested for EGFR mutations, 27% were positive; 60% of these mutations were deletions (exon 19) and 40% were L858R mutations (exon 21). Of the 57 cases tested for an EML4-ALK fusion gene, 15.8% were positive. Of the 96 patients initially treated in our institution, 6 received TKI as an initial therapy: 5 received erlotinib and one received crizotinib. Of the 69 patients followed at three months, 14 deteriorated; 24 were stable, 27 had a partial response and 4 had a complete response. In this subpopulation, 7 patients received conventional treatment prior TKI management; 6 of them received erlotinib. 49 patients had a six-month follow-up: 6 deteriorated, 13 remained stable, 25 showed a partial response and 5 had a complete response. Survival rate was 83.3% and 7.5% at 90 and 180 days, respectively. (figure. 1). An association between being non-smoker and the presence of any mutation was discovered (OR: 2.5; CI 95% 1.02 – 6.3). We did not find a significant association between age or gender and the presence of mutations.
In our series, 11 patients were ≤50 years of age: 10 were women and nine of them had never smoked. Nine had adenocarcinoma, one had large-cell carcinoma and one had giant cell carcinoma. Nine patients were diagnosed as stage IV and two as stages IA and IIB. Three patients were positive for EGFR mutations and three for EML4-ALK fusion gene. Two of them received targeted therapy with a TKI. All patients <40 years were found to have mutations. Regarding the follow-up of this sub-set of patients, 63.6% were not tracked and 27.4% died. Only one patient who received TKI with erlotinib, was followed-up for six months. We found a prevalence of 27% for EGFR mutations corresponding to the prevalence reported in Western and Asian populations. The prevalence of rearrangements in the EML4-ALK gene was 15.8%, higher than the reported worldwide.7
Patients with primary NSCLC are more likely to be non-smokers, women and have stage-IV adenocarcinoma, with a high rate of EGFR and EML4-ALK mutations. All patients <40 years had genomic alterations, with EML4-ALK fusions being the most prevalent. We found an association between being a non-smoker and the presence of mutations, regardless of age or gender. A high prevalence of mutations in patients classified as never/light smokers has been reported in the literature before.8 It is possible that the high rate of mutations discovered in this study is related to being a non-smoker and to the demographic characteristics of the study population in Colombia, specifically with the diverse ethnicity in this country. The probability of six-month survival was calculated from 40% of the initial sample, given a limited follow-up.
We recommend once the presence of EGFR and EML4-ALK mutations has been established,9 follow-up should be undertaken at an institution that facilitates molecular diagnosis, treatment and management of the evolution and clinical response of the patients. This enables better decision-making and the creation of protocols for integral care. Issues in the healthcare system in Colombia may interfere with the implementation of these recommendations.