Excessive daytime sleepiness is one of the most important symptoms in obstructive sleep apnoea and it is often used to decide whether the latter should be diagnosed as a syndrome or considered a priority in diagnosis and treatment, and whether the treatment is effective. Beyond this, one concept of enormous clinical significance has emerged: “residual excessive daytime sleepiness”, defined as excessive daytime sleepiness in the context of a diagnosed obstructive sleep apnea that is treatable with continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) or alternatives to it; it appears as a consequence of poor adaptation to, or refusal of treatment, or even sometimes in situations of good tolerance. Given the direct relationship between excessive daytime sleepiness (usually defined by an Epworth Sleepiness Scale [ESS] value of more than 10 points) and cardiovascular, neurocognitive and quality-of-life disorders, attempts have been made for years to alleviate it with drugs (modafinil, armodafinil, sodium oxybate or amphetamines), to little effect and with a large number of adverse effects. However, unlike their predecessors, two products that have recently appeared on the market – solriamfetol and pitolisant – have achieved clinically significant reductions without any major adverse effects, in most cases. In fact, a Task Force from the European Respiratory Society has even proposed an algorithm for residual excessive daytime sleepiness and its pharmacological treatment in the context of obstructive sleep apnoea. The present review aims to define the importance of excessive daytime sleepiness, especially residual excessive daytime sleepiness in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea, as well as the old and new pharmacological alternatives that have appeared.
Obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA) affects billions of individuals worldwide [1]. Among the associated clinical–physiological factors related to this impact are nocturnal intermittent hypoxia (IH) and the presence of excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) caused by sleep disruption [2]. In fact, the treatment of symptomatic OSA is fundamentally aimed at eliminating this IH, as well as normalising the values of secondary EDS [3] to avoid any future consequences [4–8].
The treatment of choice for OSA, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP), is expressly prescribed in the presence of a significantly high apnoea–hypopnoea index (AHI), with or without EDS [3]. It is crucial to both adjust the pressure (measured in cmH20) on the airway, so that both the IH and the degree of EDS descend to normal values, and detect any changes in the individual over time that may require the pressure to be modified [9].
Like any treatment, CPAP is sometimes not tolerated by the patient, despite every effort made, because he or she refuses to use it, the pressure applied or duration of use are insufficient or EDS continues to appear even when the therapeutic parameters are correct. This phenomenon is known as residual EDS [10–14]. Furthermore, the effectiveness of CPAP is limited by sub-optimal acceptance and adherence rates: 50% of individuals will discontinue CPAP treatment within 1 year and 25% will terminate CPAP treatment within 3 years. Non-adherence to treatment, estimated at 30–40%, did not vary significantly over 20 years [15].
For several decades, drugs such as modafinil or armodafinil [16,17] have been used to treat RH. In recent years, however, other newer drugs such as pitolisant [18] and solriamfetol [19] have appeared, with better tolerance and efficacy against RH. This review will attempt to describe and comment on the pros and cons of these treatments – especially the more modern ones – in patients with OSA.
Definition of residual excessive daytime sleepinessThere is no categorical definition, but in practice we can define it as EDS which is either present with a value higher than 10 points on the ESS or diagnosed by more objective tests in patients with OSA, whether treated or untreated [20,21]. Although this definition could be useful empirically, it is necessary to establish some differentiating nuances. Thus, the term “residual” would be especially appropriate for a degree of EDS that has not been normalised despite the application of treatment, while the term “untreated” would be used for EDS that persists without treatment or is not caused by OSA but by another disease – for example, narcolepsy – and “false” would refer to EDS with an abnormal ESS value that does not correspond to a return to the normality of the values in the objective EDS tests [20].
Epidemiology of residual excessive daytime sleepiness in OSAAlthough there have been no decisive studies on this subject, it is estimated that between 12 and 55% of patients with treated OSA may present residual EDS, although this figure can decrease to 6% after the appropriate exclusion of other known causes of EDS [11]. In one database of 8900 patients with OSA from the Spanish Sleep Group (data not published), 19% of patients did not present an ESS value reduced by 10 points after treatment with CPAP or alternatives to it.
Risk factors for residual excessive daytime sleepiness in OSASome authors have attempted to assess the intrinsic or post-treatment risk factors related to the persistence of abnormal EDS measurements. Of these, the severity of the initial EDS is probably the most important [12]. EDS has also been associated with a higher number of respiratory disorders during sleep and greater initial oxygen desaturation. The presence of a history of diabetes or cardiovascular disease has produced disparate results in terms of risk factors for residual EDS, but various studies have confirmed other associated factors: younger age, poor adherence to CPAP (in the use of daily hours), greater number of adverse effects from CPAP, decreased sleep latency, reduction of slow waves, greater number of abnormal leg movements, longer duration of daytime sleep and lower daytime sleep latency [12].
Approach to diagnosisThe three fundamental measures to take into account are probably [20–24]:
- 1.
Rule out concomitant diseases related to EDS (Table 1). These diseases may or may not be associated with OSA. It is necessary to carry out a complete anamnesis, evaluate drug intake, perform the necessary complementary tests, maintain a sleep diary and actigraphy, use PSG to assess alternative or concomitant diagnoses to OSA and undertake a general analysis and an iron metabolism and human leucocyte antigens (HLA) study (depending on clinical suspicion).
Table 1.Differential diagnosis of residual excessive daytime sleepiness in obstructive sleep apnoea.
Central causes-Type 1 narcolepsy-Type 2 narcolepsy-Idiopathic hypersomnia-Kleine–Levin syndrome Sleep apnoea-Obstructive sleep apnoea-Central sleep apnoea Circadian rhythm disturbances (sleep–wake cycle disruption)-Delay in the sleep phase-Advancement of the sleep phase-Irregular circadian rhythm-Non-24h circadian rhythm-“Shift work”-Jet lag-Other circadian rhythm alterations Secondary forms-Comorbidities (Parkinson's, infections, hypothyroidism, cerebral injuries, etc.)-Psychiatric comorbidities (depression, bipolar disorder, etc.)-Drugs (benzodiacepins, opioids, alcohol, etc.)-Insufficient sleep syndrome - 2.
Confirm the diagnosis of OSA. Check that the study carried out was technically in order. If necessary, carry out a supervised study using complete polysomnography.
- 3.
Evaluate the compliance with and effectiveness of CPAP (or alternative treatments to OSA). In these cases, it is necessary to ensure good adherence (which for some patients may sometimes be more than 4h per night [25], a figure that arbitrarily indicates good compliance) and the correct use and choice of interfaces, as well as assessing the correct titration of CPAP pressure over several nights, to ensure that the number of sleep-disordered breathing events is normalised in all sleeping positions. It may be necessary to perform a monitored titration using PSG or an auto-CPAP [20–24].
Once a diagnosis of OSA has been confirmed, it is clear that the presence of concomitant diseases or treatments capable of causing EDS must be rectified. Moreover, all necessary efforts must be made to achieve adequate adherence to CPAP (including masks and accessories) at a correct pressure and to monitor clinical changes. If, nevertheless, these factors cannot be controlled, or if EDS persists despite being controlled, there remains the possibility of pharmacological treatment for EDS, as explored in the next section [26–29] (Table 2).
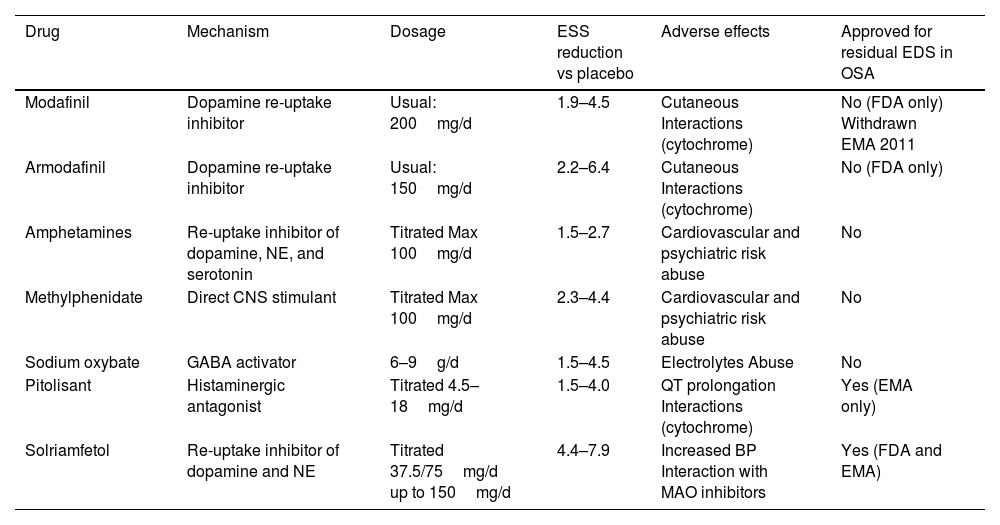
General characteristics of the main wakefulness-promoting agents.
| Drug | Mechanism | Dosage | ESS reduction vs placebo | Adverse effects | Approved for residual EDS in OSA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Modafinil | Dopamine re-uptake inhibitor | Usual: 200mg/d | 1.9–4.5 | Cutaneous Interactions (cytochrome) | No (FDA only) Withdrawn EMA 2011 |
| Armodafinil | Dopamine re-uptake inhibitor | Usual: 150mg/d | 2.2–6.4 | Cutaneous Interactions (cytochrome) | No (FDA only) |
| Amphetamines | Re-uptake inhibitor of dopamine, NE, and serotonin | Titrated Max 100mg/d | 1.5–2.7 | Cardiovascular and psychiatric risk abuse | No |
| Methylphenidate | Direct CNS stimulant | Titrated Max 100mg/d | 2.3–4.4 | Cardiovascular and psychiatric risk abuse | No |
| Sodium oxybate | GABA activator | 6–9g/d | 1.5–4.5 | Electrolytes Abuse | No |
| Pitolisant | Histaminergic antagonist | Titrated 4.5–18mg/d | 1.5–4.0 | QT prolongation Interactions (cytochrome) | Yes (EMA only) |
| Solriamfetol | Re-uptake inhibitor of dopamine and NE | Titrated 37.5/75mg/d up to 150mg/d | 4.4–7.9 | Increased BP Interaction with MAO inhibitors | Yes (FDA and EMA) |
NE: norepinephrine; CNS: central nervous system; GABA; gamma-aminobutyric acid ESS: Epworth Sleepiness Scale; BP: blood pressure; MAO: monoamine oxidase; EDS: excessive daytime sleepiness; FDA: food and drug administration; EMA: European Medicines Agency.
ESS reduction vs. placebo data represent the ranges obtained from the various randomised controlled trials (RCTs) comparing active treatment to placebo reported in the literature.
This is a dopamine re-uptake inhibitor with a usual dose of 200mg/day. In the randomised clinical trials (RCT) conducted to date (usually the oldest ones), it produced a reduction in the ESS value of between 1.8 and 4.5 points compared to placebo. Among the most frequent (and occasionally serious) adverse reactions were skin complaints. Authorisation for the use of modafinil for the treatment of excessive EDS was withdrawn by the EMA (European Medicines Agency) in 2011. In a meta-analysis of RCTs with a duration of 1–12 months conducted between 2011 and 2017, the odds ratio (OR) for achieving normalisation of the ESS (less than 10 points) with respect to placebo was 1.95 (95% CI: 1.48–2.56). Modafinil frequently interacts with other drugs due to its metabolism by hepatic cytochromes. This same meta-analysis observed an increase in adverse effects (almost four times greater than in the placebo group; 3.84 (95%CI: 1.08–13.9) [30,31].
ArmodafinilThis has a mechanism of action similar to that of modafinil. A meta-analysis of RCTs with a duration of 1–12 months conducted between 2001 and 2007 observed a decrease of 2.24 (95%CI: 3.15–1.32) points in the ESS compared to placebo. Armodafinil also presents a frequent interaction with other drugs due to metabolism by hepatic cytochromes. This same meta-analysis did not observe any increase in adverse effects, which is why this appears to be a safer drug than modafinil, but its use has become more infrequent due to the emergence of new drugs [30,31].
MethylphenidateThis is a direct stimulant of the central nervous system. It produces a reduction of between 2.3 and 4.4 points in the ESS. It also increases the cardiovascular and psychiatric risk, as well as presenting a danger of drug abuse. It is also not currently approved for use in excessive EDS in patients with OSA [32].
Amphetamine derivativesThese are associated with an inhibition of dopamine, noradrenaline and serotonin re-uptake. They produce a decrease in the ESS value of between 1.5 and 2.7 points, but their cardiovascular risk and the possibility of drug abuse have meant that their use is not currently authorised [32].
Sodium oxybateThis serves as a gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) activator at a dose of 6–9g/day. It reduces the ESS value by 1.5–4.5 points. The most significant adverse effect is alteration to electrolytes, and there is also a possibility of drug abuse. Sodium oxybate is not approved by regulatory agencies for this indication [33].
New pharmacological treatmentsAs a consequence of the frequent adverse effects and the disputed efficacy of pharmacological treatment for excessive EDS in patients with OSA, new therapeutic options began to emerge on the market. The most prominent of these are undoubtedly pitolisant and solriamfetol.
PitolisantThe main mechanism of action of this drug is that of a histaminergic H3 antagonist/inverse agonist. It was recently approved by the EMA for use in excessive EDS related to OSA – the first drug to be introduced on the market with this indication, in association with not only OSA but also other entities such as cataplexy. It is used at increasing doses from 4.5 to 18mg/d and has shown decreases in the ESS value of 1.5–4.0 points. Its adverse effects include a possible prolongation of the QT interval, as well as interactions with other drugs. It has been approved by the EMA, although in Spain it is only available at the moment as an imported medication [34]. Nevertheless, some OSA patients in Spain are already using this drug, with few adverse effects and a clear improvement in their EDS.
In the context of patients with OSA, there are currently two fundamental studies in the form of RCTs (the HAROSA programme) [35–39] that signal its effectiveness both in patients who refuse treatment with CPAP and in those who present good adherence but present excessive EDS. It is important to highlight that the treatment was considered effective if the ESS value decreased below 10 points, or at least in a clinically significant manner (2–3 points) [40,41].
In the first RCT (HAROSA I), 244 OSA participants (82.8% men; mean age, 53.1 years; baseline ESS score, 14.7) were randomised to pitolisant (n=183) or placebo (n=61). The patients persisted with an ESS>12, despite using CPAP for an average of 4.2h per night. A decrease of 2.6 points (95%CI: 1.4–3.9) vs placebo was observed, although insomnia and headache were more frequent in the pitolisant group. In general, improvements in the subjective parameters of EDS (ESS) were paralleled by improvements in the objective measurements of EDS [35].
The second pivotal study (HAROSA II) had very similar characteristics in terms of duration, diagnosis of OSA and EDS and the number of patients, but in this case, 20mg/d of pitolisant (n=200) vs placebo (n=68) were randomised for 12 weeks in an intention-to-treat analysis in patients with OSA (AHI≥15events/h) with an initial ESS greater than 12 points who refused treatment with CPAP. The main outcome was changes in the ESS value. The main results showed a significant decrease in the ESS score of 2.8 points (95%CI: 1.5–4) compared to placebo, with no differences in adverse effects [36].
A meta-analysis of individual data of both previous studies (HAROSA I+HAROSA II) including 384 patients treated with pitolisant (20mg) and 128 with placebo showed a reduction of 3.1 points (95% CI: −2.1 to 4.1). No significant differences in safety endpoints were found [37].
Furthermore, in the HAROSA III study, an RCT phase 3 multi-centre study of moderate-to-severe OSA, Dauvilliers et al. observed in 242 patients treated with CPAP and 119 receiving placebo that even 40mg of pitolisant in increased doses from 12 weeks produced a reduction of 2.6 (−3.4,−1.8; p<0.0001) in the ESS value in the former group vs placebo, regardless of CPAP use, with good tolerance and no significant side effects [38].
In 2025, Testelmans observed in a meta-analysis study of three RCTs that 20mg of pitolisant reduced ESS by 3.2 points (4.37; −2; p<0.001) and 40mg did so by 3.57 points (4.87; −2.8; p<0.001). Pitolisant 40mg was superior to the 20-mg dose for older patients (≥50 years) and higher baseline AHI values (≥15). No significant differences were observed as regards safety outcomes [38]. Furthermore, the subgroups studied – obese patients, those over 50 years of age or with greater initial EDS, men vs. women – did not present any interactions. One aspect of great importance in treatment with pitolisant in the recent meta-analysis is the lack of difference in the incidence of verified adverse effects compared to the placebo group; this was confirmed by a recent systematic review of the literature [42] which concluded that adverse effects of pitolisant are transitory and mild. In fact, in healthy volunteers, pitolisant showed good clinical and biological tolerance following single oral doses of 1–240mg [37]. The current therapeutic algorithm recommends starting with a 4.5mg dose and increasing it to 18mg until the expected results are obtained [34].
Finally, in a prolonged study including individuals from the HAROSA programme, all the patients (including those receiving placebo) were offered pitolisant (up to 20mg) continuously for 52 weeks (376 finalised the study). At one year, the decrease in ESS scale in an intention-to-treat analysis was 8 (95%CI: −8.3,−7.5). One important finding was that the efficacy of pitolisant persists in the long term (one year) in individuals with OSA, without any adverse cardiovascular effects [43].
SolriamfetolThis is another drug that has recently come on the market. Its main mechanism of action is the inhibition of dopamine and serotonin re-uptake in the central nervous system. The usual dose is from 37.5mg to 150mg per day, increasing progressively until clinical improvement is achieved. Adverse effects include a possible increase in blood pressure and interaction with monoamine oxidase inhibitor drugs. As an indication for EDS secondary to OSA, solriamfetol has been approved by both the EMA and the US FDA (Food and Drug Administration) [44].
As regards the studies carried out (in the form of RCTs or derived from them), the TONES programme [45–49] is particularly noteworthy.
In the TONES 3 efficacy and dose study, 476 patients with OSA on CPAP treatment (or alternative treatment) but an ESS of at least 10 points were included. The study lasted four weeks and four groups were established: 37.5mg (n=56); 75mg (n=58); 150mg (n=116); 300mg (n=115) of solriamfetol, compared with a placebo group (n=114). The greatest decreases in the ESS occurred with the doses of 150mg (−7.7 points) and 300mg (−7.9 points), while there was a decrease of 3.3 points with placebo, which gives a total decrease of 4.4–4.6 points. However, in the groups with intermediate doses (37.5 and 75mg), there were decreases of between 5 and 5.1 points. It is interesting to note that in the placebo group itself the decreases in the ESS were clinically significant (the minimum clinically significant difference in the ESS is estimated to be between 2 and 3 points) [16–18]. Therefore, with respect to placebo, the lower dose groups decreased the ESS by 2.3–2.4 points, while in the 150–300mg group they decreased it by 4.4–4.6 points, and, in the 300mg group specifically, by 4.6 (95% CI: −3.5, −7.9). There was no difference in response between the 150mg and 300mg groups, while the adverse effects were dose-dependent, so a dose of 150mg was concluded to be the ideal dose for the management of excessive EDS in this regard. The adverse effects were mild in most cases [45].
In the TONES 4 drug withdrawal study, 112 patients with OSA on CPAP or alternative treatment but an ESS of at least 10 points were treated entirely with solriamfetol for four weeks, achieving an approximate reduction of 10 points in the ESS (although these patients had an initial ESS of more than 15 points on average). In a second phase of the study, 60 patients continued treatment with solriamfetol for two more weeks with no change in the ESS (6.4 vs 6.4), while 62 patients were given placebo, with a significant increase in EDS from 5.9 to 10.8 points in the ESS score [46].
In the TONES 5 long-term effect study, two series of patients (n=333 and n=84) with OSA were followed for 40 and 52 weeks, respectively, with an initial decrease in the ESS value in the first two weeks of treatment from values of around 15 points to values of around 6–7 points; these were maintained until the end of the study [47].
After the TONES programme, a study was undertaken to assess the effect of solriamfetol according to adherence to CPAP, with 225 patients with OSA with good adherence to CPAP treatment compared to 78 with poor adherence; all these patients presented an ESS of at least 10 points and they were followed for 40 weeks. Independently of adherence to CPAP, a very similar decrease in the ESS from 15–16 points to 6.5–6.8 points was seen in both groups until the end of the study. This finding seems to indicate that solriamfetol acts on EDS as such, beyond any association with OSA [48]. In fact, some studies with solriamfetol have also been successfully performed on patients with narcolepsy and no OSA.
Finally, in a recent meta-analysis of the studies described above, it was observed that solriamfetol reduced EDS in a clinically and statistically significant manner by 4.4 points (95%CI: 2.8–5.5) compared to placebo [49]. In general, the improvements in the subjective parameters of EDS were paralleled by improvements in the objective measurements of EDS.
The adverse effects are mild and dose-dependent, and generally greater than those of pitolisant. Thus, a higher risk of adverse effects was not observed with low doses, but it was observed with doses of 150–300mg (OR 1.56, 95%CI: 1.31–1.87 for 150mg). Most of these effects are related to headache, pharyngitis, insomnia, nausea, dry mouth and anxiety, and they tend to be mild and reversible [44].
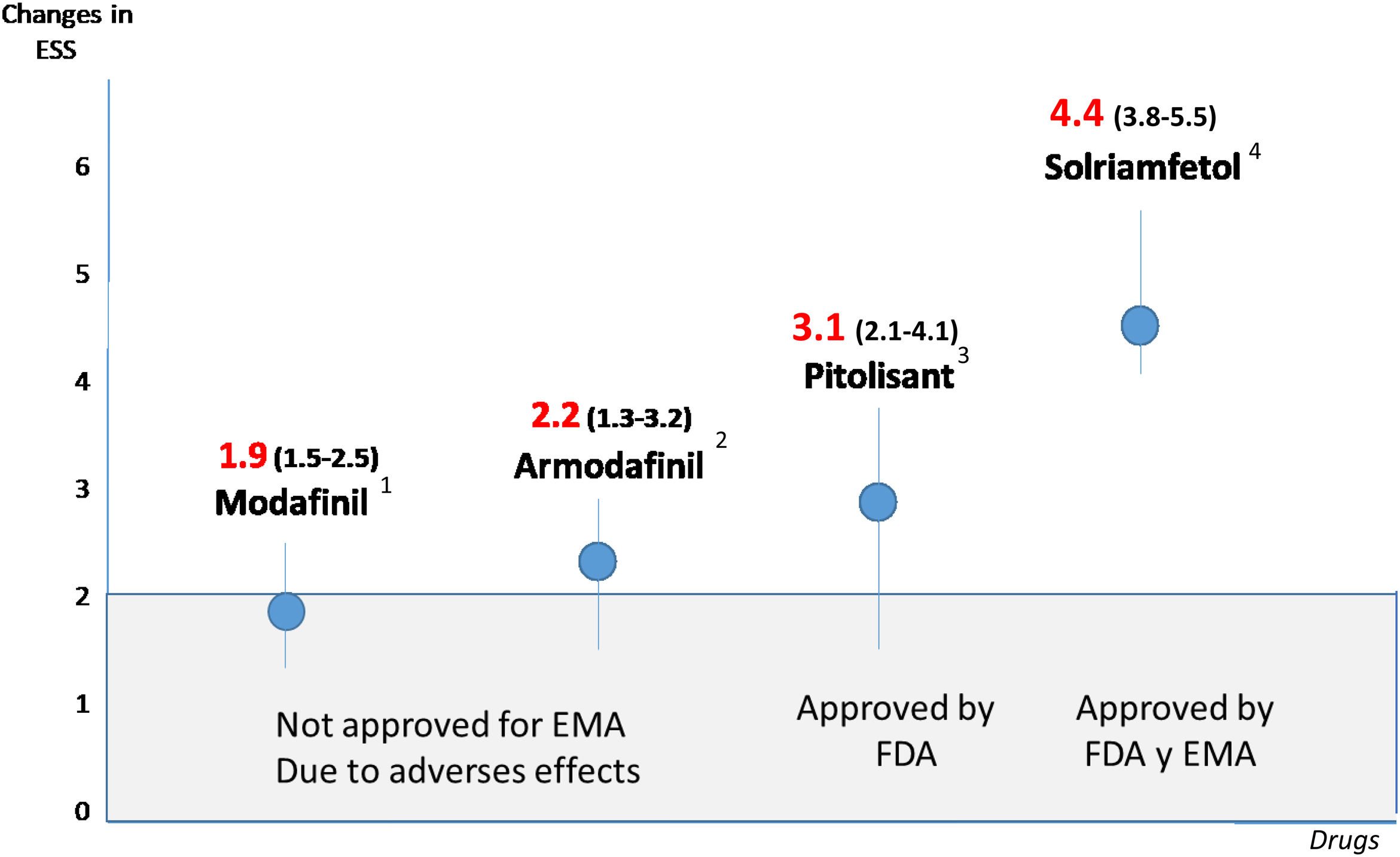
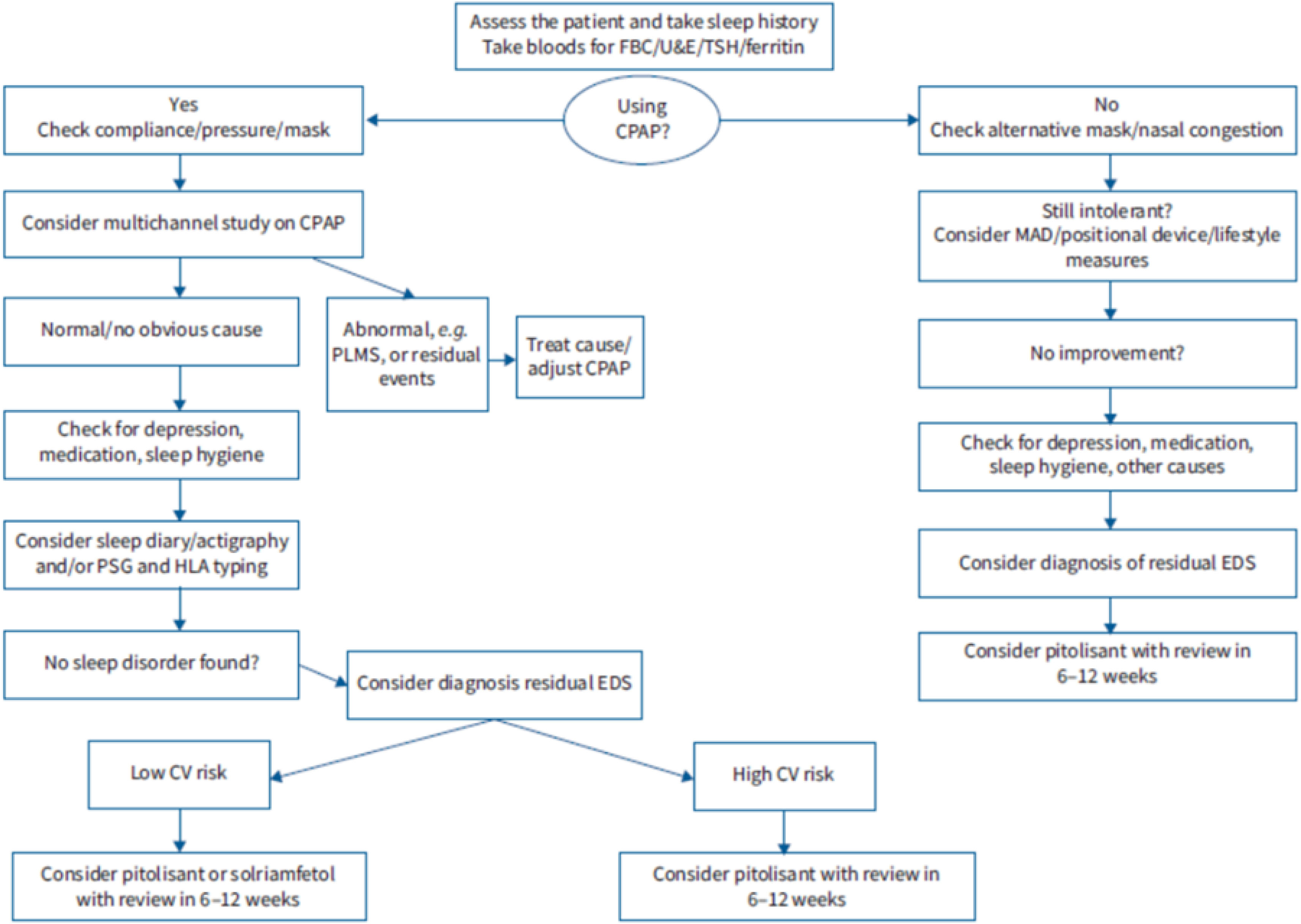
Fig. 1 shows the decreases in the ESS value according to the results of the different meta-analyses carried out with old and new drugs. It can be seen that the effectiveness of the new drugs (pitolisant and solriamfetol) is greater than that found in the old drugs. Such was the expectation created by these two drugs that a group from the European Respiratory Society met to establish guidelines for the pharmacological treatments described above. These are summarised in Fig. 2. It can be seen that the ERS Task Force first focused on establishing the existence of a real excessive EDS, once a correct diagnosis of OSA has been confirmed, and other causes of EDS such as poor sleep hygiene, unhealthy lifestyle and inadequate CPAP pressure titration have been ruled out. Pharmacological treatment can subsequently be considered, involving the introduction of pitolisant in patients with high cardiovascular risk or of either pitolisant or solriamfetol in those with a lower cardiovascular risk, given the excess cardiovascular risk associated with solriamfetol [14,24]. Similar recommendations have been issued by recently published guidelines from the French OSA group, although these guidelines take a firmer stance, particularly in advocating for the diagnosis of OSA through polysomnography, ensuring a minimum CPAP adherence of six hours per night, and conducting a broader range of complementary tests to rule out alternative causes of daytime hypersomnolence. Furthermore, special emphasis is placed on patients with psychiatric disorders, those taking psychotropic medications and those with cardiovascular disease. In these cases, the guidelines recommend optimal management of the underlying condition prior to initiating treatment with wake-promoting agents, particularly pitolisant and solriamfetol, and they also offer criteria for selecting the most appropriate agent [24].
Decrease in the Epworth Sleepiness Scale in the main wakefulness-promoting drugs in obstructive sleep apnoea. Data are presented as odds ratios (95% confidence intervals [CIs]). The minimal clinically significant difference on the Epworth Sleepiness Scale is also considered in 2 points (Cook et al. Thorax 2019; 74: 390–396). Odds ratio data (95% CI) were extracted from the following meta-analyses: 1. Kuan Y-C, et al. Effects of modafinil and armodafinil in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Clinical Therapeutics. 2016; 38: 874–888; 2. Chapman JL, et al. Modafinil/armodafinil in obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. European Respiratory Journal. 2016; 47: 1420; 3. Lehert P, et al. Efficacy of pitolisant 20mg in reducing excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Clinical Drug Investigation. 2022; 42: 65–74; 4. Subedi R, et al. Efficacy and safety of solriamfetol for excessive daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy and obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Sleep Medicine. 2020; 75: 510–521.
Algorithm of residual excessive daytime sleepiness in obstructive sleep apnoea proposed by the task force from the European Respiratory Society. PSG: polysomnography; EDS: excessive daytime sleepiness; CV: cardiovascular; continuous positive airway pressure; HLA: human leucocyte antigens; PLMS: periodic leg movements during sleep; FBC: full blood count.
Since pitolisant and solriamfetol are newly introduced pharmacological agents for patients with OSA, numerous challenges will arise in the future. Chief among these is the need to conduct appropriate assessments to confirm the presence of true excessive daytime sleepiness (EDS) not attributable to other conditions; to strengthen educational programmes aimed at improving both the qualitative and quantitative rates of effective CPAP use; and to identify biomarkers capable of predicting, a priori, which patients are more likely to experience excessive EDS, allowing for early intervention. Furthermore, important questions must be addressed regarding these novel therapies, such as identifying the specific phenotypes of CPAP-treated patients who are most likely to benefit, determining the drugs’ long-term efficacy and adverse effects and conducting cost-effectiveness analyses. The main future challenges are summarised in Table 3.
Future challenges in the treatment of wakefulness-promoting agents.
| Should they be used only in patients adequately treated with CPAP or in those patients who do not tolerate or accept this treatment? |
| What clinical or biological parameters should be considered (in addition to ESS) to consider the indication of these drugs? |
| Given that they are initially chronic treatments, are the risks of this situation compatible with the decrease in EDS they produce? |
| What is the long-term efficacy of these products? |
| What precautions should be taken when prescribing these products to patients with cardiovascular problems? |
| Cost-effectiveness studies of these products are lacking. |
EDS in patients with or without OSA undoubtedly represents a major limitation on the quality of life. In patients with OSA, this situation can be reversible, however, either through CPAP treatment or through new wakefulness-stimulating agents that have demonstrated undeniable efficacy with few adverse effects. Although these new drugs are still unknown to most clinicians in our country, they have excellent potential in terms of both care and research, and they represent one of the few occasions whereby a pharmacological alternative has been achieved in the world of OSA.
No use of artificial intelligenceThe translation into English has been carried out by a native English speaker (Matthew Clarke) with over 20 years of experience in translating medical articles. The English used is of the European variety.
Conflict of interestBioproject has granted this project but has had no involvement in any part of the manuscript.




![Decrease in the Epworth Sleepiness Scale in the main wakefulness-promoting drugs in obstructive sleep apnoea. Data are presented as odds ratios (95% confidence intervals [CIs]). The minimal clinically significant difference on the Epworth Sleepiness Scale is also considered in 2 points (Cook et al. Thorax 2019; 74: 390–396). Odds ratio data (95% CI) were extracted from the following meta-analyses: 1. Kuan Y-C, et al. Effects of modafinil and armodafinil in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Clinical Therapeutics. 2016; 38: 874–888; 2. Chapman JL, et al. Modafinil/armodafinil in obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. European Respiratory Journal. 2016; 47: 1420; 3. Lehert P, et al. Efficacy of pitolisant 20mg in reducing excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Clinical Drug Investigation. 2022; 42: 65–74; 4. Subedi R, et al. Efficacy and safety of solriamfetol for excessive daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy and obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Sleep Medicine. 2020; 75: 510–521. Decrease in the Epworth Sleepiness Scale in the main wakefulness-promoting drugs in obstructive sleep apnoea. Data are presented as odds ratios (95% confidence intervals [CIs]). The minimal clinically significant difference on the Epworth Sleepiness Scale is also considered in 2 points (Cook et al. Thorax 2019; 74: 390–396). Odds ratio data (95% CI) were extracted from the following meta-analyses: 1. Kuan Y-C, et al. Effects of modafinil and armodafinil in patients with obstructive sleep apnea: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Clinical Therapeutics. 2016; 38: 874–888; 2. Chapman JL, et al. Modafinil/armodafinil in obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis. European Respiratory Journal. 2016; 47: 1420; 3. Lehert P, et al. Efficacy of pitolisant 20mg in reducing excessive daytime sleepiness and fatigue in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Clinical Drug Investigation. 2022; 42: 65–74; 4. Subedi R, et al. Efficacy and safety of solriamfetol for excessive daytime sleepiness in narcolepsy and obstructive sleep apnea: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Sleep Medicine. 2020; 75: 510–521.](https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/03002896/unassign/S0300289625002923/v1_202508140423/en/main.assets/thumbnail/gr1.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w98FxLWLw1xoW2PaQDYY7RZU=)








