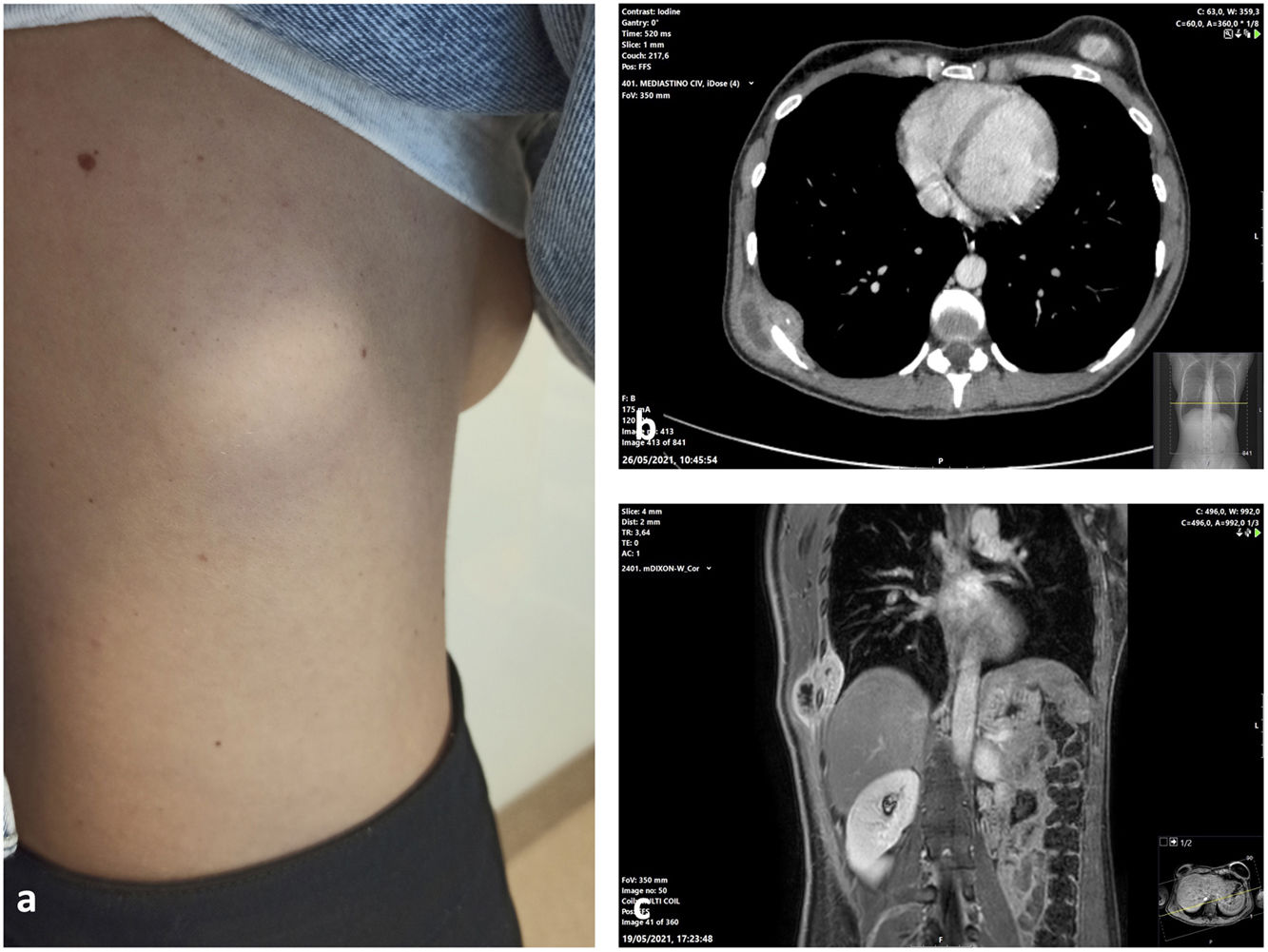
We present the case of a 36-year-old woman, who was referred, for clinical rib pain of several weeks’ development, accompanied by a fixed and indurated tumour in the right posterolateral chest wall (Fig. 1a). We conducted a computed tomography, which revealed a cystic-necrotic mass with involvement of the intermuscular plane and intrathoracic extension that presented an extrapleural soft tissue component and coarse calcifications (Fig. 1b). To better characterise the lesion, we requested a magnetic resonance. This revealed a encapsulated lesion with alteration of the signal of the musculature that suggested rupture of the lesion. In T2 sequences, we identified hypointense membranes suggestive of vesicles. Rupture of a hydatid cyst was considered as a diagnostic possibility (Fig. 1c).
Bearing these results in mind, we decided to perform a diagnostic-therapeutic surgical intervention while taking the necessary preventive measures given the possible diagnosis of hydatid cyst rupture. We performed a block resection including muscular planes along with the 8th and 9th right costal arches repairing the wall defect with a Goretex mesh. The anatomopathological analysis revealed a 5cm abscessed necrotising granulomatous inflammation, affecting the soft tissues, with the presence of acid-fast bacilli (AFB), and positive amplification for Mycobacterium tuberculosis complex.
Authors’ contributionAll authors have contributed intellectually to the case, meet the conditions of authorship and have approved the final version of the case.
FundingThere has been no funding or sponsorship for the publication of this article.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.