Small pulmonary nodules and ground-glass opacities are commonly found in medical practice, because of the widespread use of computed tomography (CT), and the overcoming lung cancer screening is expected to increase their diagnostic rate.
Magnetic tracing is a recent technique found to be very useful for sentinel-node-biopsy and non-palpable breast cancer1. Since its design, it was meant for targeting lesions on any soft tissue organ, including thyroid and lung, with European Certification (CE) and FDA (United States Food and Drugs Administration) clearance for long term implantation, but no previous experience has been reported before for pulmonary nodules on medical literature.
Describing the techniqueM-GOLL is similar to radio-guided-occult-lesion-localization (ROLL), requiring a CT-scan guided-punction.
Depending on the size and location, a surgical-steel-seed marker is placed on the pulmonary nodule or nearby, always on the surgical-resection site.
A game-changing advantage of M-GOLL, is that the targeting can be done immediately before surgery, the same as hours, days, weeks and maybe months, without any impact on the surgical procedure.
We used Sysmex-Endomag's magnetic tracker (Sentimag®) for the seed's tracing. It's important to take into consideration, that none metal instruments should be used near the tracker's end. Plastic or titanium forceps might be used to manipulate lung tissue during this phase. Titanium staples used on previous surgeries do not interfere with the magnetic tracing.
Once the steel-seed has been located, the surgeon can proceed with the lung resection according to the surgical plan, and is able to correct or check with the tracker as many times as needed.
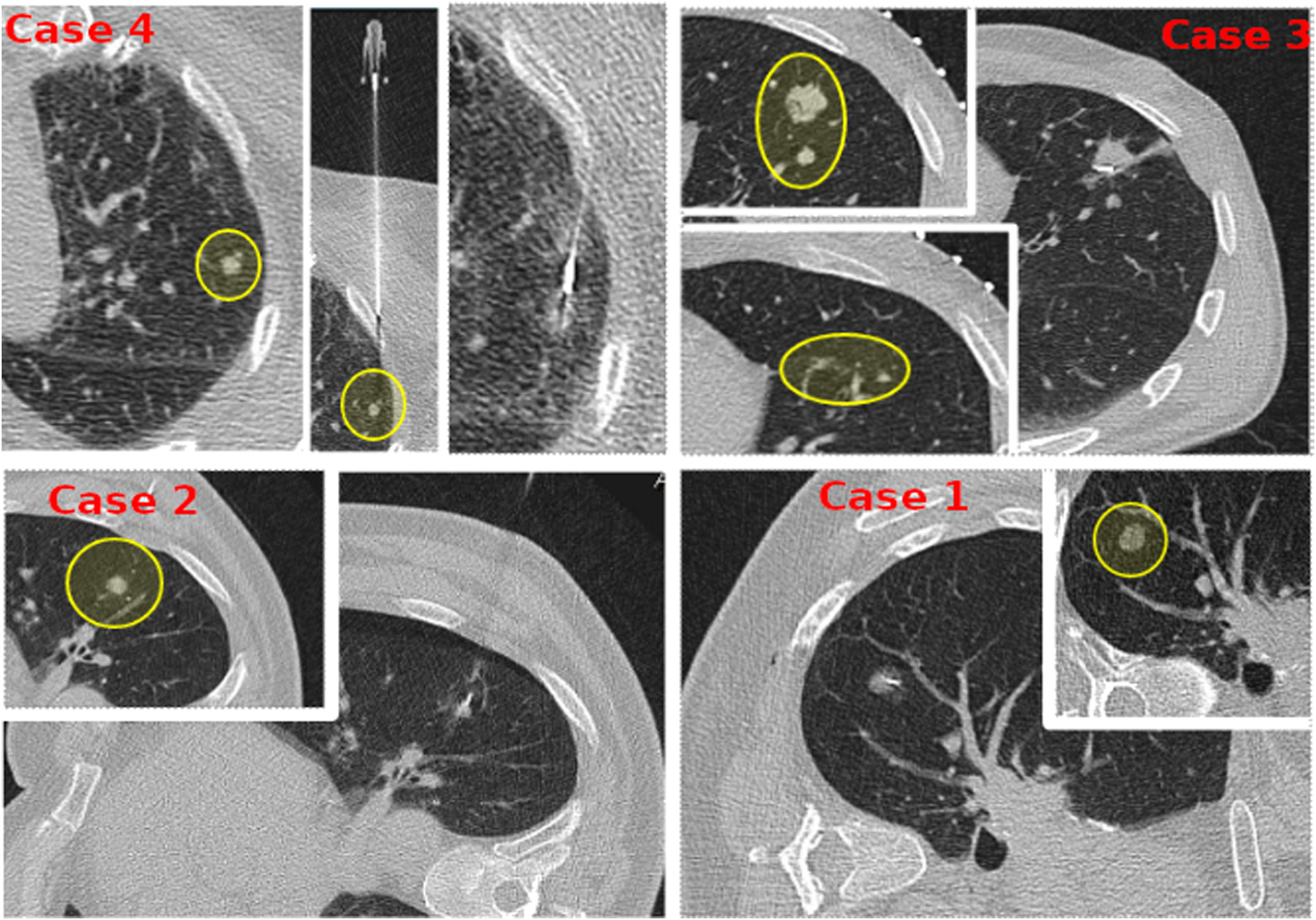
Case based discussionIn order to explain different technical variations, and better expose M-GOLL's potential usage, we present four different cases (Fig. 1).
Case#1: 62yo female patient, 2 years disease free after a right-upper lobectomy for a T3N0M0 adenocarcinoma, suspicious for relapse for a 12mm sub-solid pulmonary nodule on the right lower lobe.
Case#2: 57yo male patient with a 13mm lung colon metastasis on the 6th left segment, at 2cm from the chest-wall.
Case#3: A 53yo male with a previous SIVATS right lower lobectomy for a T3N0M0 adenocarcinoma, was diagnosed of pulmonary nodules on the left upper lobe. CT-guided core-needle biopsy reported lung cancer relapse and showed 2 more nearby micro-nodules of 5.17 and 5.68 millimeters, located at 3cm from the chest wall.
Case#4: A 72yo female with bilateral pulmonary metastases. One of them was subsolid, with a size of 5mm on the left-upper lobe, located at 1.5cm from the chest wall.
ResultsCase#1: The pulmonary nodule involved part of 6th and 10th segments. A wedge pulmonary resection was made with no lesion found on palpation, but a positive tracer mark. The final histopathological study reported a 15mm subsolid pulmonary adenocarcinoma, so the patient was sent to medical oncology for treatment.
Case#2: The surgery was programed 4h after placing the steel marker, but surgery was not possible because of unexpected events with the previous patient. The surgery was delayed for a week and went uneventful by single-incision VATS (SIVATS) approach, with no difference for delayed surgery.
Case#3: Given the small size and deep location of the nearby nodules, a SIVATS anatomical segmentectomy for the 4th and 5th segment was performed. The highest-located nodule was marked, to place the parenchymal resection limit.
Case#4: The pulmonary nodule was not visible nor palpable, but traceable with M-GOLL for a wedge resection. Histopathological study reported a 1cm subsolid non-palpable metastasis of intestinal adenocarcinoma.
ConclusionsWe found M-GOLL a very feasible procedure, and think that its ease of use may improve surgical resection of small and non-palpable pulmonary nodules. It has similar complication rates than standard guide-wire and other tracing techniques, due to the implantation method2-5.
In comparison with other widely used techniques, it has no risk of dislocation and avoids radioactive isotope manipulation. Its placement is easier than liquid tracers without pleural leak risk, and the biggest advantage is, that the steel seed may be placed even for weeks before surgery.
After a systematic review of the known medical databases, we found no other previous experience reported on G-MOLL for lung lesions. So, we expect that this brief communication will be a basis for larger series, in order to search for other possible advantages or disadvantages referable to the procedure.
Authors’ contributionsRA and GR contributed substantially to de study, design, execution, analysis and development of the M-GOLL technique.
GuarantorJosé Alejandro González García, MD.
Ethics statementConsent to participate was obtained from each patient on the clinic, when explaining the procedure and surgical plan.
FundingNone.
Conflict of interestNone declared.
We thank the Sysmex-Sentimag Spanish product management group representatives Oscar Dejean, Eduard Flaques and Sergi Lopez, who facilitated our experience with Sentimag with their assessment and orientation on its use.