Esculetin was identified to inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis or cell cycle arrest in several cancer cell lines. However, the effect of esculetin on lung cancer remains elusive.
MethodsThe anti-proliferative role of esculetin in murine Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells was evaluated by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) and colony formation assays. BALB/c mice were subcutaneously injected with LLC cells to investigate the inhibitory effect of esculetin on the growth of lung cancer xenograft. Invasive ability was detected in esculetin treated and untreated LLC cells by transwell assay. The association between esculetin and Wnt/β-catenin signaling, as well as nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB), was confirmed by testing the expression of c-myc, Cyclin D1 and NF-κB using Western blot.
ResultsEsculetin treatment in LLC cells led to significant decrease of cell proliferation in a time- and dose-dependent manner. After injection of LLC cells into mice, reduced size and weight of tumors were observed in esculetin treated mice compared to untreated mice. However, no difference in cell invasion was observed between the treated and untreated LLC cells. Notably decreased expression of c-myc, Cyclin D1 and NF-κB were observed in LLC cells with esculetin treatment compared to untreated cells.
ConclusionEsculetin plays an inhibitory role in the growth of lung cancer by down-regulating c-myc, Cyclin D1 and NF-κB.
Se ha determinado que la esculetina inhibe la proliferación celular e induce la apoptosis o la detención del ciclo celular en varias líneas celulares de cáncer. Sin embargo, su efecto sobre el cáncer de pulmón es todavía desconocido.
MétodosSe estudió el papel antiproliferativo de la esculetina en células murinas de carcinoma pulmonar de Lewis (LLC) mediante ensayos de bromuro de 3-(4,5-dimetil-2-tiazolil)-2,5-difenil-2H-tetrazolio (MTT) y de formación de colonias. Se inyectaron subcutáneamente células LLC a ratones BALB/c para investigar el efecto inhibidor de la esculetina sobre el crecimiento del xenoinjerto de cáncer de pulmón. La capacidad invasiva en células LLC tratadas o no tratadas con esculetina se evaluó mediante el ensayo transwell. La asociación entre la señalización de la esculetina y la de Wnt/β-catenina, y con el factor nuclear potenciador de las cadenas ligeras kappa de células B activadas (NF-κB) se confirmó midiendo la expresión de c-myc, de ciclina D1 y NF- κB usando Western blot.
ResultadosEl tratamiento con esculetina de las células LLC disminuyó significativamente la proliferación celular de una manera dependiente del tiempo y de la dosis. Tras la inyección de células LLC en ratones, se observó que los tumores de los ratones tratados con esculetina eran de menor tamaño y peso que los de los ratones no tratados. Sin embargo, no se observó diferencia en la invasividad celular entre las células LLC tratadas y las no tratadas. Se destacó la disminución de la expresión de c-myc, ciclina D1 y NF-κB en células LLC tratadas con esculetina en comparación con células no tratadas.
ConclusiónLa esculetina desempeña un papel inhibitorio en el crecimiento del cáncer de pulmón a través de la regulación de c-myc, ciclina D1 y NF-κ B.
Lung cancer is the third most prevalent cancer in the United States. Although less tobacco use contributes a reduced mortality rate,1 lack of efficient treatment is still an obstruction to the survival of lung cancer patients. Surgery resection, chemotherapy and radiation therapy have been used as mainstay treatments, while recent advances in early detection and targeted therapy have improved the outcome and prognosis of lung cancer. However, several limits such as therapy resistance contribute to treatment failures and cancer recurrence.2–4
Previous evidence showed that Wnt/β-catenin signaling was frequently activated in lung cancer, leading to the promotion of cell proliferation, survival and metastasis.5,6 Overexpression of Wnt genes, such as Wnt5a, is predictive of aggressive non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).7 In fact, Wnt/β-catenin signaling is not only highly activated in lung cancer but also in other cancers such as colon cancer. It is an important oncogenic factor in tumorigenesis, progression and metastasis. Accumulation of nuclear β-catenin caused by oncogenic Wnt signaling leads to its nuclear translocation and the formation of a complex with transcription factors, such as T-cell factor 4 (TCF-4), to initiation the transcription of its downstream targets such as c-Myc and cyclin D1.8
Esculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin) is a derivative of coumarin found in Artemisia capillaries, Citrus limonia and a number of other natural plants. It has been evidenced to inhibit cell proliferation and induce apoptosis or cell cycle arrest in several cancer cell lines including human malignant melanoma and colon cancer cells, and cancers including hepatocellular carcinoma.9–13 The interaction between esculetin and β-catenin disrupts the formation of β-catenin-Tcf complex in colon cancer.14 Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) activation has been documented to play an important role in the progression of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mediated lung tumor.15 Previous studies have evidenced the inhibitory effect of esculetin on NF-κB in pancreatic cancer cells and vascular smooth muscle cells.16,17 Additionally, it was reported that esculetin may protect mice from lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury via suppressing NF-κB.18 Thus, in this study, we investigated the effects of esculetin on lung cancer and the involvement of Wnt and NF-κB signaling pathways. We found that esculetin treatment exhibited inhibitory effects on the growth of lung cancer cells. Esculetin downregulated Wnt targeted genes and suppressed NF-κB.
MethodsCompoundEsculetin (6,7-dihydroxycoumarin, 98% purity) was purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO) and dissolved in dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO, 0.1%).
Cell CultureMurine Lewis lung carcinoma (LLC) cells were cultured in Dulbecco's modified Eagles medium (DMEM, Life Technology, Pleasanton, CA, USA) supplemented with and penicillin (60IU/ml)/streptomycin (50μg/ml) and 10% fetal bovine serum (Gibco, Grand Island, NY, USA) at 37°C in a 5% CO2 humidified incubator.
Measurement of Cell ProliferationCell proliferation was measured using 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2yl)-2,5-diphenyl-2H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay. LLC cells (6×103/well) were plated in 96-well plates. After 24h, phosphate buffered saline (PBS) or esculetin at various concentrations (20, 40 or 80μmol/l) was added into each well. MTT assay was performed every 24h of incubation for 5 days. Briefly, 20μl MTT (Amresco, USA) was added to each well and incubated for 4h. The formazan precipitation was dissolved in 150μl DMSO and the results were observed using a microplate reader (BioTek Instruments, Inc., Vermont, USA) at 490nm. Each test was repeated for three times.
Colony Formation AssayThe colony formation assay was performed in 6-well plates covered with 1% low melting agarose and 0.25ml 2× RPMI with 20% FBS. Cells (500cells/well)) were mixed 0.7% low melting agarose and 0.25ml 2× RPMI with 20% FBS and seeded onto the bottom layer of soft agar. The plates were incubated for 21–28 days at 37°C in a 5% CO2 humidified incubator. Colony numbers were counted after staining with crystal violet and photographed using a phase-contrast microscope (100×).
Mice ModelThe experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee. BALB/c mice (6–8-week-old female) were purchased from SLAC (Shanghai, China). LLC cells (1×106cells/100μl PBS) were subcutaneously injected in the right inguinal region of mice. Mice were divided into two groups, untreated vehicle group and esculetin (100mg/kg) treated group for 20 days. At the end of the treatment, body weight was measured and mice were sacrificed for obtaining tumor size and weight.
Transwell AssayInvasion assay was performed to test the effect of esculetin on cell invasive ability using transwell invasion chambers coated or non-coated with Matrigel (Becton Dickinson Labware, USA) according to the manufacturer's instructions. Cells (5000cells/well) were plated onto the chambers in 100μl medium containing 0.1% DMSO or esculetin (20, 40 or 80μmol/l). After 48h incubation, the cells on the bottom surface of the membrane were fixed in 90% alcohol and stained with crystal violet staining for counting using a microscope.
Western BlottingCells were treated with or without esculetin for 24h. Cell were lysed by Lysis Buffer containing PMSF on ice. Cell lysate was separated by 10% SDS-PAGE gels and transferred onto a NC membrane (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, USA). The membranes were blocked by 10% non-fat milk dissolved in 0.1% Tween 20 in TBS (TBST) at 37°C for 1h. The membranes were incubated overnight with primary antibodies including c-myc (#ab32072, Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA), cyclin D1 (#ab134175, Abcam, USA), β-catenin (#ab16051, Abcam, USA), NF-κB (#ab16502, Abcam, USA) and I-κB (#9244, Cell Signaling Technology Inc., USA), and β-actin (#ab8227, Abcam, USA) as a control for normalization. Signals were detected using an ECL Western blotting kit (Amersham Pharmacia Biotech, USA).
Statistical AnalysisStudent's t test was used to determine the significant difference between the control and experimental groups. Differences were considered to be significant at P<.05.
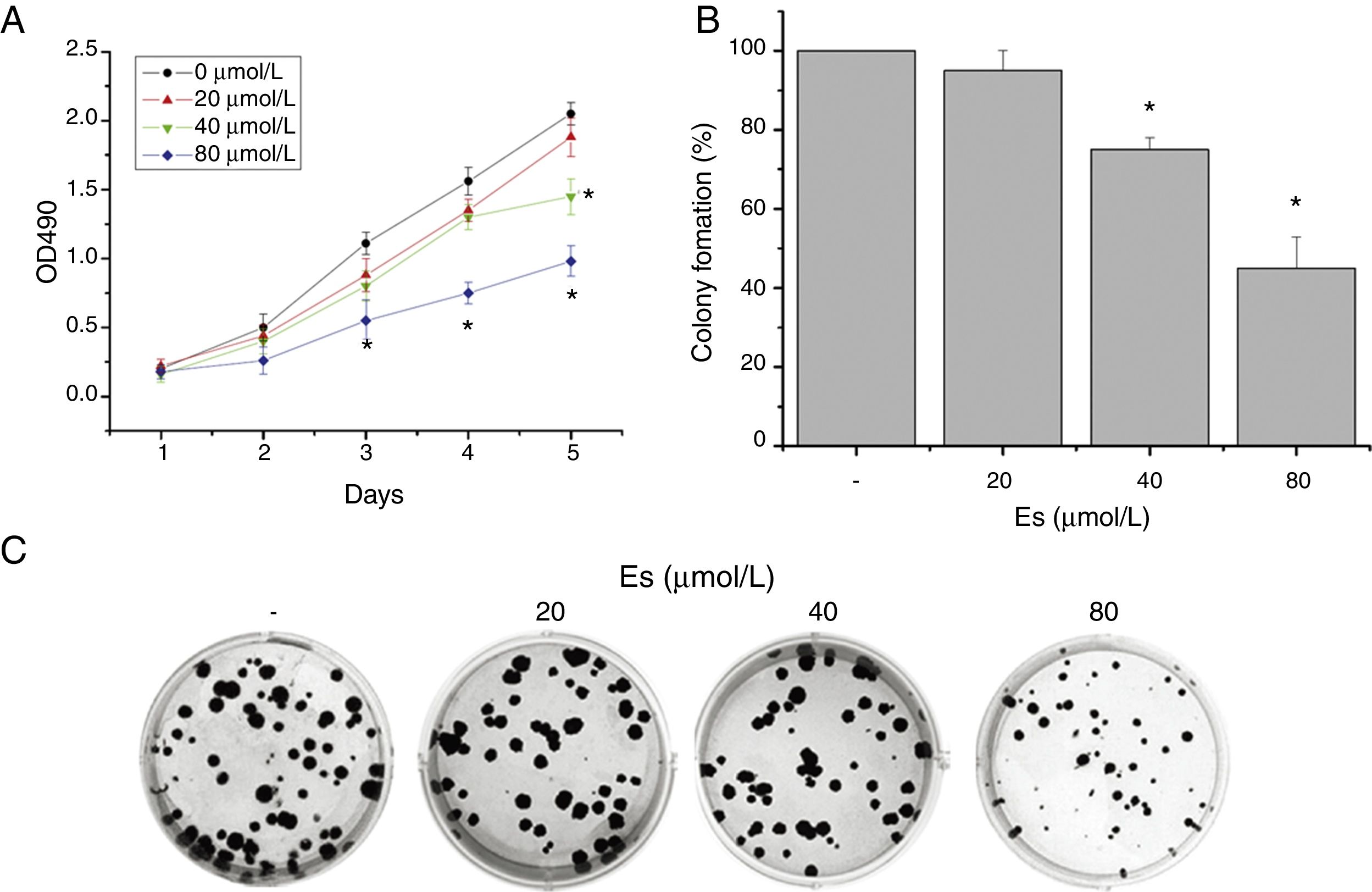
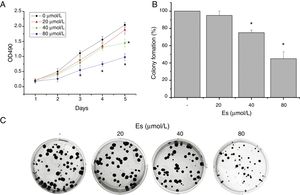
ResultsEsculetin Inhibited Cell Viability and Colony Formation of Lewis Lung CarcinomaEffect of esculetin on cell viability of murine LLC was first evaluated by MTT assay. Different doses of esculetin (0, 20, 40 and 80μM) were used to treat LLC cells. Esculetin suppressed cell viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner. As shown in Fig. 1A, 40μM significantly reduced cell viability on day 5, while 80μM had remarkably decreased cell viability since day 3 (P<.05). We also observed that 40 and 80μM esculetin led to reduced colony formation of LLC cells in soft agar (Fig. 1B and C, P<.05).
Esculetin treatment of LLC cells impaired its proliferation in liquid and semi-soft cultures. (A) Effect of esculetin treatment on LLC cell growth in liquid culture. MTT assay was performed in 96 wells plate. Mean±SD of 6 wells. (B) Effect of esculetin treatment on colony formation of LLC cells. Cells were seeded into soft agar in triplicate, and colonies were counted after 21–28 days of culturing. Mean±SD (3 wells) are expressed as percent variation relative to vehicle treated cells (control). *P<.05. (C) Representative pictures of colonies of LLC treated with esculetin.
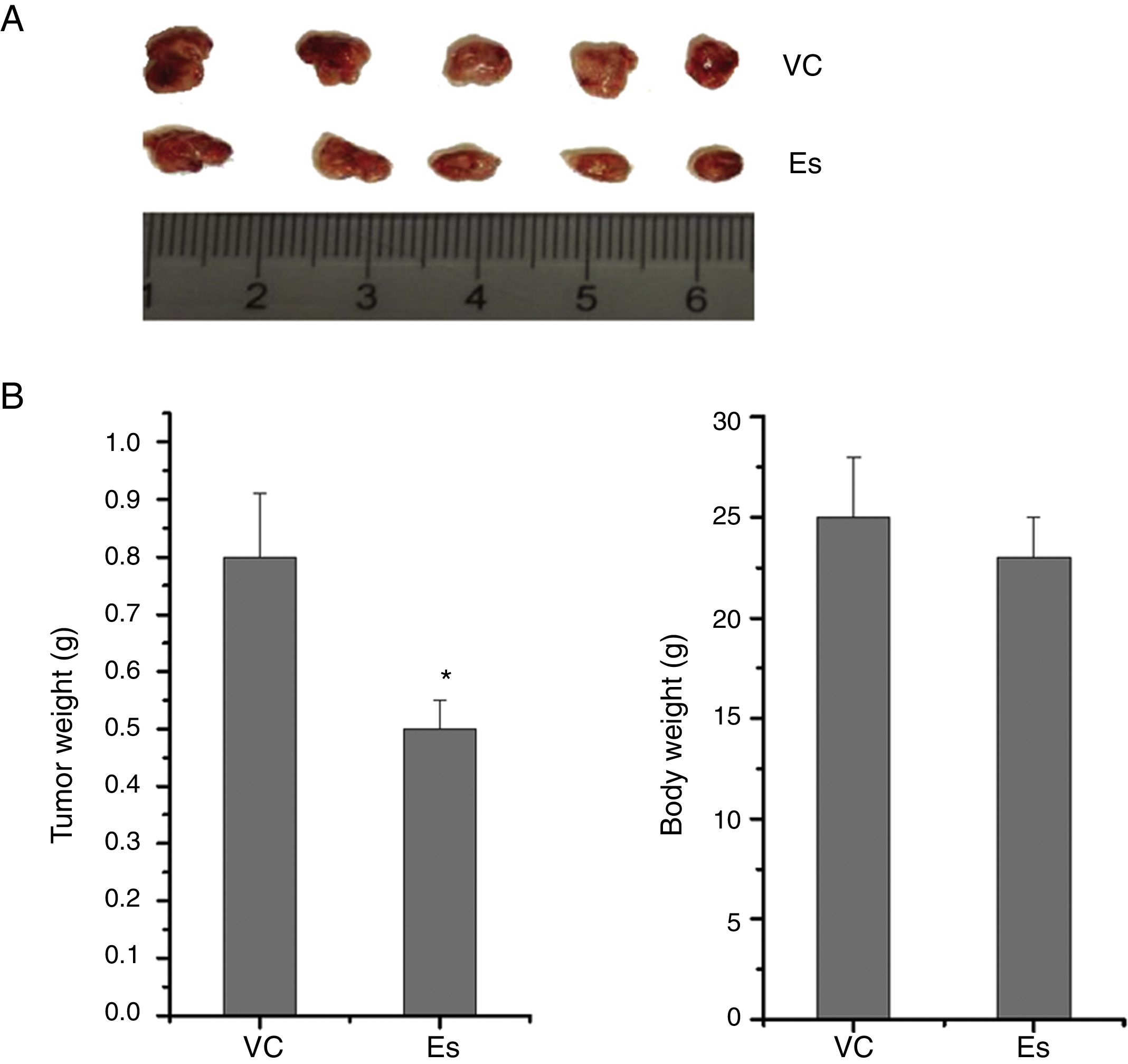
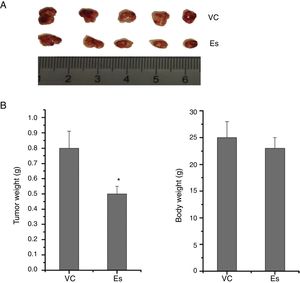
To ascertain the effect of esculetin on tumor growth in vivo, LLC cells (1×106cells/100μl PBS) were subcutaneously injected into the right inguinal region of BALB/c mice. Mice were treated with esculetin (100mg/kg bw) or PBS for 20 days. Body weight was measured after the treatment and mice were then sacrificed to obtain tumor size and weight. We found markedly reduced size and weight of tumors in mice with esculetin treatment compared to those control mice (Fig. 2A and B, P<.05). No significant change in body weight was observed between the two groups.
Esculetin treatment suppressed the growth of LLC-derived tumors. LLC cells were subcutaneously inoculated in the right inguinal region of BALB/c mice at the number of 1×106 each, which was followed by daily Es treatment at the dose of 100mg/kg bw or PBS vehicle (VC) treatment for 20 days. Tumors were dissected at the end of the experiments (A) and the tumor weight was measured (B). Body weight was measured prior to tumor dissection (B). Data were expressed as mean±S.E.M. (n=6 in each group). *Compared to that from PBS vehicle-treated LLC cells, *P<.05.
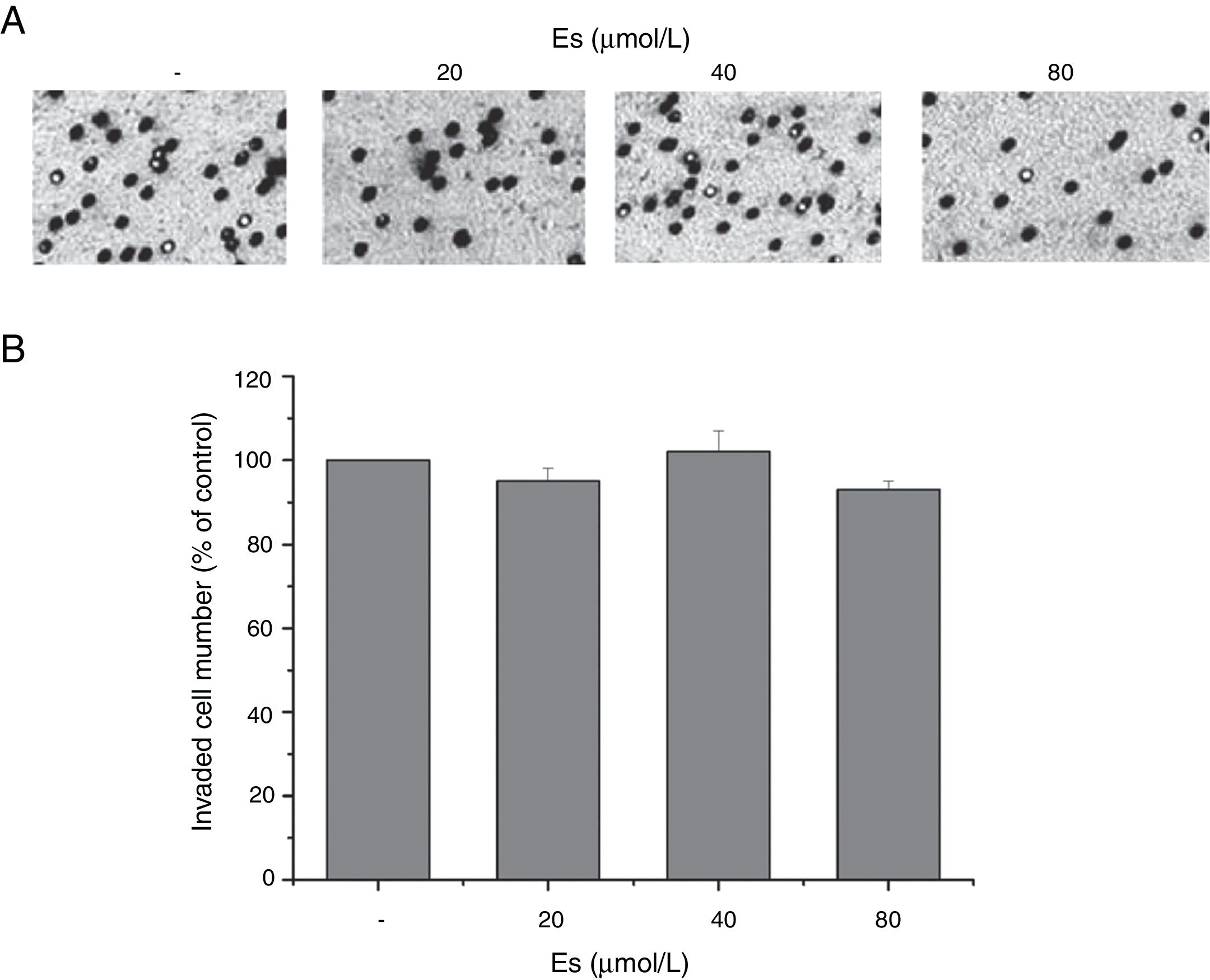
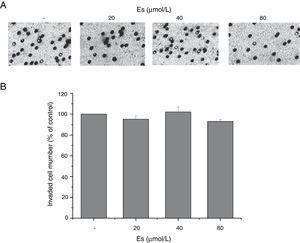
After confirming the effect of esculetin on tumor growth, we further tested whether esculetin affected cell invasion. Evaluation of cell invasion under different doses of esculetin treatment for 48h demonstrated that, esculetin had no influence on the invasive activity of LLC cells (Fig. 3A). Quantitative analysis was shown in Fig. 3B.
Esculetin at indicated concentrations does not alter invasiveness of LLC cell significantly. (A) Cell invasion ability was assessed by transwell assay after a 48-h treatment with esculetin. (B) The percentages of cells that could invade via the membrane relative to control are shown as a histogram. Data were expressed as mean±S.E.M.
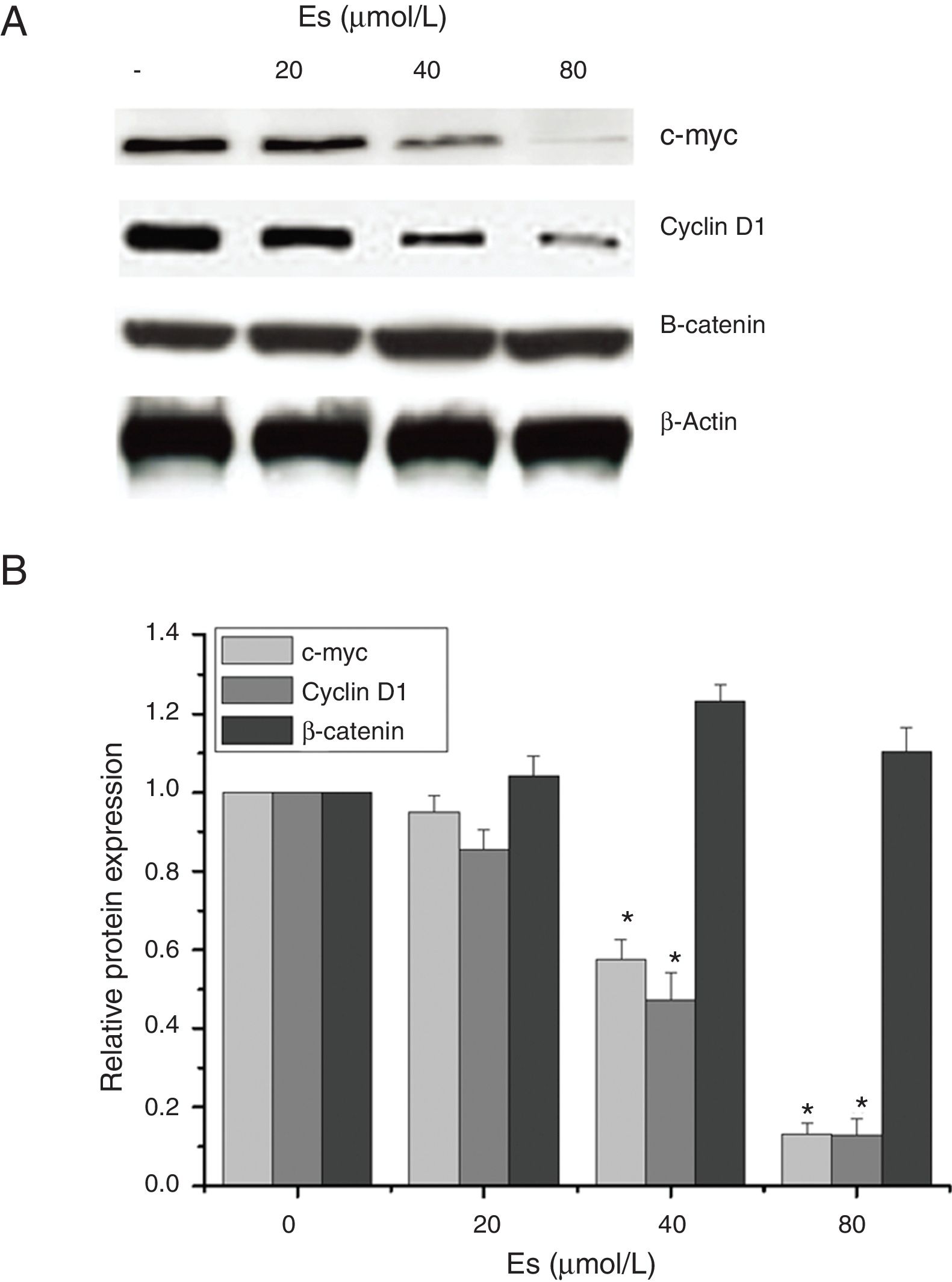
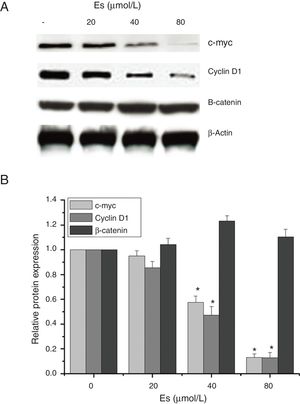
As esculetin was identified as a potential inhibitor of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, we tested the protein expressions of c-myc and cyclin D1 as the target genes of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. There were significant decreases in the protein levels of c-myc and cyclin D1 in LLC cells after 24-h treatment of esculetin (40 and 80μM) compared to untreated cells (Fig. 4A and B, P<.05).
Esculetin inhibits the expression of target proteins, c-Myc and cyclin D1, of β-catenin pathway in LLC cells, not altering the level of β-catenin itself. Proteins expression in LLC cells with or without Esculetin treatment (24h) was measured by Western blot (A). The relative protein level was normalized with β-actin and the quantitative data were represented as bar graph (B). Data were expressed as mean±S.E.M.
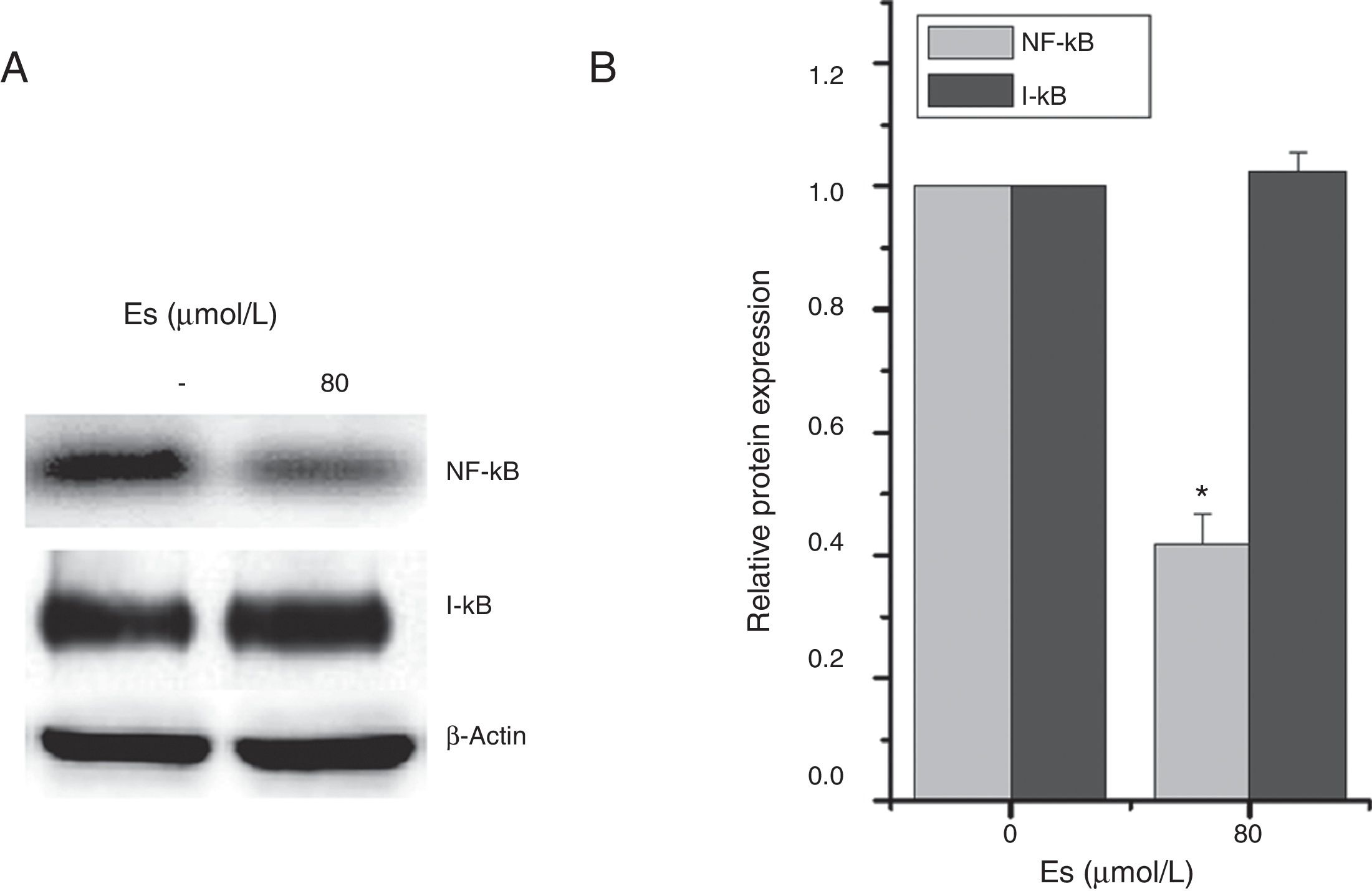
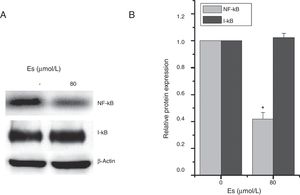
As previously reported that esculetin inhibited NF-κB pathway, we tested the protein levels of NF-κB and I-κB protein levels after 24-h of 80μM esculetin treatment in LLC cells. Compared to untreated LLC cells, esculetin significantly downregulated protein level of NF-κB (Fig. 5A and B, P<.05).
Esculetin attenuates NF-κB pathway in LLC cells. Western blot analysis shows decrease in protein levels of transcription factor NK-κB and unaltered levels of its inhibitor I-κB in LLC cells. Proteins expression in LLC cells with or without Esculetin treatment (24h) was measured by Western blot (A). The relative protein level was normalized with β-actin and the quantitative data were represented as bar graph (B). Data were expressed as mean±S.E.M. *P<.05.
The high incidence and mortality rate of lung cancer requires improvements in both early detection and therapeutic methods. Despite the development of earlier detection using low-dose computed tomographic,19 the overall survival rate was only slight increased. Thus, it is essential to identify new therapeutic compounds for effective treatment. As previously reported, esculetin is a natural compound inhibiting cell proliferation and inducing cell apoptosis in several cell lines.20 In this study, we identified its anti-proliferative effect on a lung cancer cell line, LLC. We observed that esculetin decreased cell proliferation and colony formation in a dose- and time-dependent manner, where 80μM esculetin treatment was determined to significantly affect cell proliferation and colony formation on day 3. However, the doses of esculetin varied in different cell lines. For example, 50μM of esculetin was enough to elicit a significant decrease of cell proliferation in human normal gastric epithelial cell line GES-1 on day 3, while for other cells such as human gastric cancer cell lines MGC-803 and human hepatocellular carcinoma cell line SMMC-7721, the doses were 12.5μM and 0.3mM, respectively.21,12
To confirm whether esculetin also acts as a tumor suppressor in lung cancer in vivo, we treated mice with esculetin and found significantly reduced tumor size and weight in treated mice compared to control. The anti-proliferative role was not only shown in lung cancer but also demonstrated in other cancers such as metastatic osteosarcoma22 and hepatocellular carcinoma.12 Of note, there was no difference in the body weight between treated and untreated mice, suggesting that this dose of esculetin did not exhibit toxicity to mice. It was suggested that injection of 700mg/kg esculetin per day showed no adverse effects on the body weight of mice.12 The same conclusion was drawn by another study using 50mg/kg of esculetin on rats.23
Degradation of extracellular matrix is an essential step of tumor metastasis. The inhibitory effect of esculetin on MMP regulation has been reported in several cell lines including human gastric cancer cells MGC-803,21 vascular smooth muscle cells24 and osteosarcoma LM8 cells.22 These results suggest that esculetin may suppress tumor invasion and metastasis in vivo, which was also observed in previous studies. An in vivo study on LM8-bearing mice demonstrated that less metastasis to lung and liver was found in mice treated with ∼70–140μM esculetin compared to that of untreated mice.22 However, we did not observe the change in invaded cell number in LLC cells treated with esculetin. It may be caused by differential effects of esculetin in different cell lines. Further research is needed to reveal the detailed mechanism.
In 2014, Lee SY et al. found that esculetin disrupted the formation of the β-catenin/Tcf transcriptional complex by binding with β-catenin to suppress proliferation of colon cancer cells.25 The present study further evidenced that esculetin also inhibited Wnt signaling pathway in lung cancer cells, where the expression of c-myc and Cyclin D1 was remarkably reduced by esculetin in a dose-dependent manner. A recent study showed a similar result demonstrating that esculetin supplementation effectively suppressed tumor growth by targeting to c-myc induced energy metabolism.23 As a key transcription factor participating in the progress of tumor, c-myc has been regarded as a potential target for tumor therapy. The current results provide a possibility for the clinical use of esculetin in cancer treatment. Additionally, the inhibitory effect of esculetin on Cyclin D1 has also been reported in several previous studies.26–28 In fact, the role of esculetin in regulating Cyclin D1 was first reported in 2002, where esculetin achieved anti-proliferative function by blocking phosphorylation of pRb to arrest human leukemia HL-60 cells at G1 phase.29 In addition to Wnt signaling, esculetin treatment also decreased the expression level of NF-κB in human pancreatic carcinoma cells PANC-1.30 It was reported that esculetin attenuated NF-κB activation without affecting its inhibitor, instead it was suggested that the reduced interaction between Nuclear Factor-Erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) and its inhibitor Kelch-like ECH-associated protein1 (KEAP1) after esculetin treatment led to abrogated NF-κB activity.17 Nrf2 exerts a protective function against reactive oxygen species by elevating the transcription of numerous anti-oxidant enzymes.31 Giving the result of unchanged I-κB in this study, the inhibitory effect of esculetin on NF-κB may be also due to the direct binding of esculetin to KEAP1. Additionally, it is well-known that activation of NF-κB is associated with promotion of cell survival and proliferation by several mechanisms including upregulating anti-apoptotic proteins, c-myc and Cyclin D1.32,33 Thus, in this study, down-regulated NF-κB by esculetin may also be the cause of reduced expressions of c-myc and Cyclin D1. In conclusion, we identified that esculetin could be a potential agent for treatment against lung cancer by suppressing NF-κB, c-myc and Cyclin D1.
Conflicts of InterestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.