A 40 year old patient, non smoker with no history of pathology, required hospital admission for bilateral SARS-CoV2 pneumonia and basal oxygen saturation of 93%. Received treatment with oxygen therapy, dexamethasone and a single dose of tocilizumab with correct clinical evolution.
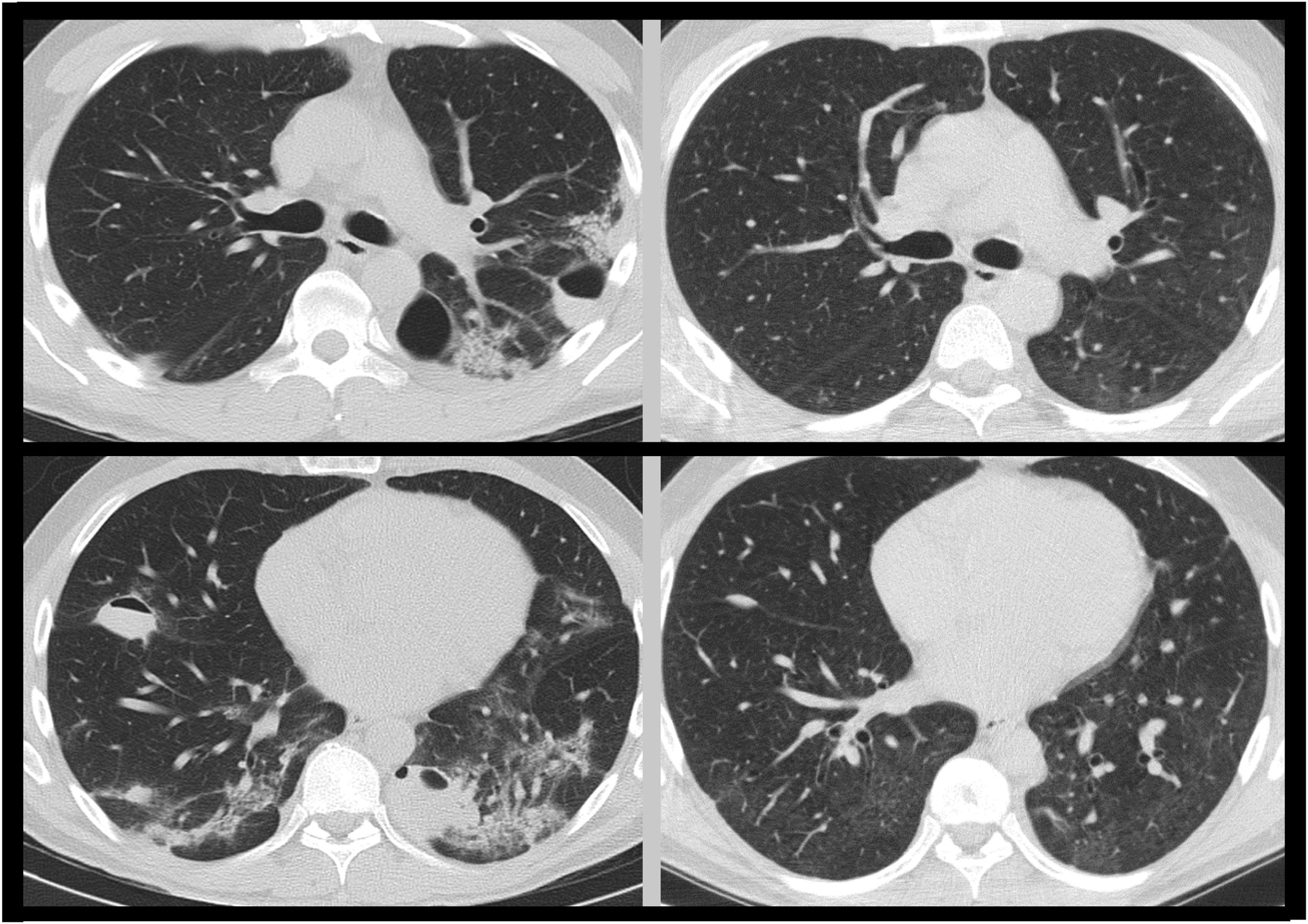
After discharge, self-limited haemoptoic expectoration was presented. A thoracic computed tomography scan showed multiple bilateral cavitated pulmonary lesions, and was readmitted to hospital. Physical examination and primary blood analysis were normal. A bronchoscopy was performed showing hematic secretions in the left lower lobe. All microbiological samples were negative.
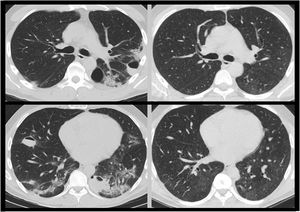
In absence of clinical manifestations and given the normality of the studies, the case was classified as post-COVID bullous disease, and an ambulatory thoracic CT scan was performed after 3 months, showing radiological resolution of lesions (Fig. 1) and normal respiratory function test.
Bullous lung disease post-COVID is a rare disease that consists on the apparition of air bullae of 1cm or larger inside of the lung parenchyma on immediate post-COVID. It has been reported some cases of gigant bulla that required surgical treatment post-COVID1 and cases of bullous lung disease in context of severe pneumonitis2 with favorable evolution without medical intervention, as it occurred in our case.
FundingThe authors declare that no funding was received for this article.
Conflicts of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.