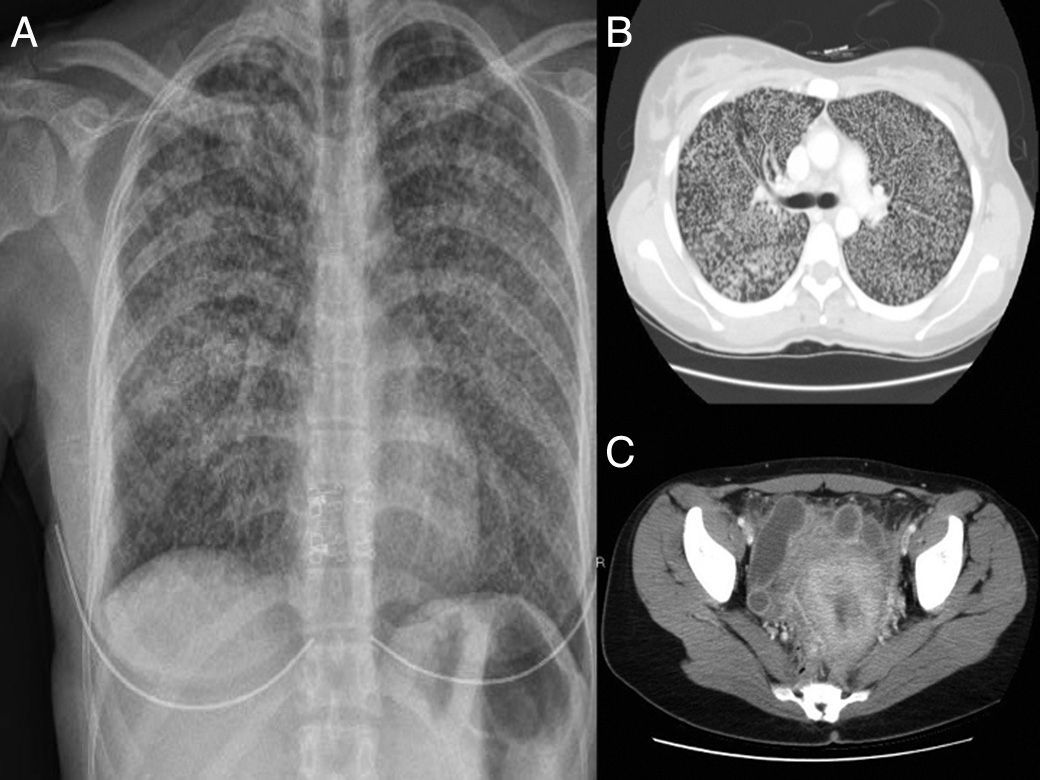
A 29-year-old woman, native of Bolivia, presented with a progressive clinical syndrome of low-grade fever, dry cough, and dyspnea on exertion. She also reported a 3-month history of abdominal pain and leukorrhea after therapeutic abortion, which had not improved despite the administration of targeted antibiotic therapy with ciprofloxacin when Escherichia coli was cultured from the vaginal discharge. Chest radiograph and computed tomography (CT) were performed showing extensive bilateral micronodular involvement (Fig. 1A and B). Abdominal CT revealed tubular parauterine cystic images with fatty peripheral edema and lamina propria with free fluid consistent with salpingitis (Fig. 1C). Mantoux testing showed no induration at all, but sputum smear and Löwenstein medium cultures of sputum samples and vaginal discharge were positive for Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
The coexistence of genital and miliary tuberculosis (TB) has been previously reported.1 Up to 8%–15% of women with pulmonary tuberculosis have genital TB.2 Genital TB is a known cause of sterility and abortions, as occurred in our patient. The patient probably had previous genital TB, and the curettage led to hematogenous spread, resulting in secondary miliary TB.
Please cite this article as: Montes Ruiz-Cabello M, Guirao Arrabal E, Aisa Denaroso LM. Tuberculosis miliar y genital simultáneas. Arch Bronconeumol. 2017;53:397.