Occurrence of dynamic hyperinflation during upper-limbs exercises in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) patients is not well established. We hypothesized that dynamic hyperinflation and thoracoabdominal asynchrony occur in COPD patients accomplishing arms exercises. We assessed the occurrence and association of dynamic hyperinflation and thoracoabdominal asynchrony in COPD patients during the accomplishment of two arm exercises.
Patients and methodsThis was a prospective study with 25 COPD patients. A maximal and a sub-maximal upper limbs exercise test with 50% load were performed with the diagonal technique and the arm cycle ergometer technique. Respiratory pattern, thoracoabdominal configuration and dynamic hyperinflation were assessed in the exercise tests.
ResultsThirty per cent and 60% of patients hyperinflated at the end of the sub-maximum exercise tests with the diagonal and cycle ergometer techniques, respectively. Thoracoabdominal asynchrony occurred in 80% and 100% of patients who hyperinflated with the diagonal and cycle ergometer techniques, respectively. For both exercises we found enhancement of pulmonary ventilation, dyspnea, central respiratory drive and shortening of expiratory time (P<.05). Upper-limbs exercises with the diagonal technique presented less number of patients with these alterations.
ConclusionsDynamic pulmonary hyperinflation and thoracoabdominal asynchrony association occurred in both upper-limbs exercises; however, the diagonal technique developed less dynamic hyperinflation and thoracoabdominal asynchrony in COPD patients than the arm cycle ergometer.
La aparición de una hiperinflación dinámica durante los ejercicios de las extremidades superiores en los pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica (EPOC) no está bien establecida. Nuestra hipótesis es que existe una asociación entre la hiperinsuflación dinámica y la asincronía toracoabdominal en pacientes con EPOC durante la realización de ejercicios de los brazos. En consecuencia, se evaluó la existencia y la asociación de asincronía toracoabdominal y de hiperinsuflación dinámica en pacientes con EPOC, durante la realización de los ejercicios con los brazos.
Pacientes y métodosSe realizó un estudio prospectivo con 25 pacientes afectados por EPOC. Se llevó a cabo una prueba de ejercicio máximo y submáximo de las extremidades superiores con un 50% de carga, utilizando la técnica diagonal y la técnica del cicloergómetro de brazo. Se evaluaron el patrón respiratorio, la configuración toracoabdominal y la hiperinsuflación dinámica en las pruebas de esfuerzo.
ResultadosEl 30 y el 60% de los pacientes presentaron hiperinsuflación al final del ejercicio submáximo con las técnicas diagonal y de cicloergómetro de brazo, respectivamente. La asincronía toracoabdominal se produjo en el 80 y el 100% de los pacientes con las técnicas diagonal y de cicloergómetro de brazo, respectivamente. Para ambos ejercicios se ha observado una mayor ventilación pulmonar, disnea, control central de la respiración y reducción del tiempo espiratorio (p<0,05). En el ejercicio de las extremidades superiores con la técnica diagonal hubo menos pacientes con estos cambios.
ConclusionesLa asociación de hiperinsuflación pulmonar dinámica y asincronía toracoabdominal se produjo en ambos ejercicios de los miembros superiores; sin embargo, la técnica diagonal produjo menos hiperinsuflación dinámica y asincronía toracoabdominal que la técnica del cicloergómetro de brazo en los pacientes con EPOC.
Rehabilitation has been a treatment method that is considered essential for patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Traditionally, this has centered on lower limb exercises, such as walking or stationary cycling. However, many patients with COPD report the onset of dyspnea and muscle fatigue when performing activities in which the upper extremities are involved, such as lifting objects, making the bed or gardening.1 At present, upper body exercises have been included in the rehabilitation programs of patients with COPD, but there is still no consensus with respect to how conduct training in these patients and why the shoulder girdle muscles limit exercise in these cases.
In 1986, Celli et al.2 were the first to describe that patients with COPD could develop thoracoabdominal asynchrony during pegboard exercise with the upper limbs. In their study, they observed 42% of patients with asynchrony who also presented major dyspnea, earlier fatigue of the upper extremities and shorter endurance exercise time.
Gigliotti et al.3 observed that patients with COPD who performed exercises on an arm cycle ergometer developed dynamic pulmonary hyperinflation, increased dyspnea and upper limb fatigue.
It seems inconceivable to admit that the restriction experienced by a patient with COPD during exercise performed with the arm could be due to an association between dynamic pulmonary hyperinflation and thoracoabdominal asynchrony. Nevertheless, this association has not been demonstrated in previous studies. It is generally considered that the technique of arm cycle ergometry is the gold standard for arm training; however, it is believed that the diagonal technique recruits the action of more muscles than other types of exercise.
Consequently, we hypothesized that dynamic hyperinflation and thoracoabdominal asynchrony occur in patients with COPD who perform arm exercises. Hence, the aim of this study was to analyze the possible onset of dynamic pulmonary hyperinflation and thoracoabdominal asynchrony in patients with COPD during two types of upper limb exercises: the arm cycle ergometer and the diagonal technique. We also evaluated the most appropriate arm training technique for use in routine clinical practice in relation to dynamic hyperinflation and thoracoabdominal asynchrony.
Patients and MethodsParticipantsThis prospective study was conducted in 25 patients with severe or very severe COPD recruited in the Federal University of São Paulo (Brazil) pulmonary rehabilitation center. Participants were duly informed about the protocol and signed an informed consent form previously approved by the university ethics committee. The inclusion criteria were as follows: patients with a clinical diagnosis of COPD stage III or IV according to GOLD guidelines4; clinically stable; absence of comorbidities that could make it difficult to perform upper limb exercises; smoking cessation in the previous year; stable clinical condition, with no exacerbation in the 30 days prior to the study. The exclusion criteria were as follows: saturation of peripheral oxygen (SpO2) less than 80% during the test and inability to perform the inspiratory capacity maneuver or the exercises.
Study DesignOn the first day, the patients’ body mass index (BMI) and spirometry were determined as described in other publications.5–7 They were also randomly assigned to performing a maximal incremental exercise using the diagonal technique or the arm cycle ergometer. On the second day, they performed another maximal incremental exercise using the technique that had not been used on the first day.
On the third and fourth days, the patients performed a sub-maximal exercise with a load corresponding to 50% of that obtained in the maximal incremental exercise. The order of the exercises was established randomly, and patients performed the exercise until exhaustion.
The inspiratory capacity (IC) was determined before and after the sub-maximal exercises. The respiratory pattern and thoracoabdominal configuration were continuously monitored throughout the entire test. The peripheral arterial oxygen saturation, dyspnea and sensations of arm fatigue, and heart and respiratory rate were determined every minute during both exercises.
MethodsDetermination of Inspiratory CapacityThe inspiratory capacity was measured using a spirometer (Koko®, U.S.A.), as described in another publication,8 before, immediately after and at five minute intervals, after the exercise and until the IC value returned to baseline values. Dynamic pulmonary hyperinflation was defined as a decrease in the IC of at least 10% and/or 150ml in the post-exercise period, as described in another publication.9,10
Ventilation MeasurementsThe ventilatory variables such as inspiratory time (Ti), inspiratory time/total breathing cycle time ratio (Ti/Ttot), expiratory time (Te), respiratory rate (RR), central respiratory drive (VT/Ti) and pulmonary ventilation (VE) were measured at rest, continually during the exercise and until the IC value returned to baseline values, using a K4b2 portable device (Cosmed®, Italy), as described in another publication.11,12
Respiratory Inductance PlethysmographyThe thoracoabdominal configuration variables were determined before and at the end of the exercises, using an inductance plethysmograph (Noninvasive Monitory Systems, Respitrace®, U.S.A.) as described in another publication.13 Asynchrony data were obtained using the maximal compartmental amplitude/tidal volume ratio (MCA/VT).
Monitoring of heart rate, SpO2 and DyspneaThe heart rate (HR), hemoglobin oxygen saturation (SpO2) (Nonin®, U.S.A.) and perceived dyspnea (Borg scale) and upper limb fatigue (Borg scale) were determined before and after the exercises.
Maximal incremental Exercises of the Upper Limbs Using the Diagonal Technique and Arm Cycle ErgometerThe second exercise using the diagonal proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation technique consisted of alternate weight lifting with both arms, as described in another publication.14 One hundred grams of weight were added every minute, without leaving a rest period between successive weight increments. The test was discontinued when there was onset of symptoms such as severe dyspnea or arm fatigue. The rationale for using proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation is based on the fact that it is considered that the execution of diagonal movements recruits more muscle groups than are recruited by other exercises. The diagonal patterns associated with resistance aim to cause muscle irradiation and recruitment. The diagonal spiral pattern with a rotary component involves movements in three directions, with sequential and simultaneous movements of various joints. The first diagonal technique includes flexion-adduction-external rotation of the shoulders, while the second diagonal technique includes a flexion-abduction-external rotation motion.14,15 Other authors have highlighted the beneficial effect provided by the proprioceptive neuromuscular facilitation method in patients with COPD, including an improvement in the functional capacity of the arm and a reduction in dyspnea and fatigue scores.1,16
The arm cycle ergometer exercise was performed with rotation movements at 50rotations per minute (rpm).4,17 Every minute, 2.5W were added to the previous load until it was not possible to continue exercising. No rest period was left between the successive weight increments.16
Sub-maximal Endurance Exercises of the Upper Limbs Using the Diagonal Technique and Arm Cycle ErgometerA constant load of 50% of the maximum load reached during the maximal exercise using the diagonal technique or the arm cycle ergometer was used for the endurance test. The exercise was discontinued when there was onset of symptoms such as severe dyspnea or arm fatigue.1,16
Statistical AnalysisThe data are expressed as mean and standard deviation. The Kolmogorov–Smirnov normality test was used, which determined that our data were non-parametric. As a result, we applied the Wilcoxon test to analyze the same variable before and after the exercise. The Mann–Whitney test was used to determine differences between groups with and without hyperinflation. Statistical significance was established at P<.05. We used the program SigmaStat® for data analysis. The sample size was calculated using the formula E/S, where E is the minimum clinical difference and S is the standard deviation of the outcome variable. Taking a reduction of 150ml in the inspiratory capacity as the minimum clinical difference (E) and the standard deviation of this variable (S), it was calculated that a minimal sample size of 17 patients was required for α=0.05 and β=0.80.3,8–10
ResultsSample Characteristics and SpirometryTwenty-five patients (18 males) with COPD were selected for the study. These patients had a mean age of 64.4 (7.9), BMI of 24.5 (3.7), packet consumption/year of 65 (40) and a Medical Research Council (MRC) score of 4 (1). The baseline ventilatory variables and pulmonary data before the second diagonal technique and their similarity with those of the arm cycle ergometer technique are shown in Table 1.
Ventilatory Variables and Pulmonary Data Obtained in 25 Patients With COPD Before the Sub-maximal Exercise Performed With the Second Diagonal Technique and Ergometer.
| Variables | Diagonal | Ergometer | P |
| Ti (s) | 1.0 (0.1) | 1.3 (0.1) | .07 |
| Ti/Ttot | 0.2 (0.10) | 0.3 (0.10) | .09 |
| Te (s) | 0.9 (0.2) | 1.1 (0.3) | .07 |
| RR (rpm) | 24 (2.0) | 23 (2.7) | .06 |
| Vt/Ti (mL/s) | 625.1 (55) | 565.8 (63) | .06 |
| VE (L) | 17.4 (4) | 15.2 (5) | .08 |
| Dyspnea | 2 (1) | 3 (1) | .1 |
| FEV1 (% of expected) | 39.4 (10.2) | 42.9 (12.9) | .06 |
| FVC (% of expected) | 78.9 (15.2) | 85.8 (16.5) | .06 |
| FEV1/FVC | 0.40 (0.10) | 0.45 (0.16) | .07 |
| IC (L) | 2.32 (0.63) | 2.32 (0.58) | .1 |
| MCA/Vt | 1.07 (0.10) | 1.05 (0.1) | .2 |
| %ABD | 58 (16) | 58 (14) | .1 |
| %Tx | 44 (12) | 45 (16) | .2 |
Ti=inspiratory time; Ti/Ttot=inspiratory time/total breathing cycle time ratio; Te=expiratory time; RR=respiratory rate; Vt/Ti=mean inspiratory flow; VE=pulmonary ventilation; FEV1=forced expiratory volume in the first second; FVC=forced vital capacity; FEV1/FVC=forced expiratory volume in the first second/forced vital capacity ratio; IC=inspiratory capacity; MCA/Vt=maximal compartmental amplitude/tidal volume ratio; %ABD=percentage abdominal contribution to the chest wall movement; %Tx=percentage thoracic contribution to the chest wall movement.
Data are presented as mean (standard deviation).
Comparison of maximum ventilatory variables with the maximal and sub-maximal exercise in the diagonal versus the arm cycle ergometer technique: After performing the maximal (Table 2) and sub-maximal exercise (Table 3) using the diagonal technique, patients showed the following differences in comparison with the arm cycle ergometer exercise: lower dyspnea, respiratory rate, inspiratory time/total breathing cycle time ratio, central respiratory drive and pulmonary ventilation values (P<.05) and longer expiratory time (P<.05). We did not observe any differences in heart rate either between the diagonal and ergometry techniques in patients with COPD who performed a maximal or sub-maximal exercise (P>.5 and P>.3, respectively) (Tables 2 and 3, respectively).
Respiratory Variables and Heart Rate Response in the Maximal Incremental Exercises of the Upper Limbs With the Diagonal Technique and the Arm Cycle Ergometry Technique in 25 Patients With COPD.
| Variables | Diagonal | Ergometer | P |
| Ti (s) | |||
| Baseline | 1.1 (0.8) | 1.0 (0.6) | .6 |
| Maximal exercise | 0.8 (0.2) | 0.8 (0.2) | .9 |
| Mean difference | −0.3 (−0.6) | −0.2 (−0.4) | .5 |
| Ti/Ttot | |||
| Baseline | 0.4 (0.1) | 0.4 (0.1) | .9 |
| Maximal exercise | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.4 (0.1) | .001 |
| Mean difference | −0.1 (0.0) | 0.0 (0.0) | .1 |
| Te (s) | |||
| Baseline | 1.7 (0.8) | 1.7 (0.8) | .9 |
| Maximal exercise | 1.6 (0.5) | 1.3 (0.4) | .02 |
| Mean difference | −0.1 (−0.3) | −0.4 (−0.4) | .03 |
| RR (rpm) | |||
| Baseline | 24.5 (8.6) | 24.6 (7.4) | .9 |
| Maximal exercise | 26.8 (7.0) | 30.8 (7.3) | .05 |
| Mean difference | 2.3 (−1.6) | 6.2 (−0.1) | .02 |
| Vt (mL) | |||
| Baseline | 500 (200) | 600 (300) | .1 |
| Maximal exercise | 1100 (300) | 1300 (400) | .07 |
| Mean difference | 600 (100) | 700 (100) | .06 |
| Vt/Ti (mL/s) | |||
| Baseline | 463 (280) | 547 (352) | .3 |
| Maximal exercise | 1368 (155) | 1659 (177) | .0001 |
| Mean difference | 905 (−125) | 1112 (−175) | .03 |
| VEt (L) | |||
| Baseline | 11.4 (2.7) | 12.2 (3.0) | .3 |
| Maximal exercise | 27.9 (7.4) | 36.7 (8.1) | .0002 |
| Mean difference | 16.5 (4.7) | 24.5 (5.1) | .001 |
| Dyspnea | |||
| Baseline | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | .9 |
| Maximal exercise | 6 (3) | 7 (2) | .1 |
| Mean difference | 6 (3) | 7 (2) | .1 |
| IC (L) | |||
| Baseline | 2.16 (0.52) | 2.32 (0.58) | .3 |
| Maximal exercise | 2.00 (0.39) | 2.25 (0.88) | .2 |
| Mean difference | −0.16 (−0.13) | −0.07 (0.3) | .2 |
| %ABD | |||
| Baseline | 57.6 (15.1) | 56.7 (16.9) | .5 |
| Maximal exercise | 73.8 (19.9) | 75.2 (25.5) | .4 |
| Mean difference | 16.2 (4.8) | 18.5 (8.6) | .2 |
| %Tx | |||
| Baseline | 47.3 (24.4) | 52.8 (27.0) | .4 |
| Maximal exercise | 52.5 (28.8) | 50.1 (26.6) | .7 |
| Mean difference | 5.2 (4.4) | −2.7 (−0.4) | .001 |
| HR, bpm | |||
| Baseline | 83.3 (21.7) | 81.7 (21.7) | .7 |
| Maximal exercise | 101.3 (27.1) | 106.6 (35.7) | .5 |
| Mean difference | 18.0 (5.4) | 24.9 (14.0) | .02 |
| SaO2, % | |||
| Baseline | 93 (3) | 93 (2) | .9 |
| Maximal exercise | 90 (4) | 91 (3) | .3 |
| Mean difference | −3 (1) | −2 (1) | .1 |
Ti=inspiratory time; Ti/Ttot=inspiratory time/total breathing cycle time ratio; Te=expiratory time; RR=respiratory rate; Vt/Ti=mean inspiratory flow; VE=pulmonary ventilation; FEV1=forced expiratory volume in the first second; FVC=forced vital capacity; FEV1/FVC=forced expiratory volume in the first second/forced vital capacity ratio; IC=inspiratory capacity; MCA/Vt=maximal compartmental amplitude/tidal volume ratio; %ABD=percentage abdominal contribution to the chest wall movement; %Tx=percentage thoracic contribution to the chest wall movement.
Data are presented as mean (standard deviation).
Respiratory Variables and Heart Rate Response at the Peak of the Sub-maximal Endurance Exercises of the Upper Limbs With the Diagonal Technique and the Arm Cycle Ergometry Technique in 25 Patients With COPD.
| Variables | Diagonal | Ergometer | P |
| Ti (s) | |||
| Baseline | 1.3 (0.6) | 1.4 (1.1) | .6 |
| Maximal exercise | 0.9 (0.3) | 0.8 (0.2) | .1 |
| Mean difference | −0.4 (−0.3) | −0.6 (−0.9) | .2 |
| Ti/Ttot | |||
| Baseline | 0.4 (0.1) | 0.4 (0.2) | .9 |
| Maximal exercise | 0.3 (0.1) | 0.4 (0.1) | .001 |
| Mean difference | −0.1 (0.0) | 0.0 (−0.1) | .1 |
| Te (s) | |||
| Baseline | 2.0 (0.9) | 2.0 (1.0) | .9 |
| Maximal exercise | 1.7 (0.6) | 1.3 (0.3) | .004 |
| Mean difference | −0.3 (−0.3) | −0.7 (−0.7) | .02 |
| RR (rpm) | |||
| Baseline | 20 (6.2) | 19.6 (6.9) | .8 |
| Maximal exercise | 25.0 (6.4) | 30.1 (5.7) | .004 |
| Mean difference | 5.0 (0.2) | 10.5 (−1.2) | .001 |
| Vt (mL) | |||
| Baseline | 600 (200) | 600 (200) | .9 |
| Maximal exercise | 1100 (400) | 1200 (300) | .3 |
| Mean difference | 500 (200) | 600 (100) | .2 |
| Vt/Ti (mL/s) | |||
| Baseline | 480 (350) | 420 (218) | .4 |
| Maximal exercise | 1247 (259) | 1594 (212) | .0001 |
| Mean difference | 767 (−91) | 1174 (−6) | .02 |
| VEt (L) | |||
| Baseline | 11.3 (3.4) | 10.9 (3.4) | .6 |
| Maximal exercise | 26.1 (9.2) | 35.6 (8.8) | .0005 |
| Mean difference | 14.8 (5.8) | 24.7 (5.4) | .001 |
| Dyspnea | |||
| Baseline | 0 (0) | 1 (1) | .9 |
| Maximal exercise | 5 (3) | 7 (3) | .02 |
| Mean difference | 5 (3) | 6 (2) | .04 |
| IC (L) | |||
| Baseline | 2.32 (0.63) | 2.32 (0.58) | .8 |
| Maximal exercise | 2.17 (0.60) | 2.15 (0.56) | .9 |
| Mean difference | −0.15 (−0.03) | −0.17 (−0.02) | .1 |
| %ABD | |||
| Baseline | 58.7 (14.9) | 58.6 (16.8) | .8 |
| Maximal exercise | 73.3 (19.6) | 75.5 (19.8) | .7 |
| Mean difference | 14.6 (4.7) | 16.9 (3.0) | .04 |
| %Tx | |||
| Baseline | 45.7 (16.7) | 51.0 (25.2) | .3 |
| Maximal exercise | 55.2 (34.7) | 51.3 (33.6) | .9 |
| Mean difference | 9.5 (18) | 0.3 (8.4) | .02 |
| HR, bpm | |||
| Baseline | 89.6 (39.8) | 81.0 (21.8) | .2 |
| Maximal exercise | 97.2 (25.7) | 106.1 (37.6) | .3 |
| Mean difference | 7.6 (−14.1) | 25.1 (15.8) | .002 |
| SaO2, % | |||
| Baseline | 92 (3) | 92 (3) | .9 |
| Maximal exercise | 91 (4) | 91 (4) | .9 |
| Mean difference | −1 (1) | −1 (1) | .4 |
Ti=inspiratory time; Ti/Ttot=inspiratory time/total breathing cycle time ratio; Te=expiratory time; RR=respiratory rate; Vt/Ti=mean inspiratory flow; VE=pulmonary ventilation; FEV1=forced expiratory volume in the first second; FVC=forced vital capacity; FEV1/FVC=forced expiratory volume in the first second/forced vital capacity ratio; IC=inspiratory capacity; MCA/Vt=maximal compartmental amplitude/tidal volume ratio; %ABD=percentage abdominal contribution to the chest wall movement; %Tx=percentage thoracic contribution to the chest wall movement.
Data are presented as mean (standard deviation).
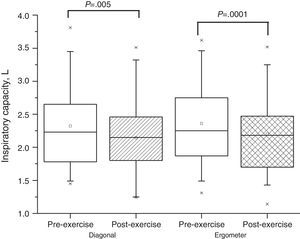
Eight (32%) of the 25 patients presented hyperinflation during the sub-maximal exercise with the diagonal technique. The mean inspiratory capacity of the group decreased from 2.32±0.63 to 2.17±0.60L (P=.005) (Fig. 1). The other patients who did not present hyperinflation finished the exercise with an inspiratory capacity of 2.29±0.45L, and it did not differ from the baseline value (P=.09).
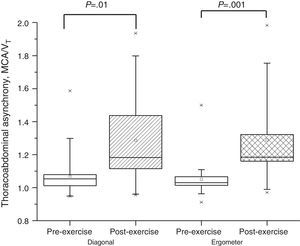
Thoracoabdominal Configuration at Rest and After the Sub-maximal Exercise Using the Diagonal TechniqueSeven (88%) of the eight patients who presented hyperinflation during the sub-maximal exercise performed with the diagonal technique presented thoracoabdominal asynchrony. The mean MCA/VT of the group was 1.07±0.10 and 1.26±0.42 (P=.01) at rest and at the end of exercise, respectively (Fig. 2). The abdominal compartment produced most of the displacement in the asynchronous chest wall movement in these patients, with an increase from 58±14 to 73%±19% (Table 3).
Inspiratory Capacity at Rest and After the Sub-maximal Exercise Using the Arm Cycle ErgometerSixteen (64%) of the 25 patients presented hyperinflation during the sub-maximal exercise with the arm cycle ergometer. The mean inspiratory capacity of the group fell from 2.32±0.58 to 2.15±0.56L (P=.0001) at rest and at the end of the exercise, respectively (Fig. 1). The other patients who did not present hyperinflation finished the exercise with an inspiratory capacity of 2.31±0.65L, which was no different from the baseline value (P=.1).
Thoracoabdominal Configuration at Rest and After the Sub-maximal Exercise Using the Arm Cycle ErgometerFourteen (88%) of the 16 patients who presented hyperinflation during the sub-maximal exercise with the arm cycle ergometer had thoracoabdominal asynchrony. The mean MCA/VT of the group was 1.05±0.1 and 1.29±0.25 (P=.001) at rest and at the end of exercise, respectively (Fig. 2). The abdominal compartment produced most of the displacement in the asynchronous chest wall movement in these patients, with an increase from 58±16 to 73%±19% (Table 3).
Sub-maximal exercise performed using the diagonal technique and the arm cycle ergometer – comparison of ventilatory variables in patients with and without hyperinflation: patients who presented hyperinflation during the diagonal and arm cycle ergometer exercise had a significantly shorter expiratory time and significantly higher respiratory rate, central respiratory drive, pulmonary ventilation, dyspnea and thoracoabdominal asynchrony values, compared to patients without hyperinflation (P>.05). There were no differences as regards the severity of the disease between the two groups according to the FEV1 and FVC measurements (Table 4).
Ventilatory Variables Obtained in Patients With and Without Hyperinflation at the End of the Sub-maximal Exercises Performed With the Second Diagonal Technique and Arm Cycle Ergometer.
| Variables | Hyperinflation | No Hyperinflation | P |
| Ti (s) | |||
| Diagonal | 1.1 (0.1) | 1.4 (0.14) | .06 |
| Ergometer | 1.2 (0.36) | 1.3 (0.40) | .20 |
| Ti/Ttot | |||
| Diagonal | 0.4 (0.10) | 0.3 (0.10) | .07 |
| Ergometer | 0.45 (0.1) | 0.28 (0.02) | .02 |
| Te (s) | |||
| Diagonal | 1.0 (0.13) | 1.3 (0.24) | .02 |
| Ergometer | 1.1 (0.26) | 2.1 (0.39) | .01 |
| RR (rpm) | |||
| Diagonal | 28.6 (3.0) | 22.3 (3.7) | .03 |
| Ergometer | 26.5 (3.6) | 17.6 (3.5) | .01 |
| Vt/TI (mL/s) | |||
| Diagonal | 804.1 (78.7) | 631.2 (70.3) | .01 |
| Ergometer | 874.2 (71.6) | 667.2 (82.1) | .01 |
| VE (L) | |||
| Diagonal | 25.3 (4.6) | 19.7 (5.5) | .03 |
| Ergometer | 27.8 (5.7) | 18.4 (3.1) | .02 |
| Dyspnea | |||
| Diagonal | 8.3 (1.4) | 6.1 (2.3) | .02 |
| Ergometer | 7.4 (2.6) | 4.9 (2.2) | .01 |
| FEV1(% of expected) | |||
| Diagonal | 39.4 (10.2) | 42.9 (12.9) | .06 |
| Ergometer | 37.2 (11.5) | 41.1 (12.6) | .06 |
| FVC (% of expected) | |||
| Diagonal | 78.9 (15.2) | 85.8 (16.5) | .06 |
| Ergometer | 80.9 (14.8) | 84.4 (18.2) | .09 |
| MCA/Vt | |||
| Diagonal | 1.29 (0.26) | 1.15 (0.42) | .04 |
| Ergometer | 1.29 (0.25) | 1.12 (0.30) | .02 |
| %ABD | |||
| Diagonal | 72 (10) | 60 (12) | .001 |
| Ergometer | 74 (11) | 58 (9) | .001 |
| %Tx | |||
| Diagonal | 48 (15) | 45 (18) | .20 |
| Ergometer | 48 (12) | 44 (17) | .20 |
Ti=inspiratory time; Ti/Ttot=inspiratory time/total breathing cycle time ratio; Te=expiratory time; RR=respiratory rate; Vt/Ti=mean inspiratory flow; VE=pulmonary ventilation; FEV1=forced expiratory volume in the first second; FVC=forced vital capacity; FEV1/FVC=forced expiratory volume in the first second/forced vital capacity ratio; IC=inspiratory capacity; MCA/Vt=maximal compartmental amplitude/tidal volume ratio; %ABD=percentage abdominal contribution to the chest wall movement; %Tx=percentage thoracic contribution to the chest wall movement.
Data are presented as mean (standard deviation).
This study enabled us to obtain the following results: firstly, at least one-third of patients with COPD had significant hyperinflation after an upper limb exercise test. Secondly, thoracoabdominal asynchrony occurred only in patients who presented dynamic pulmonary hyperinflation. Thirdly, the upper limb exercise using the diagonal technique induced less dynamic pulmonary hyperinflation, thoracoabdominal asynchrony and changes in the respiratory pattern than the arm cycle ergometer technique.
Although arm cycle ergometer training is usually considered the gold standard in rehabilitation of the upper limb muscles, the diagonal technique is also used for training the upper half of the body, as it resembles the movements of various activities of daily living, and because it involves recruitment of more muscle groups.14
Ashutosh et al.18 and Tobin et al.19,20 studied the breathing patterns in patients with COPD who performed simple activities of daily living using their arms, such as brushing their hair or tying their shoelaces, and observed that these patients had thoracoabdominal asynchrony. Gigliotti et al.3 were the first to demonstrate that patients with COPD may show dynamic pulmonary hyperinflation during upper limb exercise that leads to an increase in the ventilatory load. It is believed that there is an association between the increase in dyspnea and the increase in thoracoabdominal asynchrony with hyperinflation, but this association has not been demonstrated until now.
The onset of thoracoabdominal asynchrony is expected with an increase in respiratory resistance2,13 (upper or lower airways, lung tissue), decrease in pulmonary distensibility (parenchymal disease) and increase in chest wall distensibility20 (flexible rib cage, neuromuscular disease); this may contribute to producing respiratory muscle fatigue.21–24
Our patients did not present thoracoabdominal asynchrony before the diagonal (MCA/VT=1.07±0.12) and arm cycle ergometer exercise tests (MCA/VT=1.05±0.15). However, during the exercises, approximately 30% of patients with the diagonal technique and 60% of patients with the arm cycle ergometer presented thoracoabdominal asynchrony, with a disproportionate increase in the participation of the abdominal component with respect to the thoracic component. The abdominal motion contributed 75% to the chest wall movement, while the chest motion contributed 50%, so the sum of both compartments reached 125% with respect to the rest period; this clearly indicates thoracoabdominal asynchrony. Thus, we can hypothesize that the asynchrony presented by patients was mainly due to overwork of the diaphragm muscle. Criner and Celli24 demonstrated that, during arm exercise, the rib cage and abdominal wall should be fixed to stabilize the torso, so the rib cage becomes more rigid.
Likewise, arm exercises can produce stabilization of the rib cage and excessive movement of the abdomen, leading to increased end-expiratory lung volume. Vogiatzis et al.21 and Aliverti22 et al. observed that late hyperinflation during a leg exercise was associated with an increase in movement of the abdominal compartment. Some recent data have indicated that patients who performed an exercise with a leg cycle ergometer had increased end-tidal volume, presumably to cope with the expiratory action of the lower rib cage. One possible mechanism underlying this process is the dynamic hyperinflation that might have occurred in patients with asynchrony.22
The exercise restriction that occurs in patients with COPD is well known and is associated predominantly with ventilation.11,12 We observed an increase in the pulmonary ventilation, respiratory rate, tidal volume, mean inspiratory flow and dyspnea, and a decrease in the expiratory time in the maximal and sub-maximal exercise performed using the diagonal and arm cycle ergometer techniques. We also observed that the technique that enhanced the pulmonary ventilation and decreased the expiration time to a greater extent was the arm cycle ergometer technique, compared to the diagonal technique (Table 3). No difference was observed in the heart rate between the upper limb exercises, indicating that patients performed the exercises with the same workload (Table 3). We can probably start from the assumption that hyperventilation and shortening of the expiratory time lead to dynamic pulmonary hyperinflation that places a burden on the system, increasing the elastic work of breathing, which may predispose to fatigue. Patients with hyperinflation showed an increase in the mean inspiratory flow rate, which reflects the greater respiratory drive that these patients had to generate.
Furthermore, we observed that thoracoabdominal asynchrony only occurred in patients with hyperinflation. Regardless of the exercise, patients who presented pulmonary hyperinflation and thoracoabdominal asynchrony showed higher pulmonary ventilation, respiratory rate, central respiratory drive and dyspnea values in a manner associated with a shorter expiratory time, compared to patients without hyperinflation (Table 4). However, the percentage of patients who had these alterations was lower during the diagonal technique than during the arm cycle ergometer technique. We believe that the lower prevalence of onset of dynamic hyperinflation with the diagonal exercise is due to the increased expiratory time of the patients, and that it allows the inspiratory tidal volume to be completely expelled, thereby maintaining a more stable end-tidal lung volume. Thus, the diagonal technique may be more appropriate for exercising the upper limbs, as it not only induces less dynamic hyperinflation and thoracoabdominal asynchrony, but its introduction in a daily rehabilitation program is cheaper. However, to be precise, this observation should be evaluated using a complete rehabilitation program with the upper limbs, since long-term continuous physical training may reduce the dynamic pulmonary hyperinflation that these patients have during arm exercise testing.
Our study has three limitations: Firstly, we did not measure the total static lung volumes in our patients, and it could be argued that these measurements would help to improve evaluation of the resting respiratory status of our patients. Instead, we focused mainly on evaluating the dynamic inspiratory capacity and asynchrony at the end of the exercises and not on the degree of static pulmonary hyperinflation. Moreover, we designed the study to evaluate dynamic hyperinflation at the end of the exercise test and, unfortunately, we did not measure the inspiratory capacity when the exercises were carried out. This evaluation would have provided information relative to the exact moment of onset of dynamic hyperinflation; however, this was not the study objective and our aim was to specifically observe pulmonary hyperinflation at the end of the exercise tests. Secondly, we recruited only patients with COPD GOLD III and IV; in fact, however, we wanted to recruit these types of patients, as in our pulmonary rehabilitation clinical practice we observed that these patients presented higher dyspnea scores while they were performing arm exercises. Hence, from this clinical observation, we hypothesized that there would be differences in the primary outcome variables (inspiratory capacity and thoracoabdominal asynchrony) in these selected patients. Thirdly, we did not determine the metabolic load of either type of arm exercise; however, the workload of the diagonal exercise and the arm cycle ergometer were matched by the heart rate reached in the maximal exercise, which is a representative variable of the amount of work produced in each exercise.
As far as we know, the novel observation in this study is that, for the first time, it has been demonstrated that dynamic hyperinflation and thoracoabdominal asynchrony occurred simultaneously in patients with COPD who performed an upper limb exercise using an arm cycle ergometer or diagonal technique.
Our conclusion is that dynamic hyperinflation occurs due to superficial respiration which is detrimental to the respiratory pattern, as patients with COPD develop thoracoabdominal asynchrony and higher levels of dyspnea during the application of the diagonal and arm cycle ergometer techniques. The diagonal exercise technique may be the best technique for use in clinical practice compared to the arm cycle ergometer, as it induces less hyperinflation and thoracoabdominal asynchrony in patients with COPD.
Conflicts of InterestNone of the authors had any conflict of interests to declare in relation to this paper. We did not have any financial or personal relationships with other people or organizations that could inappropriately influence our work, such as employment, consultancies, stock ownership, honoraria, paid expert testimony, patent applications/registration and grants or other funding. No tobacco companies have financed any part of this manuscript.
Please cite this article as: Castro AAM, et al. Asincronía e hiperinsuflación en pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar obstructiva crónica durante 2 tipos de ejercicio de las extremidades superiores. Arch Bronconeumol. 2013;49:241–8.