Among all patients with hypertension, those with resistant hypertension (RH) have the highest rates of subclinical organ damage (SOD). The prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is high in RH patients, and it could contribute to SOD. We aimed to investigate how OSA and its treatment are related to SOD in a large cohort of RH patients.
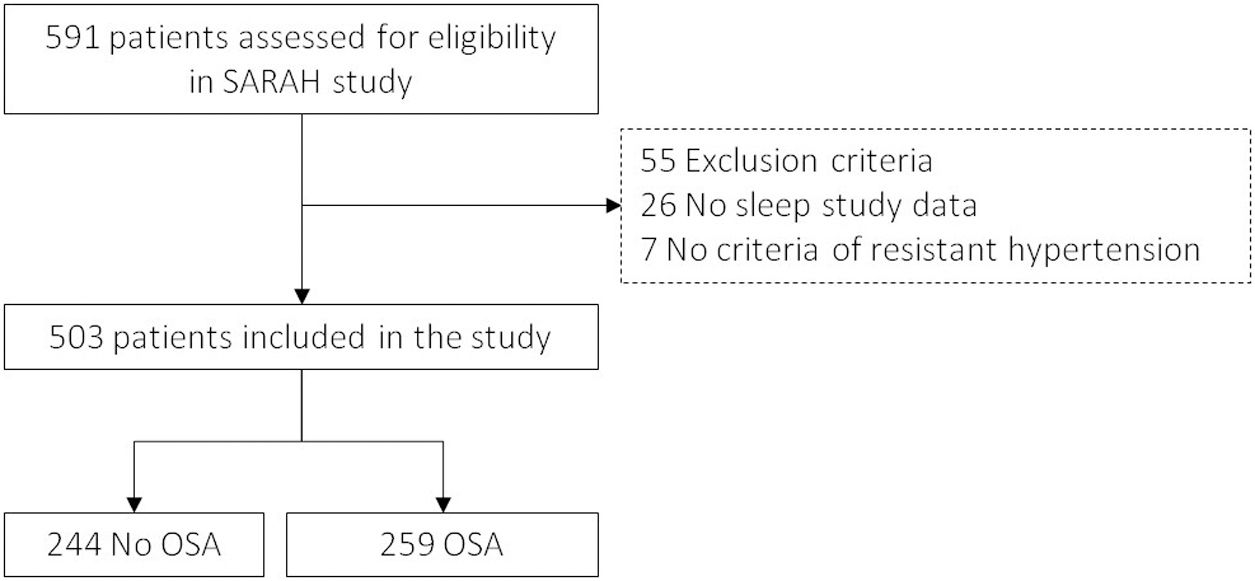
MethodsThis is an ancillary analysis to the SARAH study, a multicentre observational cohort aiming to evaluate the impact of OSA on RH. Individuals with RH who were undergoing a sleep study and have information on at least one of the SOD variables (vascular, cardiac or renal damage) were selected. Patients were followed-up for three years.
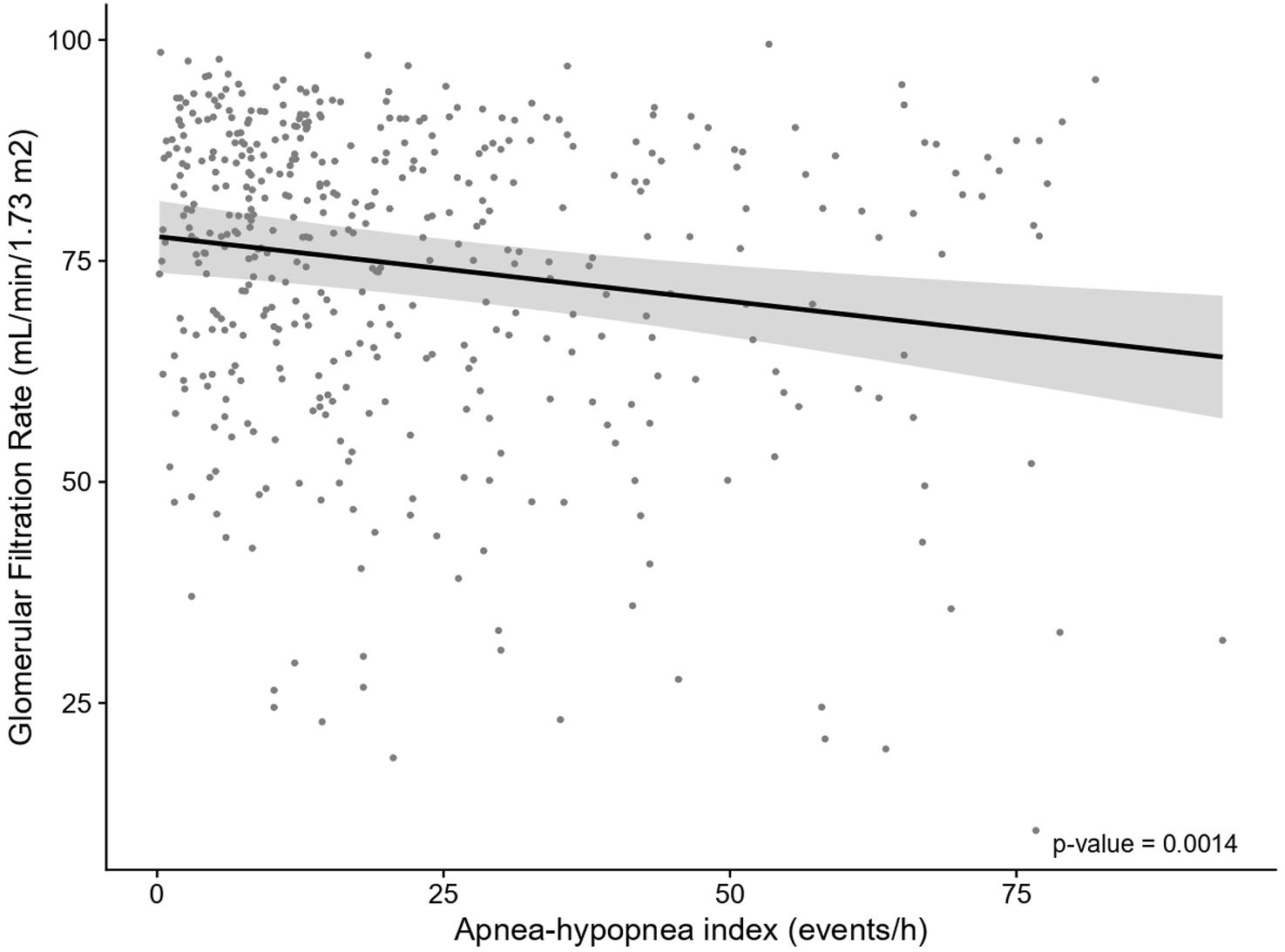
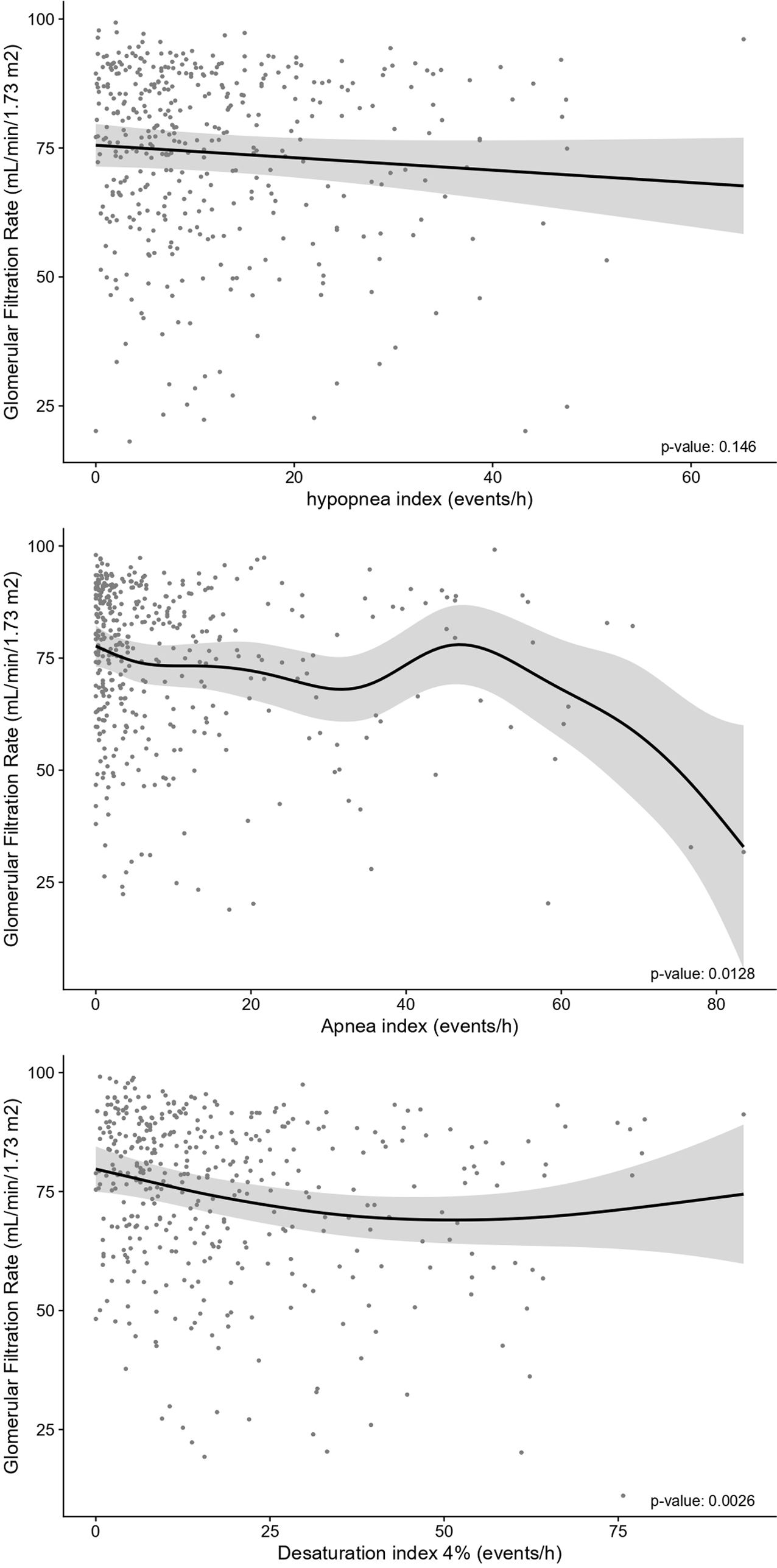
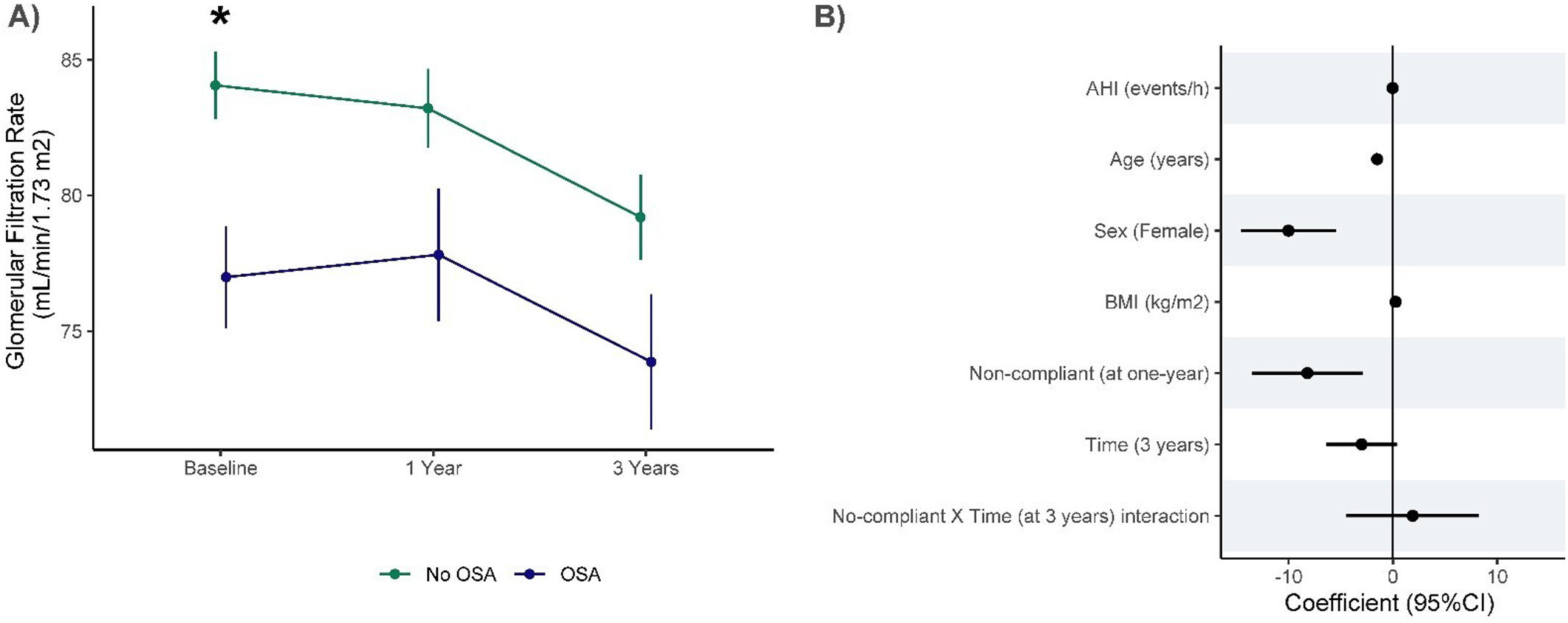
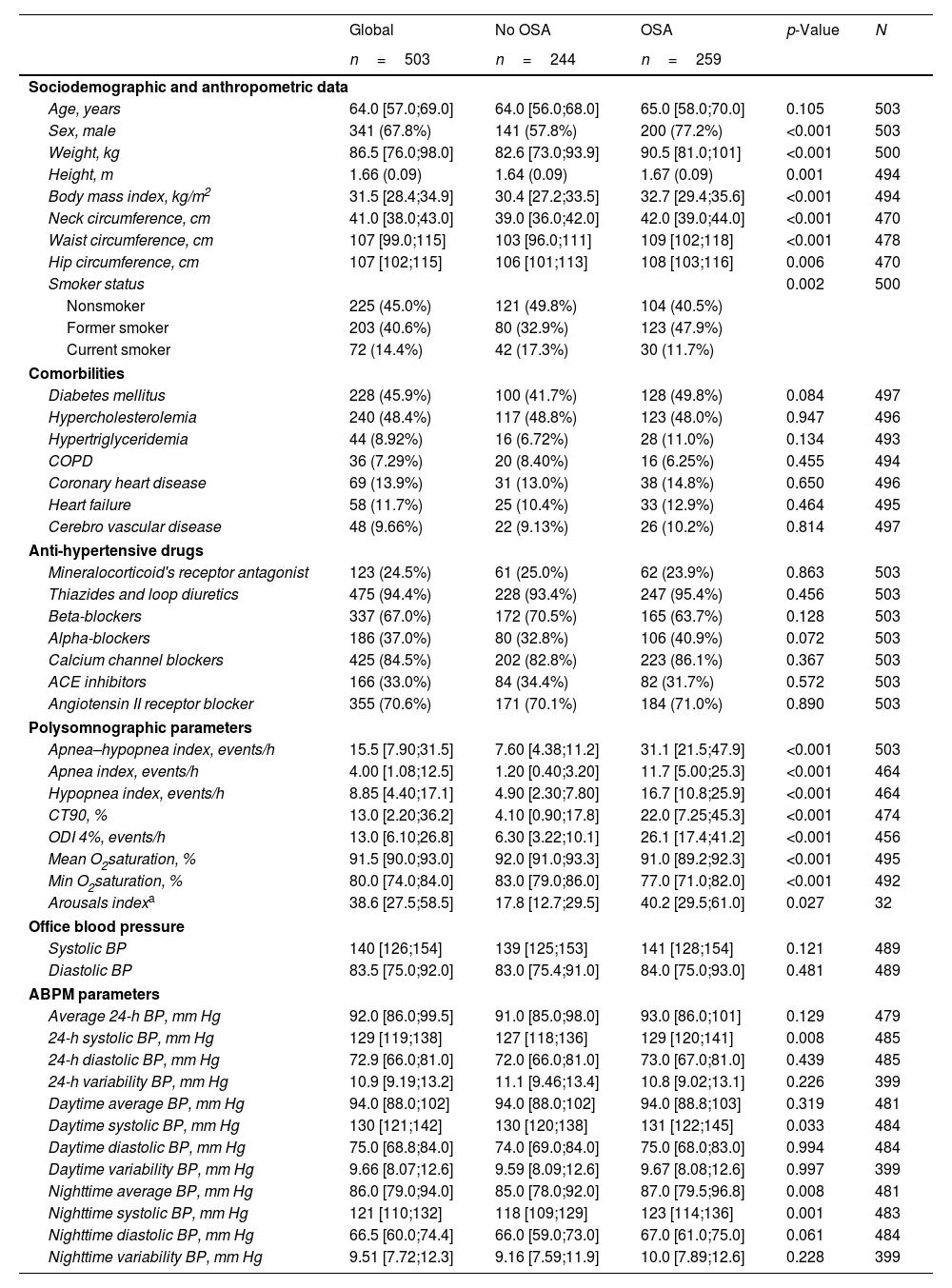
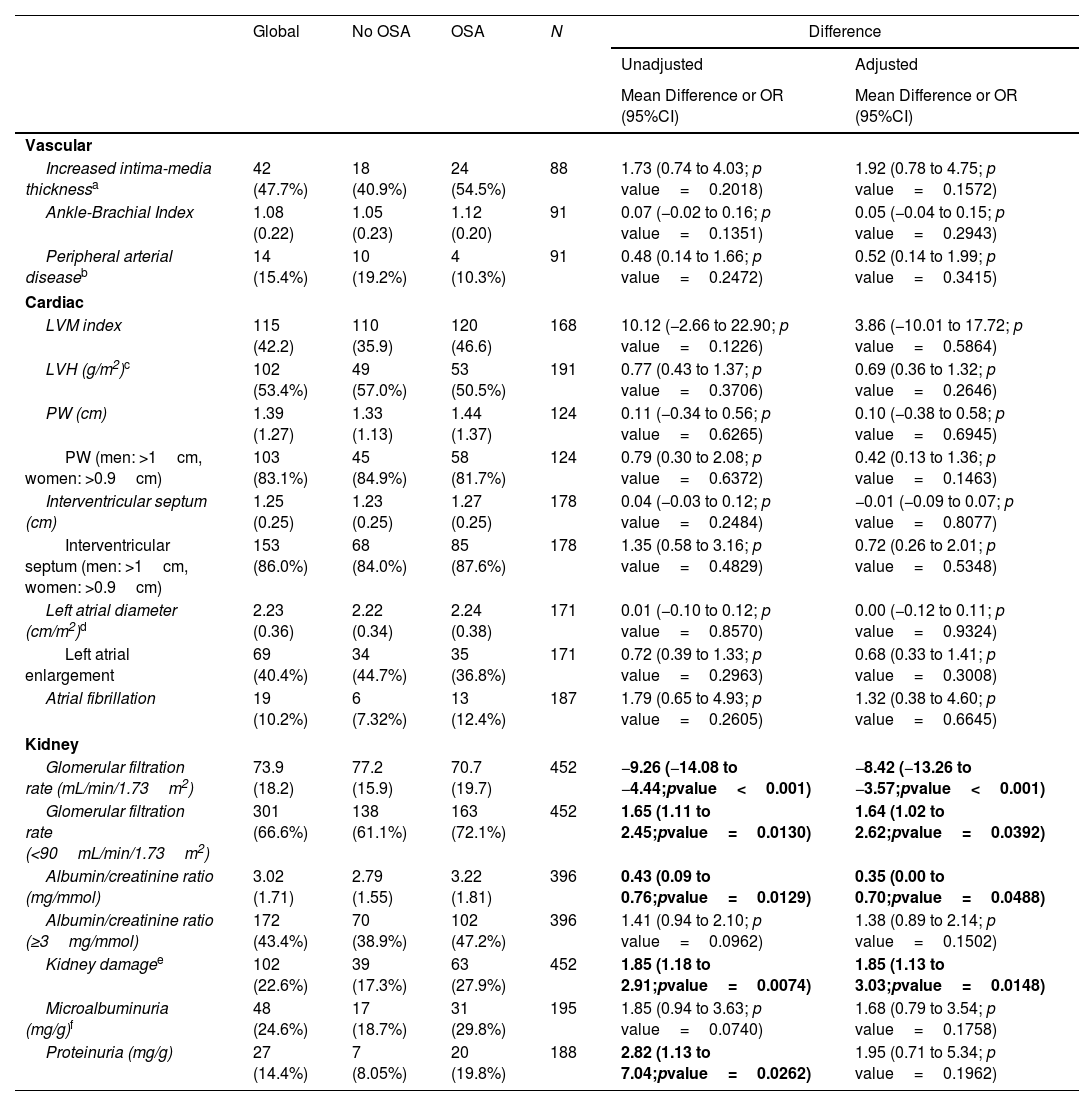
ResultsIn total, 503 subjects were included. The participants were predominantly male, obese, and the median (IQR) apnea–hypopnea index (AHI) was 15.5 (7.90–31.5)events/h. No differences in the presence of vascular or cardiac damage were observed between OSA and non-OSA patients. A lower estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was observed in participants with OSA than in those without OSA, with an adjusted effect of −8.69mL/min/1.73m2 (−13.59, −3.79; p value<0.001). Kidney damage was also greater in subjects with OSA, with an adjusted OR (95% CI) of 1.77 (1.09, 2.87; p value=0.02). The eGFR showed a linear dose–response relationship with OSA severity. Among patients treated with CPAP, lower eGFR values were observed in noncompliant subjects.
ConclusionsOSA could contribute to worsening renal function in patients with RH. No compliance with CPAP was associated with lower values of eGFR.