Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a common complication of chronic respiratory diseases (CRD) associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Early and individualized identification of PH in these patients is crucial to better understand the evolution of the disease and to assess the application of therapeutic measures aimed at its control. However, there is no consensus on how to approach the diagnostic process. The scarce scientific evidence in this field justifies the creation of this SEPAR position paper, which aims to become a tool to aid in the diagnosis of PH associated with CRD that facilitates decision making for the benefit of patients and the optimization of resources. A panel of 16 SEPAR experts has identified three critical questions. The answers to these questions were developed by the panel members, who were divided into three groups according to their expertise in the underlying disease in question: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, interstitial lung disease and obesity hypoventilation syndrome. Prior to the discussion and drafting of the document by each group, a systematic review of the literature was performed according to the guidelines recommended by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA). We generated a schematic proposal adjusted to the characteristics of each disease for the diagnostic approach to PH associated with respiratory disease.
Pulmonary hypertension (PH) is a common complication of chronic respiratory diseases.1–4 In patients with COPD, it was found that the overall prevalence of PH was 39.2%. Although patients with very severe obstruction have a mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP)>20mmHg in up to 90% of cases, the majority of COPD patients develop mild to moderate PH. Only 5% of cases reach a resting mPAP>35–40mmHg. In addition, PH in patients with mild to moderate obstruction is rare (5–10%). Like COPD, the majority of patients with ILD have mild to moderate PH with mPAP between 21 and 34mmHg. However, in patients with severe disease, the prevalence of PH can reach 15%. In the case of hypoventilation syndromes, the very limited evidence available refers only to patients with hypoventilation due to obesity. For this reason, all questions in this document will directly refer to obesity hypoventilation syndrome (OHS).
There is considerable evidence that the diagnosis of PH in patients with respiratory disease is associated with increased morbidity3 and mortality.4–6 This is particularly important for those who develop severe PH, the occurrence of which has a serious impact on survival.7,8 Although PH usually occurs in the more advanced stages of respiratory disease, its onset is sometimes not related to the evolution of lung function or structural involvement of the lung parenchyma.1 In addition, the severity and course of PH can vary depending on the underlying respiratory disease.9 For these reasons, the early and individualized identification of PH in patients with chronic respiratory disease is crucial to better understand the evolution of the disease and to assess the application of therapeutic measures aimed at its control.10,11 Although right heart catheterization (RHC) is the gold standard test to confirm the diagnosis of PH,10,11 there is no consensus on how to approach the diagnostic process in the context of chronic respiratory disease.10,11 Although echocardiography is currently the primary screening test for suspected PH, the identification of these patients in routine clinical practice remains insufficient for several reasons.12 There are technical limitations concerning the acquisition of adequate echocardiographic images due to the respiratory disease itself13,14; however, we must also consider the healthcare burden for the healthcare system,15 since the test is in high demand in hospitals and outpatients.16,17 Therefore, a correct orientation in the request for echocardiography in chronic respiratory diseases of high prevalence such as COPD, ILD or OHS allows us to optimize this valuable health resource, its availability, and diagnostic cost-effectiveness.
In view of the above, some multiparametric screening tools or even proposals for diagnostic algorithms have recently been published,18–21 but only one of these has been validated.22 As such, they are little used in the clinical setting, and their cost-effectiveness has not been studied in order to adapt them to the different levels of care.
The scarce scientific evidence in this field justifies the creation of this SEPAR position paper, which aims to become a tool to aid in the diagnosis of PH associated with chronic respiratory disease that facilitates decision making for the benefit of patients and the optimization of resources.
As a working method, the panel of 16 SEPAR experts has identified three critical questions. The answers to these questions were developed by the panel members, who were divided into three groups according to their expertise in the underlying disease in question (COPD, ILD and OHS). Prior to the discussion and drafting of the document by each group, a systematic review of the literature was performed according to the guidelines recommended by the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA).23 In addition, we have included an assessment of two patients regarding their experience with the diagnostic process of PH associated with respiratory disease (Supplementary material).
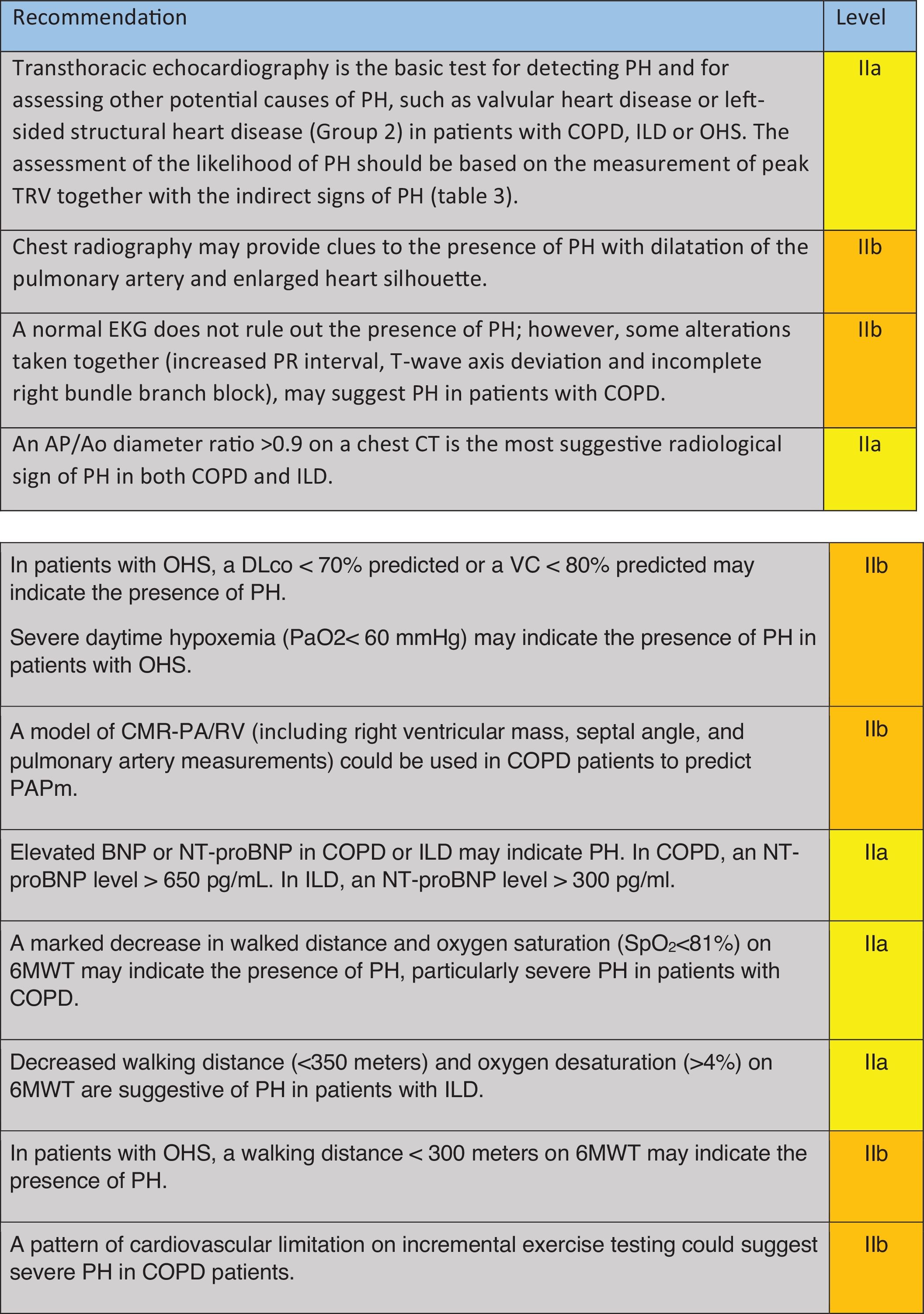
Which Clinical Data Should Lead to the Suspicion of PH in Patients With COPD, ILD, or OHS? (Table 1)A qualitative study on a small cohort of patients with COPD-PH and ILD-PH found that dyspnea, cough and fatigue were the most commonly reported symptoms,24 and that they occurred with similar frequency in both conditions. In a study where the probability of PH was assessed through echocardiography, COPD patients in both groups, with and without probable PH, presented similar modified Medical Research Council scale and COPD Assessment Test scores.25 Furthermore, some clinical signs found in PH patients, such as a loud pulmonic component of the 2nd heart sound or the pansystolic murmur of tricuspid regurgitation, might be obliterated by pulmonary hyperinflation, high respiratory swings, or pathological respiratory sounds such as rhonchi or crackles. In any event, these signs are non-specific and have low sensitivity.26
Recommendation regarding which clinical data should raise suspicions of PH in COPD, ILD and OHS.
COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ILD: interstitial lung disease; PH: pulmonary hypertension; OHS: obesity hypoventilation syndrome; BMI: body mass index; NYHA: New York Heart Association; NIV: non-invasive mechanical ventilation; CPAP: continue positive airway pressure. Green: recommended; yellow: should be considered; orange: may be considered.
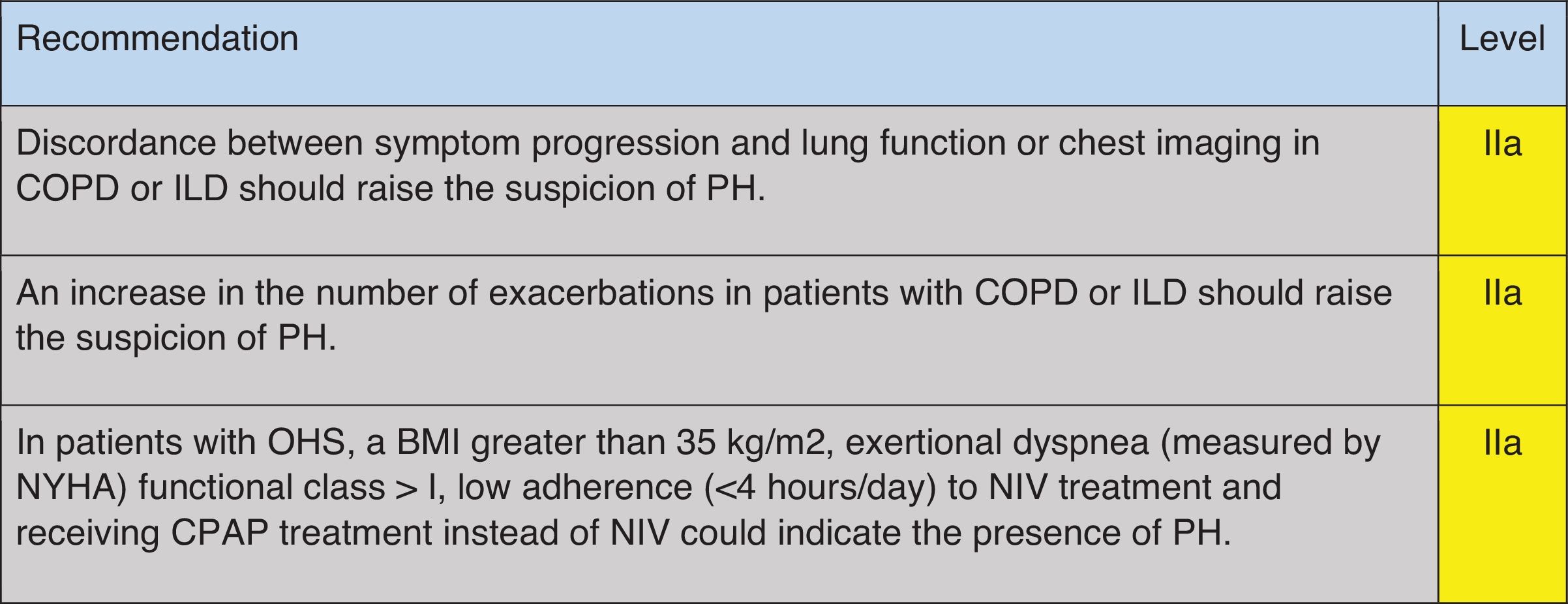
When symptoms and signs appear to be disproportionately severe compared with the respiratory function compromise or the extent of parenchymal disease in the CT scan, these should alert physicians to the potential presence of pulmonary vascular disease both in COPD and in ILD patients.7,8,10,27 In more advanced stages of the respiratory disease, more specific symptoms and signs of right heart failure might be found, including chest pain, syncope, peripheral edema, increased jugular venous pressure, or abdominal swelling.26–28 However, in COPD patients, peripheral edema may also be caused by renal hypoperfusion and activation of the renin–angiotensin–aldosterone axis promoting fluid retention, which is also favored by hypoxemia and hypercapnia; these mechanisms may be further amplified during an acute exacerbation of COPD.28 In both COPD29,30 and ILD patients,31,32 PH increases the risk of acute exacerbations regardless of its hemodynamic severity; thus, frequent exacerbations must be considered as a possible association with PH.
In patients with OHS, a higher BMI is associated with increased mPAP and a higher probability of PH.33 Furthermore, increased daytime sleepiness, reduced exercise tolerance as measured by the New York Health Association (NYHA) functional class, and lower tolerance to treatment with non-invasive mechanical ventilation may also characterize patients with OHS and PH.33
Unfortunately, there is no evidence for a single physical finding capable of accurately predicting PH in patients with lung disease.26
Which Complementary Tests Will Contribute to the Detection of PH in Patients With COPD, ILD, or OHS? (Table 2)Transthoracic Doppler EchocardiographyTransthoracic Doppler echocardiography (TTE) is considered the non-invasive test of choice for PH screening1,11 (Table 3).
Recommendations regarding which complementary tests could contribute to the detection of PH in COPD, ILD and OHS.
COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ILD: interstitial lung disease; PH: pulmonary hypertension; OHS: obesity hypoventilation syndrome; TVR: tricuspid regurgitant velocity; EKG: electrocardiogram; PA: pulmonary artery; Ao: aorta; CT: computerized tomography; FEV1: forced respiratory volume at 1second; FVC: forced vital capacity; DLCO: diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide; PaO2: partial pressure of arterial oxygen; VC: vital capacity; CMR: cardiac nuclear magnetic resonance; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide; NT-proBNP: N-terminal-BNP; 6MWT: six-minute walking test. Green: recommended; yellow: should be considered; orange: may be considered.
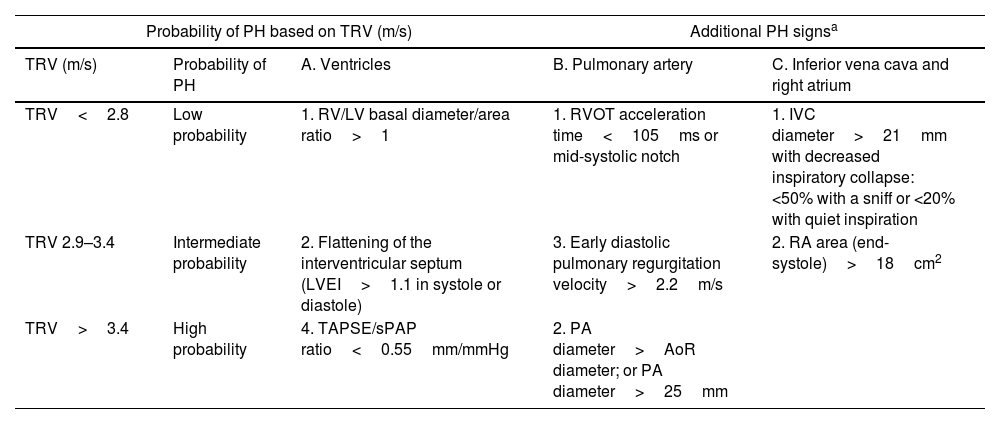
Echocardiographic signs suggestive of pulmonary hypertension.
| Probability of PH based on TRV (m/s) | Additional PH signsa | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TRV (m/s) | Probability of PH | A. Ventricles | B. Pulmonary artery | C. Inferior vena cava and right atrium |
| TRV<2.8 | Low probability | 1. RV/LV basal diameter/area ratio>1 | 1. RVOT acceleration time<105ms or mid-systolic notch | 1. IVC diameter>21mm with decreased inspiratory collapse: <50% with a sniff or <20% with quiet inspiration |
| TRV 2.9–3.4 | Intermediate probability | 2. Flattening of the interventricular septum (LVEI>1.1 in systole or diastole) | 3. Early diastolic pulmonary regurgitation velocity>2.2m/s | 2. RA area (end-systole)>18cm2 |
| TRV>3.4 | High probability | 4. TAPSE/sPAP ratio<0.55mm/mmHg | 2. PA diameter>AoR diameter; or PA diameter>25mm | |
TRV: tricuspid regurgitation velocity; RA: right atrium; PA: pulmonary artery; LVEI: left ventricle eccentricity index; sPAP: systolic pulmonary arterial pressure; AoR: aortic root; AT: acceleration time; TAPSE: tricuspid annular plane systolic excursion; RVOT: right ventricular outflow tract; IVC: inferior vena cava; RV: right ventricle; LV: left ventricle.
It is important to note that, while it may provide some indicative information regarding the origin of PH, such as left atrial dilation or left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy and limitations on its relaxation, this technique does not allow the differentiation between pre-capillary and post-capillary PH.10,11 Therefore, confirmation through RHC is always necessary, given the strictly hemodynamic definitions.10,11 It should also be noted that echocardiography may not always be able to obtain a systolic pulmonary arterial pressure (sPAP), often showing low correlation with values obtained by RHC. Thus, in mixed cohorts of advanced lung disease, the indirect estimation of sPAP is not feasible in 66% of all cases, and in 46% of those ultimately diagnosed with PH by RHC.34 In COPD patients, estimation of sPAP is achieved in only about a third of cases.34,35 Furthermore, the presence of emphysema significantly limits this assessment,35 with discordance between estimated sPAP by TTE and measured by RHC found in 44% of cases.34 Moreover, these technical limitations are not corrected by assessing signs of right ventricular (RV) overload.13 Techniques such as strain imaging to determine RV free wall tension may help identify patients with RV dysfunction, although evidence is scarce, and measurement is challenging (feasible in 57% of subjects with an inter-operator agreement of 0.85).35 In COPD patients without LV disease or comorbidities and without tricuspid regurgitation, the time to peak systolic flow in the RV outflow tract, adjusted for heart rate and the velocity–time integral (VTI) of the RV S’ wave, are simple and reproducible methods that correlate well with PA pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance.36 Other indirect signs of PH such as RV morphology, dilation of the right atrium (RA), and dilation and lack of collapse of the inferior vena cava (IVC) contribute to the diagnostic orientation of PH.10,11 Although not recommended in routine practice and reserved only for research, exercise echocardiography could be a tool to consider in the future for evaluating patients with COPD and suspected PH.37,38
In IPF, determination of PAPs via tricuspid regurgitation velocity (TRV) is equally challenging and is successful in only 50% of cases.39,40 In this regard, a case series published some years ago demonstrated that up to a third of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) without ILD presented with PH on RHC.41 More recent data suggest that a composite and stepwise TTE score could identify patients with severe PH, with or without TRV estimation. This approach combines other echocardiographic features including RA area, LV eccentricity index, and RV/LV ratio.41 In patients with ILD, TTE is currently the preferred test for investigating PH, despite the expected technical limitations in this patient profile and the limited studies published in this regard.1,10,11,33
Chest Radiography and ElectrocardiographyFew studies 42,43 have evaluated signs such as increased cardiac silhouette size (measured by the cardiothoracic ratio>35%), main pulmonary artery (PA) enlargement, and right descending PA branch (>20mm) in chest radiography of COPD patients to identify suspected PH via echocardiography or diagnosed via RHC. There are no studies available that evaluate chest radiography as a detection method for ILD or ILD-associated PH.
In severe COPD patients with associated PH, Electrocardiogram (EKG) findings may include prolonged PR interval, T wave axis deviation, and incomplete right bundle branch block.44 A staging model found that ECG evaluation in these patients has a positive predictive value of 71% and a negative predictive value of 75%.44 However, a normal ECG cannot exclude PH in COPD patients. There are no available studies that evaluate ECG as a detection method for ILD or ILD-associated PH.
Pulmonary Function TestsIn COPD, significant impairment in diffusing capacity of carbon monoxide (DLCO) or severe hypoxemia associated with mild or moderate airflow obstruction (≥50% of theoretical value) may suggest significant PH.9,45,46 This respiratory functional impairment characterizes the “pulmonary vascular phenotype”47 associated with high morbidity and mortality.7 Some studies48,49 highlight the potential utility of forced vital capacity (FVC)/DLCO ratio and FVC/DLCO corrected for alveolar volume (VA) to detect PH, although these studies are based on PH detection by echocardiography, with the limitations described. In ILD, a disproportionately marked reduction in DLCO relative to spirometric impairment or the extent of lung involvement on chest CT should raise suspicions of associated PH.50–52 Although there is no cut-off defining PH risk, some studies suggest a DLCO below 35–40% of theoretical percentage may be a good predictor of PH in this patient group.8,11,26,53 Only three studies have evaluated the role of respiratory functional parameters in identifying SOH-associated PH.33,54,55 It has been observed that SOH patients exhibit greater DLCO impairment when PH is present (68.7% vs. 82.2%; r=−0.66; p=0.002).33 Additionally, the theoretical value of FVC correlates inversely with PH (82.2% vs. 95.0%; r=−0.56; p=0.009).33 Conversely, other spirometric parameters, including forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1), the FEV1/FVC ratio, and maximal inspiratory pressure, have not proven useful for PH screening in patients with SOH.33 SOH patients with PH may exhibit greater hypoxemia compared to those without PH.33,54 In a post hoc analysis of a multicenter clinical trial including 246 SOH patients, an independent association was observed between daytime PaO2 values and suspected PH defined by PAPs>40mmHg on echocardiography, such that probable PH patients had an average PaO2 of 59mmHg, while those without PH had 64mmHg (OR 0.96 [0.93–0.98] p=0.003).54 This finding was not confirmed in another study in which PH was diagnosed by RHC, as no statistically significant differences were observed in PaO2 levels between SOH patients with and without PH (59.1mmHg vs. 62.4mmHg; p=0.55), partly explained by the study's small sample size.33
Imaging TestsA recent meta-analysis of nine studies, five of which employed RHC as the diagnostic test for PH, found that a main PA to aortic root (AoR) ratio greater than 1 was associated with PH in COPD. This sign, with a threshold of 0.93, has been incorporated into certain proposed diagnostic algorithms for the detection of severe PH in COPD.45 At the lung parenchyma level, while the amount of emphysema is not associated with mean pulmonary artery pressure (mPAP),56 bronchial remodeling in COPD has been shown to be related to PH presence.43 In IPF, an PA/AoR ratio>0.9 may predict a mPAP>20mmHg and worse survival in patients.57,58 King et al. included this parameter in a multidimensional tool alongside increased vascular resistance and mortality.58 They found that mPAP correlated with the combination of different parameters, including: sPAP measured by TTE; main PA area (before bifurcation); and the ratio of segmental artery diameter to adjacent bronchus diameter in the posterior apical segment of the left upper lobe. This composite index had a sensitivity and specificity of 100% and 53%, respectively, in patients with IPF and suspected PH.59 No studies exist in SOH that evaluate the role of CT in PH detection.
Regarding the cost-effectiveness of cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) imaging in COPD, a model called CMR-PA/RV (including RV mass, septal angle, and PA measurements) has shown a good correlation with invasive hemodynamic variables.60 No studies exist in IPD and SOH that evaluate CMR as a PH detection method.
Natriuretic PeptidesAn elevation in brain natriuretic peptide (BNP, with a normal value of less than 100pg/ml) or N-terminal-BNP (NT-proBNP, with a normal value of less than 125pg/ml) in patients with severe PH and COPD45 can reflect volume and pressure overload at the RV level. However, their elevation can be influenced by many other factors, such as alterations at the level of the left heart cavities, which are very common in COPD patients due to tobacco exposure,61 or renal insufficiency.62 For these reasons, a high BNP level alone is not sufficient to support the diagnosis of PH63 and should be combined with the results of other complementary tests.
Sonti et al. associated elevated BNP with the presence of PH in patients with ILD.18 Additionally, BNP has been correlated with the distance walked in the 6-minute walking test (6MWT), with NYHA functional class,64 and with the RV function, particularly in patients with signs of PH and RV dysfunction.65 No studies exist in subjects with SOH that specifically evaluate BNP or NT-proBNP as a method of detecting PH.
Exercise TestsSix-minute walk distance (6MWD) in the 6MWT is significantly lower in COPD patients with PH, regardless of the hemodynamic severity,24,66,67 compared to those without PH. By contrast, another study found that in patients with COPD and mild to moderate PH diagnosed by RHC, the 6MWD did not significantly differ from that of patients without PH. A significantly reduced walking distance was observed only in those with severe PH.45 In a single published study, it was observed that oxygen saturation (SaO2) at the end of the 6MWT inversely correlates with mPAP,68 such that a drop in SaO2<81% can identify the presence of PH in COPD patients with a sensitivity and specificity of 86% and 84%, respectively. A decrease in the 6MWD has also been associated with the presence of PH in ILD patients.8,18,69–71 One study in SOH patients found that a reduced 6MWD (<300m) in the 6MWT could indicate PH.33
In patients with COPD and non-severe PH, Cardiopulmonary exercise testing (CPET) typically shows a marked reduction in exercise tolerance with predominantly ventilatory limitation. However, early exhaustion of the cardiac reserve, along with a reduced maximum workload, peak oxygen consumption, and maximum oxygen pulse, associated with marked desaturation while preserving ventilatory reserve, suggests significant PH.72,73
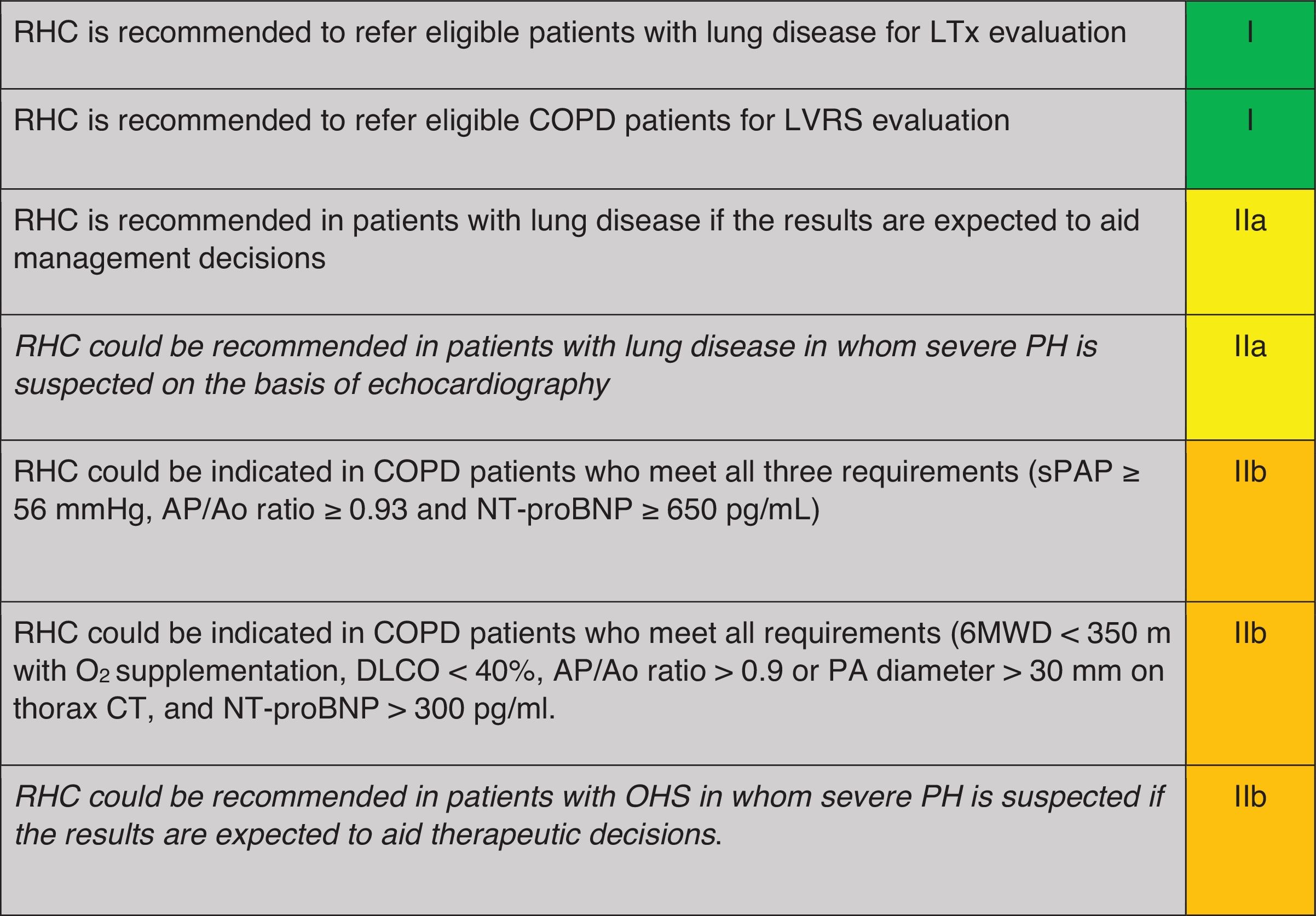
When is Right Heart Catheterisation Indicated for the Diagnosis of PH in Patients With COPD, ILD or OHS? (Table 4)Right heart catheterisation (RHC) is not indicated in the general workup of patients with respiratory disease, except in those who are candidates for lung transplant or lung volume reduction surgery,10,11 when severe PH is suspected or when its result may aid in management decision.10,11
Recommendation regarding when to perform RHC for diagnosis of PH in COPD, ILD or OHS.
RHC: right heart catheterization; LTx: COPD: chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; ILD: interstitial lung disease; PH: pulmonary hypertension; OHS: obesity hypoventilation syndrome; sPAP: systolic pulmonary arterial pressure; TVR: tricuspid regurgitant velocity; PA: pulmonary artery; Ao: aorta; CT: computerized tomography; FEV1: forced respiratory volume at 1second; FVC: forced vital capacity; DLCO: diffusing capacity of the lungs for carbon monoxide; PaO2: partial pressure of arterial oxygen; VC: vital capacity; CMR: cardiac nuclear magnetic resonance; BNP: brain natriuretic peptide; NT-proBNP: N-terminal-BNP; 6MWT: six-minute walking test. Green: recommended; yellow: should be considered; orange: may be considered.
A monocentric, retrospective analysis of COPD patients who underwent RHC proposed a risk score assessment for the probability of severe PH, using a combination of three criteria: NT-proBNP≥650pg/mL, sPAP value≥56mmHg and PA/Ao ratio≥0.93 at the CT scan. The combination of all three criteria provided a 98% sensitivity and 95% specificity for the detection of severe PH.45
In ILD patients, another monocentric retrospective study which enrolled mostly IPF patients (41%) used clinical features (physical signs of PH, syncope and long-term oxygen use), 6MWD<350m, NT-proBNP>300pg/ml, PA/Ao ratio>0.9 or PA diameter>30mm on the CT scan and DLCO<40% to detect PH.18,22 Through multivariate analysis, ILD patients were stratified into low (≤3 points), intermediate (4–5 points), or high probability (≥6 points) of PH. In cases of low probability clinical follow-up is recommended, while with intermediate and high probability an echocardiography should be performed, and with high probability patients should also be referred to an expert PH center. Within this last group, the model predicted the presence of PH with a sensitivity of 86.5% and a specificity of 86.3%, an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.92 (IC 95%: 0.878–0.962, p<0.001); the rate of false positives was 7.1% and false negatives 6.5%. Furthermore, a score≥8 is correlated with high mortality risk, with an AUC of 0.680 (IC 95%: 0.581–0.778), a sensitivity of 53.3% and a specificity of 82.6%.
OHS patients in which severe PH is suspected, or if pulmonary vasodilator treatment is being considered, should be referred to an expert PH center in order to assess the indication for a RHC.10,11
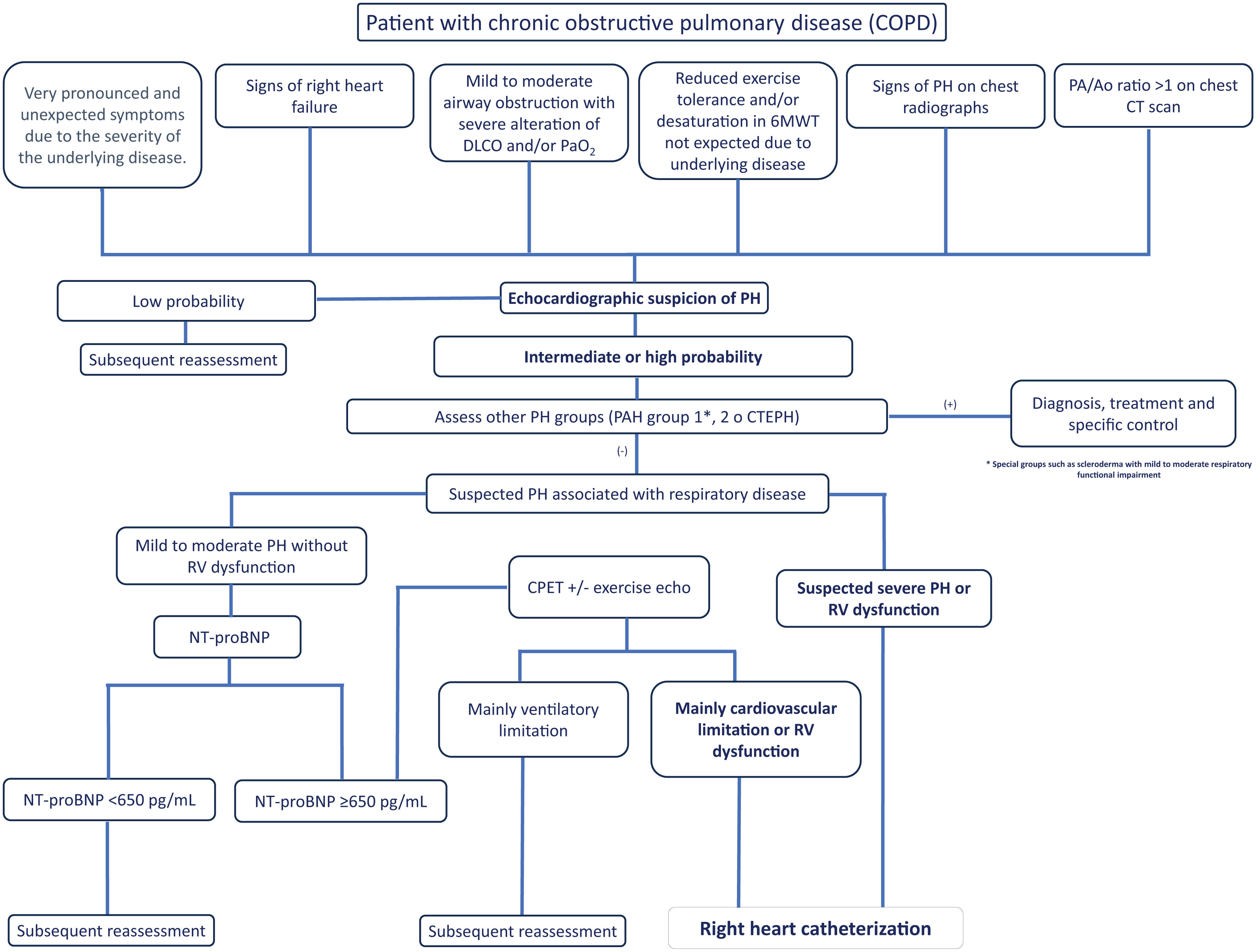
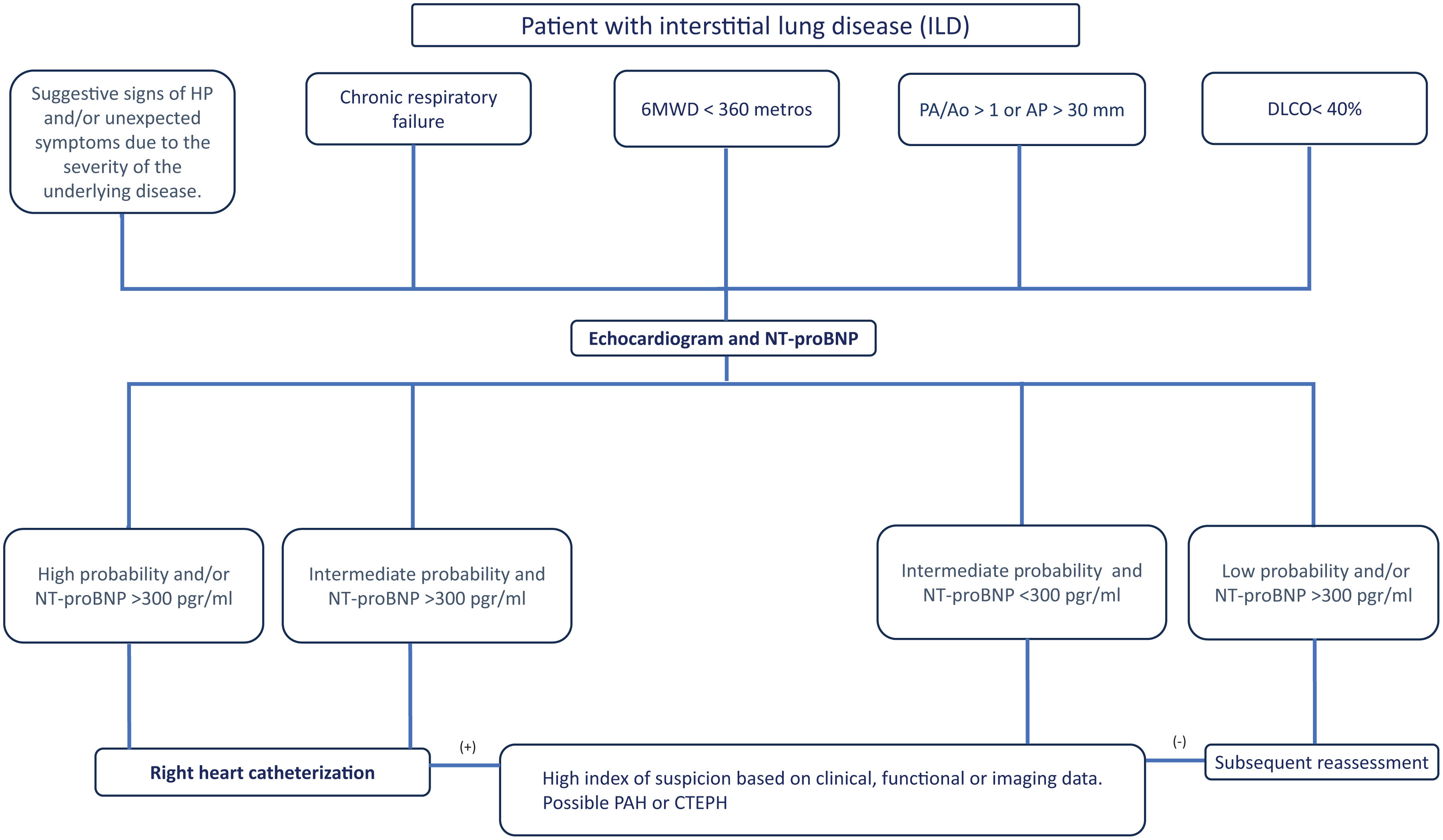
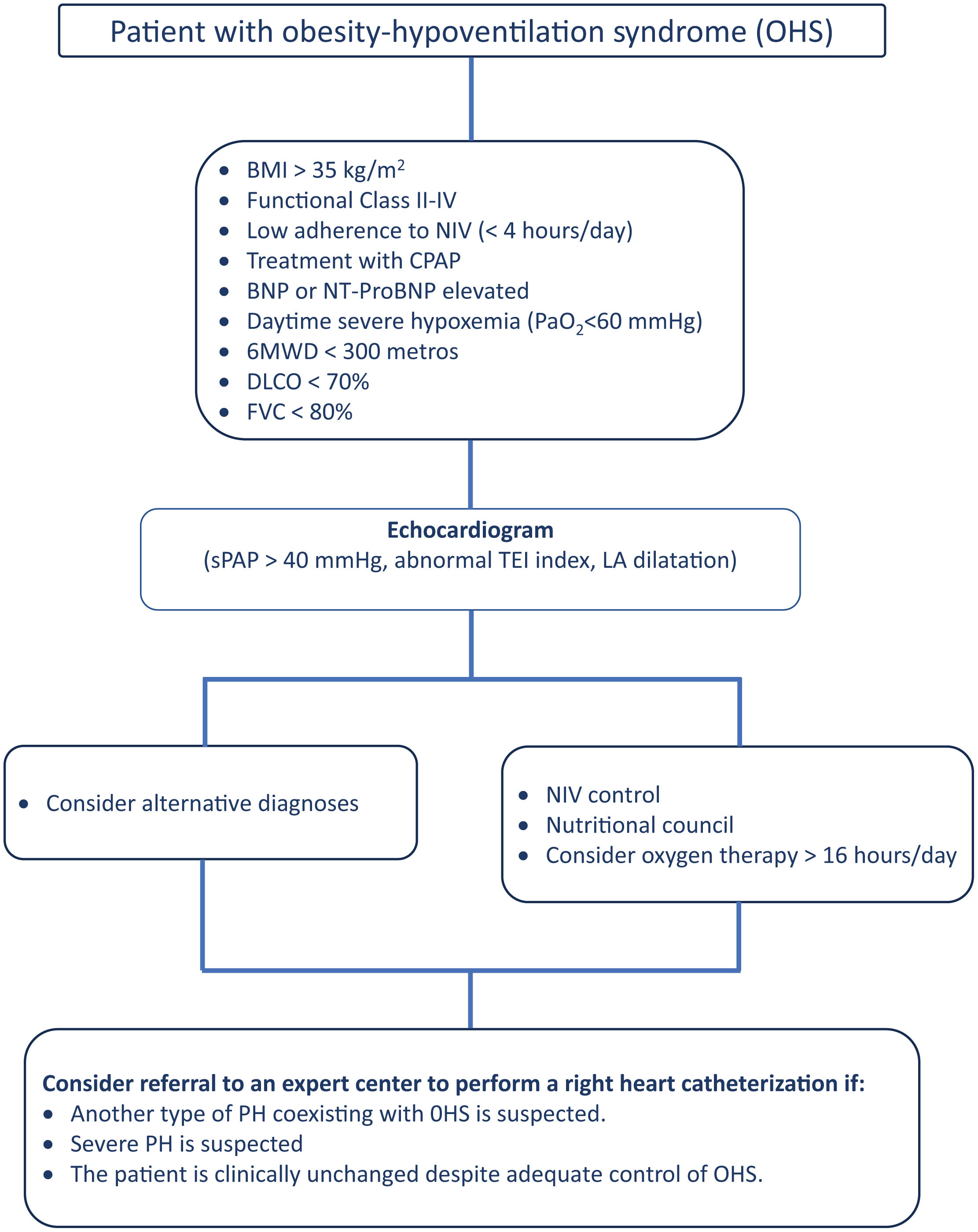
Proposal of Diagnostic AlgorithmsFig. 1 (COPD), Fig. 2 (EPID) and Fig. 3 (OHS) represent a schematic proposal adjusted to the characteristics of each disease for the diagnostic approach to PH associated with respiratory disease.
Diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary hypertension associated with COPD. Abbreviations: DLCO: diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; PaO2: partial pressure of oxygen; 6MWT: 6-minute walk test; PA: pulmonary artery; Ao: aorta; PH: pulmonary hypertension; PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension (Group 1); CTEPH: chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; NT-ProBNP: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide fragment; CPET: cardiopulmonary exercise test; RV: right ventricle.
Diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary hypertension associated with ILD. Abbreviations: PH: pulmonary hypertension; 6MWD: 6-minute walk distance; PA: pulmonary artery; Ao: aorta; DLCO: diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; FVC: forced vital capacity; NT-ProBNP: terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide fragment; PAH: pulmonary arterial hypertension (Group 1); CTEPH: chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension.
Diagnostic algorithm for pulmonary hypertension associated with OHS. Abbreviations: BNP: brain natriuretic peptide; BMI: body mass index; NT-ProBNP: N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide fragment; DLCO: diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide; NIV: noninvasive mechanical ventilation; sPAP: systolic Pulmonary arterial Pressure; LA: left atrium.
DARC has received honoraria for lectures, participation in clinical studies, congresses, conferences and courses sponsored by: MSD, Ferrer, Janssen, Esteve, Vifor, Chiesi, Bial, GSK.
RTC: does not declare conflict of interest.
LP: has received fees for lectures, participation in clinical studies, consultancies, congresses, conferences and courses sponsored by: MSD, Ferrer, Menarini, United Therapeutics and Janssen.
AGO: has received honoraria for lectures, participation in clinical studies, congresses, conferences and courses sponsored by: MSD, Bial, Novartis, Ferrer and Janssen.
GMPP: has received fees for lectures, consultancies, congresses, conferences and courses sponsored by: MSD, Ferrer. Menarini and Janssen.
JdMD: has received honoraria for presentations, participation in clinical studies, congresses, consultancies, conferences and courses sponsored by: AstraZeneca, Bial, Boehringer, Chiesi, FAES, Gebro, GSK, Menarini, Novartis, Roche, Teva and Pfizer.
RPR: has received fees for lectures, congresses, consultancies, conferences and courses sponsored by: Boehringer, Ferrer and Roche.
ICP: has received fees for lectures and consulting services: Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Philips and Bioprojet.
VMC: does not declare conflict of interest.
IB: has received fees for lectures, consulting services, participation in clinical studies, congresses, conferences and courses sponsored by: MSD, Ferrer and Janssen.
JMFG: has received honorary lecture fees, participation in clinical studies, congresses, conferences and courses sponsored by: Esteve, MundiPharma, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingel-heim, Ferrer, Menarini, Rovi, GlaxoSmithKline, Chiesi, Novartis, and Gebro Pharma.
RdP: has received honoraria for lectures, participation in clinical studies, congresses, conferences and courses sponsored by: Boehringer, Chiesi and Janssen.
MLM: has received fees for lectures, consulting services, participation in clinical studies, congresses, conferences and courses sponsored by: MSD, Ferrer and Janssen.
AMM: has received honoraria for papers, congresses, conferences and courses sponsored by: AOP orphan,Rovi, Leo Pharma, Chiesi, MSD,and Janssen.
AT: has received honoraria for lectures and courses sponsored by: Janssen, Ferrer, MSD, AOP pharma, AstraZeneca, GSK.
MMM: has received honoraria for lectures, participation in clinical studies, congresses, conferences and courses sponsored by: Boehringer, Ferrer, Pfizer and Roche.
JAB: has received honoraria for presentations, participation in clinical studies, congresses, consultancies, conferences and courses sponsored by: MSD, Ferrer, Acceleron Pharma and Janssen.