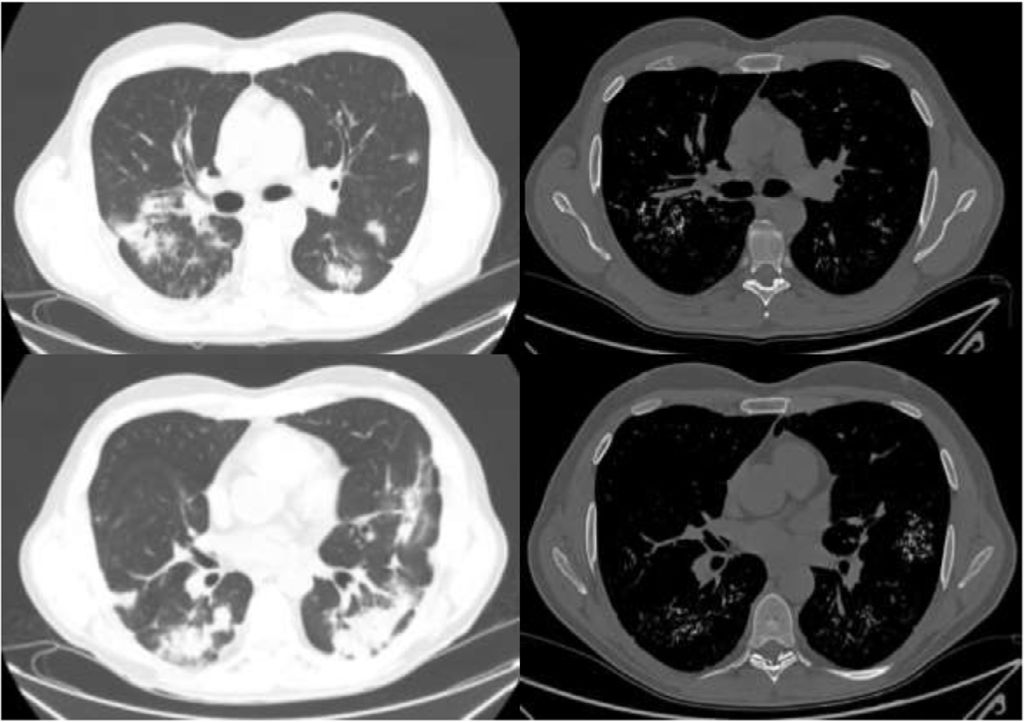
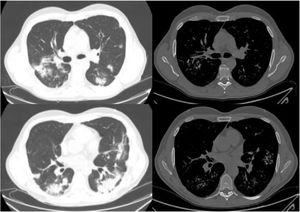
A 49-year-old man with Liddle syndrome type 1 with high blood pressure and chronic renal impairment, kidney transplant recipient, with hypoparathyroidism due to parathyroidectomy was admitted for bilateral COVID-19 pneumonia. Chest computed tomography (CT) performed at admission showed multiple foci of pulmonary calcifications coinciding with areas of opacities seen on a CT performed before admission, corresponding to foci of bronchopneumonia (Fig. 1).
The images on the left show lung window slices from the computerized tomography performed at admission, revealing multiple patchy consolidations associated with COVID-19 pneumonia. On the right, bone window slices with lung calcifications that coincide with the previous opacities. The variability between the slices is due to the fact that the tomography scan at admission obtained 2.5mm slices and the follow-up CT scan obtained 1mm slices.
Several factors contribute to calcium deposition in the organs, including alterations in calcium-phosphorus metabolism, alkaline phosphatase activity, and basic pH.1 Pulmonary calcifications can be identified as metastatic or dystrophic calcifications and pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis. Metastatic calcifications occur mainly in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease requiring hemodialysis,2 while dystrophic calcifications occur in previously damaged tissue, such as in the context of an infectious process.1 Our patient had a history of chronic kidney disease, alterations in phosphorus-calcium metabolism, and was receiving hemodialysis, factors that favor the generation of calcifications on a susceptible substrate, such as lung tissue damaged by infection.
FundingThis paper has not received any funding.
Conflict of InterestThe authors state that they have no conflict of interests.